函数(4)中讲解了函数的嵌套使用与函数的链式访问,以及定义函数时参数与返回类型的一些问题。
一、函数的嵌套
函数的嵌套指的是一个函数调用了另一个函数。
//函数的嵌套调用练习
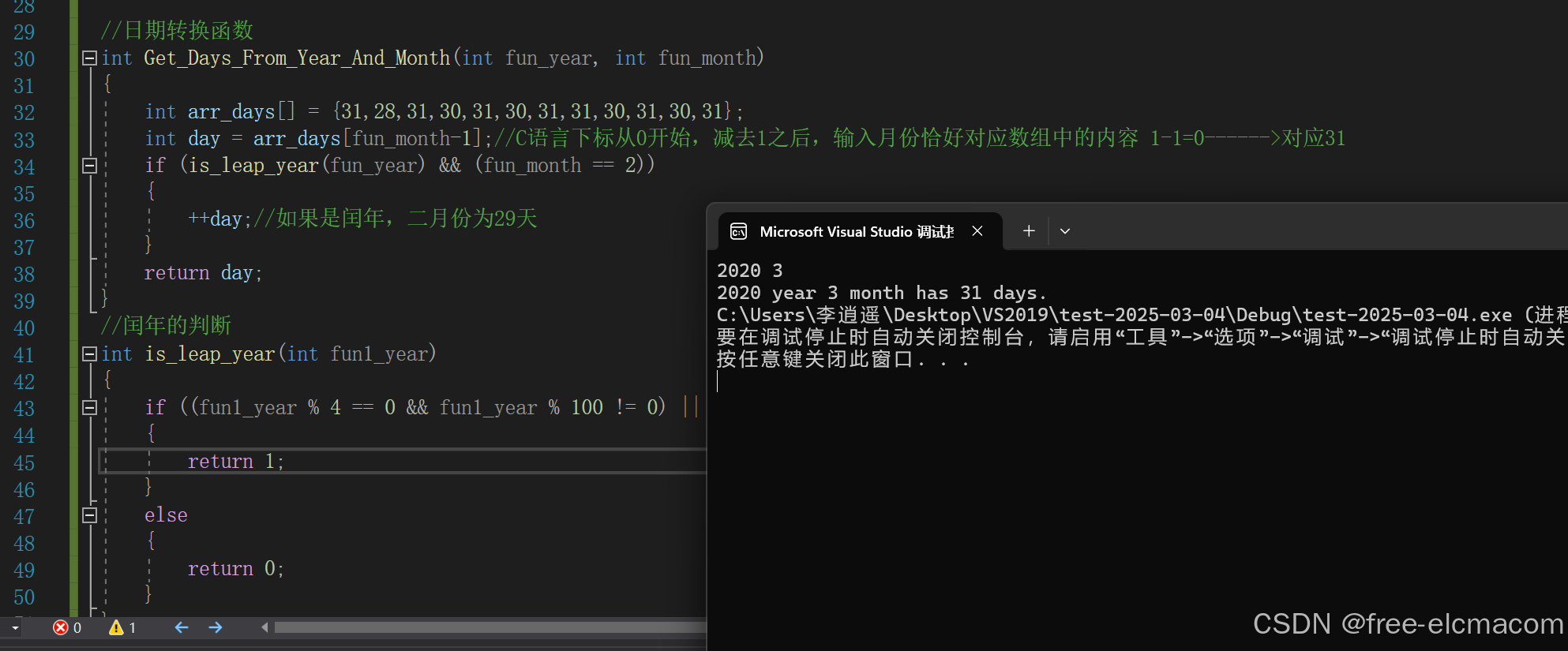
//设计一个函数:输入年份和月份得到相应的天数
//例如:
//输入:2025 3
//输出:31
#include <stdio.h>
//日期转换函数
int Get_Days_From_Year_And_Month(int fun_year, int fun_month)
{
int arr_days[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int day = arr_days[fun_month-1];//C语言下标从0开始,减去1之后,输入月份恰好对应数组中的内容 1-1=0------>对应31
if (is_leap_year(fun_year) && (fun_month == 2))
{
++day;//如果是闰年,二月份为29天
}
return day;
}
//闰年的判断
int is_leap_year(int fun1_year)
{
if ((fun1_year % 4 == 0 && fun1_year % 100 != 0) || fun1_year % 400 == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int main()
