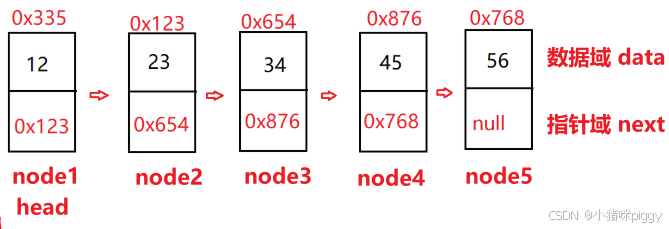
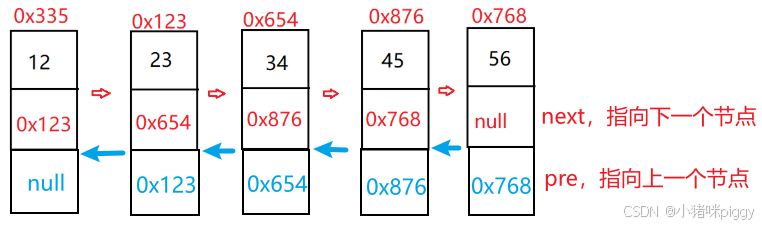
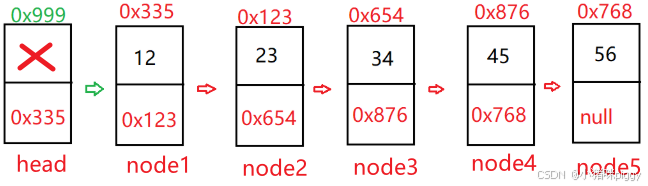
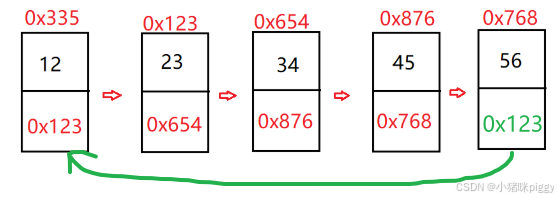
一、什么是链表
1、链表与顺序表对比
| 不同点 | LinkedList | ArrayList |
| 物理存储上 | 不连续 | 连续 |
| 随机访问效率 | O(N) | O(1) |
| 插入、删除效率 | O(1) | O(N) |
3、链表的分类
链表根据结构分类,可分为单向/双向、无头结点/有头节点、非循环/循环链表,这三组每组各取一个就构成一种结构链表。其中,单向、不带头、非循环链表是学习的重点;双向、不带头、非循环链表在实际开发中常用。
以单向、不带头、非循环链表为例:
双向、不带头、非循环链表:
单向、带头、非循环链表(好处在于,不用特别处理头节点,比如增删时):
单向、不带头、循环链表:
二、单向、不带头、非循环链表的实现
1、IList 接口
定义 IList 接口,声明线性表需要实现的方法:
package listinterface;
public interface IList {
//头插法
void addFirst(int data);
//尾插法
void addLast(int data);
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
void addIndex(int index,int data);
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
boolean contains(int key);
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
void remove(int key);
//删除所有值为key的节点
void removeAllKey(int key);
//得到单链表的长度
int size();
void clear();
void display();
}
2、结点内部类
结点仅由链表内部使用,且每个结点的产生不依赖于某个链表,可定义为链表的私有静态内部类:
public class MySingleList implements IList {
// 结点内部类
private static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// 头结点
private Node head;
// 链表长度
private int size;
............
