cropnet_on_device
This notebook shows you how to fine-tune CropNet models from TensorFlow Hub on a dataset from TFDS or your own crop disease detection dataset.
You will:
- Load the TFDS cassava dataset or your own data
- Enrich the data with unknown (negative) examples to get a more robust model
- Apply image augmentations to the data
- Load and fine tune a CropNet model from TF Hub
- Export a TFLite model, ready to be deployed on your app with Task Library, MLKit or TFLite directly
Instead of using a TFDS dataset, you can also train on your own data. This code snippet shows how to load your own custom dataset. See this link for the supported structure of the data. An example is provided here using the publicly available Cassava Leaf Disease dataset
data_root_dir = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'cassavaleafdata.zip',
'https://storage.googleapis.com/emcassavadata/cassavaleafdata.zip',
extract=True)
data_root_dir = os.path.splitext(data_root_dir)[0] # Remove the .zip extension
builder = tfds.ImageFolder(data_root_dir)
ds_info = builder.info
ds_train = builder.as_dataset(split='train', as_supervised=True)
ds_validation = builder.as_dataset(split='validation', as_supervised=True)
ds_test = builder.as_dataset(split='test', as_supervised=True)
Add additional unknown (negative) examples to the training dataset and assign a new unknown class label number to them. The goal is to have a model that, when used in practice (in the field), has the option of predicting “Unknown” when it sees something unexpected
Below you can see a list of datasets that will be used to sample the additional unknown imagery. It includes 3 completely different datasets to increase diversity. One of them is a beans leaf disease dataset, so that the model has exposure to diseased plants other than cassava
For all the images, to make them more diverse, you’ll apply some augmentation, like changes in:
- Brightness
- Contrast
- Saturation
- Hue
- Crop
To use these dataset with Model Maker, they need to be in a ImageClassifierDataLoader class
To fine tune the model, you will use Model Maker. This makes the overall solution easier since after the training of the model, it’ll also convert it to TFLite
Model Maker makes this conversion be the best one possible and with all the necessary information to easily deploy the model on-device later
One important detail here is setting train_whole_model which will make the base model fine tuned during training. This makes the process slower but the final model has a higher accuracy. Setting shuffle will make sure the model sees the data in a random shuffled order which is a best practice for model learning
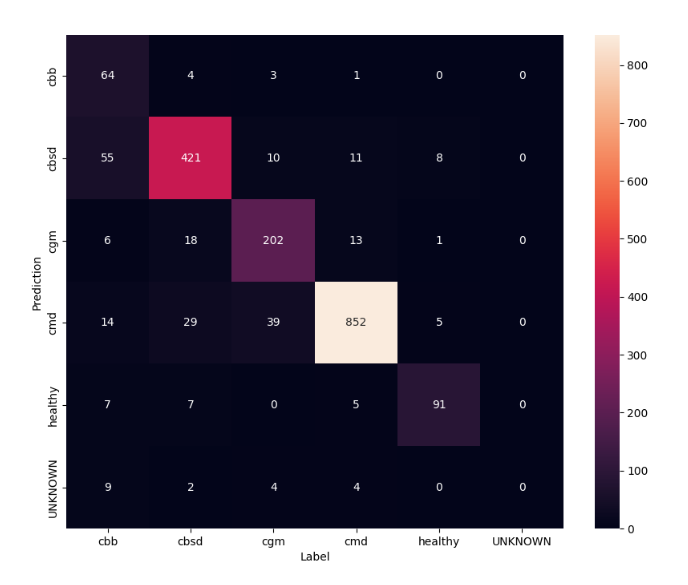
To have an even better understanding of the fine tuned model, it’s good to analyse the confusion matrix. This will show how often one class is predicted as another
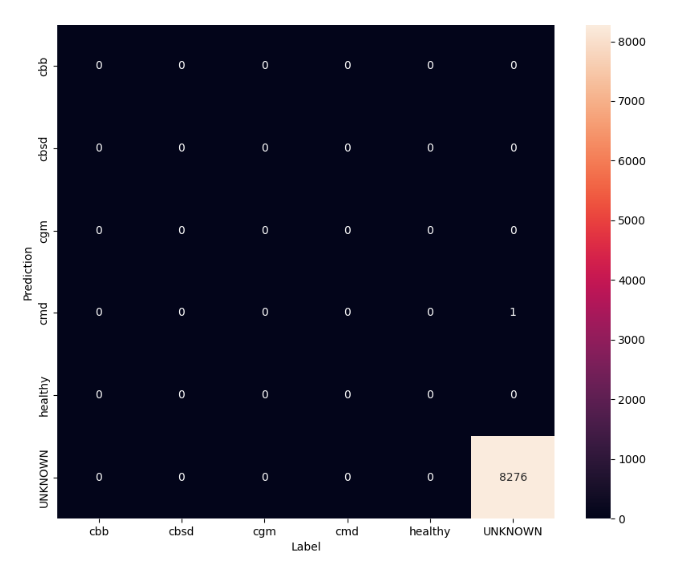
