TensorFlow 是一个广泛应用的开源深度学习框架,支持多种机器学习任务,如深度学习、神经网络、强化学习等。以下是 TensorFlow 的详细教程,涵盖基础使用方法和示例代码。
1. 安装与导入
安装 TensorFlow:
pip install tensorflow导入 TensorFlow:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
验证安装:
print(tf.__version__) # 查看 TensorFlow 版本
2. TensorFlow 基础
2.1 张量(Tensor)
TensorFlow 的核心数据结构是张量,它是一个多维数组。
# 创建张量
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3], dtype=tf.float32) # 常量张量
b = tf.Variable([4, 5, 6], dtype=tf.float32) # 可变张量
# 基本运算
c = a + b
print(c.numpy()) # 转换为 NumPy 数组输出
输出结果
[5. 7. 9.]2.2 自动求导
TensorFlow 支持自动计算梯度。
x = tf.Variable(3.0)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
y = x**2 # 定义目标函数
dy_dx = tape.gradient(y, x) # 自动求导
print(dy_dx.numpy())
输出结果
6.03. 构建模型
3.1 使用 Sequential API
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
# 构建简单神经网络
model = Sequential([
Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(10,)),
Dense(32, activation='relu'),
Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
# 查看模型结构
model.summary()
输出结果
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 64) 704
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 32) 2080
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 1) 33
=================================================================
Total params: 2,817
Trainable params: 2,817
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________3.2 自定义模型
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
class MyModel(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = Dense(64, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = Dense(32, activation='relu')
self.output_layer = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.dense1(inputs)
x = self.dense2(x)
return self.output_layer(x)
model = MyModel()
input_shape = (None, 128, 128, 3)
model.build(input_shape)
model.summary()
输出结果
Model: "my_model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) multiple 256
dense_1 (Dense) multiple 2080
dense_2 (Dense) multiple 33
=================================================================
Total params: 2,369
Trainable params: 2,369
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________4. 数据处理
4.1 数据加载
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
# 加载 MNIST 数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处理
x_train = x_train / 255.0 # 归一化
x_test = x_test / 255.0
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28*28) # 展平
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 28*28)
4.2 创建数据管道
# 使用 Dataset API 创建数据管道
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
dataset = dataset.shuffle(10000).batch(32).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
5. 模型训练与评估
5.1 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
5.2 训练模型
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.2)
5.3 评估模型
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
print(f"Test accuracy: {test_acc}")
完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
# 加载MNIST数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处理:归一化到 [0, 1]
x_train = x_train / 255.0
x_test = x_test / 255.0
# 构建模型
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)), # 将28x28的图像展平为1维
Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 全连接层,128个神经元
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层,10个类别
])
# 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 模型训练
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.2)
# 模型评估
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
print(f"Test accuracy: {test_acc}")
输出结果
Epoch 1/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2894 - accuracy: 0.9178 - val_loss: 0.1607 - val_accuracy: 0.9547
Epoch 2/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.1301 - accuracy: 0.9614 - val_loss: 0.1131 - val_accuracy: 0.9656
Epoch 3/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0875 - accuracy: 0.9736 - val_loss: 0.1000 - val_accuracy: 0.9683
Epoch 4/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0658 - accuracy: 0.9804 - val_loss: 0.0934 - val_accuracy: 0.9728
Epoch 5/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0506 - accuracy: 0.9852 - val_loss: 0.0893 - val_accuracy: 0.9715
Epoch 6/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0397 - accuracy: 0.9878 - val_loss: 0.0908 - val_accuracy: 0.9731
Epoch 7/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0311 - accuracy: 0.9906 - val_loss: 0.0882 - val_accuracy: 0.9749
Epoch 8/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0251 - accuracy: 0.9924 - val_loss: 0.0801 - val_accuracy: 0.9777
Epoch 9/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0196 - accuracy: 0.9945 - val_loss: 0.0866 - val_accuracy: 0.9755
Epoch 10/10
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0166 - accuracy: 0.9949 - val_loss: 0.0980 - val_accuracy: 0.9735
313/313 [==============================] - 0s 863us/step - loss: 0.0886 - accuracy: 0.9758
Test accuracy: 0.9757999777793884代码说明
-
数据加载与预处理:
mnist.load_data():加载手写数字数据集。- 数据归一化:将像素值从 0-255 归一化到 0-1,有助于加速训练。
-
模型构建:
Flatten层:将二维的图像数据展平为一维数组,便于输入全连接层。Dense层:- 第一层使用 ReLU 激活函数。
- 第二层是输出层,使用 Softmax 激活函数,用于多分类任务。
-
模型编译:
- 优化器:
adam是一种适用于大多数情况的优化算法。 - 损失函数:
sparse_categorical_crossentropy,用于分类任务。
- 优化器:
-
训练:
validation_split=0.2:从训练数据中划分 20% 用作验证集。epochs=10:训练 10 个轮次。
-
评估:
model.evaluate():评估模型在测试集上的性能,返回损失值和准确率。
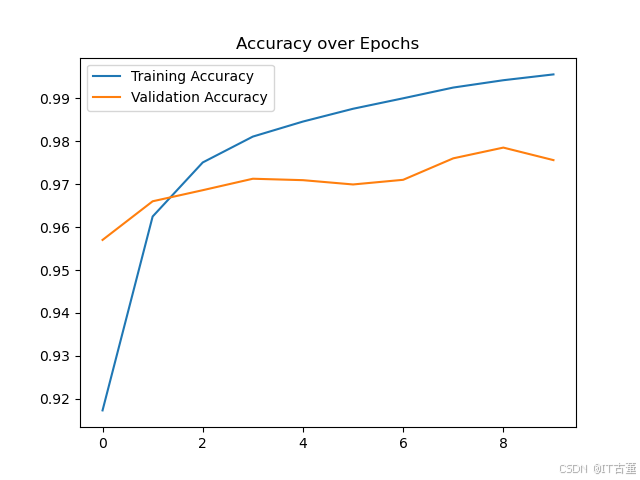
6. 可视化
6.1 绘制训练过程
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制训练与验证准确率
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Accuracy over Epochs')
plt.show()
6.2 绘制模型预测
# 显示预测结果
predictions = model.predict(x_test[:10])
print("Predicted labels:", np.argmax(predictions, axis=1))
print("True labels:", y_test[:10])
输出结果
Predicted labels: [7 2 1 0 4 1 4 9 5 9]
True labels: [7 2 1 0 4 1 4 9 5 9]7. 高级功能
7.1 保存与加载模型
# 保存模型
model.save('my_model.h5')
# 加载模型
loaded_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('my_model.h5')
7.2 自定义训练过程
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
loss_fn = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy()
for epoch in range(5):
for x_batch, y_batch in dataset:
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predictions = model(x_batch, training=True)
loss = loss_fn(y_batch, predictions)
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1} Loss: {loss.numpy()}")
完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
# 加载 MNIST 数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 将标签二值化(偶数为 1,奇数为 0)
y_train = (y_train % 2 == 0).astype(int)
y_test = (y_test % 2 == 0).astype(int)
# 数据预处理
x_train = x_train / 255.0 # 归一化
x_test = x_test / 255.0
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) # 展平
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
# 使用 Dataset API 创建数据管道
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
dataset = dataset.shuffle(10000).batch(32).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
# 定义模型
class MyModel(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = Dense(64, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = Dense(32, activation='relu')
self.output_layer = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid') # 输出单个概率
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.dense1(inputs)
x = self.dense2(x)
return self.output_layer(x)
model = MyModel()
# 自定义训练模型
# 优化器和损失函数
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
loss_fn = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()
# 模型训练
for epoch in range(5):
for x_batch, y_batch in dataset:
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predictions = model(x_batch, training=True)
loss = loss_fn(y_batch, predictions) # 使用二分类损失函数
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1} Loss: {loss.numpy()}")
输出结果
Epoch 1 Loss: 0.14392520487308502
Epoch 2 Loss: 0.013877220451831818
Epoch 3 Loss: 0.006577217951416969
Epoch 4 Loss: 0.004411072935909033
Epoch 5 Loss: 0.00379082607105374348. 实际应用案例
8.1 图像分类
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import fashion_mnist
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
# 加载数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处理
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
y_train, y_test = to_categorical(y_train), to_categorical(y_test)
# 模型构建与训练
model = Sequential([
Dense(128, activation='relu', input_shape=(28*28,)),
Dense(64, activation='relu'),
Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train.reshape(-1, 28*28), y_train, epochs=5, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.2)
输出结果
Epoch 1/5
1500/1500 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5128 - accuracy: 0.8172 - val_loss: 0.3955 - val_accuracy: 0.8561
Epoch 2/5
1500/1500 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3794 - accuracy: 0.8621 - val_loss: 0.3925 - val_accuracy: 0.8546
Epoch 3/5
1500/1500 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3403 - accuracy: 0.8741 - val_loss: 0.3721 - val_accuracy: 0.8661
Epoch 4/5
1500/1500 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3158 - accuracy: 0.8826 - val_loss: 0.3390 - val_accuracy: 0.8767
Epoch 5/5
1500/1500 [==============================] - 2s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3011 - accuracy: 0.8883 - val_loss: 0.3292 - val_accuracy: 0.8790总结
TensorFlow 提供了从数据处理到模型训练和部署的完整解决方案。其灵活的 API 和强大的功能使得研究人员和工程师可以快速实现复杂的机器学习和深度学习任务。通过不断实践,可以深入了解 TensorFlow 的更多特性。