}3、打印链表
@Override
public void display() {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println(" size: " + size);
}4、清空链表、获取链表长度
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
head = null;
size = 0;
}head 为空,没有引用指向 node1,自动回收 node1;node1 回收,没有引用指向 node2,自动回收 node2……故 clear 只需 head 设为 null 即可。
5、头插法
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
// if (head != null) {
// newNode.next = head;
// }
// head = newNode;
size++;
}6、尾插法
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
size++;
return;
}
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) { // 找到尾节点
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = newNode;
size++;
}7、任意位置插入
(受查异常,父类方法没抛出异常,子类方法不能抛出异常;父类抛出了,子类不做要求。非受查异常,不做要求。)为了不改动 IList,且让 addIndex 抛出异常,以便在 main 处对异常做处理,链表下标越界异常选择继承非受查异常 RuntimeExcption。
package myexception;
public class ListIndexOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException {
public ListIndexOutOfBoundsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
} private void checkIndexOutOfBounds(int index) throws ListIndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new ListIndexOutOfBoundsException("插入位置不合法。" + "Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
}
private Node findIndex(int index) {
Node cur = head;
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt != index) {
cur = cur.next;
cnt++;
}
return cur;
}
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) throws ListIndexOutOfBoundsException {
// 先检查索引是否越界
checkIndexOutOfBounds(index);
if (index == 0) { // 在 0 处插入,没有前驱节点
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size) { // 在末尾插入
addLast(data);
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// 找到插入位置前的节点
