目录
前言:
本篇基于上篇【红黑树的实现】,代码也是基于红黑树的代码实现map和set的封装。
一,库中map和set的大致结构
库中部分源代码如下:
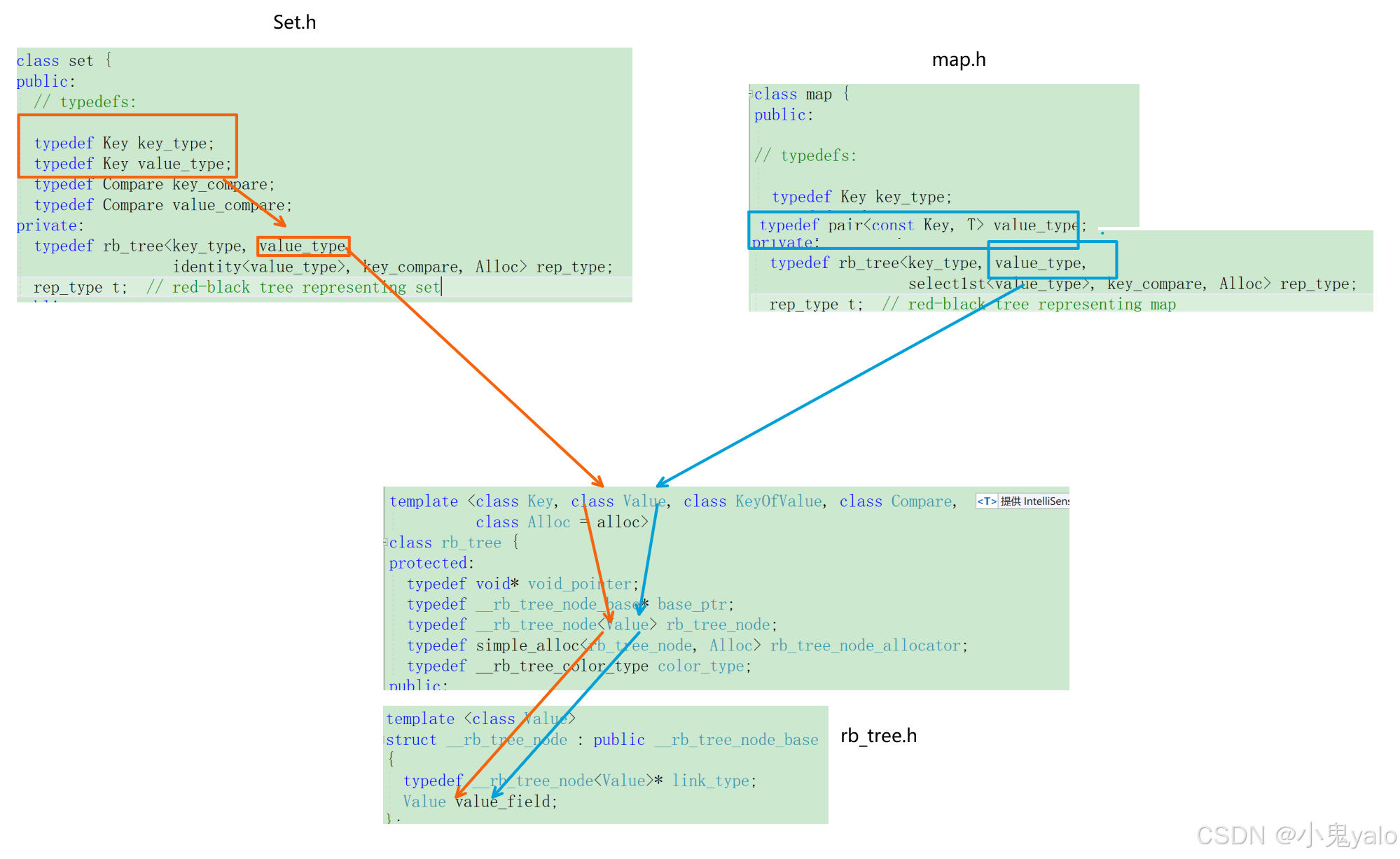
//set
class set {
public:
// typedefs:typedef Key key_type;
typedef Key value_type;//...
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,
identity<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing set};
//map
class map {
public://typedefs:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
//...
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,
select1st<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing map};
//rb_tree红黑树
template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;
Value value_field;
};template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare,
class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree {typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;
};
通过上面的源码可以分析出,map和set的实现采用了泛型思想实现。本来map和set各需要一颗红黑树rb_tree来实现的,这样的话两份代码相似部分极多。而采用泛型的思想,让rb_tree成为一个泛型模板,通过传参的差异决定是 map还是set,这样只需一份rb_tree即可。
rb_tree是实现key的搜索场景,还是实现key/value的搜索场景,是通过第二个模板参数Value决定的,Value的类型确定了,__rb_tree的存储数据的类型就确定了。
对于set,它的底层封装了rb_tree,第二个模板参数传的是key,实例化出的rb_tree,就是支持key的搜索场景。
对于map,它的底层也封装了rb_tree,第二个参数传的是pair<const k,v>,实例化出的rb_tree,就是支持key/value的搜索场景。
还有一点,对于map和set,我们可以知道关键在于底层rb_tree的第二个模板参数,那为什么还要再传第一个模板参数?
对于set类型,通过源码可以发现,底层rb_tree的第一个模板参数和第二个模板参数其实是一样的,都是key。但对于map来说,底层rb_tree的第一个模板参数是key,第二个模板参数是pair<k,v>。由于我们在使用rb_tree的查找(find)接口时,是根据key值来查找的,所以需要传第一个模板参数key。可以认为对于set来说时多余的,而对于map来说是必不可少的。为了实现代码的统一,所以set也要传。
二,模拟实现
2.1,大致框架
set.h
#include "RBTree.h"
//xg
//key
namespace xg
{
template<class k>
class set
{
public:
//...
private:
//底层调用红黑树
//k键值是不能修改的,所以 加上const
RBTree<k, const k> _t;
};
}map.h
#include "RBTree.h"
//map
//pair<k,v>
namespace xg
{
template<class k,class v>
class map
{
public:
//...
private:
//底层调用红黑树
//key值不能修改
RBTree<k, pair<const k, v>> _t;
};
}同时,我们也采取库中的方法,对rb_tree进行修改,使其成为一个泛型结构。
rb_tree.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum color
{
Red,
Black
};
//由类型T决定红黑树为key还是pair类型
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_data(data)
{}
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
T _data;
color _col;
};
//T决定是k还是pair
template<class k,class T>
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
//...
private:
Node* _root=nullptr;
};2.2,复用红黑树实现insert接口
对于set和map,底层直接调用红黑树rb_tree的insert接口。
//set
bool insert(const k& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}//map
bool insert(const pair<k, v>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
我们看看rb_tree中的insert接口(部分代码):
这里需要将参数类型改为T类型,由map和set决定它的类型是key还是pair。
在插入逻辑中,我们需要比较插入元素的key值,从而找到插入位置。
对于set,比较的就是key值。但是对于map,比较的就是kv.fist。
为了满足两种不同的比较,我们可以通过仿函数的方式实现。map和set各实现一个仿函数,用来获取各自的key值。
通过分析源码可知,map和set的第三个模板参数就是为了解决这个问题。
set.h
#include "RBTree.h"
//xg
//key
namespace xg
{
template<class k>
class set
{
public:
struct SetOfk
{
const k& operator()(const k& key)
{
return key;
}
};
bool insert(const k& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
//底层调用红黑树
RBTree<k, const k,SetOfk> _t;
};
}map.h
#include "RBTree.h"
//map
//pair<k,v>
namespace xg
{
template<class k,class v>
class map
{
public:
struct MapOfk
{
const k& operator()(const pair<k, v>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
bool insert(const pair<k, v>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
//底层调用红黑树
RBTree<k, pair<const k, v>,MapOfk> _t;
};
}rb_tree的insert部分:
template<class k,class T,class ValueOfk>
class RBTree{//插入k或者pair类型
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = Black;
//return pair<Iterator,bool>({_root,_root},true);
return {Iterator(_root,_root),true};
}
ValueOfk kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
//用键值k比较
if (kot(cur->_data)< kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) >kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur =cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//......旋转+变色//......
//......
}
};
2.3,迭代器iterator的实现
迭代器本质上是对红黑树节点的封装。我们需要实现对*,->的重载,以及对++,--的实现。
template<class T,class Ref,class ptr>
class RBTreeIterator
{
public:
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, ptr> Self;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//......
//......
private:
//当前节点
Node* _node;
};这里的迭代器实现与list的迭代器实现思路大致相同,通过传Ref和ptr两个参数,从而通过一份模板,实现出iterator和const_iterator.
一些操作符的重载:
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return s._node != _node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return s._node == _node;
}
operator++()的实现:
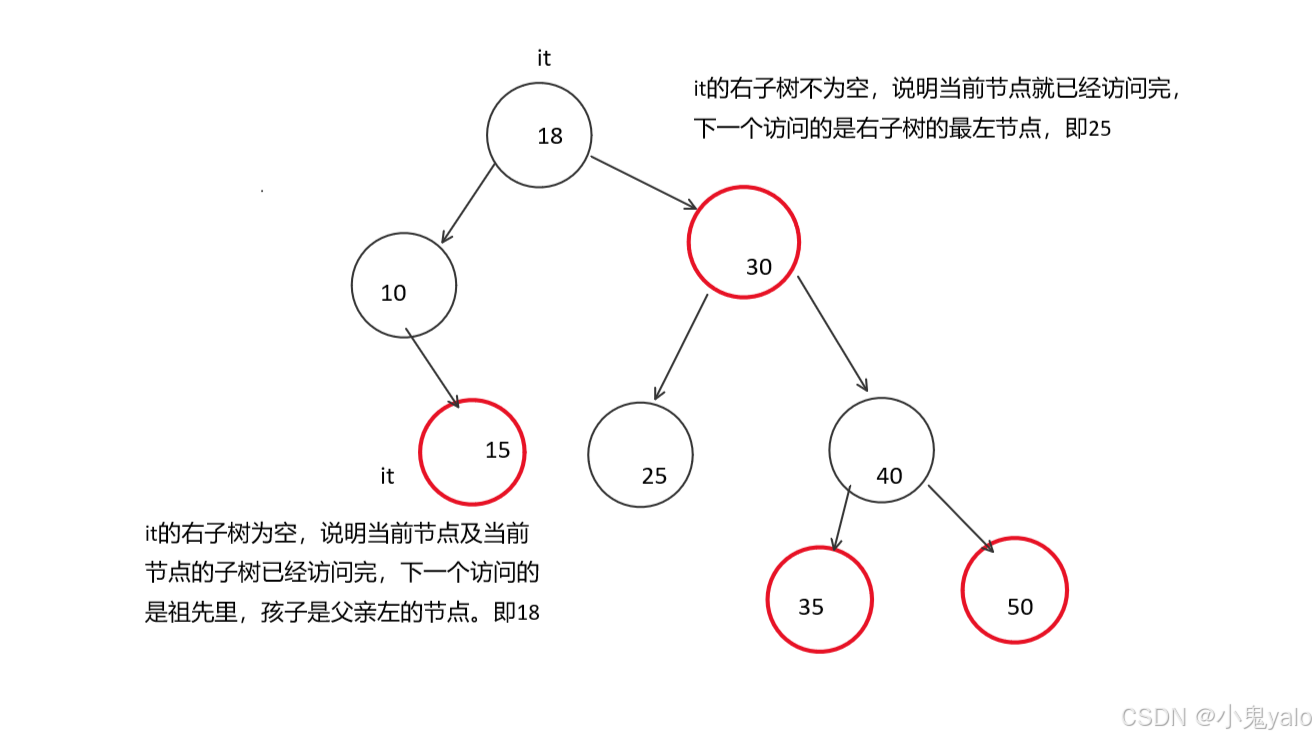
(1)首先,我们要知道map和set的迭代器遍历走的是中序遍历,左子树->根节点->右子树,那么begin()应该返回 中序第一个节点,也就是红黑树的最左节点。而对于end(),我们可以让它是空节点。
(2)迭代器++时,如果it指向的节点的右子树不为空时,说明当前节点已经访问完,下一个节点访问是右子树的中序第一个,也就是右子树的最左节点。
(3)迭代器++时,如果it指向的节点的右子树为空,说明当前节点已经当前节点所在的子树已经访问完了,要访问的下一个节点在当前节点的祖先里面,要沿着当前节点到根的路径找。并且该节点一定满足孩子是父亲的左子树。
Self operator++()
{
//左根右
//当前节点的右子树不为空,继续找右子树的最左节点
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* cur = _node->_right;
while ( cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
_node = cur;
}
else
{
//当前节点的右子树为空,说明当前子树已经访问完
//找孩子为祖先左的祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}operator--()的实现:
实现思路与operator++()相反
(1)迭代器--时,如果it指向的节点的左子树不为空时,说明当前节点已经访问完,下一个节点访问是左子树的最右节点。
(2)迭代器--时,如果it指向的节点的左子树为空,说明当前节点已经当前节点所在的子树已经访问完了,要访问的下一个节点在当前节点的祖先里面,要沿着当前节点到根的路径找。并且该节点一定满足孩子是父亲的右子树。
(3)需要注意的是,可能会遇到end()--的情况,而end()是空节点,会报错。我们可以进行特殊处理,当it==end()时,让 它等于中序遍历的最后一个节点,也就是红黑树的最右节点。
而在最右节点的时候,需要根节点,所以需要在iterator中再加入根节点。
Self operator--()
{
//右根左
if (_node == nullptr) //end()--
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
//当前节点的左子树不为空,继续找左子树的最右节点
else if (_node->_left)
{
Node* cur = _node->_left;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
else
{
//左子树为空,当前子树已访问完
//找孩子为祖先右的节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}对insert返回值的更改:
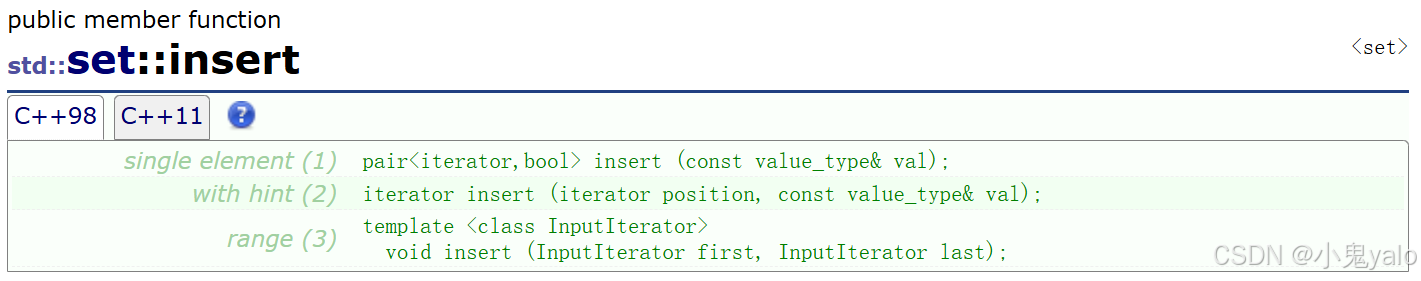
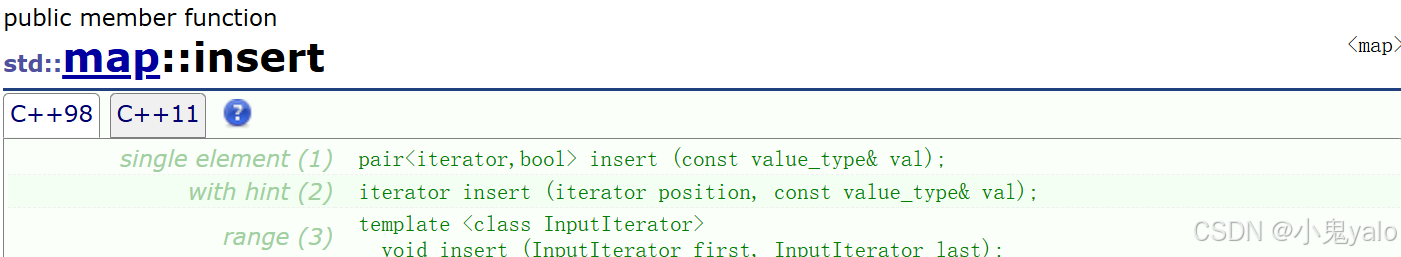
库中的insert方法实现了返回pair<iterator,bool>类型,iterator表示 插入节点的迭代器,bool值表示是否插入成功。 我们只需在返回值处修改,返回iterator迭代器和bool构成的pair类型。
//插入k或者pair类型
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = Black;
//return pair<Iterator,bool>({_root,_root},true);
return {Iterator(_root,_root),true};
}
ValueOfk kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
//用键值k比较
if (kot(cur->_data)< kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) >kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur =cur->_left;
}
else
{
//return pair<Iterator,bool>({cur,_root},false);
return { Iterator(cur, _root), false };
}
}//插入
cur = new Node(data);//cur在下述调整过程中会向上更新变化,需要提前保存下来
Node* newnode = cur;
cur->_col = Red;
if (kot(parent->_data) <kot(data))
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;//颜色处理+旋转
while (parent&& parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
// g
// p u
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//叔叔不存在或者叔叔为黑
// g
// p u
// c
//u为黑,则c是之前是黑的
//u不存在,则c是新插入的
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
// g
// u p
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return pair<Iterator,bool>({newnode,_root},true);
}
2.4,map支持[ ]
map需要支持operator[ ]来实现对value值的访问及修改。
我们在上述实现了insert接口返回pair<iterator,bool>类型,就可以直接复用。
v& operator[](const k& key)
{//key不存在就插入该值和value的缺省值,并返回
//key存在就得到key位置的iterator
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ key,v() });
return ret.first->second;
}
2.5,整体代码
rb_tree.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum color
{
Red,
Black
};
//由类型T决定红黑树为key还是pair类型
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_data(data)
{}
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
T _data;
color _col;
};
template<class T,class Ref,class ptr>
class RBTreeIterator
{
public:
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, ptr> Self;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node,Node* root)
:_node(node)
,_root(root)
{}
Self operator++()
{
//左根右
//当前节点的右子树不为空,继续找右子树的最左节点
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* cur = _node->_right;
while ( cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
_node = cur;
}
else
{
//当前节点的右子树为空,说明当前子树已经访问完
//找孩子为祖先左的祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self operator--()
{
//右根左
if (_node == nullptr) //end()--
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
//当前节点的左子树不为空,继续找左子树的最右节点
else if (_node->_left)
{
Node* cur = _node->_left;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
_node = cur;
}
else
{
//左子树为空,当前子树已访问完
//找孩子为祖先右的节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const//请const吃一顿
{
return s._node != _node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const //请coonst吃一顿
{
return s._node == _node;
}
private:
//当前节点
Node* _node;
Node* _root;//根节点
};
//T决定是k还是pair
template<class k,class T,class ValueOfk>
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;
//迭代器为中序遍历
Iterator Begin()
{
//找最左节点
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur&&cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Iterator(cur,_root);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr,_root);
}
ConstIterator Begin() const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return ConstIterator(cur,_root);
}
ConstIterator End() const
{
return ConstIterator(nullptr,_root);
}
//插入k或者pair类型
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = Black;
//return pair<Iterator,bool>({_root,_root},true);
return {Iterator(_root,_root),true};
}
ValueOfk kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
//用键值k比较
if (kot(cur->_data)< kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) >kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur =cur->_left;
}
else
{
//return pair<Iterator,bool>({cur,_root},false);
return { Iterator(cur, _root), false };
}
}
//插入
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
cur->_col = Red;
if (kot(parent->_data) <kot(data))
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
//颜色处理+旋转
while (parent&& parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
// g
// p u
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//叔叔不存在或者叔叔为黑
// g
// p u
// c
//u为黑,则c是之前是黑的
//u不存在,则c是新插入的
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
// g
// u p
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return pair<Iterator,bool>({newnode,_root},true);
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* pparent = parent->_parent;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pparent->_left == parent)
pparent->_left = subL;
else
pparent->_right = subL;
subL->_parent = pparent;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* pparent = parent->_parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
subR->_left = parent;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pparent->_left == parent)
pparent->_left = subR;
else
pparent->_right = subR;
subR->_parent = pparent;
}
}
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