In this evaluation we expect the model to have accuracy of almost 1. All images the model is tested on are not related to the normal dataset and hence we expect the model to predict the “Unknown” class label
Now we can export the trained models in TFLite and SavedModel formats for deploying on-device and using for inferece in TensorFlow
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import seaborn as sns
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
from tensorflow_examples.lite.model_maker.core.export_format import ExportFormat
from tensorflow_examples.lite.model_maker.core.task import image_preprocessing
from tflite_model_maker import image_classifier
from tflite_model_maker import ImageClassifierDataLoader
from tflite_model_maker.image_classifier import ModelSpec
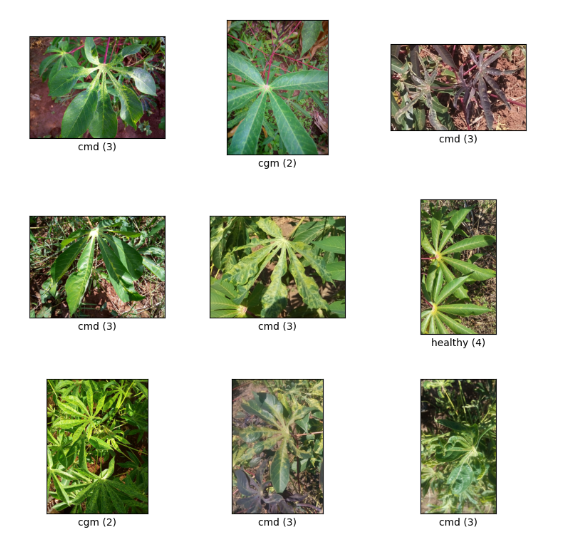
tfds_name = 'cassava'
(ds_train, ds_validation, ds_test), ds_info = tfds.load(
name=tfds_name,
split=['train', 'validation', 'test'],
with_info=True,
as_supervised=True)
TFLITE_NAME_PREFIX = tfds_name
_ = tfds.show_examples(ds_train, ds_info)
UNKNOWN_TFDS_DATASETS = [{
'tfds_name': 'imagenet_v2/matched-frequency',
'train_split': 'test[:80%]',
'test_split': 'test[80%:]',
'num_examples_ratio_to_normal': 1.0,
}, {
'tfds_name': 'oxford_flowers102',
'train_split': 'train',
'test_split': 'test',
'num_examples_ratio_to_normal': 1.0,
}, {
'tfds_name': 'beans',
'train_split': 'train',
'test_split': 'test',
'num_examples_ratio_to_normal': 1.0,
}]
# Load unknown datasets.
weights = [
spec['num_examples_ratio_to_normal'] for spec in UNKNOWN_TFDS_DATASETS
]
num_unknown_train_examples = sum(
int(w * ds_train.cardinality().numpy()) for w in weights)
ds_unknown_train = tf.data.experimental.sample_from_datasets([
tfds.load(
name=spec['tfds_name'], split=spec['train_split'],
as_supervised=True).repeat(-1) for spec in UNKNOWN_TFDS_DATASETS
], weights).take(num_unknown_train_examples)
ds_unknown_train = ds_unknown_train.apply(
tf.data.experimental.assert_cardinality(num_unknown_train_examples))
ds_unknown_tests = [
tfds.load(
name=spec['tfds_name'], split=spec['test_split'], as_supervised=True)
for spec in UNKNOWN_TFDS_DATASETS
]
ds_unknown_test = ds_unknown_tests[0]
for ds in ds_unknown_tests[1:]:
ds_unknown_test = ds_unknown_test.concatenate(ds)
# All examples from the unknown datasets will get a new class label number.
num_normal_classes = len(ds_info.features['label'].names)
unknown_label_value = tf.convert_to_tensor(num_normal_classes, tf.int64)
ds_unknown_train = ds_unknown_train.map(lambda image, _:
(image, unknown_label_value))
ds_unknown_test = ds_unknown_test.map(lambda image, _:
(image, unknown_label_value))
# Merge the normal train dataset with the unknown train dataset.
weights = [
ds_train.cardinality().numpy(),
ds_unknown_train.cardinality().numpy()
]
ds_train_with_unknown = tf.data.experimental.sample_from_datasets(
[ds_train, ds_unknown_train], [float(w) for w in weights])
ds_train_with_unknown = ds_train_with_unknown.apply(
tf.data.experimental.assert_cardinality(sum(weights)))
print((f"Added {ds_unknown_train.cardinality().numpy()} negative examples."