Node pre = findIndex(index - 1);
// 插入新节点
newNode.next = pre.next;
pre.next = newNode;
size++;
}8、删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
private Node findKey(int key) {
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.data == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
if (head == null) { // 空链表
return;
}
if (head.data == key) { // 头节点就是要删除的节点
head = head.next;
size--;
return;
}
Node pre = findKey(key);
if (pre != null) { // 找到了要删除的节点
pre.next = pre.next.next;
size--;
} else { // 要删除的节点不存在
System.out.println("要删除的节点不存在。");
}
}9、删除所有关键字为 key 的节点
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (head == null) { // 空链表
return;
}
Node pre = head;
Node cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.data == key) {
pre.next = cur.next;
// cur = cur.next;
}
else {
pre = cur;
// cur = cur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (head.data == key) {
head = head.next;
size--;
}
}三、链表面试题练习
1、反转链表
思路:从头开始,边遍历边反转,最后尾结点为 head。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 特殊处理 空链表、只有一个结点的链表
if(head == null || head.next == null) { // 两者顺序不能反,因为 null 没有next
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
// 头结点,其 next 为 null
head.next = null;
// 边反转边遍历,直到反转完尾结点
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curN;
}
return head;
}
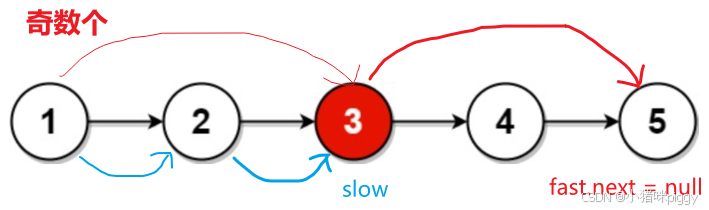
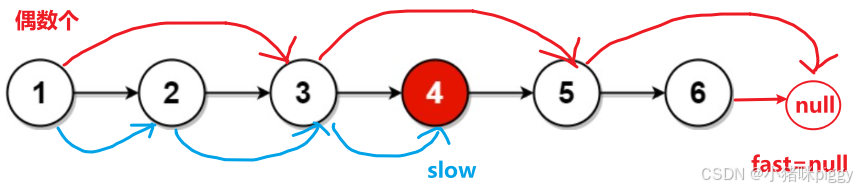
}2、链表的中间结点
思路:
1、计算链表长度的一半,再走一半长。时间复杂度 O(N) + O(N/2)。
2、设置 slow 和 fast 从 head 开始走,slow 每次走 1 步,fast 每次走 2 步。那么 fast 走完全程(fast = null 或者 fast.next = null),必是 slow 的两倍长度,故 slow 就是中间节点的位置。时间复杂度 O(N/2) ,更优。
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) { // 根据题目,链表非空
// 从头节点开始
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// fast 走完整个链表
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
// slow 每次走 1 步,fast 每次走 2 步
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// slow 就是中间结点
return slow;
}
}3、返回倒数第 k 个结点
面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:slow 从 head 开始,fast 比 slow 先多走 k-1 步,然后 slow、fast 每次只走一步,直到 fast 走到尾结点。
class Solution {
public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {
// 根据题目,k 保证有效,因此不用判断 k<=0 和 k > len 的情况
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// 当 fast 先走 k-1 步
int cnt = k-1;
// k保证有效,fast 不会走过头
while(cnt != 0) {
fast = fast.next;
cnt--;
}
// 让 fast 走到尾结点,slow 就是倒数第 k 个结点
while(fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
}4、合并两个有序列表
思路:分别同时遍历两个链表,更小的插入新链表,插入的链表插入后更新为 next,直到 l1 或者 l2 遍历完了。没遍历完的那个链表,把剩的接在新链表尾。为了不单独处理头指针,新链表带头节点。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(); // 创建头节点
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode cur1 = list1;
ListNode cur2 = list2;
// 其中一个遍历完就退出
while(cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {
if(cur1.val < cur2.val) {
cur.next = cur1;
// cur = cur.next;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
else {
cur.next = cur2;
// cur = cur.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 没遍历完的,接在后面
if(cur1 != null) {
cur.next = cur1;
}
if(cur2 != null) {
cur.next = cur2;
}
return head.next; // 不带头节点
}
}5、链表分割
思路:先创建两个链表,依次遍历原链表,小于和大于等于 x 的分开尾插入两个链表,再合并。
public class Partition {
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
// 创建两个头节点
ListNode head1 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode head2 = new ListNode(-1);
// 遍历原链表,每个结点与 x 比大小,分类放在两个新链表中
ListNode cur1 = head1;
ListNode cur2 = head2;
while(pHead != null) {
if(pHead.val < x) {
cur1.next = pHead;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
else {
cur2.next = pHead;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
pHead = pHead.next;
}
// 现在 cur1、cur2 分别指向两个链表的尾结点。
cur1.next = head2.next; // 链表1的尾接上链表2的头
cur2.next = null; // 链表2的尾接上 null
// 如果最后链表1为空,cur1就是head1,没问题
// 如果最后链表2为空,cur2就是head2,没问题
return head1.next;
}
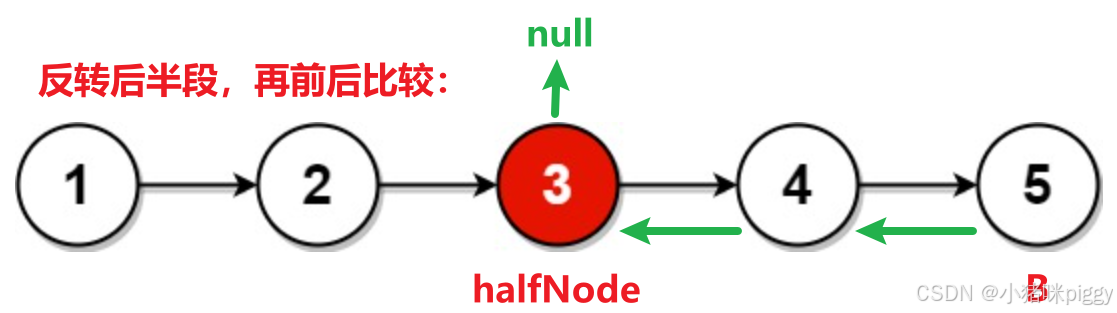
}6、链表的回文结构
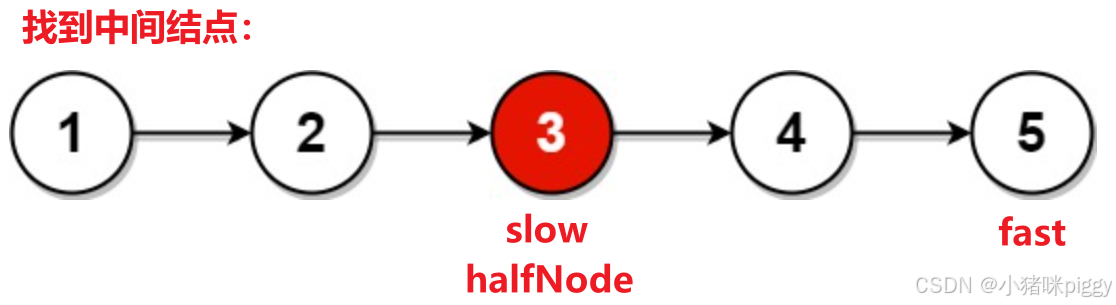
思路:
1、求尾结点,头、尾同时前进并比较,到 head = tail(奇数长度) 或者 head.next = tail (偶数长度)为止。tail 往前走行不通,因为是单链表。
2、把原链表的后一半反转,再将反转链表与原链表对比,直到反转链表遍历完。时间复杂度O(N/2)+O(N/2)+O(N/2)=O(N)。找到一半处、将一半反转、对比一半。
public class PalindromeList {
private ListNode findHalf(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curN;
}
return head;
}
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
// 找到中间结点
ListNode halfNode = findHalf(A);
// 将后一半反转
ListNode B = reverse(halfNode);
// 将后半段与前半段对比,后半段遍历完退出
while(B != null) {
if(A.val != B.val) {
return false;
}
A = A.next;
B = B.next;
}
return true;
}
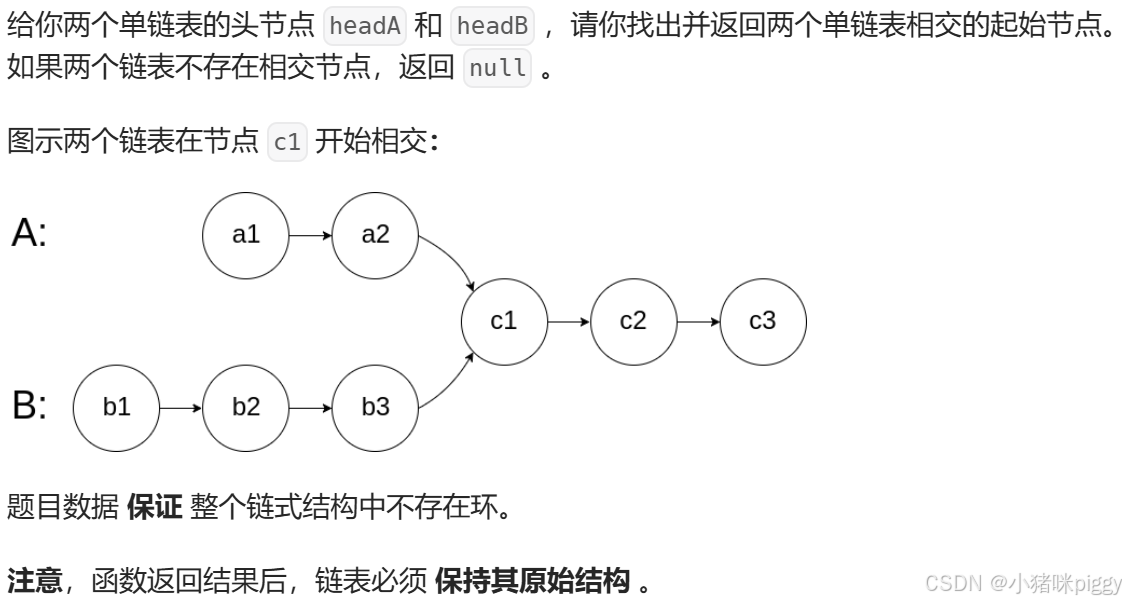
}7、相交链表
思路:可能分叉的地方,前边或后边。但是对于链表不可能后边分叉,因为如果后边分叉了,当你遍历一条单链时,遍历到后边分叉的地方,就不知道继续走哪条路了,这样就不是单链表了。因此只有可能如上图的Y型,或者在一条直线上。
如果同时各自出发,每次走一步,直到有一方到达尾结点,那么短的链表总是先到达,并且它们的最终距离是两链表的长度差。长度差来自分叉的部分,而不是相交的部分。那么如果让长的先走长度差步,再同时走,它们碰面的地方将是相交处。
public class Solution {
private int size(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
int cnt = 0;
while(cur != null) {
cnt++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cnt;
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 求两条链的长度
int size1 = size(headA);
int size2 = size(headB);
// 让长的作为 headA,求两链表长度差(正),
int len = size1 - size2;
if(size1 < size2) {