{
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int days = 0;
scanf("%d%d",&year,&month);
days=Get_Days_From_Year_And_Month(year,month);
printf("%d year %d month has %d days.",year,month,days);
return 0;
}运行结果:
二、函数的链式访问
函数的链式访问指的是一个函数的返回结果作为另一个函数的参数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
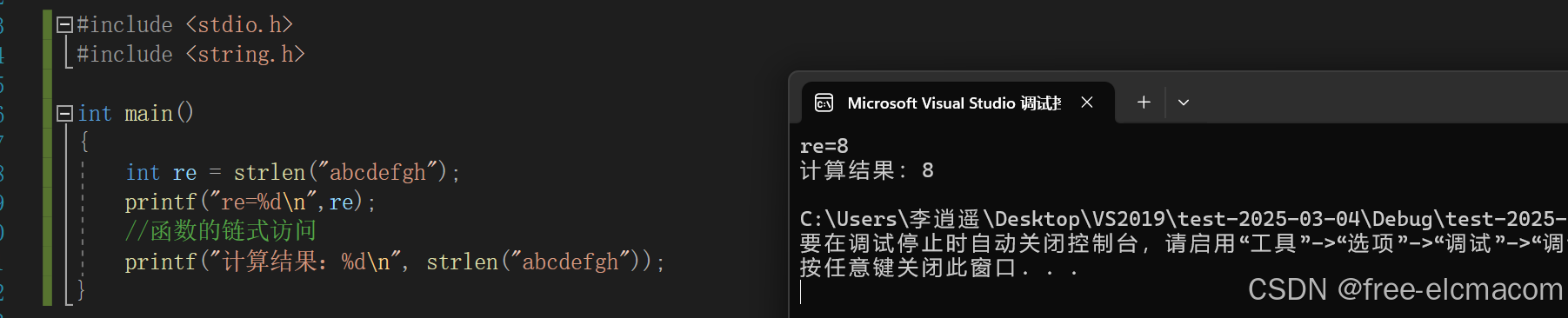
int re = strlen("abcdefgh");
printf("re=%d\n",re);
//函数的链式访问
printf("计算结果:%d\n", strlen("abcdefgh"));
}运行结果:
练习参考:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
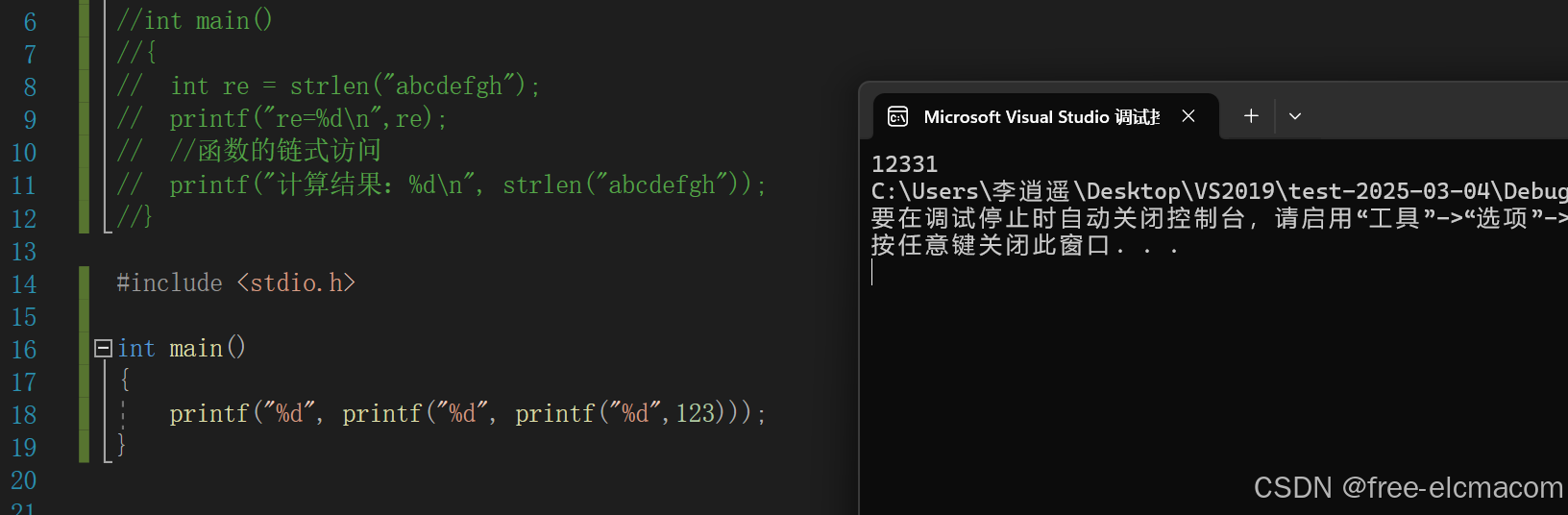
{
printf("%d", printf("%d", printf("%d",123)));
}
运行结果:
三、函数参数与返回类型的注意事项
(1)函数的返回类型不写时,默认返回类型为int,为此当不需要返回时可以写void
参考代码:
#include <stdio.h>
//函数的返回类型不写时,默认返回类型为int
//为此当不需要返回时可以写void
test(void)
{
printf("hello\n");
}
int main()
{
int ret = test();
printf("ret=%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}运行结果:
(2)函数定义时若没有形式参数,则实参传入形参时没有影响,但是这个是十分不合理的。
参考代码:
#include <stdio.h>
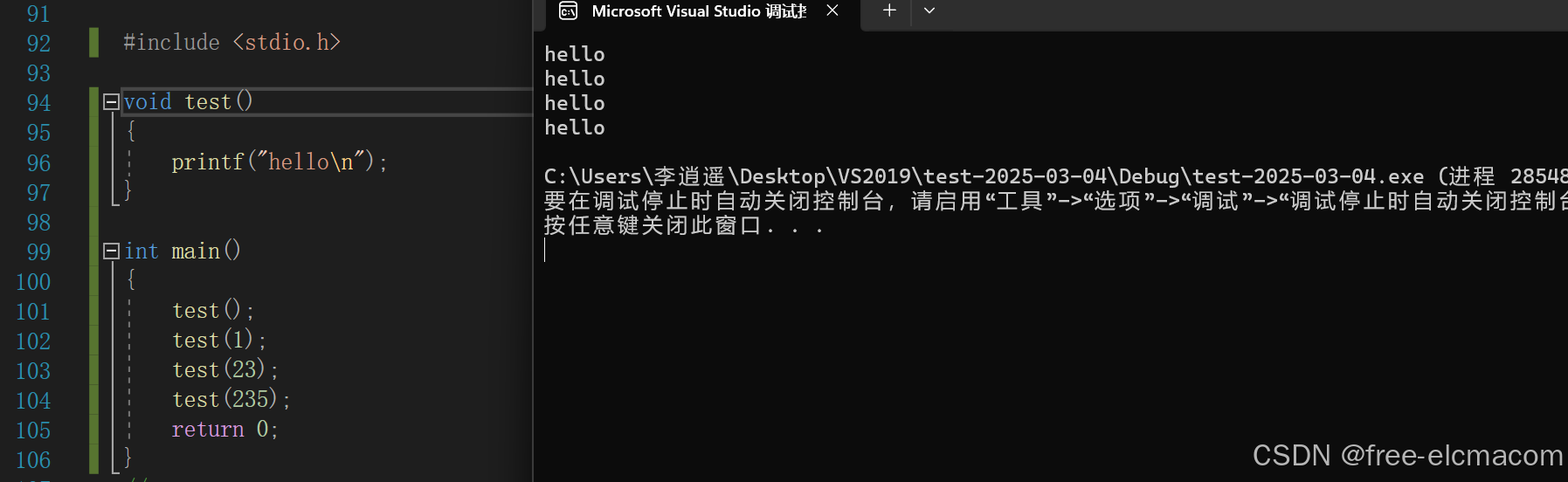
void test()
{
printf("hello\n");
}
int main()
{
test();
test(1);
test(23);
test(235);
return 0;
}运行结果:
为了解决这种不合理性,不需要传入参数时我们在函数的定义时在参数中加入void即可。
修改结果:
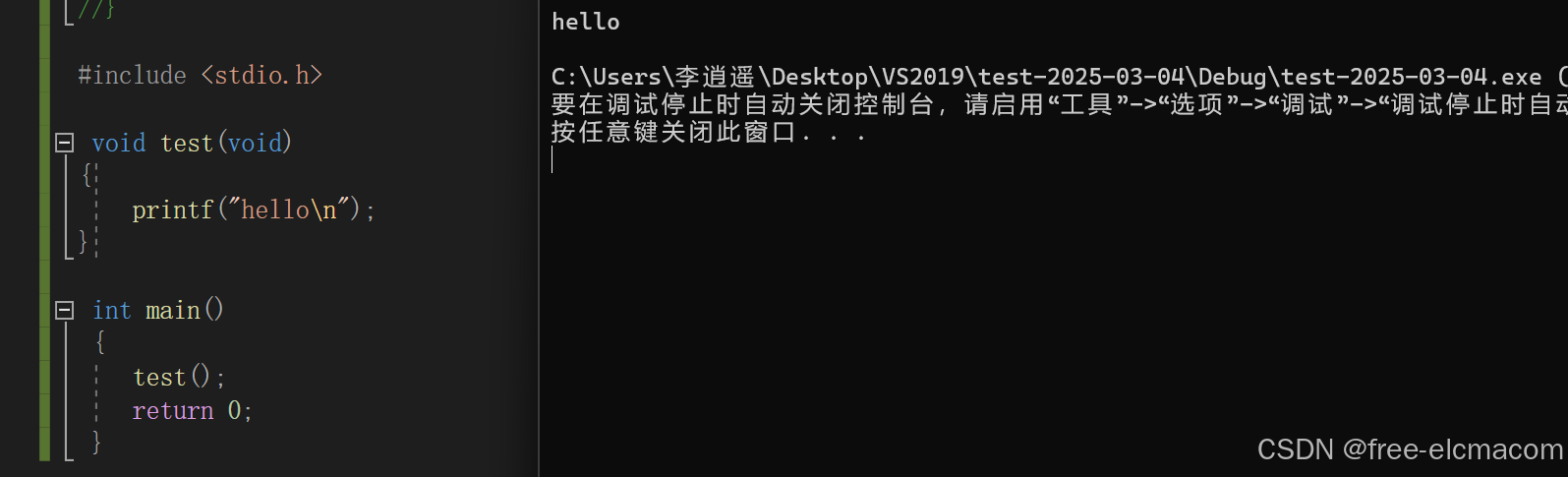
#include <stdio.h>
void test(void)
{
printf("hello\n");
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}运行结果: