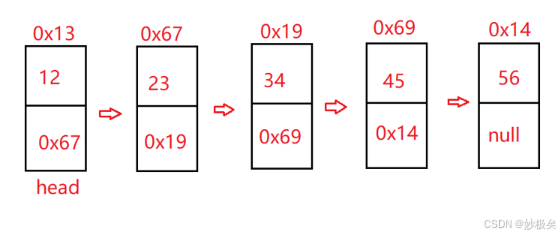
观察ArrayList 顺序表的源码发现,底层是使用数组实现的。由于其底层是一段连续空间,当在ArrayList任意位置插入或者删除元素时,就需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。因此:java集合中又引入了LinkedList,即链表结构。
链表概念
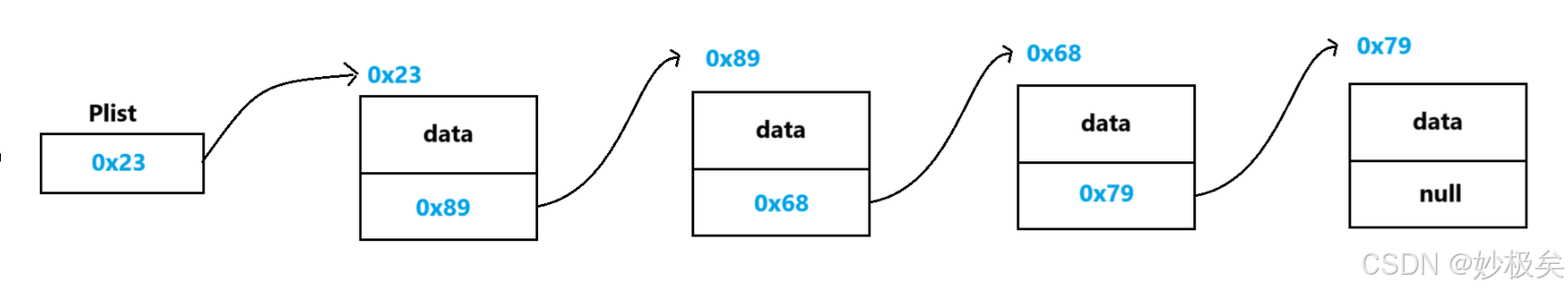
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
由上图可以看出链表在逻辑上是连续的,但是在逻辑上不一定连续
链表有很多不同的结构:
1.不带头单向非循环
2.不带头单向循环
3.不带头双向非循环
4.不带头双向循环
5.带头单向非循环
6.带头单向循环
7.带头双向非循环
8.带头双向循环
共八种不同的结构
本篇文章主要介绍 不带头单向非循环 的链表结构及其方法的实现。
链表的使用
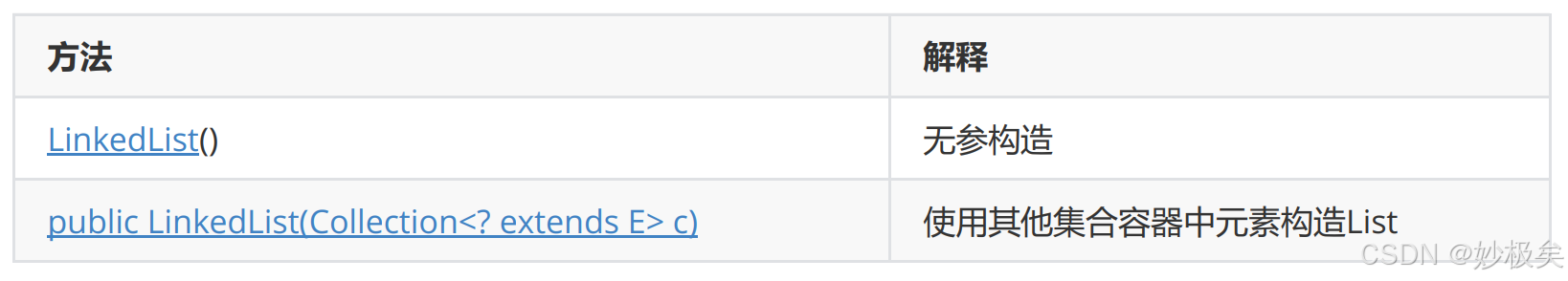
LinkedList的构造
创建LinkedList的代码示例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造一个空的LinkedList
List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> list2 = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
list2.add("JavaSE");
list2.add("JavaWeb");
list2.add("JavaEE");
// 使用ArrayList构造LinkedList
List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
}
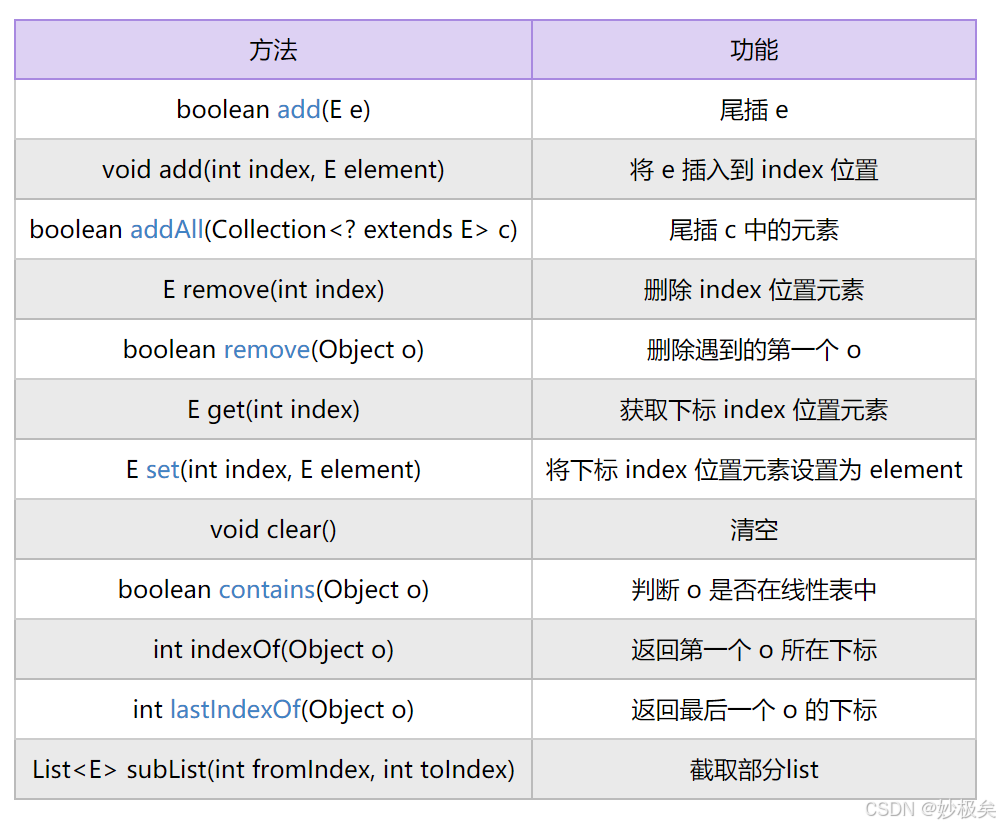
LinkedList的常用方法
LinkedList 的几种遍历方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
System.out.println(list.size());
// foreach遍历
for (int e:list) {
System.out.print(e + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (rit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
单链表的模拟实现(不带头)
LinkedList中常用的方法如下:
// 1、无头单向非循环链表实现
public class SingleLinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
return -1;
}
//清空链表
public void clear() {
}
//打印链表
public void display() {}
}
核心就是遍历链表,所有方法的具体实现如下:
public class MySingleList {
//内部类 节点
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
ListNode head;
//创建单链表
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(11);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(56);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(42);
head = node1;
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
}
//打印单链表
public void show() {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val +" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//计算单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
//查找是否包含key
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//头插法
public void headAdd(int val) {
ListNode headAdd = new ListNode(val);
headAdd.next = head;
head = headAdd;
}
//尾插法
public void endAdd(int val) {
ListNode endAdd = new ListNode(val);
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = endAdd;
}
//在index位置插入数据val
public void addIndex(int index,int val) {
if(index < 0 || index > size()-1) {
throw new OutOfIndexException("index不合法");
}
else if(index == 0) {
headAdd(val);
}
else if(index == size()-1) {
endAdd(val);
}
else {
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 1; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode addVal = new ListNode(val);
addVal.next = cur.next;
cur.next = addVal;
}
}
//删除数据第一次出现的key
public void remove(int key) {
if(head == null) return;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
//判断第一个节点的val值是否为key
if(head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode lastKeyNode = findLastKey(key);
if(lastKeyNode == null) {
return;//没有找到要删除 val值为key 的节点
}
lastKeyNode.next = lastKeyNode.next.next;
return;
}
}
//找到第一个值为key的节点 的前一个节点
public ListNode findLastKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
//删除 所有 值为key 的节点
public void removeAll(int key) {
if(head == null) return;
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode pre = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}
//清空所有的节点
public void clear() {
if(head == null) return;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = tmp;
}
head = null;
}
}
链表面试题
- 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
上述方法已经实现,代码示例如下:
//删除 所有 值为key 的节点
public void removeAll(int key) {
if(head == null) return;
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode pre = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}
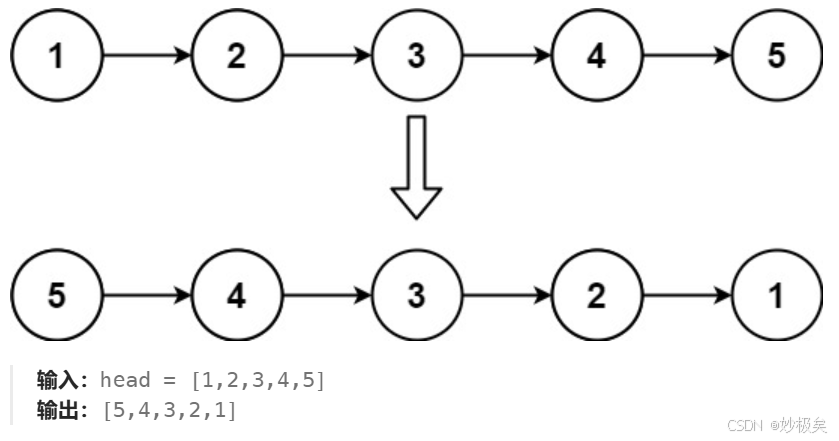
- 反转一个单链表。 OJ链接
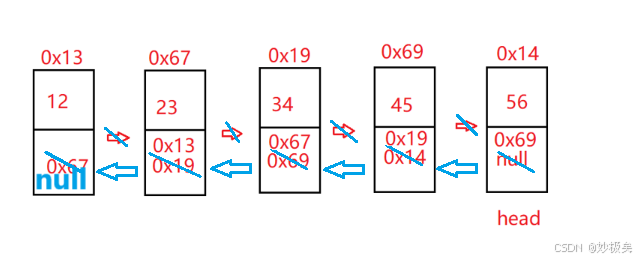
【解题思路】每个链表中的结点都有自己的地址,假设原链表的指向如下图所示:
实现翻转链表就可以把后一个结点的next域,指向前一个结点,遍历整个链表之后,这样每一个结点的next域就会指向前一个结点,此时head走到了最后一个节点,返回head。实现这些操作后的链表中结点的指向如下图:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode tmp = null;
head.next = null;
while(cur != null) {
tmp = cur.next; //使用tmp标记cur的下一个指向的结点
cur.next = head; //后一个结点的next域指向前一个结点
head = cur; //head 向后走一步
cur = tmp; //cur 向后走一步
}
return head;
}
}
- 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。OJ链接
方法一:先求出链表的长度 len,不管长度len 是奇数还是偶数,中间结点就是 head 向前移动 len/2 次后所在的结点。
I. 先求出链表的长度:遍历链表,代码示例如下:
public int size(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return -1;
}
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
II.求出长度len后,让head结点向前移动 len/2 次,此时head结点指向的就是中间节点,完整代码示例如下:
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
int len = size(head);
int count = len / 2;
ListNode cur = head;
while(count != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
count--;
}
return cur;
}
public int size(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return -1;
}
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
}
方法二:使用快慢指针。定义快指针 fast,慢指针 slow ,初始 fast 和 slow 都指向head,fast 一次向前移动两步,slow 一次向前移动一步,当fast走到最后时,此时slow就指向 中间结点。那么fast走到最后的循环终止条件如何设置? —> 当链表中结点个数为奇数时,fast走完 刚好指向最后一个结点,所以终止条件为 fast.next == null;当当链表中结点个数为偶数时,fast走完 刚好指向最后一个结点的下一个结点(也就是null),所以终止条件为 fast == null。所以只要满足这两个条件中的其中一个就会终止,转换到代码层面为: fast.next == null || fast == null因此while()中的条件应该为 fast.next != null && fast != null
【 注意 】这里while() 中的判断条件并不是fast.next != null || fast != null !!!
代码示例如下:
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
4.输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
这道题和上一道题一样的思路,也是有两种解决方法。
方法一:求链表长度len ,让head 向后走 len - k 步,此时head 就指向了倒数第K个结点
//输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
//方法一
public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {
if(k <= 0 || k > size(head)) {
return -1;
}
int len = size(head);
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(count < len -k) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur.val;
}
private int size(ListNode head) {
int count = 0;
while(head != null) {
count++;
head = head.next;
}
return count;
}
方法二:还是使用快慢指针,快指针 fast ,慢指针 slow,初始 fast 和 slow 都指向head ,此时需要先让fast 向前走 k-1 步,然后 fast 和 slow 绑着一块向前走,一次走一步,当 fast 走到最后时,slow 就指向了倒数第K个结点.代码示例如下:
//方法二
public int kthToLast2(ListNode head, int k) {
if(k <= 0) {
return -1;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
int count = k - 1;
while(count != 0) {
fast = fast.next;
if(fast == null) {
return -1;
}
count--;
}
while(fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
- 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。OJ
链接
两个有序链表的合并,一定是要遍历两个链表,最后返回拼接后的链表的头结点,
我们可以定义一个伪结点 newH(用来表示合并后新链表的带头结点),newH.next 中存的是新链表的第一个结点,也是data域最小的结点,所以最终返回的结点为 newH.next 。
定义 tmpH 结点,使 tmpH 指向 newH 所指向的对象,只操作tmpH 的next 域 按照升序来拼接结点,最终返回的是newH.next,此时tmpH已经完成了结点的拼接
遍历两个链表,循环条件为 headA 和 headB 都不为null 。每次比较 headA.val 和 headB.val 的大小,哪个小 就把哪个结点 赋值给 tmpH.next。遍历完成之后,如果其中一个结点不为空,就把 这一个结点 赋给 tmpH.next(原本都是升序链表,连接后 后面也一定是升序)
本人注意:【newH 和 tmpH 的关系理解为 head 和 cur 的关系】
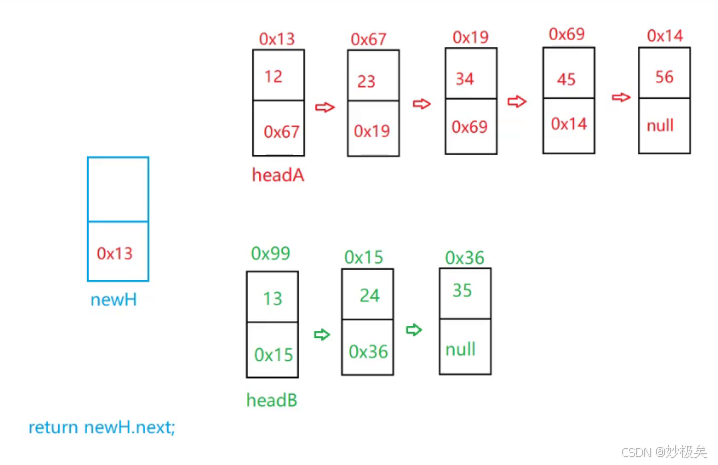
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null && headB == null) return null;
ListNode newH = new ListNode();
ListNode tmpH = newH;
while(headA != null && headB != null) {
if(headA.val < headB.val) {
tmpH.next = headA;
tmpH = headA;
headA = headA.next;
}else {
tmpH.next = headB;
tmpH = headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
}
if(headA == null) {
tmpH.next = headB;
}else {
tmpH.next = headA;
}
return newH.next;
}