breast_cancer数据集分析——乳腺癌诊断
#读取乳腺癌数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
data = load_breast_cancer()
X = data.data
y = data.target
.. _breast_cancer_dataset: Breast cancer wisconsin (diagnostic) dataset -------------------------------------------- **Data Set Characteristics:** :Number of Instances: 569 :Number of Attributes: 30 numeric, predictive attributes and the class :Attribute Information: - radius (mean of distances from center to points on the perimeter) - texture (standard deviation of gray-scale values) - perimeter - area - smoothness (local variation in radius lengths) - compactness (perimeter^2 / area - 1.0) - concavity (severity of concave portions of the contour) - concave points (number of concave portions of the contour) - symmetry - fractal dimension ("coastline approximation" - 1) The mean, standard error, and "worst" or largest (mean of the three worst/largest values) of these features were computed for each image, resulting in 30 features. For instance, field 0 is Mean Radius, field 10 is Radius SE, field 20 is Worst Radius. - class: - WDBC-Malignant - WDBC-Benign :Summary Statistics: ===================================== ====== ====== Min Max ===================================== ====== ====== radius (mean): 6.981 28.11 texture (mean): 9.71 39.28 perimeter (mean): 43.79 188.5 area (mean): 143.5 2501.0 smoothness (mean): 0.053 0.163 compactness (mean): 0.019 0.345 concavity (mean): 0.0 0.427 concave points (mean): 0.0 0.201 symmetry (mean): 0.106 0.304 fractal dimension (mean): 0.05 0.097 radius (standard error): 0.112 2.873 texture (standard error): 0.36 4.885 perimeter (standard error): 0.757 21.98 area (standard error): 6.802 542.2 smoothness (standard error): 0.002 0.031 compactness (standard error): 0.002 0.135 concavity (standard error): 0.0 0.396 concave points (standard error): 0.0 0.053 symmetry (standard error): 0.008 0.079 fractal dimension (standard error): 0.001 0.03 radius (worst): 7.93 36.04 texture (worst): 12.02 49.54 perimeter (worst): 50.41 251.2 area (worst): 185.2 4254.0 smoothness (worst): 0.071 0.223 compactness (worst): 0.027 1.058 concavity (worst): 0.0 1.252 concave points (worst): 0.0 0.291 symmetry (worst): 0.156 0.664 fractal dimension (worst): 0.055 0.208 ===================================== ====== ====== :Missing Attribute Values: None :Class Distribution: 212 - Malignant, 357 - Benign :Creator: Dr. William H. Wolberg, W. Nick Street, Olvi L. Mangasarian :Donor: Nick Street :Date: November, 1995 This is a copy of UCI ML Breast Cancer Wisconsin (Diagnostic) datasets. https://goo.gl/U2Uwz2 Features are computed from a digitized image of a fine needle aspirate (FNA) of a breast mass. They describe characteristics of the cell nuclei present in the image. Separating plane described above was obtained using Multisurface Method-Tree (MSM-T) [K. P. Bennett, "Decision Tree Construction Via Linear Programming." Proceedings of the 4th Midwest Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science Society, pp. 97-101, 1992], a classification method which uses linear programming to construct a decision tree. Relevant features were selected using an exhaustive search in the space of 1-4 features and 1-3 separating planes. The actual linear program used to obtain the separating plane in the 3-dimensional space is that described in: [K. P. Bennett and O. L. Mangasarian: "Robust Linear Programming Discrimination of Two Linearly Inseparable Sets", Optimization Methods and Software 1, 1992, 23-34]. This database is also available through the UW CS ftp server: ftp ftp.cs.wisc.edu cd math-prog/cpo-dataset/machine-learn/WDBC/ .. dropdown:: References - W.N. Street, W.H. Wolberg and O.L. Mangasarian. Nuclear feature extraction for breast tumor diagnosis. IS&T/SPIE 1993 International Symposium on Electronic Imaging: Science and Technology, volume 1905, pages 861-870, San Jose, CA, 1993. - O.L. Mangasarian, W.N. Street and W.H. Wolberg. Breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis via linear programming. Operations Research, 43(4), pages 570-577, July-August 1995. - W.H. Wolberg, W.N. Street, and O.L. Mangasarian. Machine learning techniques to diagnose breast cancer from fine-needle aspirates. Cancer Letters 77 (1994) 163-171... 乳腺癌数据集: 威斯康星州乳腺癌(诊断)数据集 -------------------------------------------- **数据集特征:** :实例数: 569 属性数 30 个数字、预测属性和类 :属性信息: - 半径(从中心到周边各点距离的平均值) - 纹理(灰度值的标准偏差) - 周长 - 面积 - 平滑度(半径长度的局部变化) - 紧凑性(周长^2 / 面积 - 1.0) - 凹度(轮廓凹陷部分的严重程度) - 凹点(轮廓凹陷部分的数量) - 对称性 - 分形维度(“海岸线近似值” - 1) 平均值、标准误差和 “最差 ”或最大值(三个最差/最大值的平均值 计算出每幅图像的这些特征的平均值、标准误差和 “最差 ”或最大值(三个最差/最大值的平均值)、 得出 30 个特征值。 例如,字段 0 是平均半径,字段 10 为半径 SE,字段 20 为最差半径。 - 类别 - WDBC-恶性 - WDBC-良性 :统计摘要: ===================================== ====== ====== 最小值 最大值 ===================================== ====== ====== 半径(平均值): 6.981 28.11 纹理(平均值): 9.71 39.28 周长(平均值): 43.79 188.5 面积(平均值): 143.5 2501.0 平滑度(平均值): 0.053 0.163 密实度(平均值): 0.019 0.345 凹度(平均值): 0.0 0.427 凹点(平均值): 0.0 0.201 对称性(平均值): 0.106 0.304 分形维度(平均值): 0.05 0.097 半径(标准误差): 0.112 2.873 纹理(标准误差): 0.36 4.885 周长(标准误差): 0.757 21.98 面积(标准误差): 6.802 542.2 平滑度(标准误差): 0.002 0.031 紧凑性(标准误差): 0.002 0.135 凹度(标准误差): 0.0 0.396 凹点(标准误差): 0.0 0.053 对称性(标准误差): 0.008 0.079 分形维度(标准误差): 0.001 0.03 半径(最差): 7.93 36.04 纹理(最差): 12.02 49.54 周长(最差): 50.41 251.2 面积(最差): 185.2 4254.0 平滑度(最差): 0.071 0.223 紧凑性(最差): 0.027 1.058 凹度(最差): 0.0 1.252 凹点(最差): 0.0 0.291 对称性(最差): 0.156 0.664 分形维度(最差): 0.055 0.208 ===================================== ====== ====== :缺失属性值: 无 :类别分布:212 - 恶性,357 - 良性 :Creator: William H. Wolberg 博士、W. Nick Street、Olvi L. Mangasarian :Donor: 尼克-斯切特 :Date: 1995 年 11 月 这是 UCI ML 乳腺癌威斯康星(诊断)数据集的副本。 https://goo.gl/U2Uwz2 根据乳腺肿块的细针穿刺(FNA)数字化图像计算特征。 乳腺肿块的细针抽吸(FNA)的数字化图像计算得出的。 它们描述了 图像中细胞核的特征。 上述分离平面是通过 多面方法树(MSM-T)[K. P. Bennett,“通过线性规划构建决策树”。 通过线性规划构建决策树"。第四届 中西部人工智能与认知科学学会论文集》、 pp. 97-101, 1992],这是一种使用线性规划来构建决策树的分类方法。 编程来构建决策树的分类方法。 相关特征 在 1-4 个特征和 1-3 个分离平面的空间内进行穷举搜索,选出相关特征。 特征和 1-3 个分离平面的空间中进行穷举搜索,选出相关特征。 实际用于获取三维空间中分离平面的线性规划 在三维空间中的分离平面的实际线性编程方法见以下文献: [K. P. Bennett 和 O. L. Mangasarian: "Robust Linear Robust Linear Programming Discrimination of Two Linearly Inseparable Sets"、 Optimization Methods and Software 1, 1992, 23-34]。 该数据库也可通过华盛顿大学计算机科学与技术系的 ftp 服务器获取: ftp ftp.cs.wisc.edu cd math-prog/cpo-dataset/machine-learn/WDBC/ .下拉菜单:: 参考文献 - W.N. Street、W.H. Wolberg 和 O.L. Mangasarian. 核特征提取 用于乳腺肿瘤诊断。IS&T/SPIE 1993 国际电子成像研讨会。 电子成像: 科学与技术》,第 1905 卷,第 861-870 页、 加利福尼亚州圣何塞,1993 年。 - O.L. Mangasarian、W.N. Street 和 W.H. Wolberg。乳腺癌诊断和 通过线性规划的预后。运筹学》,43(4),第 570-577 页、 1995年7月-8月。 - W.H. Wolberg、W.N. Street 和 O.L. Mangasarian。机器学习技术 从细针抽吸物诊断乳腺癌。癌症通讯 77 (1994) 163-171.威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集简介
from sklearn import datasets # 加载威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集 cancer_data = datasets.load_breast_cancer() # 特征数据 X = cancer_data.data # 目标变量 y = cancer_data.target
威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集是scikit-learn(sklearn)库中一个常用的内置数据集,用于分类任务。该数据集包含了从乳腺癌患者收集的肿瘤特征的测量值,以及相应的良性(benign)或恶性(malignant)标签。以下是对该数据集的简单介绍:
数据集名称:威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集(Breast Cancer Wisconsin Dataset)
数据集来源:数据集最初由威斯康星州医院的Dr. William H. Wolberg收集。
数据集特征:数据集包含30个数值型特征,这些特征描述了乳腺肿瘤的不同测量值,如肿瘤的半径、纹理、对称性等。
目标变量:数据集的目标变量是二分类的,代表肿瘤的良性(benign)或恶性(malignant)状态。良性表示肿瘤是非恶性的,恶性表示肿瘤是恶性的。
样本数量:数据集包含569个样本,其中良性样本357个,恶性样本212个。
数据集用途:该数据集被广泛用于分类任务、特征选择、模型评估等机器学习任务和实验中。
在使用sklearn库时,可以通过调用datasets.load_breast_cancer()函数加载威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集。加载后的数据集包含两个主要部分:data和target。data存储特征数据,target存储目标变量(标签)数据。
#读取乳腺癌数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
data = load_breast_cancer()
X = data.data
y = data.target
#显示数据集
print(data.DESCR)
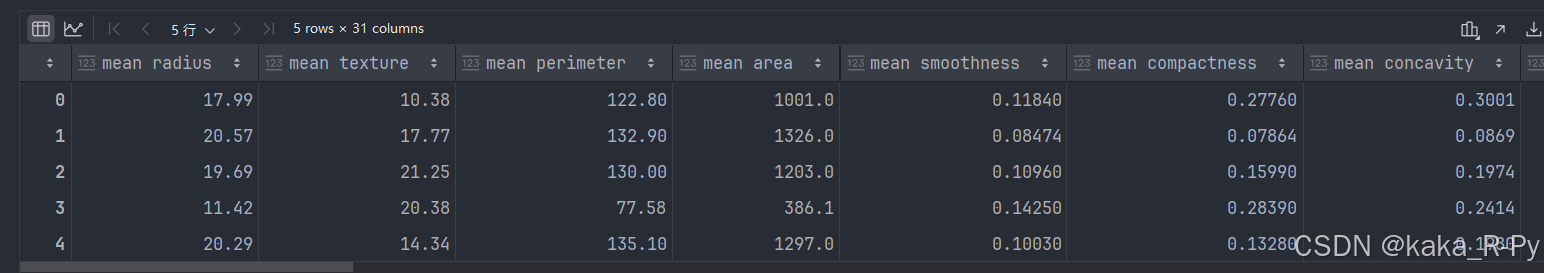
#显示数据dataframe结果
df = pd.DataFrame(data.data, columns=data.feature_names)
df['target'] = data.target
df.head()
#写入csv文件
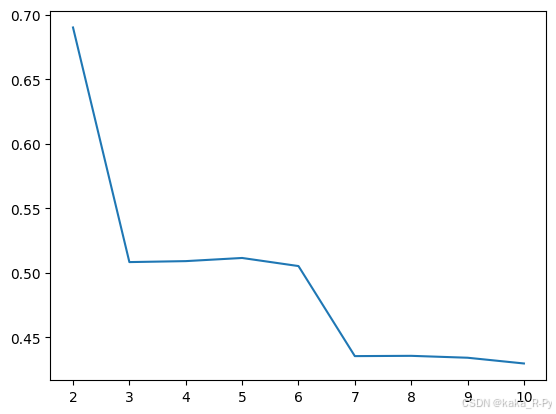
df.to_csv('breast_cancer.csv', index=False)聚合系数法确定最优聚类数。
#使用聚合系数确定最佳聚类数
from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sil = []
for i in range(2,11):
model = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=i)
y_pred = model.fit_predict(X)
sil.append(silhouette_score(X, y_pred))
plt.plot(range(2,11), sil)
plt.show()
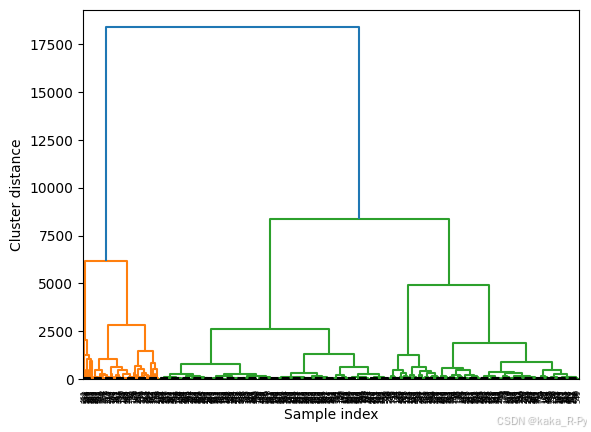
谱系图绘制
#根据最佳聚类数绘制树状图
from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import dendrogram, ward
model = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2)
y_pred = model.fit_predict(X)
linkage_array = ward(X)
dendrogram(linkage_array)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlabel("Sample index")
ax.set_ylabel("Cluster distance")
bounds = ax.get_ybound()
ax.plot(bounds, [40, 40], '--', c='k')
ax.plot(bounds, [5, 5], '--', c='k')
plt.show()