}
int Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
int size()
{
return _size(_root);
}
int _size(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
return _size(root->_left) + _size(root->_right) + 1;
}
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root=nullptr;
};
set.h
#include "RBTree.h"
//xg
//key
namespace xg
{
template<class k>
class set
{
public:
struct SetOfk
{
const k& operator()(const k& key)
{
return key;
}
};
typedef typename RBTree<k, const k, SetOfk>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<k, const k, SetOfk>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const k& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
//底层调用红黑树
RBTree<k, const k,SetOfk> _t;
};
}map.h
include "RBTree.h"
//map
//pair<k,v>
namespace xg
{
template<class k,class v>
class map
{
public:
struct MapOfk
{
const k& operator()(const pair<k, v>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
typedef typename RBTree<k, pair<const k, v>, MapOfk>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<k, pair<const k, v>, MapOfk>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<k, v>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
v& operator[](const k& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ key,v() });
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
//底层调用红黑树
RBTree<k, pair<const k, v>,MapOfk> _t;
};
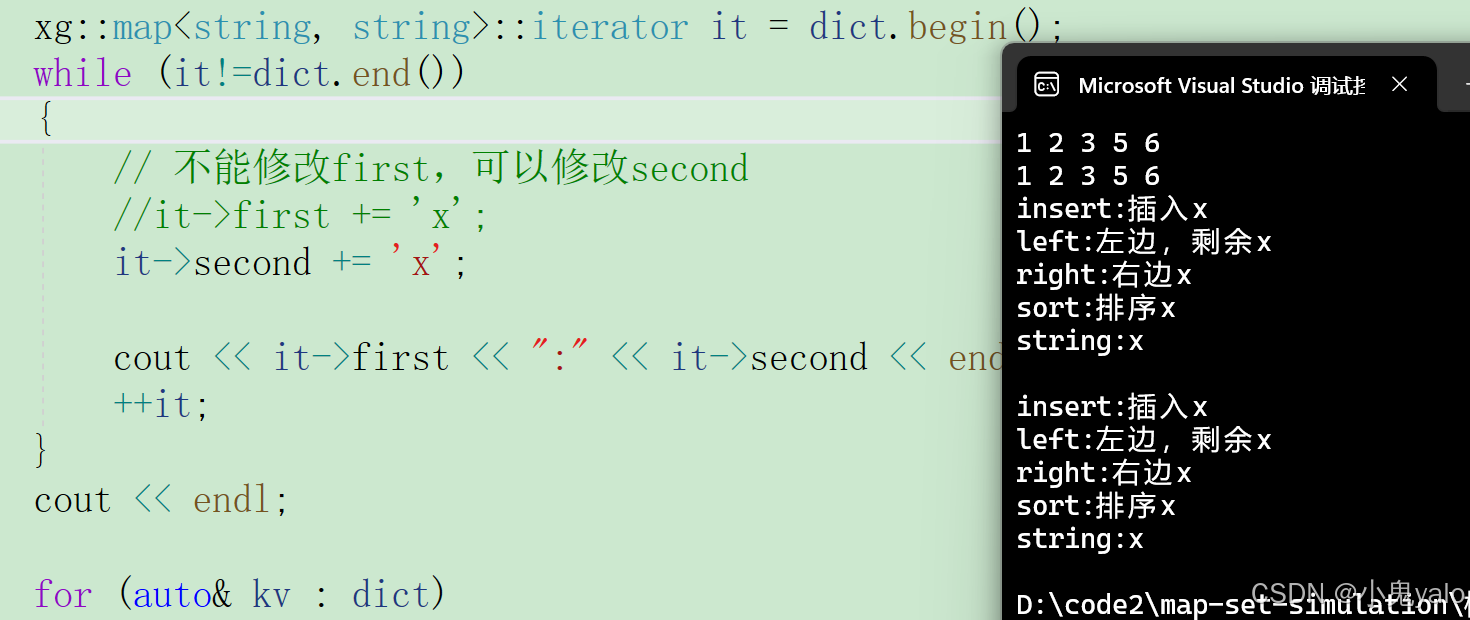
}2.6,代码测试
#include "map.h"
#include "set.h"
#include <string>int main()
{
xg::set<int> s;
s.insert(5);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(6);xg::set<int>::iterator sit = s.begin();
while (sit != s.end())
{
cout << *sit << " ";
++sit;
}
cout << endl;for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;xg::map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });
dict.insert({ "left", "左边" });
dict.insert({ "right", "右边" });dict["left"] = "左边,剩余";
dict["insert"] = "插入";
dict["string"];xg::map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it!=dict.end())
{
// 不能修改first,可以修改second
//it->first += 'x';
it->second += 'x';cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;for (auto& kv : dict)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}return 0;
}