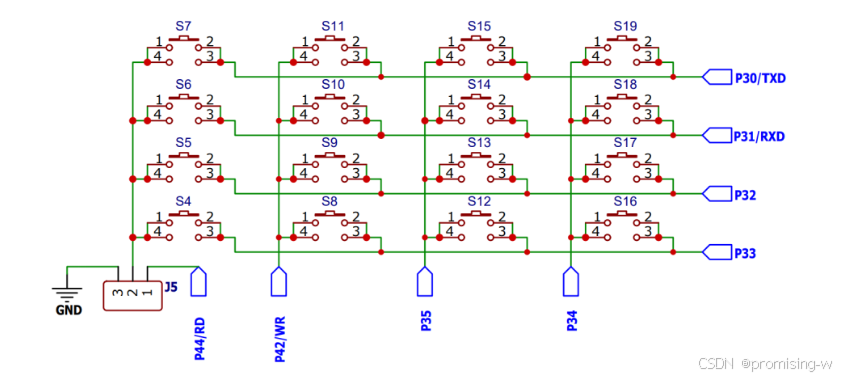
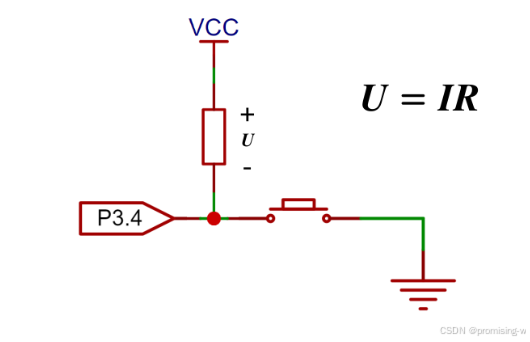
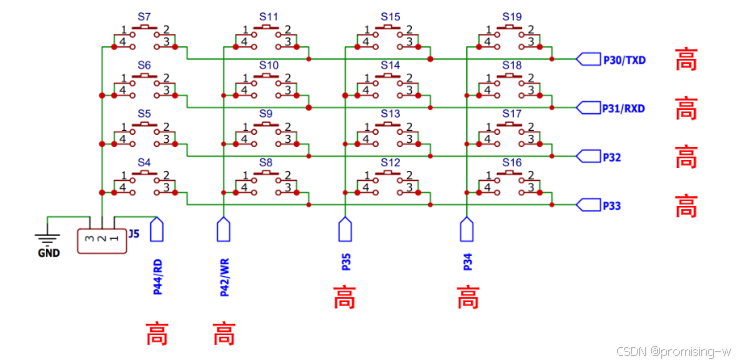
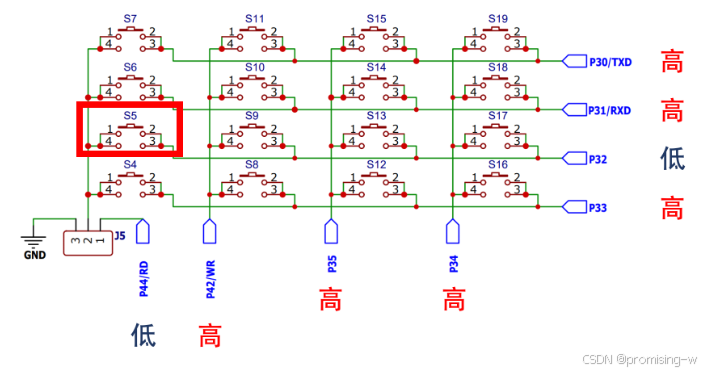
一、按键原理图
当把跳线帽J5放在右侧,属于独立按键模式(BTN模式),放在左侧为矩阵键盘模式(KBD模式)
整体结构是一端接地,一端接控制引脚
之前提到的都是使用了GPIO-准双向口的输出功能,按键模块用到的是输入功能
实际每一个按键的原理图如下,vcc和电阻都在芯片内部,当按键断开时,流过电阻的电流称为灌电流,大概几十毫安,因此此时引脚为高电平。按下时与地接通为低电平
二、独立按键模块代码
#include "key.h"
unsigned char Key_Read_BTN(void)
{
if(P33==0)
return 4;
else if(P32 ==0)
return 5;
else if(P31 ==0)
return 6;
else if(P30 ==0)
return 7;
else
return 0;
}三、矩阵键盘
矩阵键盘用到8个引脚,下方的四个作为输出引脚用,右侧四个用做输入引脚用,矩阵键盘的原理利用扫描法
下面的四个引脚都输出高电平的话,那么无论是否按下,根据上面的原理图可知,右边都会监测到低电平
如果P44设置为低电平,当按下S5时,由于S9,S13,S17均断开,所以P32连接到S5为低电平
四、独立按键与矩阵键盘对比
- 独立按键:
优点:操作简便
缺点:占用I/O资源多
- 矩阵键盘:
优点:节省I/O资源
缺点:操作较为复杂
五、矩阵键盘模块代码
这里将Key_New设置为unsigned int型,因为有16个按键,需要16位数据来存储
#include "key.h"
unsigned char Key_Read_BTN(void)
{
if(P33==0)
return 4;
else if(P32 ==0)
return 5;
else if(P31 ==0)
return 6;
else if(P30 ==0)
return 7;
else
return 0;
}
unsigned char Key_Read_KBD(void)
{
unsigned int Key_New;//16_bit
unsigned char Key_Val;
P44=0;
P42=1;
P35=1;
P34=1;
Key_New=(P3&0x0f); //xxxx xxxx xxxx s4 s5 s6 s7
P44=1;
P42=0;
P35=1;
P34=1;
Key_New=(Key_New<<4)|(P3&0x0f); //xxxx xxxx s4 s5 s6 s7 s8 s9 s10 s11
P44=1;
P42=1;
P35=0;
P34=1;
Key_New=(Key_New<<4)|(P3&0x0f); //xxxx s4 s5 s6 s7 s8 s9 s10 s11 s12 s13 s14 s15 s16
P44=1;
P42=1;
P35=1;
P34=0;
Key_New=(Key_New<<4)|(P3&0x0f); //s4 s5 s6 s7 s8 s9 s10 s11 s12 s13 s14 s15 s16 s17 s18 s19 s20
//s4
//0111 1111 1111 1111b =0xFFFF
//1000 0000 0000 0000b =0x8000
switch(~Key_New)
{
case 0x8000:
Key_Val =4;
break;
case 0x4000:
Key_Val =5;
break;
case 0x2000:
Key_Val =6;
break;
case 0x1000:
Key_Val =7;
break;
case 0x0800:
Key_Val =8;
break;
case 0x0400:
Key_Val =9;
break;
case 0x0200:
Key_Val =10;
break;
case 0x0100:
Key_Val =11;
break;
case 0x0080:
Key_Val =12;
break;
case 0x0040:
Key_Val =13;
break;
case 0x0020:
Key_Val =14;
break;
case 0x0010:
Key_Val =15;
break;
case 0x0008:
Key_Val =16;
break;
case 0x0004:
Key_Val =17;
break;
case 0x0002:
Key_Val =18;
break;
case 0x0001:
Key_Val =19;
break;
default:
Key_Val=0;
}
return Key_Val;
}六、主函数代码
#include "STC15F2K60S2.H"
#include "seg.h"
#include "tim.h"
#include "led.h"
#include "init.h"
#include "key.h"
//Seg
unsigned char pucSeg_Buf[9],pucSeg_Code[9],pucSeg_Pos=0;//字符数组以/0结尾,所以要有9位
//Key
unsigned char ucKey_Val =0;
//Timer
unsigned long ulms =0;
unsigned int uiSeg_Dly=0;
unsigned int uiKey_Dly=0;
void Seg_Proc(void);
void Key_Proc(void);
void main(void)
{
Cls_Peripheral();
Timer0Init();
EA=1;
while(1)
{
Seg_Proc();
Key_Proc();
}
}
void Seg_Proc(void)
{
if(uiSeg_Dly<200)
return;
uiSeg_Dly =0;
sprintf(pucSeg_Buf,"%02d ",(int)ucKey_Val);//奖读取到的按键数制进行输出 加7个空格键熄灭后面的数码管
Seg_Tran(pucSeg_Buf,pucSeg_Code);
}
void Key_Proc(void)
{
if(uiKey_Dly<20)//20毫秒的间隔进行读取,避免漏掉读取
return;
uiKey_Dly =0;
ucKey_Val =Key_Read_KBD();
}
void Time_0(void) interrupt 1
{
ulms++;
uiSeg_Dly++;
uiKey_Dly++;
if(ulms % 2==0)
{
pucSeg_Pos=(pucSeg_Pos+1)%8;//实现pucSeg_Pos从0-7循环的操作
Seg_Disp(pucSeg_Code,pucSeg_Pos);
}
}