一、什么是直接内存?
Direct Memory:系统内存
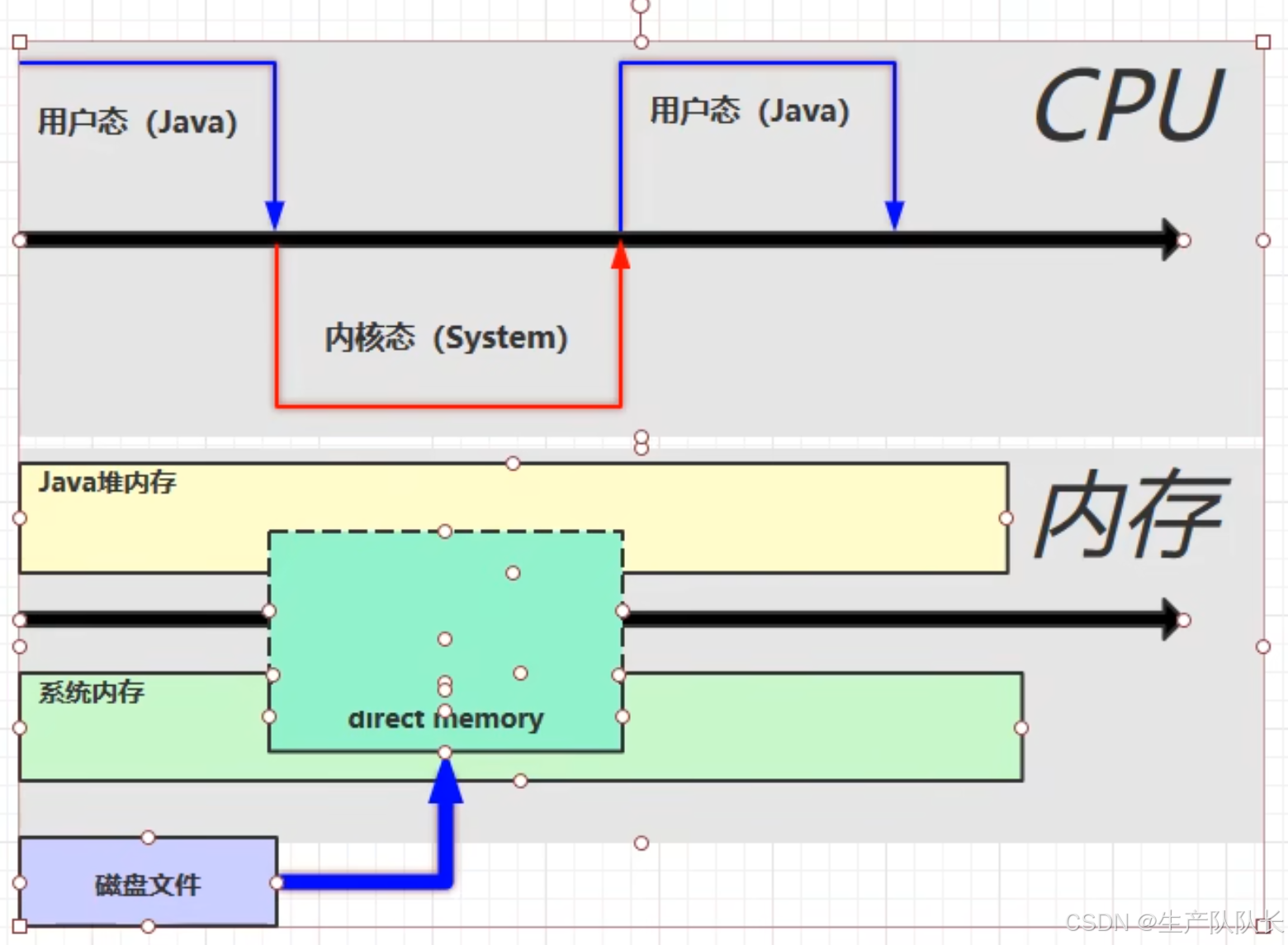
普通IO,运行原理图
磁盘到系统内存,系统内存到jvm内存。
NIO,运行原理图
划分了一块区域,JVM和系统共享的内存区间,这样,就减少了一次IO操作。
二、特点
常见于 NIO 操作时,用于数据缓冲区
分配回收成本较高,但读写性能高
不受 JVM 内存回收管理
所以,我们可以在IO程序中,使用直接内存来优化程序的读写性能。
三、使用案例
关键代码:ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Mb);
public class Demo1_9 {
static final String FROM = "E:\\sbPSjI4tt10.mp4";
static final String TO = "E:\\a.mp4";
static final int _1Mb = 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) {
io(); // io 用时:1535.586957 1766.963399 1359.240226
directBuffer(); // directBuffer 用时:479.295165 702.291454 562.56592
}
private static void directBuffer() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try (FileChannel from = new FileInputStream(FROM).getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream(TO).getChannel();
) {
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Mb);
while (true) {
int len = from.read(bb);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
bb.flip();
to.write(bb);
bb.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("directBuffer 用时:" + (end - start) / 1000_000.0);
}
private static void io() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try (FileInputStream from = new FileInputStream(FROM);
FileOutputStream to = new FileOutputStream(TO);
) {
byte[] buf = new byte[_1Mb];
while (true) {
int len = from.read(buf);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
to.write(buf, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("io 用时:" + (end - start) / 1000_000.0);
}
}
但是,直接内存,是不受JVM管理的
另外,我们显示调用gc,JVM也不是立马就执行gc。
而且,一般我们会在项目中禁用显示调用gc,因为,Full GC影响性能。
禁用参数:-XX:+DisableExplicitGC
四、直接内存的管理
底层是如何回收直接内存的?
- 使用了
Unsafe对象完成直接内存的分配回收,并且回收需要主动调用freeMemory方法 ByteBuffer的实现类内部,使用了Cleaner(虚引用)来监测ByteBuffer对象,一旦
ByteBuffer对象被垃圾回收,那么就会由ReferenceHandler线程通过Cleaner的clean方法调
用freeMemory来释放直接内存
我们知道,不建议程序员显示调用gc,来回收JVM对象。
但是,等待JVM自主的Full GC,又是不确定的。
所以,还是,建议我们自己手动回收直接内存。
public class Demo1_27 {
static int _1Gb = 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
// 分配内存
long base = unsafe.allocateMemory(_1Gb);
unsafe.setMemory(base, _1Gb, (byte) 0);
System.in.read();
// 释放内存
unsafe.freeMemory(base);
System.in.read();
}
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) f.get(null);
return unsafe;
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}