===============================================================
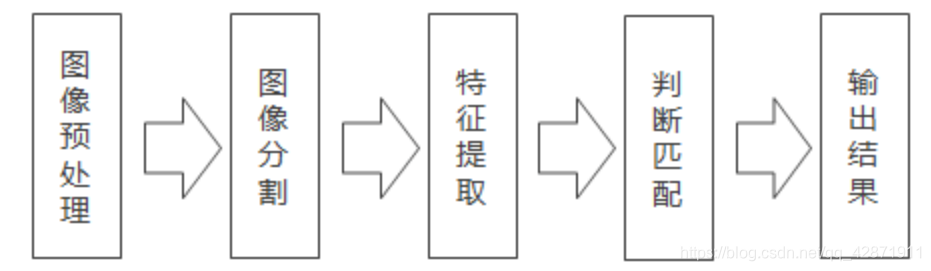
图像识别,是指利用计算机对图像进行处理、分析和理解,以识别各种不同模式的目标和对像的技术。根据观测到的图像,对其中的物体分辨其类别,做出有意义的判断。利用现代信息处理与计算技术来模拟和完成人类的认识、理解过程。一般而言,一个图像识别系统主要由三个部分组成,分别是:图像分割、图像特征提取以及分类器的识别分类。
其中,图像分割将图像划分为多个有意义的区域,然后将每个区域的图像进行特征提取,最后分类器根据提取的图像特征对图像进行相对应的分类。实际上,图像识别和图像分割并不存在严格的界限。从某种意义上,图像分割的过程就是图像识别的过程。图像分割着重于对象和背景的关系,研究的是对象在特定背景下所表现出来的整体属性,而图像识别则着重于对象本身的属性。
图像识别的发展经历了三个阶段:文字识别、数字图像处理与识别、物体识别。
图像识别作为计算视觉技术体系中的重要一环,一直备受重视。微软在两年前就公布了一项里程碑式的成果:它的图像系统识别图片的错误率比人类还要低。如今,图像识别技术又发展到一个新高度。这有赖于更多数据的开放、更多基础工具的开源、产业链的更新迭代,以及高性能的AI计算芯片、深度摄像头和优秀的深度学习算法等的进步,这些都为图像识别技术向更深处发展提供了源源不断的动力。
其实对于图像识别技术,大家已经不陌生,人脸识别、虹膜识别、指纹识别等都属于这个范畴,但是图像识别远不只如此,它涵盖了生物识别、物体与场景识别、视频识别三大类。发展至今,尽管与理想还相距甚远,但日渐成熟的图像识别技术已开始探索在各类行业的应用。
==========================================================================
基于BSD许可(开源)发行的跨平台计算机视觉库,可以运行在Linux、Windows、Android和Mac OS操作系统上。
轻量级而且高效——由一系列 C 函数和少量 C++ 类构成,同时提供了Python、Ruby、MATLAB等语言的接口,实现了图像处理和计算机视觉方面的很多通用算法
TensorFlow是一个深度学习框架,支持Linux平台,Windows平台,Mac平台,甚至手机移动设备等各种平台。
TensorFlow提供了非常丰富的深度学习相关的API,可以说目前所有深度学习框架里,提供的API最全的,包括基本的向量矩阵计算、各种优化算法、各种卷积神经网络和循环神经网络基本单元的实现、以及可视化的辅助工具、等等。
YOLO (You Only Look Once)是一种快速和准确的实时对象检测算法。
YOLOv3 在 TensorFlow 中实现的完整数据管道。它可用在数据集上来训练和评估自己的目标检测模型。
- ……
=====================================================================
介绍使用OpenCV来实现指定图像识别的DEMO:
①打开应用的同时开启摄像头
②对实时摄像头拍摄的图像封装成MAT对象进行逐帧比对:
-
获取目标特征并针对各特征集获取描述符
-
获取两个描述符集合间的匹配项
-
获取参考图像和空间匹配图像间的单应性
-
当图像矩阵符合单应性时,绘制跟踪图像的轮廓线
权限设置
AndroidMainifest.xml
<uses-feature
android:name=“android.hardware.camera.autofocus”
android:required=“false” />
<uses-feature
android:name=“android.hardware.camera.flash”
android:required=“false” />
权限提示方法
private void requestPermissions() {
final int REQUEST_CODE = 1;
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.CAMERA) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, new String[]{
Manifest.permission.CAMERA, Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE},
REQUEST_CODE);
}
}
界面设计
activity_img_recognition.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><RelativeLayout xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:opencv=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto”
xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:id=“@+id/activity_img_recognition”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
tools:context=“com.sueed.imagerecognition.CameraActivity”>
<org.opencv.android.JavaCameraView
android:id=“@+id/jcv”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
android:visibility=“gone”
opencv:camera_id=“any”
opencv:show_fps=“true” />
主要逻辑代码
CameraActivity.java 【相机启动获取图像和包装MAT相关】
因为OpenCV中JavaCameraView继承自SurfaceView,若有需要可以自定义编写extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback的xxxSurfaceView替换使用。
package com.sueed.imagerecognition;
import android.Manifest;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.Toast;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat;
import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat;
import com.sueed.imagerecognition.filters.Filter;
import com.sueed.imagerecognition.filters.NoneFilter;
import com.sueed.imagerecognition.filters.ar.ImageDetectionFilter;
import com.sueed.imagerecognition.imagerecognition.R;
import org.opencv.android.CameraBridgeViewBase;
import org.opencv.android.CameraBridgeViewBase.CvCameraViewFrame;
import org.opencv.android.CameraBridgeViewBase.CvCameraViewListener2;
import org.opencv.android.JavaCameraView;
import org.opencv.android.OpenCVLoader;
import org.opencv.core.Mat;
import java.io.IOException;
// Use the deprecated Camera class.
@SuppressWarnings(“deprecation”)
public final class CameraActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements CvCameraViewListener2 {
// A tag for log output.
private static final String TAG = CameraActivity.class.getSimpleName();
// The filters.
private Filter[] mImageDetectionFilters;
// The indices of the active filters.
private int mImageDetectionFilterIndex;
// The camera view.
private CameraBridgeViewBase mCameraView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(final Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON);
//init CameraView
mCameraView = new JavaCameraView(this, 0);
mCameraView.setMaxFrameSize(size.MaxWidth, size.MaxHeight);
mCameraView.setCvCameraViewListener(this);
setContentView(mCameraView);
requestPermissions();
mCameraView.enableView();
}
@Override
public void onPause() {
if (mCameraView != null) {
mCameraView.disableView();
}
super.onPause();
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
OpenCVLoader.initDebug();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
if (mCameraView != null) {
mCameraView.disableView();
}
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(final Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_camera, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(final MenuItem item) {
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.menu_next_image_detection_filter:
mImageDetectionFilterIndex++;
if (mImageDetectionFilters != null && mImageDetectionFilterIndex == mImageDetectionFilters.length) {
mImageDetectionFilterIndex = 0;
}
return true;
default:
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
@Override
public void onCameraViewStarted(final int width, final int height) {
Filter Enkidu = null;
try {
Enkidu = new ImageDetectionFilter(CameraActivity.this, R.drawable.enkidu);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Filter akbarHunting = null;
try {
akbarHunting = new ImageDetectionFilter(CameraActivity.this, R.drawable.akbar_hunting_with_cheetahs);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to load drawable: " + “akbar_hunting_with_cheetahs”);
e.printStackTrace();
}
mImageDetectionFilters = new Filter[]{
new NoneFilter(),
Enkidu,
akbarHunting
};
}
@Override
public void onCameraViewStopped() {
}
@Override
public Mat onCameraFrame(final CvCameraViewFrame inputFrame) {
final Mat rgba = inputFrame.rgba();
if (mImageDetectionFilters != null) {
mImageDetectionFilters[mImageDetectionFilterIndex].apply(rgba, rgba);
}
return rgba;
}
}
ImageRecognitionFilter.java【图像特征过滤比对及绘制追踪绿框】
package com.nummist.secondsight.filters.ar;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.opencv.android.Utils;
import org.opencv.calib3d.Calib3d;
import org.opencv.core.Core;
import org.opencv.core.CvType;
import org.opencv.core.DMatch;
import org.opencv.core.KeyPoint;
import org.opencv.core.Mat;
import org.opencv.core.MatOfDMatch;
import org.opencv.core.MatOfKeyPoint;
import org.opencv.core.MatOfPoint;
import org.opencv.core.MatOfPoint2f;
import org.opencv.core.Point;
import org.opencv.core.Scalar;
import org.opencv.features2d.DescriptorExtractor;
import org.opencv.features2d.DescriptorMatcher;
import org.opencv.features2d.FeatureDetector;
import org.opencv.imgcodecs.Imgcodecs;
import org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc;
import android.content.Context;
import com.nummist.secondsight.filters.Filter;
public final class ImageDetectionFilter implements Filter {
// The reference image (this detector’s target).
private final Mat mReferenceImage;
// Features of the reference image.
private final MatOfKeyPoint mReferenceKeypoints = new MatOfKeyPoint();
// Descriptors of the reference image’s features.
private final Mat mReferenceDescriptors = new Mat();
// The corner coordinates of the reference image, in pixels.
// CvType defines the color depth, number of channels, and
// channel layout in the image. Here, each point is represented
// by two 32-bit floats.
private final Mat mReferenceCorners = new Mat(4, 1, CvType.CV_32FC2);
// Features of the scene (the current frame).
private final MatOfKeyPoint mSceneKeypoints = new MatOfKeyPoint();
// Descriptors of the scene’s features.
private final Mat mSceneDescriptors = new Mat();
// Tentative corner coordinates detected in the scene, in
// pixels.
private final Mat mCandidateSceneCorners = new Mat(4, 1, CvType.CV_32FC2);
// Good corner coordinates detected in the scene, in pixels.
private final Mat mSceneCorners = new Mat(0, 0, CvType.CV_32FC2);
// The good detected corner coordinates, in pixels, as integers.
private final MatOfPoint mIntSceneCorners = new MatOfPoint();
// A grayscale version of the scene.
private final Mat mGraySrc = new Mat();
// Tentative matches of scene features and reference features.
private final MatOfDMatch mMatches = new MatOfDMatch();
// A feature detector, which finds features in images.
private final FeatureDetector mFeatureDetector = FeatureDetector.create(FeatureDetector.ORB);
// A descriptor extractor, which creates descriptors of
// features.
private final DescriptorExtractor mDescriptorExtractor = DescriptorExtractor.create(DescriptorExtractor.ORB);
// A descriptor matcher, which matches features based on their
// descriptors.
private final DescriptorMatcher mDescriptorMatcher = DescriptorMatcher.create(DescriptorMatcher.BRUTEFORCE_HAMMINGLUT);
// The color of the outline drawn around the detected image.
private final Scalar mLineColor = new Scalar(0, 255, 0);
public ImageDetectionFilter(final Context context, final int referenceImageResourceID) throws IOException {
// Load the reference image from the app’s resources.
// It is loaded in BGR (blue, green, red) format.
mReferenceImage = Utils.loadResource(context, referenceImageResourceID, Imgcodecs.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
// Create grayscale and RGBA versions of the reference image.
final Mat referenceImageGray = new Mat();
Imgproc.cvtColor(mReferenceImage, referenceImageGray, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Imgproc.cvtColor(mReferenceImage, mReferenceImage, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2RGBA);
// Store the reference image’s corner coordinates, in pixels.
mReferenceCorners.put(0, 0, new double[]{0.0, 0.0});
mReferenceCorners.put(1, 0, new double[]{referenceImageGray.cols(), 0.0});
mReferenceCorners.put(2, 0, new double[]{referenceImageGray.cols(), referenceImageGray.rows()});
mReferenceCorners.put(3, 0, new double[]{0.0, referenceImageGray.rows()});
// Detect the reference features and compute their
// descriptors.
mFeatureDetector.detect(referenceImageGray, mReferenceKeypoints);
mDescriptorExtractor.compute(referenceImageGray, mReferenceKeypoints, mReferenceDescriptors);
}
@Override
public void apply(final Mat src, final Mat dst) {
// Convert the scene to grayscale.
Imgproc.cvtColor(src, mGraySrc, Imgproc.COLOR_RGBA2GRAY);
// Detect the scene features, compute their descriptors,
// and match the scene descriptors to reference descriptors.
mFeatureDetector.detect(mGraySrc, mSceneKeypoints);
mDescriptorExtractor.compute(mGraySrc, mSceneKeypoints, mSceneDescriptors);
mDescriptorMatcher.match(mSceneDescriptors, mReferenceDescriptors, mMatches);
最后
其实要轻松掌握很简单,要点就两个:
- 找到一套好的视频资料,紧跟大牛梳理好的知识框架进行学习。
- 多练。 (视频优势是互动感强,容易集中注意力)
你不需要是天才,也不需要具备强悍的天赋,只要做到这两点,短期内成功的概率是非常高的。
对于很多初中级Android工程师而言,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,不成体系的学习效果低效漫长且无助。
阿里P7Android高级教程
下面资料部分截图,诚意满满:特别适合有3-5年开发经验的Android程序员们学习。
附送高清脑图,高清知识点讲解教程,以及一些面试真题及答案解析。送给需要的提升技术、近期面试跳槽、自身职业规划迷茫的朋友们。
Android核心高级技术PDF资料,BAT大厂面试真题解析;
《Android学习笔记总结+移动架构视频+大厂面试真题+项目实战源码》,点击传送门,即可获取!
tor.detect(mGraySrc, mSceneKeypoints);
mDescriptorExtractor.compute(mGraySrc, mSceneKeypoints, mSceneDescriptors);
mDescriptorMatcher.match(mSceneDescriptors, mReferenceDescriptors, mMatches);
最后
其实要轻松掌握很简单,要点就两个:
- 找到一套好的视频资料,紧跟大牛梳理好的知识框架进行学习。
- 多练。 (视频优势是互动感强,容易集中注意力)
你不需要是天才,也不需要具备强悍的天赋,只要做到这两点,短期内成功的概率是非常高的。
对于很多初中级Android工程师而言,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,不成体系的学习效果低效漫长且无助。
阿里P7Android高级教程
下面资料部分截图,诚意满满:特别适合有3-5年开发经验的Android程序员们学习。
[外链图片转存中…(img-ztlcOXVM-1714511116464)]
附送高清脑图,高清知识点讲解教程,以及一些面试真题及答案解析。送给需要的提升技术、近期面试跳槽、自身职业规划迷茫的朋友们。
Android核心高级技术PDF资料,BAT大厂面试真题解析;
[外链图片转存中…(img-Br7Z8q3g-1714511116467)]
《Android学习笔记总结+移动架构视频+大厂面试真题+项目实战源码》,点击传送门,即可获取!