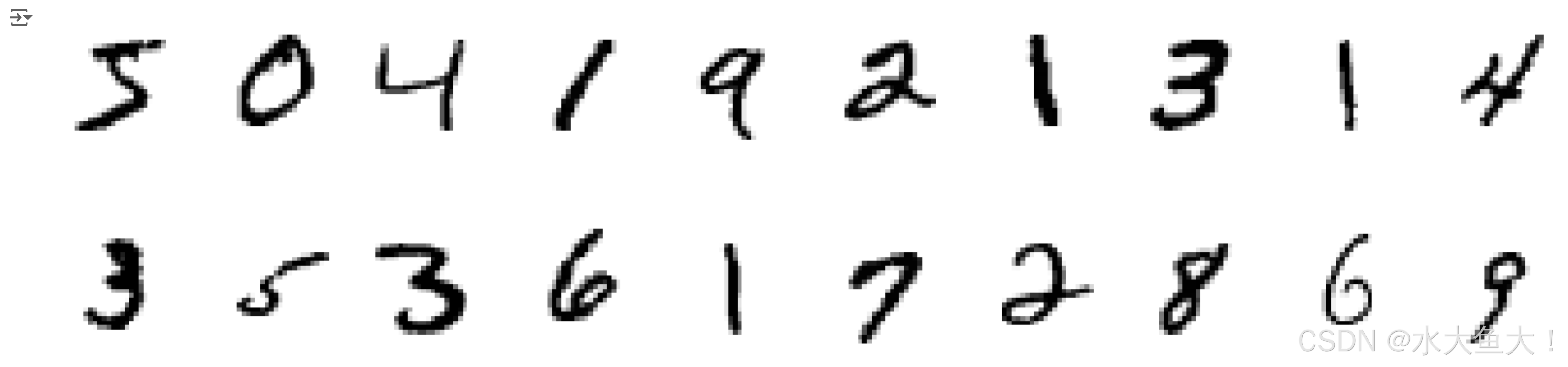前言
>- **🍨 本文为[🔗365天深度学习训练营](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Z9yL_wt7L8aPOr9Lqb1K3w) 中的学习记录博客**
>- **🍖 原作者:[K同学啊](https://mtyjkh.blog.csdn.net/)**前期准备
运行环境
- 语言环境:Python 3.10
- 编译器:Google Colab
- 深度学习环境:
- torch==2.3.1+cu121
- torchvision==0.18.1+cu121
模块导入
# Import package
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchsummary import summary
import warnings# Training our model using GPU
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device)数据导入
torchvision.datasets是Pytorch自带的一个数据库,我们可以通过代码在线下载数据,这里使用的是torchvision.datasets中的MNIST数据集。
torch.utils.data.DataLoader是Pytorch自带的一个数据加载器,结合了数据集和取样器,并且可以提供多个线程处理数据集。
# Download data and convert data types into tensors
train_ds = torchvision.datasets.MNIST('data', train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), download=True)
test_ds = torchvision.datasets.MNIST('data', train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), download=True)
# Load data
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=32)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=32)# Retrieve one batch of images and labels
imgs, labels = next(iter(train_dl))
# Check the shape of the images tensor
imgs.shape 代码输出
数据的结构为 [batch size, channel, height, width],其中,batch size 为先前的设定值,channel、height 和 width 分别是图片的通道数、高度和宽度。
数据可视化
# Specify the figure size, with a width of 20 inches and height of 5 inches
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
for i, imgs in enumerate(imgs[:20]):
# Reduce the dimensions
npimg = np.squeeze(imgs.numpy())
# Divide the figure into 2 rows and 10 columns, and plot the (i+1)th subplot.
plt.subplot(2, 10, i+1)
# Display the image in binary colormap
plt.imshow(npimg, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
# Turn off the axis
plt.axis('off')np.squeeze(imgs.numpy()) 的作用是把 PyTorch 的张量转换为 NumPy 数组,并去掉不必要的维度,使图像数据变成一个更容易处理的二维数组(高 x 宽)。比如,如果 imgs 的形状是 (1, 28, 28),np.squeeze() 会将形状变为 (28, 28),去掉第一个无用的维度。
代码输出
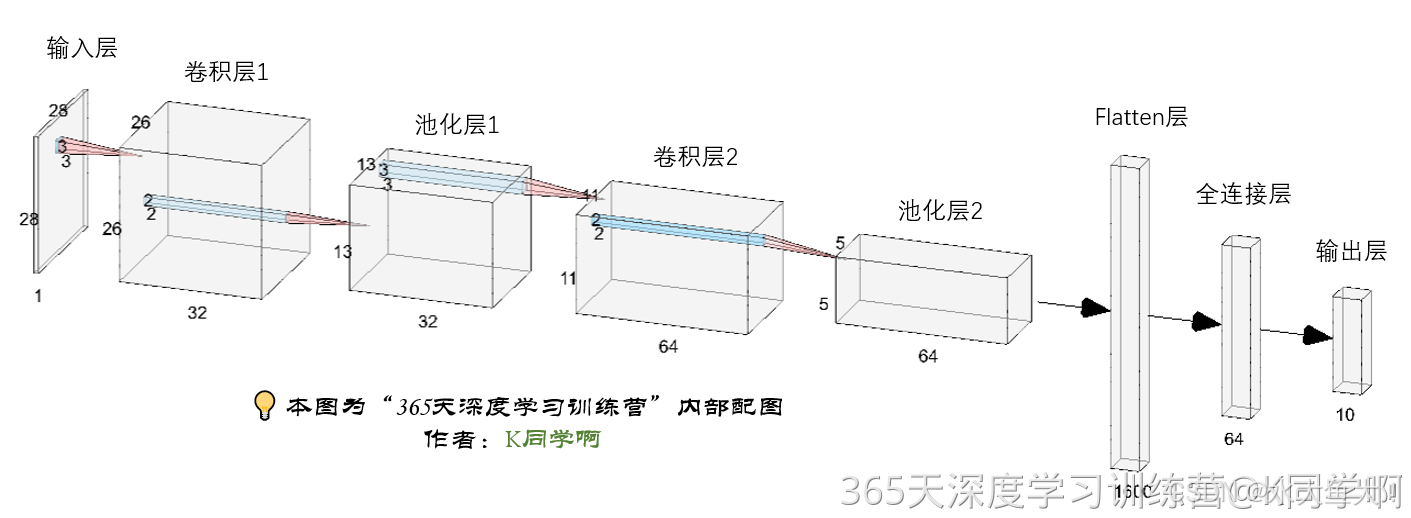
构建简单的CNN网络
对于一般的 CNN 网络来说,它通常由特征提取网络和分类网络两部分构成。特征提取网络用于提取图片的特征,而分类网络则用于将图片分类。
nn.Conv2d是卷积层,用于提取图片的特征。传入的参数包括输入通道数、输出通道数以及卷积核的大小。nn.MaxPool2d是池化层,用于进行下采样,通过更高层次的抽象来表示图像特征。传入的参数是池化核的大小。nn.ReLU是激活函数,使模型能够拟合非线性数据。nn.Linear是全连接层,可以起到特征提取的作用。最后一层全连接层也可以看作输出层。传入的参数是输入特征数和输出特征数(输入特征数是由特征提取网络计算得到的,如果不确定,可以直接运行网络,报错信息中会提示输入特征数的大小。下方网络中第一个全连接层的输入特征数为 1600)。nn.Sequential可以按构造顺序连接网络,在初始化阶段就设定好网络结构,不需要在前向传播中重新编写一遍。
num_classes = 10 # Number of image classes
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# Feature extraction network
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3) # First convolutional layer, kernel size is 3x3
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2) # Pooling layer, pool size is 2x2
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3) # Second convolutional layer, kernel size is 3x3
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
# Classification network
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1600, 64)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, num_classes)
# Forward propagation
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool1(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool2(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
return xModel类:定义了一个卷积神经网络(CNN)。- 特征提取网络:由两层卷积层(
conv1和conv2)和两层池化层(pool1和pool2)组成,主要用于提取输入图片的特征。 - 分类网络:由两层全连接层(
fc1和fc2)组成,负责将提取的特征映射到分类结果上。
- 特征提取网络:由两层卷积层(
forward函数:定义了数据如何通过网络进行前向传播,依次经过卷积层、池化层、ReLU激活函数、展平操作和全连接层,最终输出预测结果。
# Create the model instance
model = Model().to(device)
# Summarize the model
summary(model, input_size=(1, 28, 28))summary:这是torchsummary库中的一个函数,用于提供模型结构的详细摘要。model:你之前创建的Model类的实例。input_size=(1, 28, 28):指定模型期望的输入数据的形状。1:输入图像的通道数(例如,灰度图像的通道数为 1)。28:输入图像的高度,以像素为单位。28:输入图像的宽度,以像素为单位。
代码输出
训练模型
设置超参数
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # Create loss function
learn_rate = 1e-2 # Learning rate
opt = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learn_rate) # Optimizer
编写训练函数
optimizer.zero_grad()
函数会遍历模型的所有参数,通过内置方法截断反向传播的梯度流,并将每个参数的梯度值设为 0,即清空上一次的梯度记录。
loss.backward()
PyTorch 的反向传播(即 tensor.backward())是通过 autograd 包来实现的。autograd 包会根据 tensor 进行的数学运算自动计算其对应的梯度。具体来说,torch.tensor 是 autograd 包的基础类。如果你将 tensor 的 requires_grad=True 设置为真,它就会开始跟踪这个 tensor 上的所有运算。当运算完成后,使用 tensor.backward(),所有的梯度会自动计算,并累加到 tensor 的 .grad 属性中。
更具体地说,损失函数 loss 是由模型的所有权重 w 经过一系列运算得到的。如果某个权重 w 的 requires_grad=True,则 w 的所有上层参数(即后续层的权重)的 .grad_fn 属性中会保存相应的运算。当使用 loss.backward() 后,反向传播会层层进行,计算每个 w 的梯度值,并将其保存到该 w 的 .grad 属性中。如果没有执行 tensor.backward(),梯度值将会是 None。因此,loss.backward() 应该在 optimizer.step() 之前执行。
optimizer.step()
step() 函数的作用是执行一次优化步骤,通过梯度下降法更新参数的值。由于梯度下降是基于梯度的,所以在执行 optimizer.step() 函数之前,应先执行 loss.backward() 函数来计算梯度。注意:optimizer 只负责通过梯度下降进行优化,而不负责产生梯度,梯度是由 tensor.backward() 方法产生的。
# Training loop
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # Size of the training dataset, 60000 images in total
num_batches = len(dataloader) # Number of batches, 1875 (60000/32)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # Initialize training loss and accuracy
for X, y in datloader: # Get images and their labels
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# Compute prediction error
pred = model(X) # Model output
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # Calculate the difference between model output and true values (targets), this difference is the loss
# Backpropagation
optimizer.zero_grad() # Reset gradients to zero
loss.backward() # Backpropagation
optimizer.step() # Update model parameters automatically
# Record accuracy and loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_losspred.argmax(1)返回数组pred在第一个轴(即行)上最大值所在的索引。这通常用于多类分类问题中,其中pred是一个包含预测概率的二维数组,每行表示一个样本的预测概率分布。(pred.argmax(1) == y)是一个布尔值数组,其中每个元素表示对应样本的预测是否正确(True表示正确,False表示错误)。.type(torch.float)将布尔数组的数据类型转换为浮点数类型,即将True转换为1.0,将False转换为0.0。.sum()对数组中的元素求和,计算出预测正确的样本数量。.item()将求和结果转换为标量值,以便在 Python 中使用或打印。
编写测试函数
测试函数和训练函数大致相同,但是由于不进行梯度下降对网络权重进行更新,所以不需要传入优化器。
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # Size of the test dataset, 10,000 images in total
num_batches = len(dataloader) # Number of batches, 313 (10000/32 = 312.5, rounded up)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# Disable gradient updates to save memory and computation since we are not training
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# Calculate loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss
正式训练
model.train()model.train()的作用是启用 Batch Normalization 和 Dropout。
如果模型中有 BN 层(Batch Normalization)和 Dropout,需要在训练时添加 model.train()。model.train() 是为了确保 BN 层能够使用每一批数据的均值和方差。对于 Dropout,model.train() 是随机选择一部分网络连接来训练和更新参数。
model.eval()model.eval()的作用是不启用 Batch Normalization 和 Dropout。
如果模型中有 BN 层(Batch Normalization)和 Dropout,在测试时需要添加 model.eval()。model.eval() 是为了确保 BN 层使用全部训练数据的均值和方差,即在测试过程中保证 BN 层的均值和方差不变。对于 Dropout,model.eval() 是利用所有网络连接,即不进行随机舍弃神经元。
训练完 train 样本后,生成的模型 model 要用来测试样本。在执行 model(test) 之前,需要加上 model.eval(),否则即使不训练,只要有输入数据,模型的权值也可能会发生改变。这是由于模型中含有 BN 层和 Dropout 所带来的性质。
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train() # Set the model to training mode
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, opt)
model.eval() # Set the model to evaluation mode
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc) # Store the training accuracy for the current epoch
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss) # Store the training loss for the current epoch
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc) # Store the test accuracy for the current epoch
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss) # Store the test loss for the current epoch
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss))
print('Done')代码输出
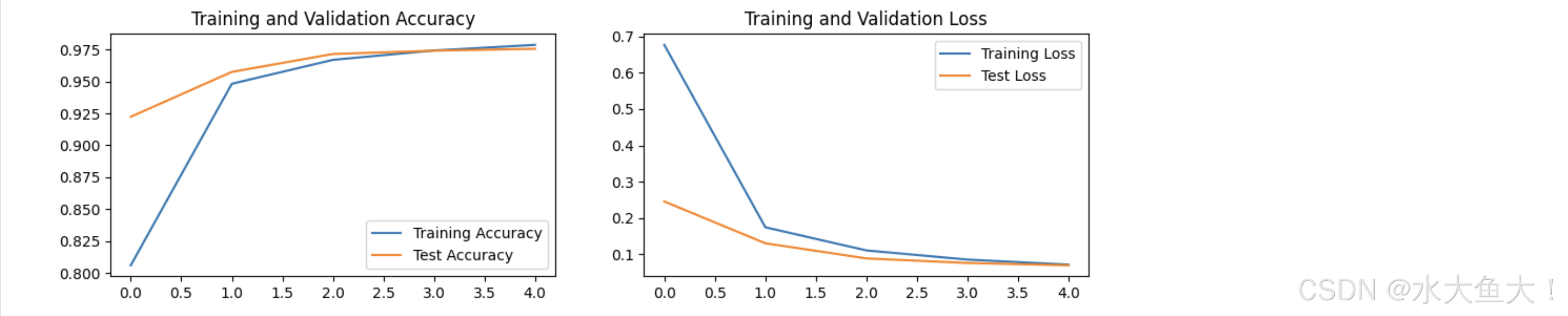
结果可视化
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # Ignore warning messages
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # Ensure minus signs are displayed correctly
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 # Set resolution (dots per inch)
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()
代码输出
学习总结
使用 PyTorch 实现 MNIST 手写数字识别包括以下步骤(同时也是训练深度学习的一般步骤):加载和预处理数据;构建卷积神经网络模型;定义损失函数和优化器;通过训练循环更新模型参数;使用测试集评估模型性能;并最终可视化训练和测试过程中的准确率和损失曲线。