map
1. 关联式容器
vector、list、deque、forward_list(C++11) 等STL容器,其底层为线性序列的数据结构,里面存储的是元素本身,这样的容器被统称为序列式容器。而 map、set 是一种关联式容器,关联式容器也是用来存储数据的,与序列式容器不同的是,关联式容器里面存储的是 <key, value> 结构的键值对,在数据检索时比序列式容器效率更高。map 和 set 的键是唯一的,但是 mutimap 和 multiset 支持多个同名且有不同映射的键共存。
2. 键值对
用来表示具有一一对应关系的一种结构,该结构中一般只包含两个成员变量 key 和 value, key 代表键值,value 表示与 key 对应的信息。比如:学生的姓名和他的学号是一一对应的,那么就可以通过查找学生的姓名来查找到对应的学号。map容器是 Key,Value 结构,允许修改 value,且允许多个相同的 value 存在。但 map 不允许存在相同的 key(multimap 除外),且 key 不可修改(因为会破坏内部的红黑树结构)。
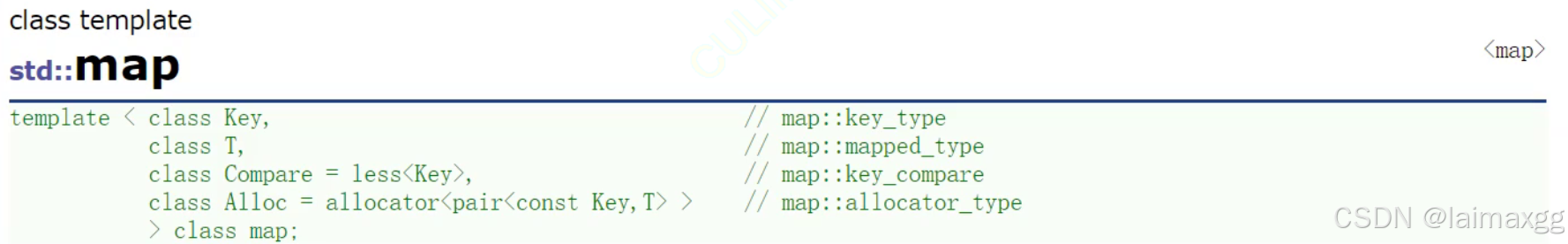
3. map容器
形参含义:
key:键值对应 key 的类型
T:键值对应 value 的类型
Compare:比较器的类型,map 中的元素是按照 key 来比较的,缺省情况下按照小于来比较,一般情况下(内置类型元索)该参数不需要传递,如果无法比较时(自定义类型),需要用户自己显式传递比较规则(一般情况下按照函数指针或者仿函数来传递)
Alloc:通过空间配置器来申请底层空间,不需要用户传递,除非用户不想使用标准库提供的空间配置器
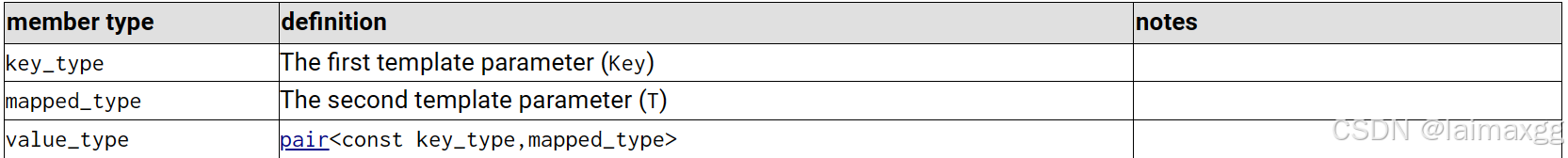
4. map的成员变量
map 中键是不允许被修改的(因为修改键会破坏搜索二叉树的结构),但是映射可以被修改。map 在 value_type 中使用了 pair 来保护键。map 实例化的格式,实际上是调用了 pair 模板的显式实例化。
pair:
template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{
typedef T1 first_type;
typedef T2 second_type;
T1 first;
T2 second;
pair():first(T1()),second(T2())
{}
pair(const T1& a, const T2& b):first(a),second(b)
{}
};
5. map的成员函数
5.1 map的成员函数介绍
map的构造:
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| map<K,V>m() | 构造一个空的map。 |
map的迭代器:
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| begin()和end() | begin:首元素的位置;end:下一个元素的位置。 |
| cbegin()和cend() | c 指const,cbegin和cend指向的内容不能修改。 |
| rbegin()和rend() | 反向迭代器,rbegin 从 end 开始,rend 从 begin 开始,其 ++ 和 – 的方向相反。 |
| crbegin()和crend() | 与前一个功能相同,但指向的内容不能修改。 |
map的容量与元素访问:
| 函数名 | 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| empty | bool empty() const | 检测 map 中的元素是否为空,为空返回 ture,不为空返回 false。 |
| size | size_type size() const | 返回 map 中有效元素的个数。 |
| operator[] | mapped type& operator[] (const key_type& k) | 返回 key 对应的 value。 |
