字典序
在刷题和计算机科学领域,字典序(Lexicographical order)也称为词典序、字典顺序、字母序,是一种对序列元素进行排序的方式,它模仿了字典中单词的排序规则。下面从不同的数据类型来详细解释字典序:
字符串的字典序
在字典中,单词是按照字母的先后顺序排列的。对于两个字符串,字典序的比较规则如下:
-
比较过程:从两个字符串的第一个字符开始逐个比较,如果对应位置的字符不同,则字符 ASCII 码值小的字符串排在前面;如果对应位置字符相同,则继续比较下一个位置的字符,直到出现不同字符或者其中一个字符串结束。
-
示例:
-
比较 "apple" 和 "banana",因为第一个字符 'a' 的 ASCII 码值小于 'b',所以 "apple" 在字典序中排在 "banana" 前面。
-
比较 "apple" 和 "app",前三个字符都相同,但 "app" 先结束,所以 "app" 在字典序中排在 "apple" 前面。
-
整数序列的字典序
对于整数序列,同样可以按照字典序进行比较:
-
比较过程:将整数序列看作由数字组成的字符串,从序列的第一个元素开始逐个比较元素的大小,如果对应位置的元素不同,则元素值小的序列排在前面;如果对应位置元素相同,则继续比较下一个位置的元素,直到出现不同元素或者其中一个序列结束。
-
示例:
-
比较序列
[1, 2, 3]和[2, 1, 3],第一个元素 1 小于 2,所以[1, 2, 3]在字典序中排在[2, 1, 3]前面。 -
比较序列
[1, 2, 3]和[1, 2],前两个元素都相同,但[1, 2]先结束,所以[1, 2]在字典序中排在[1, 2, 3]前面。
-
在刷题中的应用
在很多算法题中,字典序常常作为排序的依据或者要求输出的结果满足字典序的要求,例如:
-
全排列问题:要求输出给定序列的所有全排列,并且按照字典序输出。例如,对于序列
[1, 2, 3],其全排列按照字典序输出为[1, 2, 3]、[1, 3, 2]、[2, 1, 3]、[2, 3, 1]、[3, 1, 2]、[3, 2, 1]。 -
子集问题:可能要求输出所有子集,并且按照字典序排列。
代码示例(C++ 实现全排列并按字典序输出)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
std::vector<int> nums = {1, 2, 3};
do {
for (int num : nums) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
} while (std::next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end()));
return 0;
}这些代码示例展示了如何生成全排列并按字典序输出,在刷题中可以根据具体需求对代码进行调整。
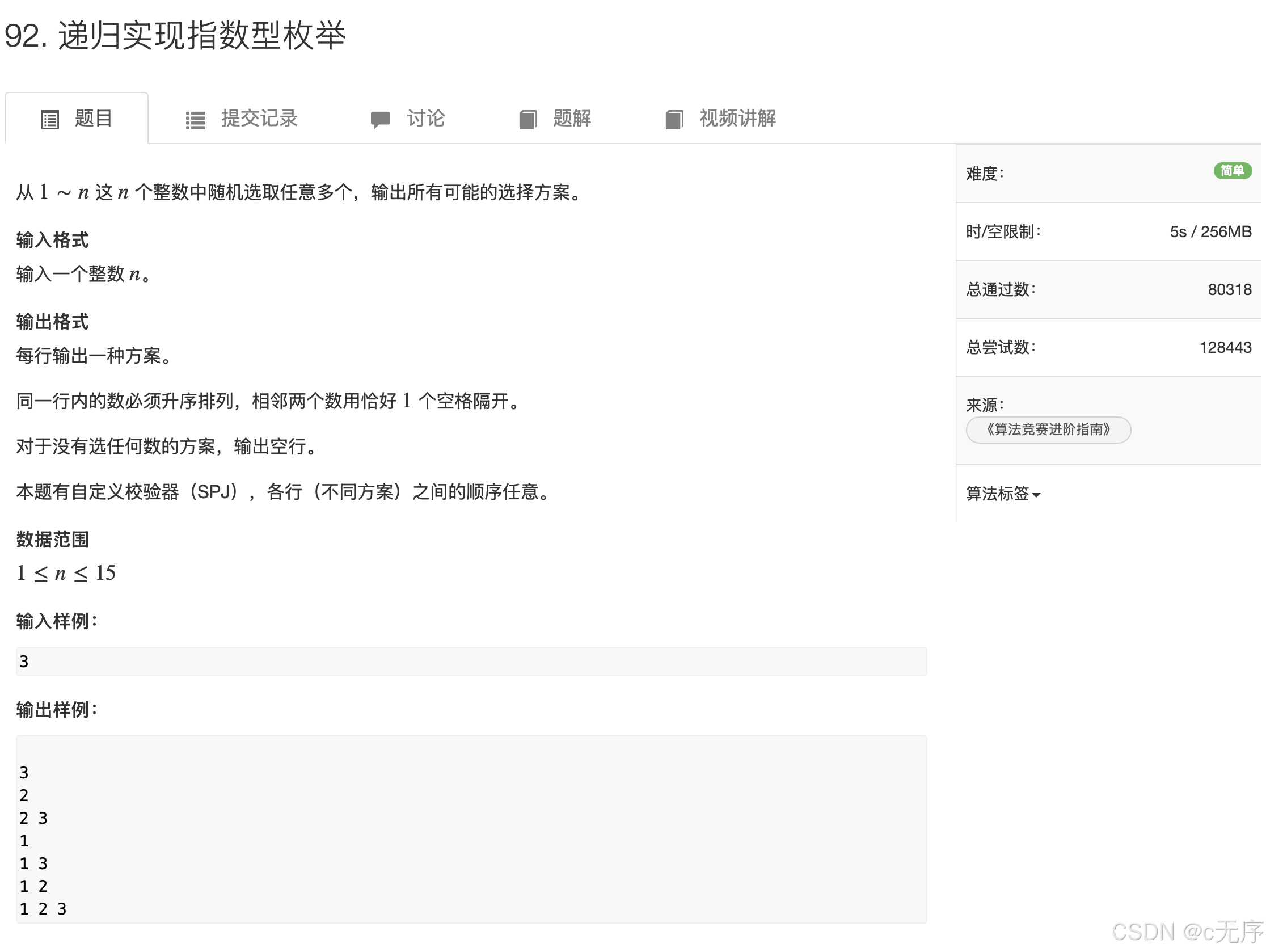
92.递归实现指数型枚举
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 16; // 最大数据范围
int statu[N]; // 状态数组 0表示未考虑 1表示选 2表示不选
int n; // 标准输入
void dfs(int u) // d
{
if(u > n) // 考虑到了最后一个位置 -- 递归出口
{
// 打印所有的数
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
if(statu[i] == 1)
printf("%d ", i);
}
printf("\n");// 打印换行,表示这一次枚举完毕
return;// 返回上一层
}
// 不选的情况
statu[u] = 2;
dfs(u+1);
statu[u] = 0;// 恢复现场
// 选的情况
statu[u] = 1;
dfs(u+1);
statu[u] = 0;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs(1); //对第1个数进行考虑
return 0;
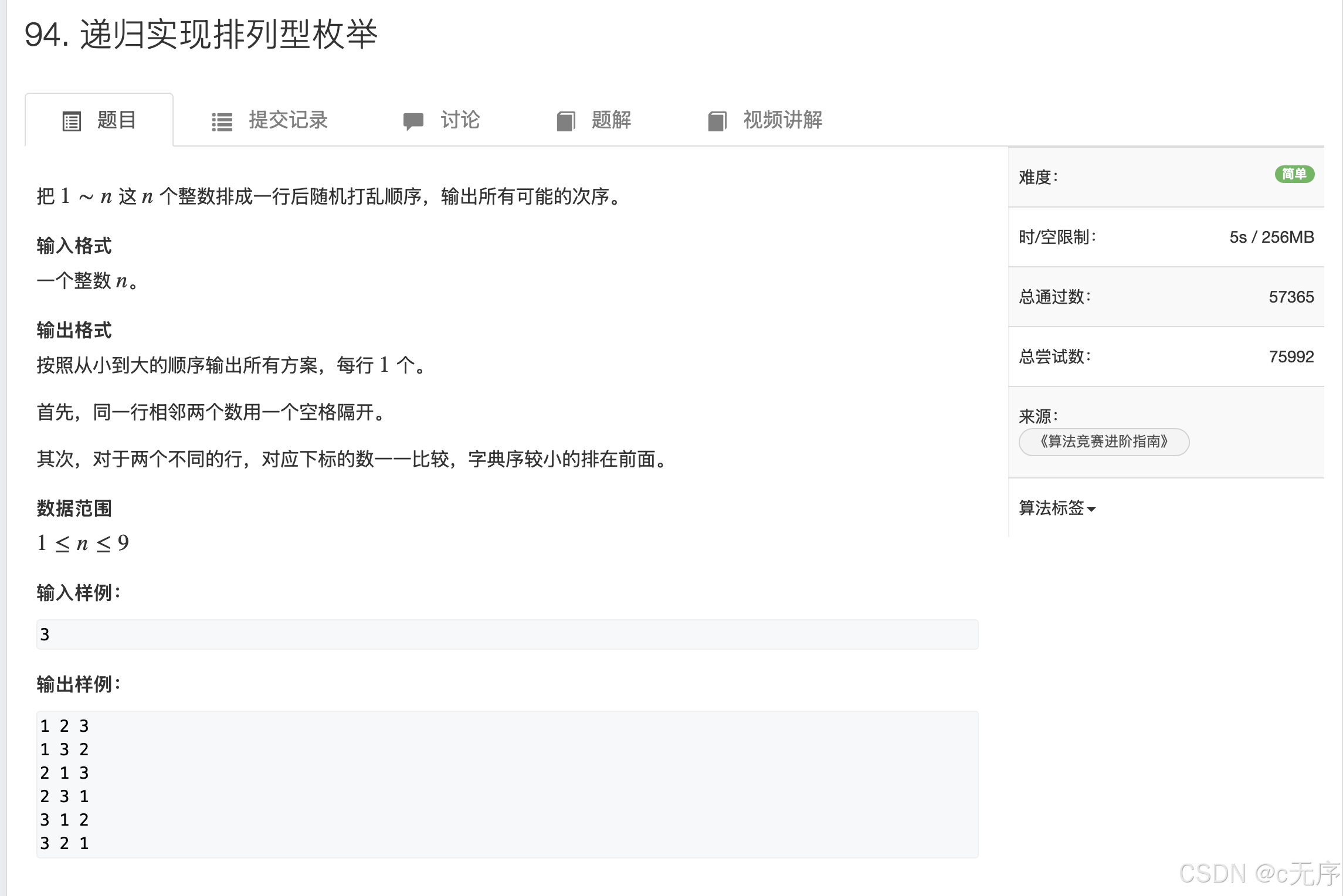
}94.递归实现排列型枚举
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 数组定义成全局变量,初始值一定是0,如果定义成局部变量,初始值随机
const int N = 10;
int status[N]; // 0表示未填入 1—n表示填入的数
bool used[N];// 标记这个数有没有被用过 true用过 false没有用过
int n;
void dfs(int u)
{
// 递归出口
if(u > n)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ", status[i]);
puts("");
return;
}
// 依此枚举每个分支,即当前位置可以填哪些数
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(!used[i]) // 当前的数没有用
{
status[u] = i; // 填入这个数
used[i] = true; // 标记已使用
dfs(u + 1);
// 恢复现场
used[i] = false;
status[u] = 0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
dfs(1);
return 0;
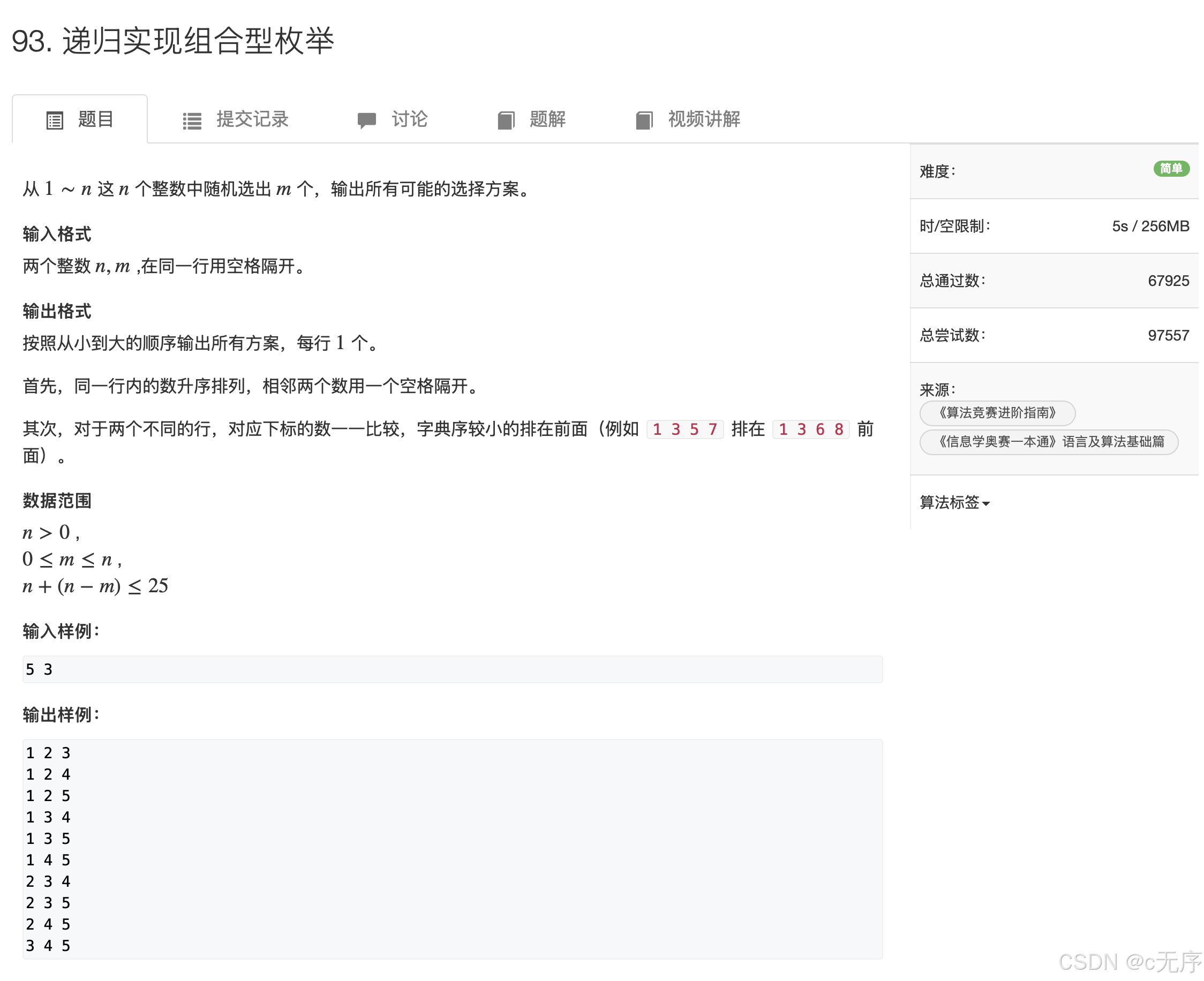
}93.递归实现组合型枚举
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
const int N = 30;
int status[N];
void dfs(int u, int start)
{
// (u-1 + n - start + 1 < m)
if(u + n - start < m) return; // 剪枝 -- start后面的数加起来都不够凑m个数
// 递归出口
if(u > m)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) printf("%d ", status[i]);
puts("");
return;
}
for(int i = start; i <= n; i++)
{
status[u] = i;
dfs(u+1, i+1);
// 恢复现场
status[u] = 0;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
dfs(1, 1);
return 0;
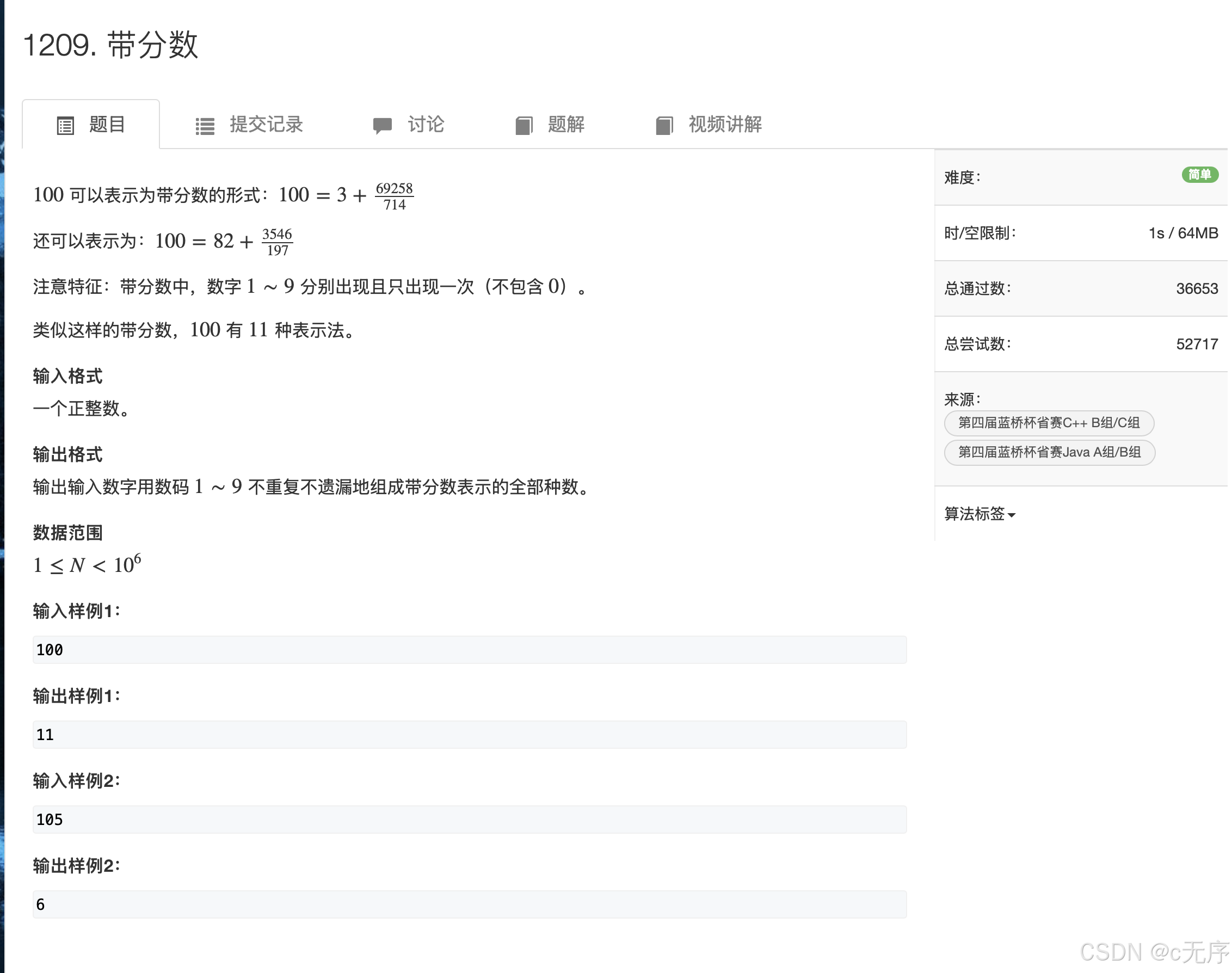
}1209.带分数
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int ans = 0;
int n;
bool status[N]; // 判重数组
bool backup[N];
bool check(int a, int c)
{
long long b = n * (long long)c - a * c;
// a b c 不能为0
if(!a || !b || !c) return false;
memcpy(backup, status, sizeof(status));
while(b)
{
int x = b % 10;
b = b / 10;
// x在ac中不能出现, x不能为0
if(!x || backup[x]) return false;
backup[x] = true;
}
// 看看每个数字是否出现过 -- 必须全部出现
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
{
if(!backup[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
void dfs_c(int u, int a, int c)
{
if(u == n) return;
if(check(a, c)) ans++;
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
{
if(!status[i])
{
status[i] = true;
dfs_c(u+1, a, c * 10 +i);
status[i] = false;
}
}
}
void dfs_a(int u, int a)
{
if(a >= n) return;
if(a) dfs_c(u, a, 0); // 只要a小于n,每种情况下都有dfs_c
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
{
if(!status[i])
{
status[i] = true;
dfs_a(u+1, a * 10 + i);
status[i] = false;
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs_a(0, 0); // 当前已经用了多少个数字, 最开始a是0
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
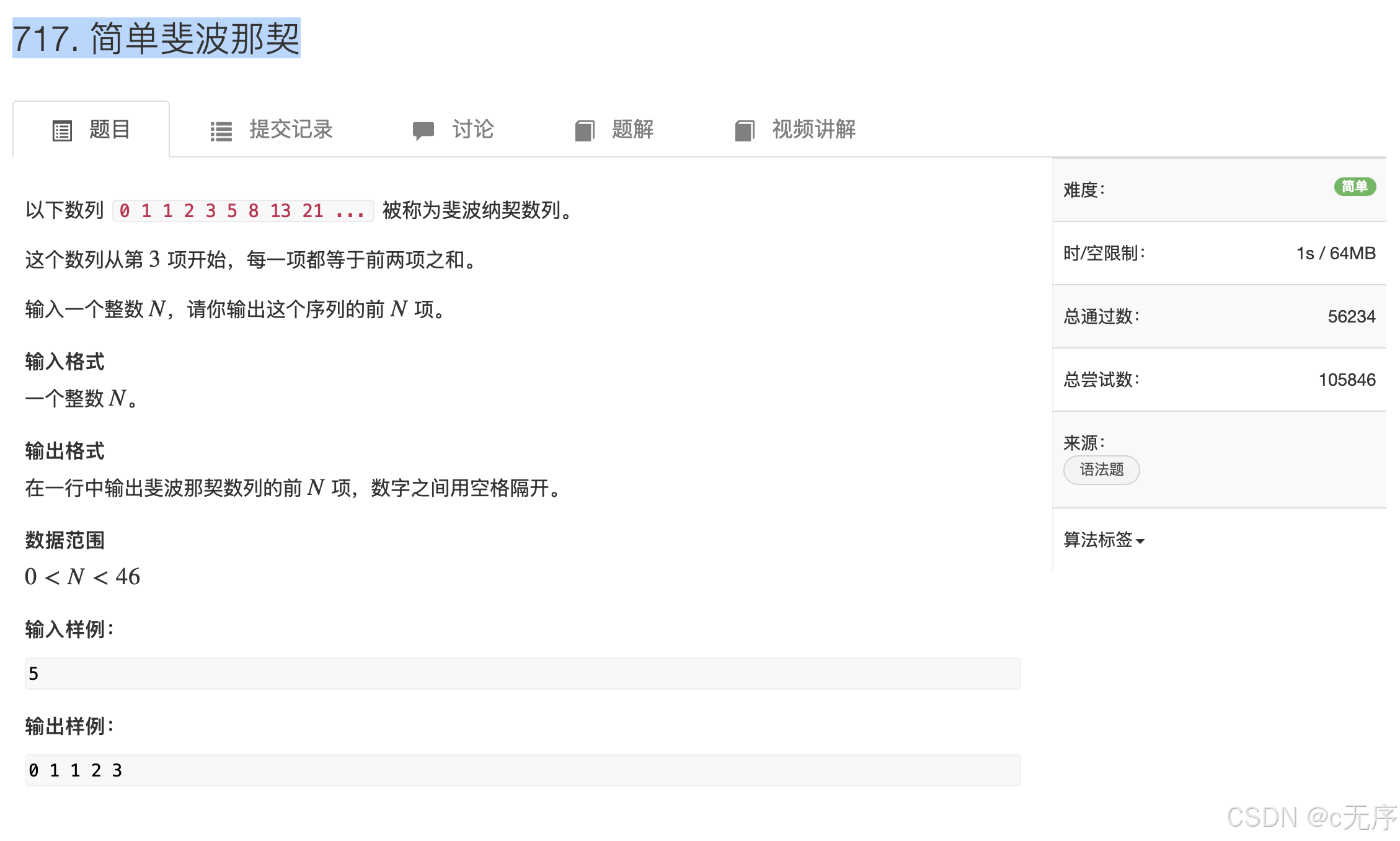
}717.简单斐波那契
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 0;
cin >> n;
int F[47];
F[0] = 0, F[1] = 1, F[2] = 1;
for(int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
F[i] = F[i-1] + F[i-2];
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << F[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}优化
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
int a = 0, b = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cout << a << ' ';
int fn = a + b;
a = b; b = fn;
}
return 0;
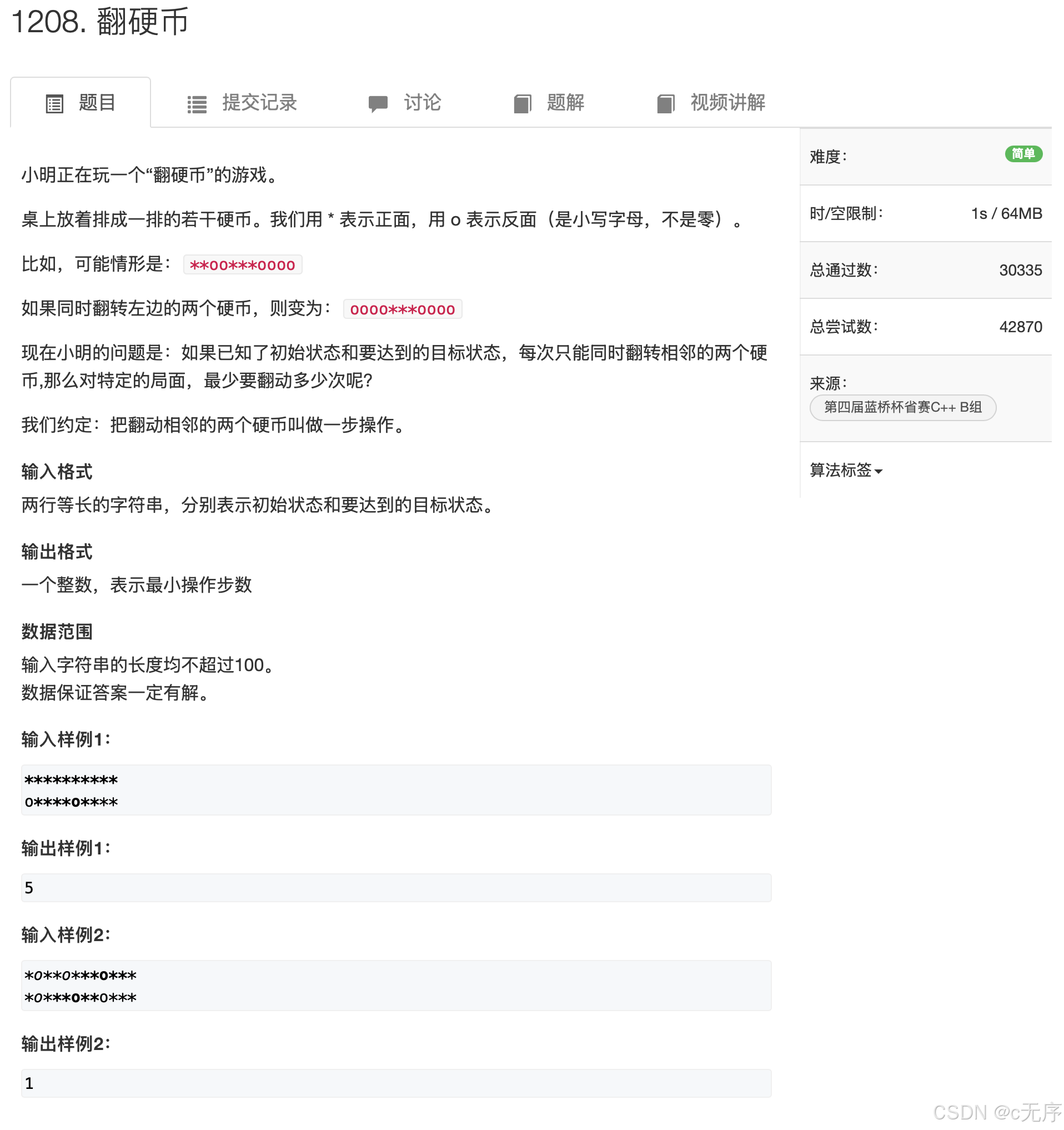
}1208.翻硬币
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
char start[N], aim[N];
void turn(int i)
{
if(start[i] == '*') start[i] = 'o';
else start[i] = '*';
}
int main()
{
cin >> start >> aim;
int n = strlen(start);// 计算输入长度
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
if(start[i] != aim[i])
{
turn(i), turn(i+1);
ret++;
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
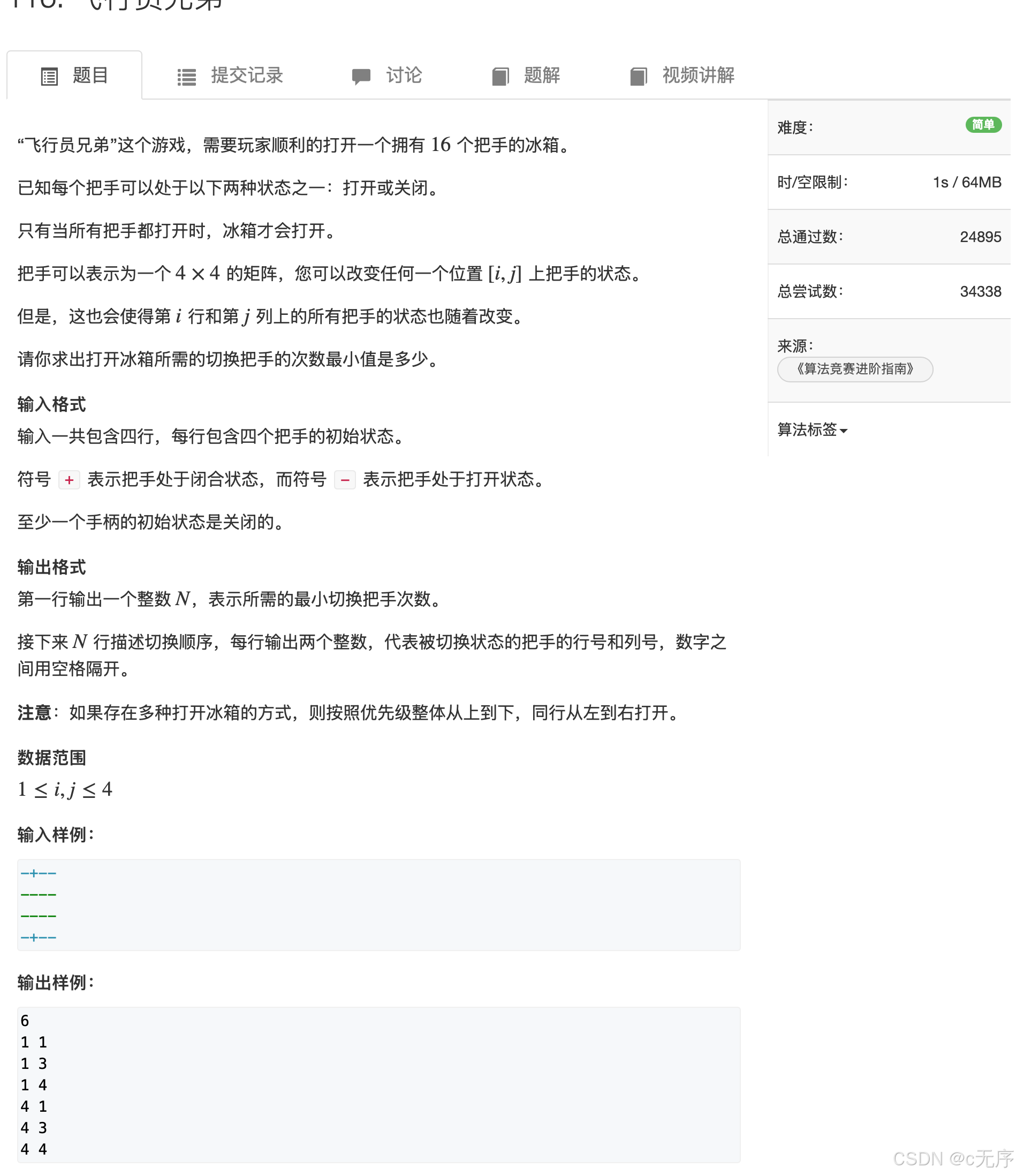
}116.飞行员兄弟
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5;
char g[N][N], backup[N][N];
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
// 映射函数
int get(int i, int j)
{
return i * 4 + j;
}
void turn_one(int x, int y)
{
if(g[x][y] == '-') g[x][y] = '+';
else g[x][y] = '-';
}
void turn_all(int x, int y)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
turn_one(x, i);
turn_one(i, y);
}
turn_one(x, y); // xy在循环中被按了两次,现在调回去
}
int main()
{
vector<PII> res;
// 输入
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
cin >> g[i][j];
// 枚举所有方案
for(int op = 0; op < (1 << 16); op++)
{
vector<PII> temp; // 存储方案
memcpy(backup, g, sizeof(g)); // 备份方案
// 枚举16个位置
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
if(op >> get(i, j) &1) // 判断是不是要按开关
{
temp.push_back({i, j});
turn_all(i, j);
}
}
bool hash_close = false;
// 判断是否全部灯泡已经亮了
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
if(g[i][j] == '+')
hash_close = true;
if(!hash_close)
{
if(res.empty() || res.size() > temp.size() ) res = temp;
}
memcpy(g, backup, sizeof(backup)); // 恢复方案
}
cout << res.size() << endl;
for (auto op : res) cout << op.first + 1 << ' ' << op.second + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}