f"Training dataset has now {ds_train_with_unknown.cardinality().numpy()}"
' examples in total.'))
def random_crop_and_random_augmentations_fn(image):
# preprocess_for_train does random crop and resize internally.
image = image_preprocessing.preprocess_for_train(image)
image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, 0.2)
image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, 0.5, 2.0)
image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, 0.75, 1.25)
image = tf.image.random_hue(image, 0.1)
return image
def random_crop_fn(image):
# preprocess_for_train does random crop and resize internally.
image = image_preprocessing.preprocess_for_train(image)
return image
def resize_and_center_crop_fn(image):
image = tf.image.resize(image, (256, 256))
image = image[16:240, 16:240]
return image
no_augment_fn = lambda image: image
train_augment_fn = lambda image, label: (
random_crop_and_random_augmentations_fn(image), label)
eval_augment_fn = lambda image, label: (resize_and_center_crop_fn(image), label)
ds_train_with_unknown = ds_train_with_unknown.map(train_augment_fn)
ds_validation = ds_validation.map(eval_augment_fn)
ds_test = ds_test.map(eval_augment_fn)
ds_unknown_test = ds_unknown_test.map(eval_augment_fn)
label_names = ds_info.features['label'].names + ['UNKNOWN']
train_data = ImageClassifierDataLoader(ds_train_with_unknown,
ds_train_with_unknown.cardinality(),
label_names)
validation_data = ImageClassifierDataLoader(ds_validation,
ds_validation.cardinality(),
label_names)
test_data = ImageClassifierDataLoader(ds_test, ds_test.cardinality(),
label_names)
unknown_test_data = ImageClassifierDataLoader(ds_unknown_test,
ds_unknown_test.cardinality(),
label_names)
model_name = 'mobilenet_v3_large_100_224'
map_model_name = {
'cropnet_cassava':
'https://tfhub.dev/google/cropnet/feature_vector/cassava_disease_V1/1',
'cropnet_concat':
'https://tfhub.dev/google/cropnet/feature_vector/concat/1',
'cropnet_imagenet':
'https://tfhub.dev/google/cropnet/feature_vector/imagenet/1',
'mobilenet_v3_large_100_224':
'https://tfhub.dev/google/imagenet/mobilenet_v3_large_100_224/feature_vector/5',
}
model_handle = map_model_name[model_name]
image_model_spec = ModelSpec(uri=model_handle)
model = image_classifier.create(
train_data,
model_spec=image_model_spec,
batch_size=64,
learning_rate=0.03,
epochs=5,
shuffle=True,
train_whole_model=True,
validation_data=validation_data)
model.evaluate(test_data)
def predict_class_label_number(dataset):
"""Runs inference and returns predictions as class label numbers."""
rev_label_names = {l: i for i, l in enumerate(label_names)}
return [
rev_label_names[o[0][0]]
for o in model.predict_top_k(dataset, batch_size=128)
]
def show_confusion_matrix(cm, labels):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
sns.heatmap(cm, xticklabels=labels, yticklabels=labels,
annot=True, fmt='g')
plt.xlabel('Label')
plt.ylabel('Prediction')
plt.show()
confusion_mtx = tf.math.confusion_matrix(
predict_class_label_number(test_data),
list(ds_test.map(lambda x, y: y)),
num_classes=len(label_names))
show_confusion_matrix(confusion_mtx, label_names)
model.evaluate(unknown_test_data)
unknown_confusion_mtx = tf.math.confusion_matrix(
predict_class_label_number(unknown_test_data),
list(ds_unknown_test.map(lambda x, y: y)),
num_classes=len(label_names))
show_confusion_matrix(unknown_confusion_mtx, label_names)
tflite_filename = f'{TFLITE_NAME_PREFIX}_model_{model_name}.tflite'
model.export(export_dir='.', tflite_filename=tflite_filename)
# Export saved model version.
model.export(export_dir='.', export_format=ExportFormat.SAVED_MODEL)