| at | mapped_type& at (const key_type& k);const mapped_type& at (const key_type& k) const; | 返回 key 对应的 value。 |
注意:
在元素访问时,
at()(该函数不常用)函数,于 operator[] 功能相同但有一点区别:当 key 不存在时,operator[] 用默认value 与 key 构造键值对然后插入,返回该默认 value,at()函数直接抛异常。
map的修改:
| 函数名 | 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| insert | pair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& val) | 在 map 中插入键值对 x,注意 x 是一个键值对,返回值也是键值对;iterator 代表新插入元素的位置,bool 代表插入成功。 |
| erase | void erase (iterator position) size_type erase (const key_type& k) void erase (iterator first, iterator last) | 删除 position 位置上的元素。 删除键值为 x 的元素。 删除 [first,last) 区间中的元素。 |
| swap | void swap (map& x) | 交换两个 map 中的元素。 |
| clear | void clear() | 删除 map 里所有的元素。 |
map的操作:
| 函数名 | 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| find | iterator find (const key_type& k) | 搜索 map 里键等于 k 的元素,如果找到返回一个映射的迭代器,找不到返回 end 的迭代器。 |
| count | size_type count (const key_type& k) const | 搜索 map 里键等于 k 的元素,找到返回 1,找不到返回 0。 |
| lower_bound | iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k) | 在 map 里找 >=k 的元素,返回符合情况的最小键的迭代器。 |
| upper_bound | iterator upper_bound (const key_type& k) | 在 map 里找 >k 的元素,返回符合情况的最小键的迭代器。 |
| equal_range | pair<iterator,iterator>equal_range (const key_type& k) |
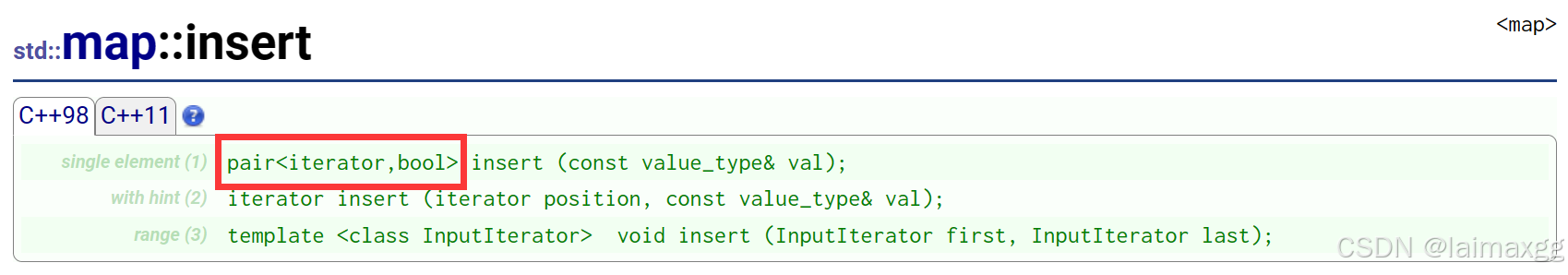
5.2 insert
insert 的返回值是一个 pair 类模板,而它的参数 val 也有一个 pair 类模板。insert 使用 pair 类模板使得它同时具有插入和搜索的功能。 bool 值用来判断 map 中需要插入的值是否已经存在,iterator 是指向 val 值的迭代器。
insert 的返回值:
如果 insert 搜索的 val 值存在,bool 值就为 false(判断插入失败),iterator 会指向 map 中已经存在的 val 值;如果 insert 搜索的 val值不存在,bool 值就为 true(判断插入成功),iterator 会指向新插入的 val 值。
使用 insert 进行搜索:
由于 insert 使用 pair 类模板,所以它也有搜索的功能:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
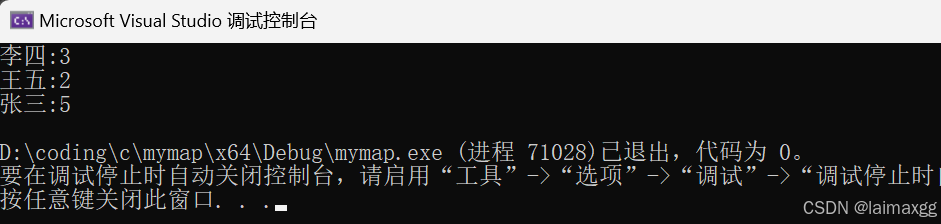