len = size2 - size1;
ListNode tmp = headA;
headA = headB;
headB = tmp;
}
// 让长的先走 len 步
while(len != 0) {
headA = headA.next;
len--;
}
// 再同时走,相等的地方就是相交结点
while(headA != headB) {
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return headA;
}
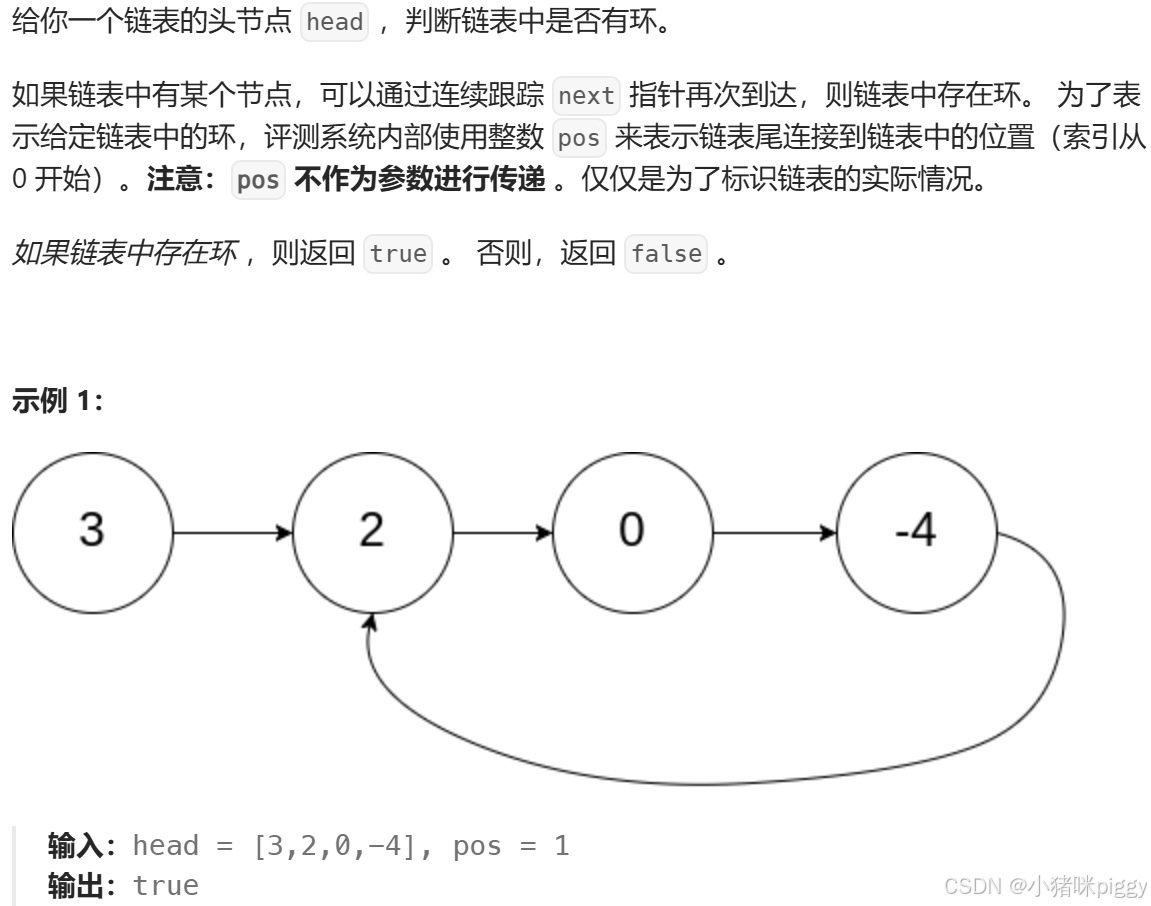
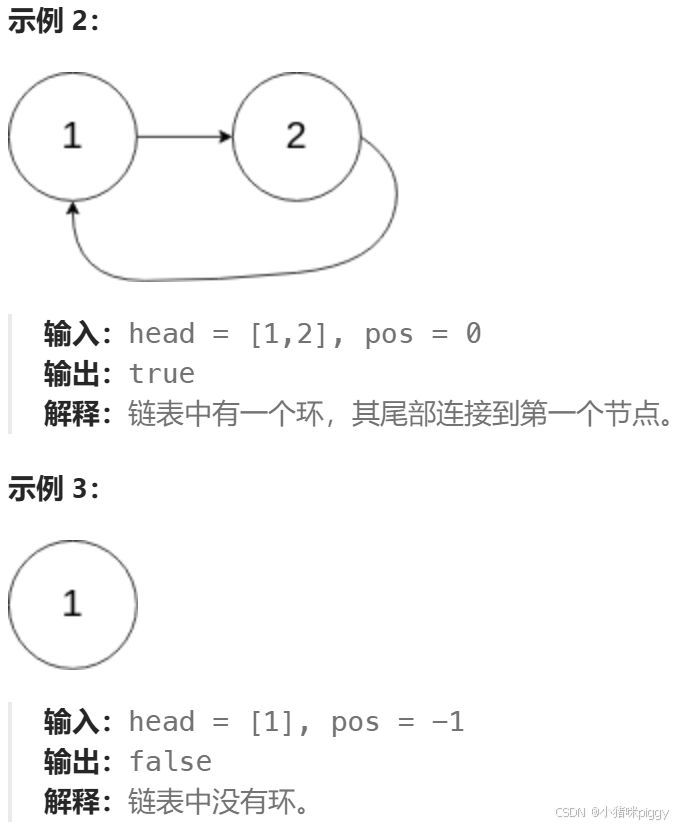
}8、环形链表
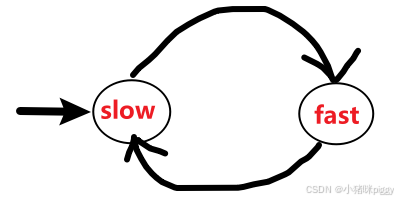
思路:慢指针和快指针同时走,如果有环,那么快、慢指针总会在环里相遇(快指针多跑 k 圈,然后追上慢指针);如果没环,快指针先走完全程结束。我们设慢指针每次走1步,快指针每次走2步。
为什么快指针不能是 3、4、……、n 步?如果是3步,存在以下情况,无论走多久都不会相遇:
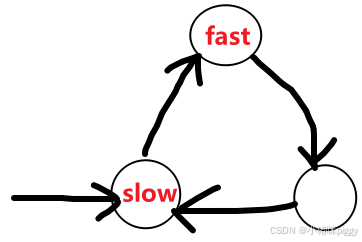
快指针如果走 4 步,存在以下情况,无论走多久都不会相遇:
以此类推……
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 设置快、慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// slow 每次走1步,fast 每次走2步
// 直到 fast = null(偶数个) 或者 fast.next = null(奇数个) 返回 flase
// 或者 slow = fast 返回 true
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}9、环形链表Ⅱ
思路:
若一指针 head1 从相遇点开始,一指针 head2 从头指针开始,同时走,每次走一步。当 head1 走 X 步到达入口;同时,head2 从相遇点开始走了 (k-1) 圈回到相遇点,再走 N 步到入口。即两指针相遇处,就是入口结点。
public class Solution {
private ListNode getMeetNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast) {
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
// 获得 slow 与 fast 的相遇结点
ListNode meetNode = getMeetNode(head);
// 链表无环,返回 null
if(meetNode == null) {
return null;
}
// 分别从头指针,相遇结点开始走,两指针相遇处就是入口
while(head != meetNode) {
head = head.next;
meetNode = meetNode.next;
}
return head;
}
}四、双向、不带头、非循环链表的实现
1、Node 内部类和属性
public class MyLinkedList implements IList {
private static class Node {
int val;
Node next; // 后继指针
Node prev; // 前驱指针
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
private Node head; // 头指针
private Node tail; // 尾指针
private int size; // 链表大小
............
}2、清空链表
与单向不同直接 head = null,双向需要遍历结点并释放 node,原因如下:head 为空,还有 node2 指向 node1,所以手动置 node2 的 pre 为空,node1释放;还有 node3 指向 node2,手动置 node3 的 pre 未空……
@Override
public void clear() {
Node cur = head;
while (cur!= null) {
Node curN = cur.next;
cur.prev = null;
cur.next = null;
cur = curN;
}
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}3、头插法
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = head;
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
size++;
}4、尾插法
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}
size++;
}5、任意位置插入
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
// 先检查索引是否越界
checkIndexOutOfBounds(index);
if (index == 0) { // 在 0 处插入,没有前驱节点
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size) { // 在末尾插入
addLast(data);
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// 找到插入位置
Node cur = findIndex(index);
// 插入新节点
newNode.next = cur;
newNode.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev.next = newNode;
cur.prev = newNode;
size++;
}6、删除第一次出现的 key
private Node findKey(int key) {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
Node deleteNode = findKey(key); // 找到待删除节点,如果不存在,返回 null
if (deleteNode == null) { // 包含空链表的情况
System.out.println("要删除的节点不存在。");
return;
}
if (deleteNode == head) { // 待删除节点是头节点,包含了链表只有一个结点的情况
head = deleteNode.next;
if (head == null) { // 链表只有一个节点
tail = null;
}
else {
head.prev = null;
}
} else if (deleteNode == tail) { // 待删除节点是尾节点
tail = deleteNode.prev;
tail.next = null;
} else { // 待删除节点是中间节点
deleteNode.prev.next = deleteNode.next;
deleteNode.next.prev = deleteNode.prev;
}
size--;
}7、删除所有 key
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
if (cur == head) { // 待删除节点是头节点
head = cur.next;
if (head == null) { // 链表中只有一个节点
tail = null;
}
else {
head.prev = null;
}
} else if (cur == tail) { // 待删除节点是尾节点
tail = cur.prev;
tail.next = null;
} else { // 待删除节点是中间节点
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
size--;
// cur = cur.next; // 跳过已删除节点,继续遍历
} /*else {
cur = cur.next;
}*/
cur = cur.next;
}
}五、LinkedList 的使用
集合类中,LinkedList 的底层是双向链表。
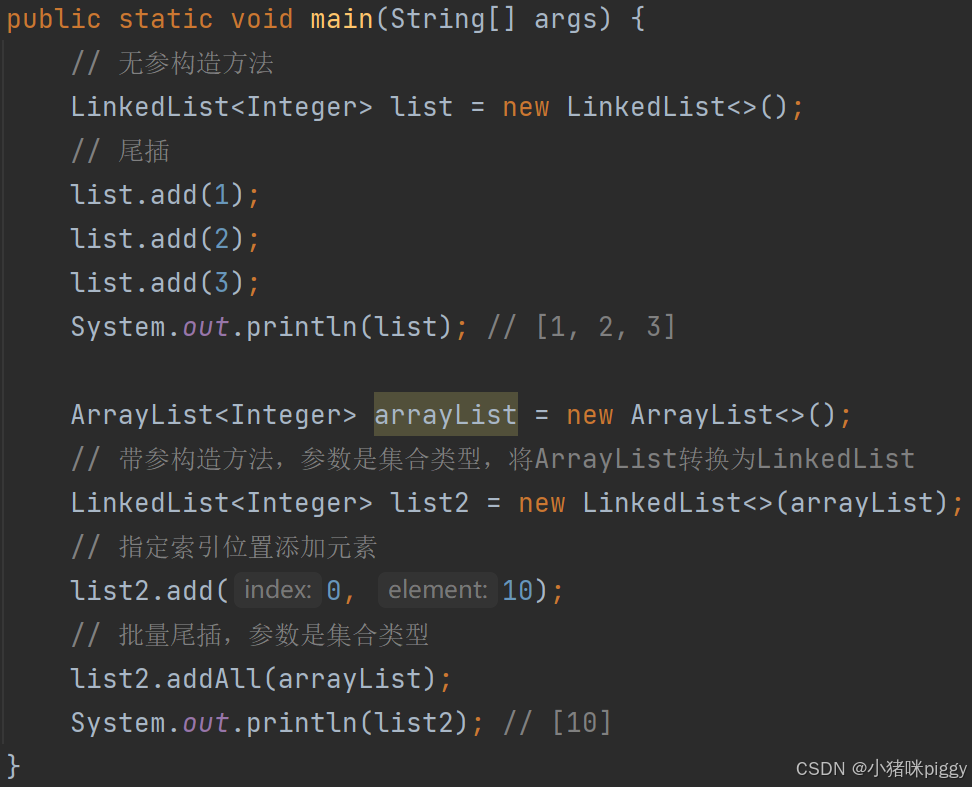
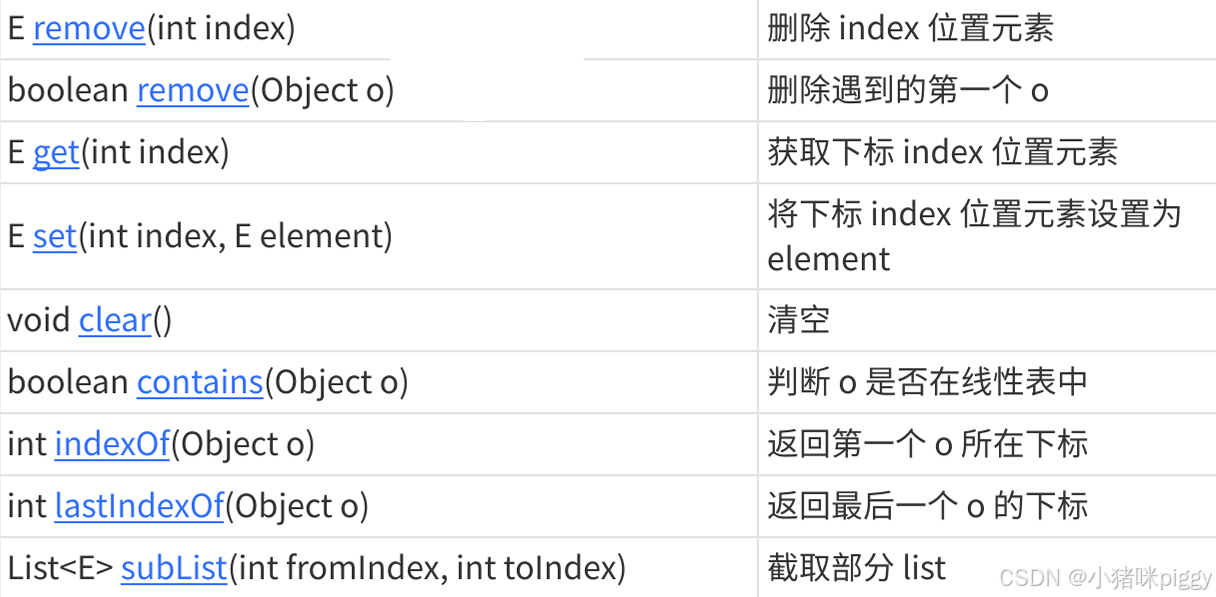
1、常用方法的使用
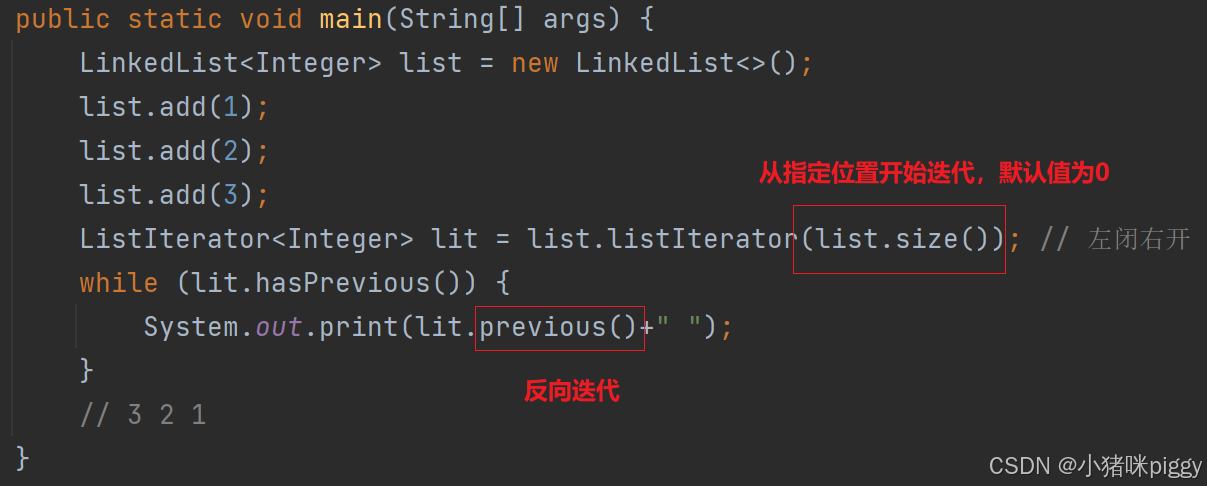
2、迭代器
Iterator<E> 是集合类通用的迭代器,线性表专用的迭代器 ListIterator<E> 功能更强,可以反向迭代: