在 React 中,props(即属性)是组件之间传递数据的一种方式。它是 React 组件的基础,用于将数据从父组件传递到子组件。
一、类组件中
1. props 的作用
- 数据传递:
props允许父组件向子组件传递数据。子组件可以使用这些数据来渲染内容、改变显示的内容等。 - 控制组件行为: 通过
props,父组件可以控制子组件的行为和外观。这些属性可以是基本数据类型、函数、数组等。 - 组件间的通信:
props是父子组件通信的重要机制。子组件不能直接修改父组件的状态,但可以通过props收到函数作为属性,进而通知父组件去更新状态。
2. 基本语法
传递 props
父组件可以向子组件传递 props,使用自定义标签时就像设置 HTML 属性一样:
// 父组件
class ParentComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<ChildComponent name="Alice" age={10} />
);
}
}
在上面的例子中,父组件 ParentComponent 向子组件 ChildComponent 传递了两个属性:name 和 age。
接收 props
子组件通过 this.props 访问传递给它的 props,可以在 render() 方法或其他生命周期方法中使用:
// 子组件
class ChildComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>Name: {this.props.name}</p>
<p>Age: {this.props.age}</p>
</div>
);
}
}
3. props 的特点
-
不可变性:
props是只读的,子组件不能直接修改从父组件传递来的props。如果需要更新状态,应该通过回调函数通知父组件由父组件来更改状态。 -
动态更新: 当父组件的状态发生变化时,React 会重新渲染子组件,并更新
props中的值。
// 父组件
class ParentComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "Alice",
age: 10
};
}
incrementAge = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({ age: prevState.age + 1 }));
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<ChildComponent
name={this.state.name}
age={this.state.age}
incrementAge={this.incrementAge}
/>
</div>
);
}
}
// 子组件
class ChildComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Name: {this.props.name}</h1>
<h2>Age: {this.props.age}</h2>
<button onClick={this.props.incrementAge}>Increment Age</button>
</div>
);
}
}
// 渲染组件
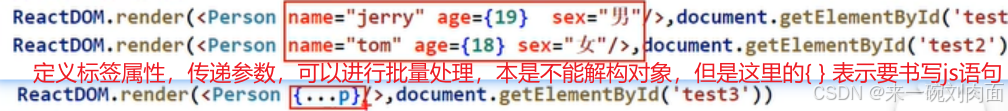
ReactDOM.render(<ParentComponent />, document.getElementById('root'));
4. 组件的 propTypes 和默认 props
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
// 定义属性类型
Person.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 必传,字符串
age: PropTypes.number.isRequired, // 必传,数字
sex: PropTypes.string // 可选,字符串
speak:PropTypes.func // 可选,函数
};
// 定义默认属性(可选)
Person.defaultProps = {
sex: '未知' // 如果未传性别,默认是 '未知'
};// 定义规则
// Sum.属性规则 = {
// name:'必传,字符串'
// }
// 定义属性类型
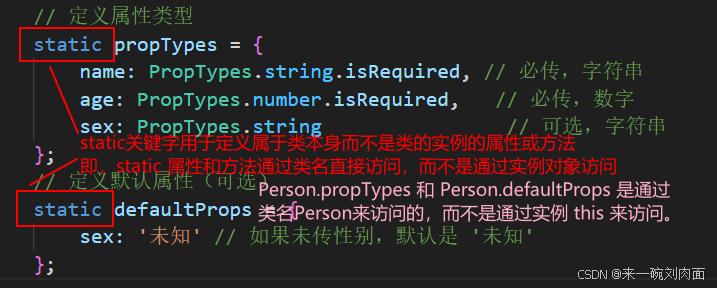
static propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 必传,字符串
age: PropTypes.number.isRequired, // 必传,数字
sex: PropTypes.string // 可选,字符串
};
// 定义默认属性(可选)
static defaultProps = {
sex: '未知' // 如果未传性别,默认是 '未知'
};// 可以这样访问
console.log(Person.propTypes); // 访问类中的静态 propTypes
console.log(Person.defaultProps); // 访问类中的静态 defaultProps
// 而不能这样访问
const instance = new Person();
console.log(instance.propTypes); // 这会返回 undefined,因为 propTypes 是静态的
使用 static 关键字的主要目的是将某些属性或方法与类本身关联,而不是与任何实例相关。在 React 组件中,这通常用于定义 propTypes 和 defaultProps,确保这些配置在类的上下文中清晰可见,并且可以通过类来直接访问。
二、函数组件中
函数式组件中三大属性只有Props属性可以使用
与类组件不同,函数组件没有实例,直接接受 props 作为参数。
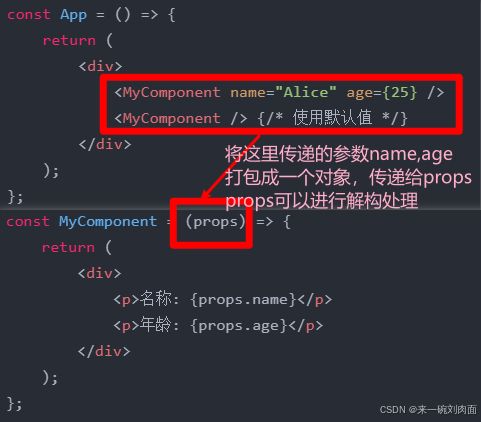
import React from 'react';
const MyComponent = (props) => {
// const {title,content} = props
return (
<div>
<h1>{props.title}</h1>
<p>{props.content}</p>
</div>
);
};
// 或
//const MyComponent = ({ name, age }) => {
// return (
// <div>
// <p>名称: {name}</p>
// <p>年龄: {age}</p>
// </div>
// );
//};
// 默认属性
MyComponent.defaultProps = {
name: '匿名',
age: 0,
};