string arr[] = { "张三","李四","王五","张三","张三","李四","张三","李四","王五","张三" };
map<string, int> countmap;
for (auto& e : arr)//传引用是为了拷贝临时变量浪费资源
{
pair<map<string, int>::iterator, bool>ret = countmap.insert(make_pair(e, 1));
if (ret.second == false)
{
ret.first->second++;
}
}
for (auto& i : countmap)
{
cout << i.first << ":" << i.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
5.3 operator[]
map 的 operator[] 是借助 inert 来实现的:
因此 map 的 operator[] 同时具有插入、查找和修改的功能:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> m;
m.insert(make_pair("first", "first"));
m.insert(make_pair("second", "second"));
cout << "before:" << endl;
for (auto& i : m)
{
cout << i.first << " : " << i.second << endl;
}
m["third"];//插入
printf("\n");
cout << m["first"] << endl;//查找
m["first"] = "x";//修改
m["fourth"] = "xxxx";//插入+修改
printf("\n");
cout << "after:" << endl;
for (auto& i : m)
{
cout << i.first << " : " << i.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
6. map的特点
STL 里的 map 和 set 用的是同一颗红黑树来实现的。
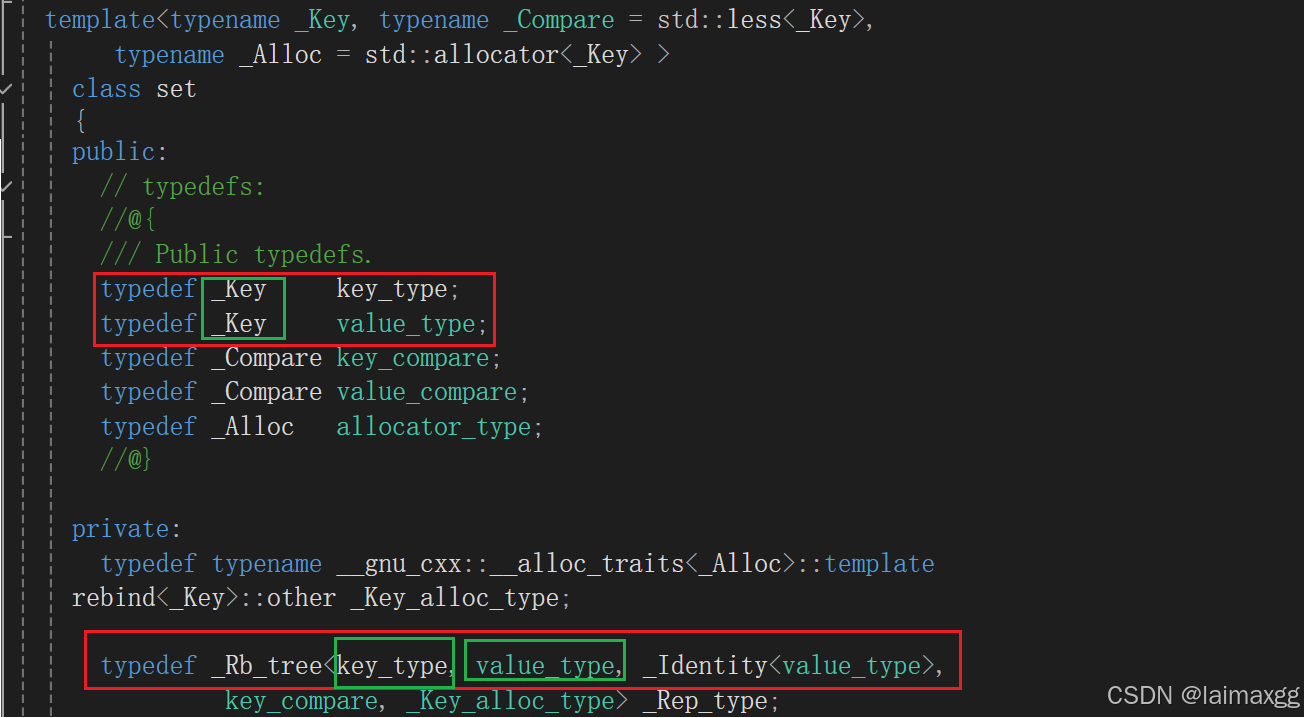
set:
注意:Rb_tree 里有一个 key_type 和一个 value_type,但 set 应该是 key 和 key 的映射关系,所以在成员变量里,STL 把 key_type和 value_type 都定义了为 _key
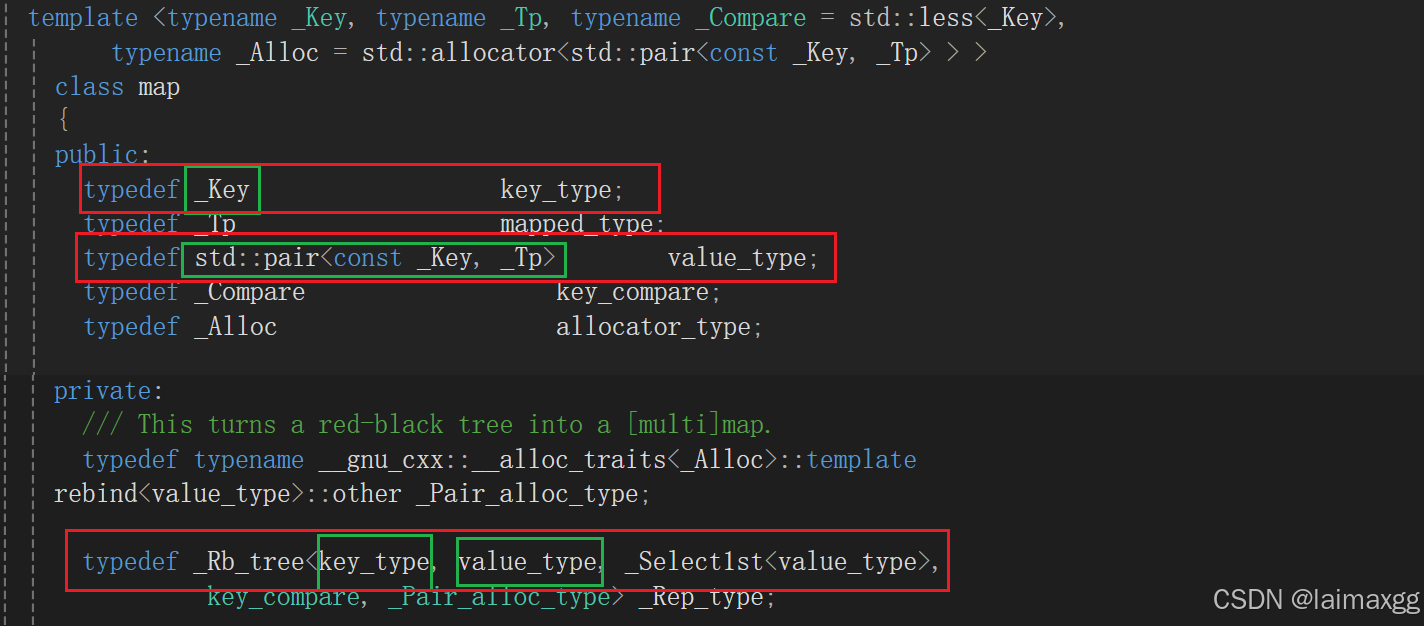
map:
而在 STL 的 map 里,value_type 则定义了一个 pair ,这样做的目的就是为了复用同一颗红黑树。
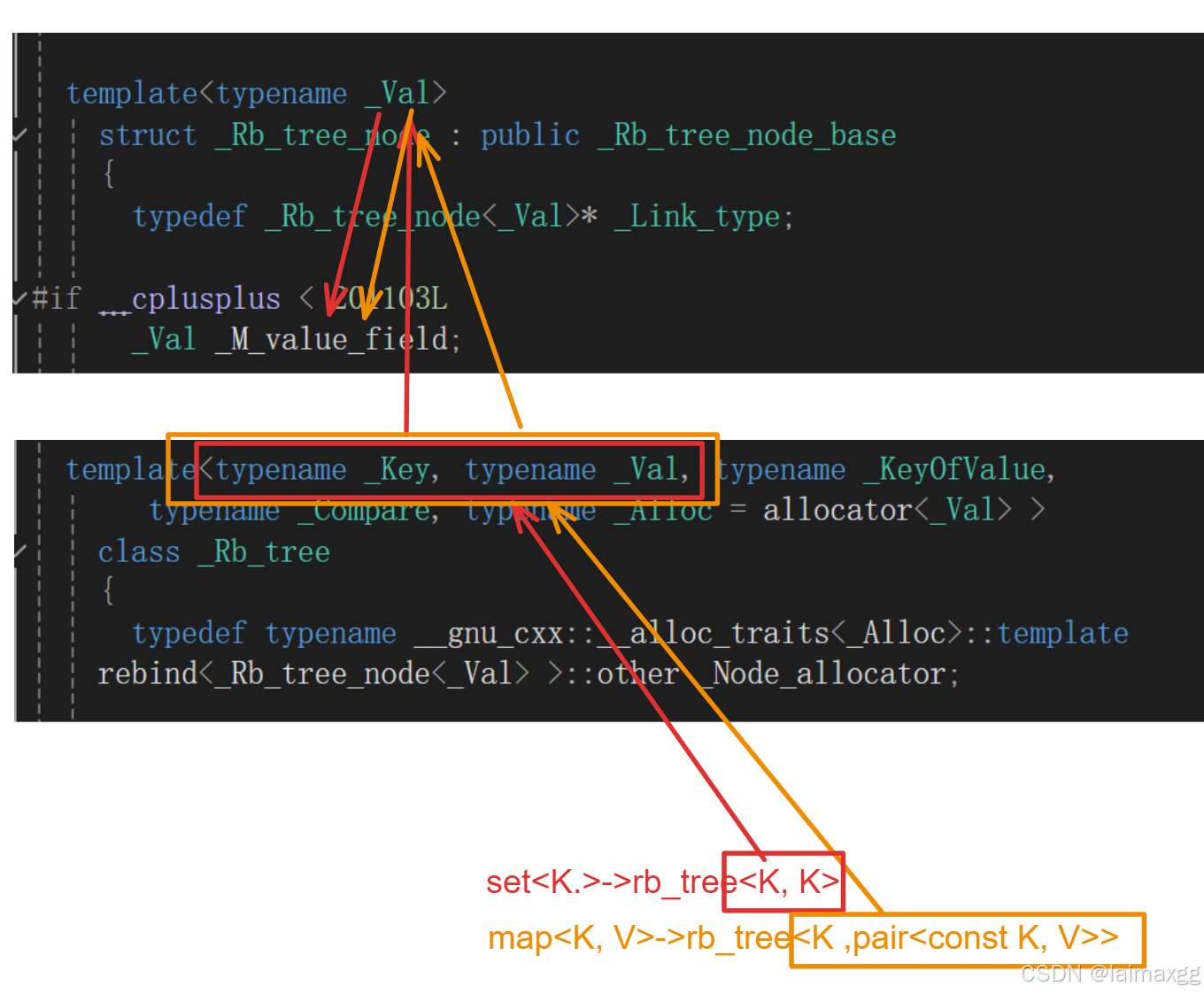
所以从set和map的底层来看,它们的实现方法分别是:
set<K.> ⟶ \longrightarrow ⟶ rb_tree<K, K>
map<K, V> ⟶ \longrightarrow ⟶ rb_tree<K ,pair<const K, V>>
这种写法实际上是由 stl_tree.h 文件中的 val 模板决定你是 key 的 set,还是 key/value 的map:
8. map的复现
rbtree.h
#pragma once
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
enum color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
color _col;
T _data;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_data(data)
,_col(RED)//默认新结点都是红色结点
{}
};
template<class T, class Ptr, class Ref>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ptr, Ref> Self;
Node* _node;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator=(Self node)
{
swap(node);
return *this;
}
void swap(Self& node)
{
std::swap(_node->_data, _node->_data);
}
Self& operator++() //中序遍历
{
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft->_left) //找到左子树的最后一个
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)//如果parent为空,当前结点是根;如果cur不是parent的右,返回parent
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;//如果cur是parent的右,那么说明parent已经被遍历,返回parent的父结点
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
//KeyOfT仿函数用来取出key
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T*, T&> iterator;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T*, const T&> const_iterator;
iterator begin() //返回中序遍历的第一个结点
{
Node* subLeft = _root;
while (subLeft && subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
return iterator(subLeft);
}
iterator end()
{
return nullptr;
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
_size++;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
//找最开始的插入位置的parent
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))//保证插入只比较k
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;//大的往右
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;//小的往左
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
//决定插入到parent的哪一边
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//开始调整树的结构
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情况一:叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//情况二:叔叔不存在或存在且为黑
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
//情况三:情况二但插入在parent的右边
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//parent是grandfather的右子树
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情况一:叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//情况二:叔叔不存在或存在且为黑
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
//情况三:情况二但插入在parent的左边
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_size++;
_root->_col = BLACK;//防止向上更新把根的颜色改了
return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}
// 检测红黑树是否为有效的红黑树,注意:其内部主要依靠_IsValidRBTRee函数检测
bool IsValidRBTRee()
{
return _IsValidRBTRee(_root);
}
bool Empty() const
{
return _root == nullptr;
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return iterator(cur);
}
}
return end();
}
size_t Size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t Count(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if(kot(cur->_data)==key)
{
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
void Clear()
{
_Clear(_root);
}
void Erase(iterator pos) //del是删除节点,repl是替换节点,repl_parent是替换节点的父结点,bro的删除节点的兄弟节点
{
Node* del = pos._node;
if (del == nullptr) // 如果待删除节点为空,则直接返回
return;
Node* repl = del;
Node* subrepl = nullptr;
Node* repl_parent = nullptr;
if (repl->_left == nullptr) // 待删除节点最多只有一个非空子节点,此时 repl == del
subrepl = repl->_right;
else if (repl->_right == nullptr)
subrepl = repl->_left;
else // 待删除节点有两个非空子节点
{
repl = repl->_right; // 选择右子树的最左子节点作为替代节点
while (repl->_left != nullptr)
repl = repl->_left;
subrepl = repl->_right; // subrepl 可能为空
}
if (repl != del) // 如果替代节点 repl 不等于原始待删除节点 del,将 repl 移动到 del 的位置,并进行颜色交换
{
del->_left->_parent = repl;
repl->_left = del->_left;
if (repl != del->_right)
{
repl_parent = repl->_parent;
if (subrepl)
subrepl->_parent = repl->_parent;
repl->_parent->_left = subrepl; // repl 必然是左子节点
repl->_right = del->_right;
del->_right->_parent = repl;
}
else
repl_parent = repl;
if (_root == del)
_root = repl;
else if (del->_parent->_left == del)
del->_parent->_left = repl;
else
del->_parent->_right = repl;
repl->_parent = del->_parent;
swap(repl->_col, del->_col);
repl = del;
}
else // 如果替代节点 repl 等于原始待删除节点 del
{
repl_parent = repl->_parent;
if (subrepl)
subrepl->_parent = repl->_parent;
if (_root == del)
_root = subrepl;
else if (del->_parent->_left == del)
del->_parent->_left = subrepl;
else
del->_parent->_right = subrepl;
}
if (repl->_col != RED) // 如果删除的节点颜色不是红色,则需要重新平衡树
{
while (subrepl != _root && (subrepl == nullptr || subrepl->_col == BLACK))
{
if (subrepl == repl_parent->_left) //注意repl_parent可以是repl的父结点或它本身
{
Node* bro = repl_parent->_right;
if (bro->_col == RED) // 情况1:兄弟节点 bro 是红色
{
bro->_col = BLACK;
repl_parent->_col = RED;
RotateL(repl_parent);
bro = repl_parent->_right;
}
if ((bro->_left == nullptr || bro->_left->_col == BLACK) &&
(bro->_right == nullptr || bro->_right->_col == BLACK)) // 情况2:兄弟节点 bro 为黑色,并且其两个子节点也为黑色
{
bro->_col = RED;
subrepl = repl_parent;
repl_parent = repl_parent->_parent;
}
else
{
if (bro->_right == nullptr || bro->_right->_col == BLACK) // 情况3:兄弟节点 bro 为黑色,左子节点为红色,右子节点为黑色
{
if (bro->_left)
bro->_left->_col = BLACK;
bro->_col = RED;
RotateR(bro);
bro = repl_parent->_right;
}
// 情况4:兄弟节点 bro 为黑色,右子节点为红色
bro->_col = repl_parent->_col;
repl_parent->_col = BLACK;
if (bro->_right)
bro->_right->_col = BLACK;
RotateL(repl_parent);
break;
}
}
else // 对称地处理右子树的情况
{
Node* bro = repl_parent->_left;
if (bro->_col == RED) // 情况1:兄弟节点 bro 是红色
{
bro->_col = BLACK;
repl_parent->_col = RED;
RotateR(repl_parent);
bro = repl_parent->_left;
}
if ((bro->_right == nullptr || bro->_right->_col == BLACK) &&
(bro->_left == nullptr || bro->_left->_col == BLACK)) // 情况2:兄弟节点 bro 为黑色,并且其两个子节点也为黑色
{
bro->_col = RED;
subrepl = repl_parent;
repl_parent = repl_parent->_parent;
}
else
{
if (bro->_left == nullptr || bro->_left->_col == BLACK) // 情况3:兄弟节点 bro 为黑色,右子节点为红色,左子节点为黑色
{
if (bro->_right)
bro->_right->_col = BLACK;
bro->_col = RED;
RotateL(bro);
bro = repl_parent->_left;
}
// 情况4:兄弟节点 bro 为黑色,左子节点为红色
bro->_col = repl_parent->_col;
repl_parent->_col = BLACK;
if (bro->_left)
bro->_left->_col = BLACK;
RotateR(repl_parent);
break;
}
}
}
if (subrepl)
subrepl->_col = BLACK;
}
delete repl; // 删除节点
_size--; // 更新树的大小
}
private:
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)//b不一定有
subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)//判断100为根结点的情况
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else //判断100还有父结点的情况
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)//判断100在它父结点的左边的情况
{
ppnode->_left = subR;
}
else //判断100在它父结点的右边的情况
{
ppnode->_right = subR;
}
}
subR->_parent = ppnode;
//parent->_bf = 0;
//subR->_bf = 0;
}
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
subL->_right = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppnode;
}
//subL->_bf = 0;
//parent->_bf = 0;
}
void _Clear(Node* node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
_Clear(node->_left);
_Clear(node->_right);
delete node;
_size = 0;
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
size_t _size = 0;
};
map.h
#pragma once
#include"RBtree.h"
namespace mymap
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
map()
{}
map(const pair<K, V>& m)
{
for (auto& e : m)
{
insert(m);
}
}
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
size_t size() const
{
return _t.Size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _t.Empty();
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
size_t count(const K& key)
{
return _t.Count(key);
}
void clear()
{
_t.Clear();
}
void erase(iterator pos)
{
_t.Erase(pos);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}