大一课程设计——不会五子棋
在编写此次课程设计后,我了解到其实C语言不但可以在黑白色的命令提示符界面进行运行,还可以有很美观的窗口界面。课程设计中我完成了自学EasyX这一图形库内各种函数的使用,不仅掌握了如何学习课本之外的知识,更获得了通过交流论坛和查找资料解决实际应用中的问题的能力。对于这个初级的五子棋小游戏仍有许多可以改进的地方,比如写一个智能化程度更高的AI,亦或是写个电脑对战电脑的DLC,作为计算机专业的学生的乐趣也在于这种理解和创造的过程。
文章目录
一.简单双人五子棋
简单的双人五子棋只需要克服绘制(插入)棋盘、放置棋子和判断胜负几个难点,可以用来熟悉EasyX的基本操作。
可以使用EasyX实现棋盘图片的插入(附上棋盘图片)。
代码展示:
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int chess[35][35];
int judge(int x, int y, int type) //左右上下斜判断
{
// x = (x + 15) / 25;
// y = (y + 15) / 25;
int i = 0, number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //上
{
if (chess[x][y - i - 1] == type && y - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //下
{
if (chess[x][y + i + 1] == type)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //左
{
if (chess[x - i - 1][y] == type && x - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //右
{
if (chess[x + i + 1][y] == type)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //左上
{
if (chess[x - i - 1][y - i - 1] == type && x - i - 1 >= 0 && y - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //右上
{
if (chess[x + i + 1][y - i - 1] == type && y - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //左下
{
if (chess[x - i - 1][y + i + 1] == type && x - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //右下
{
if (chess[x + i + 1][y + i + 1] == type)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
return 0;
}
int make(int x, int y, int type)
{
int x1, y1, n = 5;
if (x < 15 || y < 15 || y >= 385 || x >= 385)
return 0;
else
{
x = (x + 15) / 25;
y = (y + 15) / 25;
if (chess[x][y] != 0)
return 0;
else
{
x1 = x * 25;
y1 = y * 25;
if (type == 1)
{
setfillcolor(BLACK);
chess[x][y] = 1;
}
else
{
setfillcolor(WHITE);
chess[x][y] = 2;
}
fillcircle(x1, y1, 5);
n = judge(x, y, type);
if (n == 1) //五子连珠
return 2;
else
return 1;
}
}
}
int main()
{
HWND my_consle = GetForegroundWindow();
ShowWindow(my_consle, SW_SHOW);
int choice = 0, n = 5;
IMAGE img;
MOUSEMSG m;
loadimage(&img, L"五子棋棋盘.gif");
int w, h;
w = img.getwidth();
h = img.getheight();
initgraph(w, h);
putimage(0, 0, &img);
while (1)
{
out:
Sleep(5);
m = GetMouseMsg();
if (m.uMsg == WM_LBUTTONDOWN && choice == 0) //
{
n = make(m.x, m.y, 1);
if (n == 1)
choice = 1;
else if (n == 2)
{
settextstyle(20, 0, L"楷体");
setbkmode(TRANSPARENT);
settextcolor(RED);
outtextxy(120, 150, L"黑方胜利");
break;
}
else
goto out;
}
else if (m.uMsg == WM_LBUTTONDOWN && choice == 1)
{
n = make(m.x, m.y, 2);
if (n == 1)
{
choice = 0;
}
else if (n == 2)
{
settextstyle(20, 0, L"楷体");
setbkmode(TRANSPARENT);
settextcolor(RED);
outtextxy(120, 150, L"白方胜利");
break;
}
else
goto out;
}
else
continue;
}
getchar();
}
1.judge函数
int judge(int x, int y, int type) //左右上下斜判断
{
// x = (x + 15) / 25;
// y = (y + 15) / 25;
int i = 0, number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //上
{
if (chess[x][y - i - 1] == type && y - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //下
{
if (chess[x][y + i + 1] == type)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //左
{
if (chess[x - i - 1][y] == type && x - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //右
{
if (chess[x + i + 1][y] == type)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //左上
{
if (chess[x - i - 1][y - i - 1] == type && x - i - 1 >= 0 && y - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //右上
{
if (chess[x + i + 1][y - i - 1] == type && y - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //左下
{
if (chess[x - i - 1][y + i + 1] == type && x - i - 1 >= 0)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) //右下
{
if (chess[x + i + 1][y + i + 1] == type)
{
number++;
}
}
if (number == 4)
return 1;
else
number = 0;
return 0;
}
judge函数判断先向上检索,若该方向上检索,若连续四个棋子颜色一致则number=4且返回返回值1,否则number依然为0并进行另一方向的检索直至八个方向结束或出现五子连珠。
2.make函数
int make(int x, int y, int type)
{
int x1, y1, n = 5;
if (x < 15 || y < 15 || y >= 385 || x >= 385)
return 0;
else
{
x = (x + 15) / 25;
y = (y + 15) / 25;
if (chess[x][y] != 0)
return 0;
else
{
x1 = x * 25;
y1 = y * 25;
if (type == 1)
{
setfillcolor(BLACK);
chess[x][y] = 1;
}
else
{
setfillcolor(WHITE);
chess[x][y] = 2;
}
fillcircle(x1, y1, 5);
n = judge(x, y, type);
if (n == 1) //五子连珠
return 2;
else
return 1;
}
}
}
make函数用于绘制棋子,并为judge函数提供坐标以判断胜负
二.人机五子棋
1.内容提要
在初步还原了简单五子棋的实现方法后就可以尝试更高级的界面、更高级的AI,因此我选择五子棋作为课程设计。
本五子棋学习了https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45669199/article/details/101145656和https://blog.csdn.net/ChinaJane163/article/details/52599787两篇文章作为参考。
人机对战参考了用评估函数求评估值的方法实现电脑落子,评估函数的对象为(假设电脑为白子):
【1】多少白子连成线(因为越多白子练成线,对电脑越有利)
【2】多少将要连成线的黑子,被这个白子打断了(还要考虑填了这个子后,电脑对人所落的子的破坏)。
评估函数得到的值越大,电脑越倾向在那个位置落子。简单的说,就是此AI返回的是第一个评估值最高的位置。
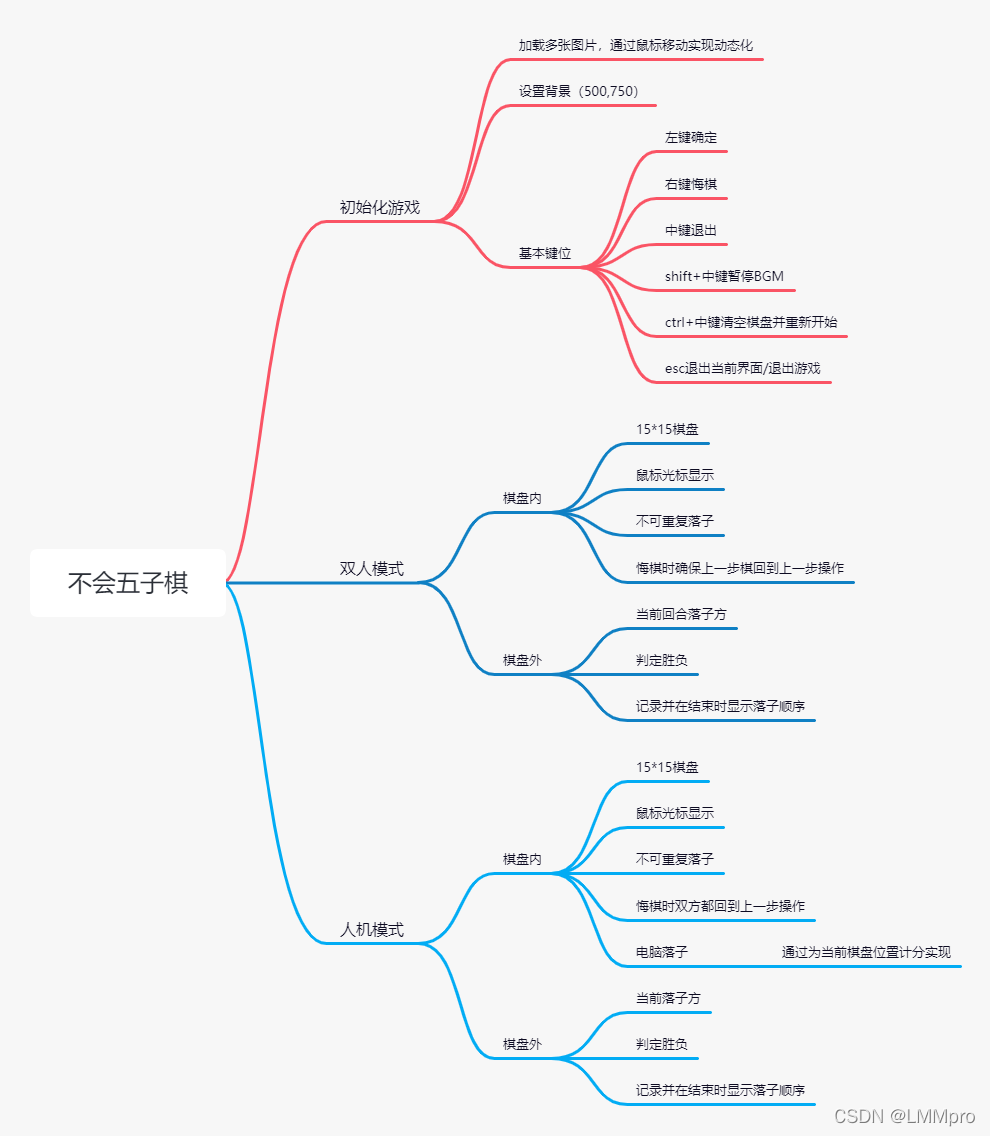
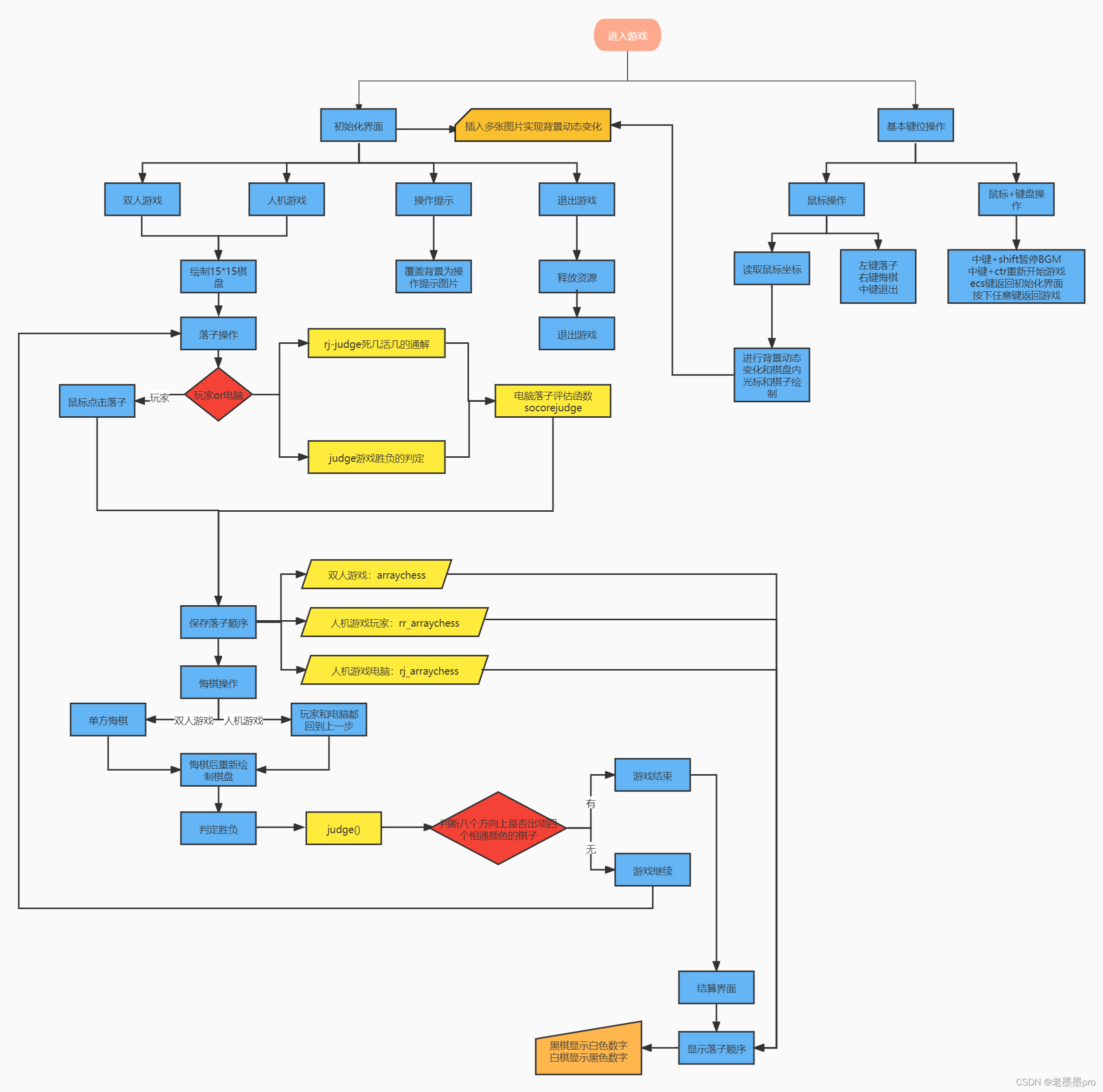
2.设计内容
思维导图:
流程图:
3.功能模块详细设计
3.1 游戏初始化
设置窗口大小与背景图片一致,让窗口名称变为“不会五子棋”并使用API函数修改窗口名称。加载多张图片以实现颜色的动态效果,通过鼠标移动和点击的位置实现背景的变化和交互。
void initgame()
{
//设置窗口大小
initgraph(500, 750);
//让窗口名称变成不会五子棋
// 获得窗口句柄
HWND hWnd = GetHWnd();
// 使用 API 函数修改窗口名称
SetWindowText(hWnd, "不会五子棋");
B:;
//加载图片
IMAGE background;
loadimage(&background, "back.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &background);
//设置背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195, 195, 195)); //目的是为了让显示的文字看起来没有边框
//设置五张图片来显示出颜色动态效果
IMAGE ch1, ch2, ch3, ch4, ch5, ch6;
loadimage(&ch1, "1.jpg", 500, 750);
loadimage(&ch2, "2.jpg", 500, 750);
loadimage(&ch3, "3.jpg", 500, 750);
loadimage(&ch4, "4.jpg", 500, 750);
//游戏界面选择
MOUSEMSG m; // 定义鼠标消息
while (true)
{
// 获取鼠标消息
m = GetMouseMsg();
//清除鼠标缓存
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
//放置背景避免黑屏
putimage(0, 0, &background);
switch (m.uMsg)
{
case WM_MOUSEMOVE:
if (m.x >= 0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) //(0,495)(220,545) 开始游戏
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch1);
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) // (275,495)(500,545) 人机对战
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch2);
}
if (m.x >= 0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (0,615)(220,665) 操作提示
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch3);
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (275,615)(500,665) 退出游戏
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch4);
}
break;
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN:
if (m.x >= 0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) //(0,495)(220,545) 开始游戏
{
goto A;
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) // (275,495)(500,545) 人机对战
{
rj_begingame();
}
if (m.x >= 0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (0,615)(220,665) 操作提示
{
IMAGE explain;
loadimage(&explain, "操作提示.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &explain);
system("pause");
goto B;
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (275,615)(500,665) 退出游戏
{
//先释放资源
closegraph();
exit(0);
}
}
}
A:;
}
3.2 双人游戏进行
以(25,325)(425,725)画棋盘,从(50,350)开始划线,光标最初设置于(225,525)(即(25+425)/2,(325,725)/2,即正中间),定义一个有225个元素的结构体数组来代表光标的所有分布的可能性并以index作为结构体数组下标进行填充。定义并获取鼠标信息和键盘信息,在下棋过程中通过array保存下棋顺序,通过getpixel()(getpixel(int x, int y)用于获取点的颜色)防止重复下棋,使用judge判断胜负并输出结果。悔棋时保证保证是悔的上一颗的棋。
void begingame()
{
//加载背景音乐
mciSendString("open BGM1.mp3 alias bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
mciSendString("play bg repeat", NULL, 0, NULL);
C:
//显示背景音乐开关
IMAGE BGM;
loadimage(&BGM, "BGM.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &BGM);
//棋盘加载
setlinecolor(BLACK);
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID);
setfillcolor(RGB(223, 200, 158));
fillrectangle(25, 325, 425, 725); //计算而来的
for (int i = 1; i < 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < 15; j++)
{
rectangle(25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, 50 + j * 25, 350 + i * 25); //棋盘左上是50 350
}
}
//黑子先手 游戏开始光标默认在正中间
//绘制光标
xy.x = 225;
xy.y = 525; // 这个坐标是推出来的 就是最中心的坐标
setlinecolor(RED);
setlinestyle(PS_DOT);
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
//定义一个有225个元素的结构体数组来代表光标的所有分布的可能性
post master[225];
//填充电脑位置 //棋盘左上是50 350
int index = 0; //定义结构体数组的下标
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= 15; j++)
{
// 25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, //棋盘左上是50 350
master[index].x = 25 + j * 25;
master[index].y = 325 + i * 25;
index++;
}
}
//清除上一下鼠标缓存
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
MOUSEMSG m; // 定义鼠标消息
while (true)
{
//按下esc返回游戏界面
if (_kbhit())
{
char key;
key = _getch();
switch (key)
{
case 27:
{
//重置color
color = 0;
//音乐暂停
mciSendString("close bg", NULL, 0, NULL); //竟然神奇的把pause改成close就可以消除按下esc会页面在点击开始游戏直接出来棋子的bug
main();
}
}
}
//清除上一下鼠标缓存让光标更加灵活
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
//获取一条鼠标消息
m = GetMouseMsg();
//是否暂停音乐
if (bgm % 2 == 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(25, 730, "背景音乐:OFF");
mciSendString("pause bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
else
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(25, 730, "背景音乐:O N");
mciSendString("resume bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
//显示提示黑子先手或者显示提示当前将要下的棋子颜色
if (color == 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "黑子先手"); //
}
else if (color % 2 != 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "轮到棋子:");
//提示落子颜色
setfillcolor(WHITE);
setlinecolor(WHITE);
fillcircle(130, 310, 10);
}
else
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "轮到棋子:");
//提示落子颜色
setfillcolor(BLACK);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
fillcircle(130, 310, 10);
}
switch (m.uMsg)
{
case WM_MOUSEMOVE:
for (int i = 0; i < 225; i++)
{
if ((m.x >= master[i].x - 10 && m.x <= master[i].x + 10) && (m.y >= master[i].y - 10 && m.y <= master[i].y + 10)) // m.x == master[i].x && m.y == master[i].y
{
//(m.x >= master[i].x - 5 && m.x <= master[i].x + 5) && (m.y >= master[i].y - 5 && m.y <= master[i].y + 5)
setlinecolor(RGB(223, 200, 158));
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
xy.x = master[i].x;
xy.y = master[i].y;
setlinecolor(RED);
setlinestyle(PS_DOT);
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
}
}
break;
case WM_MBUTTONDOWN:
if (m.mkShift)
{
bgm++; // 如果按下中键同时按下shift就决定音乐是否暂停(先按住shift在按住鼠标中键)
Sleep(100);
break;
}
if (m.mkCtrl)
{
//如果按下中键同时按下ctrl就重新开始游戏
color = 0; //重置颜色
IMAGE background;
loadimage(&background, "back.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &background); //重置画面
goto C;
}
exit(0); //设置强制退出游戏功能
case WM_LBUTTONUP:
//不可以重复下棋 通过getpixel这个函数来实现
if (getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) == RGB(0, 0, 0) || getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) == RGB(255, 255, 255))
{
break;
}
if (color % 2 == 0)
{
//把下的棋的顺序保存在array数组里面
array[color] = xy;
setfillcolor(BLACK);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
PlaySound("104.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
COLORREF hei = getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3);
//胜负判断
int a = judge(hei, xy.x, xy.y);
if (a == 1)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(120, 200, "恭喜黑棋获胜");
outtextxy(80, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
char str[30];
sprintf_s(str, "战了%d回合", color / 2 + 1);
outtextxy(120, 230, str);
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示落子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//加入平局的判断
if (a == 0 && color == 224) // color最大值是224
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(250, 200, "平局");
outtextxy(65, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
}
else
{
//把下的棋的顺序保存在array数组里面
array[color] = xy;
setfillcolor(WHITE);
setlinecolor(WHITE);
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
PlaySound("104.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
COLORREF bai = getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3);
//胜负判断
int b = judge(bai, xy.x, xy.y);
if (b == 1)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(120, 200, "恭喜白棋获胜!");
outtextxy(80, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
char str[30];
sprintf_s(str, "大战了%d回合!", color / 2 + 1);
outtextxy(120, 230, str);
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//加入平局的判断
if (b == 0 && color == 224)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(105, 200, "平局!");
outtextxy(65, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
}
//把当前下的棋保存在huixy中
huixy.x = xy.x;
huixy.y = xy.y;
color++;
Sleep(100);
break;
case WM_RBUTTONDOWN: //设置悔棋功能
//保证是悔的上一颗的棋
if (huixy.x == xy.x && huixy.y == xy.y && getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) != RGB(223, 200, 158))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(223, 200, 158));
setlinecolor(RGB(223, 200, 158));
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
for (int i = 1; i < 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < 15; j++)
{
rectangle(25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, 50 + j * 25, 350 + i * 25);
}
}
color--;
break;
}
}
//来一个重新检查 主要是让白棋不存在中心有黑线的情况
for (int i = 0; i < 255; i++)
{
if (getpixel(master[i].x - 3, master[i].y - 3) == RGB(0, 0, 0))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
setlinecolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
fillcircle(master[i].x, master[i].y, 10);
}
if (getpixel(master[i].x - 3, master[i].y - 3) == RGB(255, 255, 255))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
setlinecolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
fillcircle(master[i].x, master[i].y, 10);
}
}
}
}
3.3 人机游戏进行
思路和画棋盘等操作与双人游戏一致,但是电脑使用评估函数判断落子方位
核心代码:
case 1:
{
for (int i = 0; i < 225; i++)
{
if (RGB(0, 0, 0) != getpixel(alphcat[i].x - 3, alphcat[i].y - 3) && RGB(255, 255, 255) != getpixel(alphcat[i].x - 3, alphcat[i].y - 3)
/*当前落棋点没有落棋 (这个点的颜色是背景色)*/)
{
//RGB(255, 255, 255) != getpixel(alphcat[i].x - 3, alphcat[i].y - 3)
alphcat[i].score = scorejudge(alphcat[i].x, alphcat[i].y);
}
}
//再来选出一个得分最大的,如果得分一样就随机从最大的一个选一个
alph alphmax;
alphmax.score = alphcat[0].score;
for (int i = 1; i < 225; i++)
{
if (alphcat[i].score >= alphmax.score)
{
alphmax = alphcat[i];
}
}
// 把下的棋的顺序保存在array数组里面
rjarray[color] = alphmax;
//根据这个点画白棋
setfillcolor(WHITE);
setlinecolor(WHITE);
fillcircle(alphmax.x, alphmax.y, 10);
PlaySound("104.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
for (int i = 0; i < 225; i++)
{
alphcat[i].score = 0;
}
COLORREF bai = getpixel(alphmax.x - 3, alphmax.y - 3);
3.4 胜负判定函数——judge
返回1表示胜负已定,返回0表示胜负未分。
检查一个方向的5个格子,通过颜色判断,若该方向未定胜负则还原落子位置继续判断。(与简单五子棋思路相似)
int judge(COLORREF cl, int x, int y)
{
int a, b;
//定义上下总个数
int i = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
/*x = xy.x;
y = xy.y;*/
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 - 25))
{
i++;
b -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 + 25))
{
i++;
b += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (i >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
//定义左右总个数
int j = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查左面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (j >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
//定义'\'总个数
int k = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
k++;
a -= 25;
b -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
k++;
a += 25;
b += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (k >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
//定义'/'总个数
int l = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
l++;
a += 25;
b -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
l++;
a -= 25;
b += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (l >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
3.5 显示落子顺序函数——arraychess、rr_arraychess、rj_arraychess
arraychess用于显示双人游戏落子顺序
rr_arraychess用于显示人机游戏玩家落子顺序
rj_arraychess用于显示人机游戏电脑落子顺序
主要实现的功能是在黑色的棋上显示白色顺序,在白色棋子上显示黑色的顺序,在结束后恢复背景颜色。
void arraychess()
{
//主要实现的功能是在黑色的棋上显示白色顺序 在白色棋子上显示黑色的顺序
for (int i = 0; i <= color; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
setbkcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%-2d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(array[i].x - 7, array[i].y - 7, arr);
}
else
{
setbkcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%-2d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(array[i].x - 7, array[i].y - 7, arr);
}
}
//恢复了背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195, 195, 195));
}
void rj_arraychess()
{
// 在白色棋子上显示黑色的顺序
for (int i = 0; i <= color; i++)
{
if (i % 2 != 0)
{
setbkcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%-2d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(rjarray[i].x - 7, rjarray[i].y - 7, arr);
}
}
//恢复了背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195, 195, 195));
}
void rr_arraychess()
{
// 在黑色棋子上显示白色的顺序
for (int i = 0; i <= color; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
setbkcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%-2d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(array[i].x - 7, array[i].y - 7, arr);
}
}
//恢复了背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195, 195, 195));
}
3.6 人机判断函数——rj_judge
创建一个人机判断 死几活几的通解 参数分别是颜色,x坐标,y坐标,死活判断(1代表死,2代表活),死几或者活几,返回1代表成立,返回0代表不成立,具体见代码部分注释。(https://blog.csdn.net/ChinaJane163/article/details/52599787)
int rj_judge(COLORREF cl, int x, int y, int q, int p)
{
//用一个K来体现某一个方向的下一个是背景而不是有另外颜色的(活) K = 1 表示下一个为背景色
int K = 0;
int a, b;
//定义上下总个数
int i = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 - 25))
