字符和字符串
字符类型
Java 中一个字符保存一个Unicode字符,所以一个中文和一个英文字母都占用两个字节。
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char a = 'A';
char b = '中';
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
需要显示 Unicode 编码,可以直接将char值赋给int类型。
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char a = 'A';
char b = '中';
System.out.println((int) a); // 65
System.out.println((int) b); // 20013
}
}
可以用'\u'+Unicode编码转义成字符
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char a = 'A';
char b = '中';
char c = '\u0041'; // 使用\u + Unicode 来进行转义,这里0041是16进制 = 十进制65
System.out.println((int) a);
System.out.println((int) b);
System.out.println(c); // A
}
}
字符串类型
一个字符串可以存储一个到任意个字符,字符串用"..."来进行表示,类似c++。可以使用\来表示转义字符,如\"就可以用来表示":
\"表示字符"\'表示字符'\\表示字符\\n表示换行符\r表示回车符\t表示Tab\u####表示一个Unicode编码的字符
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "\"-\'=\',反斜杠:\\\\来表示\n换行输出,回车符:\r好的\t经过了一个Tab\u0024";
System.out.println(str);
}
}
输出结果:
字符串连接
可以用+来连接字符串和其他的任意类型,但是会将所有的类型先转化成字符串类型,并不会中途进行运算。
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "a";
String b = "b";
String plus = a + b;
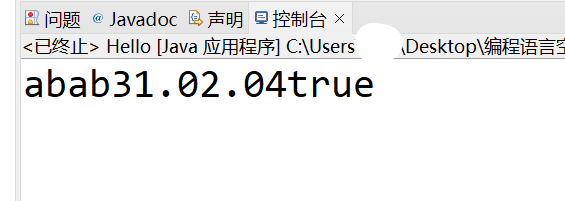
System.out.println(a + b + plus + '3' + 1.0 + 2f + 4 + true);
}
}
输出结果:
多行字符串
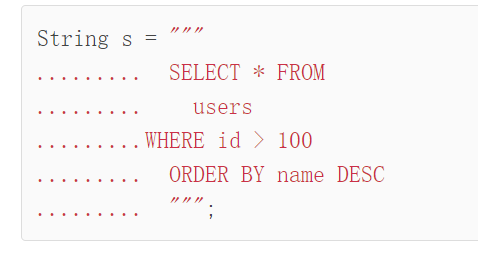
从Java 13开始,可以用 """..."""来表示多行字符串:
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String mutiple_line_string = """
窗前明月光,疑似地上霜。
举头望明月,低头思故乡。
""";
System.out.println(mutiple_line_string);
}
}
输出结果:
这里实际上是三行,因为最后还有一个\n,如果不需要这个换行符,将'''移动到低头思故乡。的后面即可:
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String mutiple_line_string = """
窗前明月光,疑似地上霜。
举头望明月,低头思故乡。""";
System.out.println(mutiple_line_string);
}
}
有一点需要注意的就是,多行字符串前面共同的空格都会被忽略。
图片来自:廖雪峰的官网
不可变特性
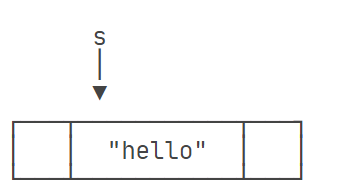
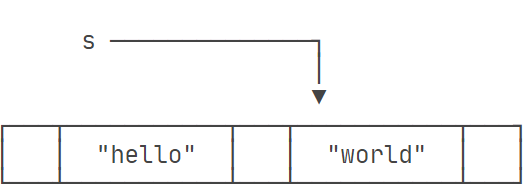
java 中的字符串在创建的过程中经过了如下过程:首先,JVM虚拟机在内存中创建了一个字符串,并让指针指向这个字符串。所以在为字符串变量赋新的值的时候,只是将这个变量指向了内存中新的字符串,原来的字符串还会保留在那里。
// 计算1 + .. + 100
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "Hello";
String b = a;
a = "World";
System.out.println(a); // World
System.out.println(b); // b 仍然指向 Hello
}
}
参考廖雪峰的图:
空值 null
引用对象可以指向一个null表示变量不存在,不指向任何对象。但是请注意,null不等于"“,”" 代表空字符串,是一个有效的字符串。
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = null;
String b = null;
String c = "";
System.out.println(a == b); // true
System.out.println(a == c); // false
}
}
练习
用 int 值存储 Unicode 编码,并将它们拼成一个字符串。
答案
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 72;
int b = 105;
int c = 65281;
// FIXME:
String s = "" + (char) a + (char) b + (char) c;
System.out.println(s);
}
}
廖雪峰的答案中String s = a + b + c ,在我这里是报错的,不确定是否是因为我是Java8的原因。