{
i++;
b -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 - 25) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && b - 25 > 350)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 + 25))
{
i++;
b += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 + 25) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && b + 35 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (i == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
//重置K
K = 0;
//定义左右总个数
int j = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查左面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && a - 35 > 50)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && a + 35 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (j == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
//重置K
K = 0;
//定义'\'总个数
int k = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
k++;
a -= 25;
b -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 - 25) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && a - 25 > 50 && b - 25 > 350)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
k++;
a += 25;
b += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 + 25) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && a + 25 < 400 && b + 25 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (k == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
//重置K
K = 0;
//定义'/'总个数
int l = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
l++;
a += 25;
b -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 - 25) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && a + 25 < 400 && b - 25 > 350)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
l++;
a -= 25;
b += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 + 25) == RGB(223, 200, 158) && a - 25 > 50 && b + 25 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (l == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
3.7 人机判断函数——scorejudge
参考了CSDN上的粗暴版AI,通过评估函数返回值的大小确定落子位置,
计分表如下:
| 白子为电脑 | 黑子为玩家 |
|---|---|
| 白子连成五子 +10000 | 阻碍黑子连成五子 +1000 |
| 白子连成活四 +200 | 阻碍黑子连成活四 +100 |
| 白子连成死四 +50 | 阻碍黑子连成死四 +20 |
| 白子连成活三 +30 | 阻碍黑子连成活三 +10 |
| 白子连成死三 +8 | 阻碍黑子连成死三 +5 |
| 白子成成活二 +2 | 阻碍黑子连成活二 +1 |
| 白子连成死二 +2 | 阻碍黑子连成死二 +1 |
| 白子连成活一 +1 | 阻碍黑子连成活一 +0 |
| 白子连成活二 +1 | 阻碍黑子连成死一 +0 |
————————————————
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ChinaJane163/article/details/52599787
int scorejudge(int x, int y)
{
/*主要思想(来自https://blog.csdn.net/ChinaJane163/article/details/52599787)
电脑白子 自己黑子
白子连成五子 +10000 阻碍黑子连成五子 +1000
白子连成活四 +200 阻碍黑子连成活四 +100
白子连成死四 +50 阻碍黑子连成死四 +20
白子连成活三 +30 阻碍黑子连成活三 +10
白子连成死三 +8 阻碍黑子连成死三 +5
白子连成活二 +2 阻碍黑子连成活二 +1
白子连成死二 +2 阻碍黑子连成死二 +1
白子连成活一 +1 阻碍黑子连成活一 +0
白子连成死一 +1 阻碍黑子连成死一 +0
*/
int a = x;
int b = y;
//定义一个得分
int score = 0;
//白子连成五子 +10000
if (judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b)) //这个函数只是i的值与k的值不一样 所以可以加两个变量在函数里面
{
score += 10000;
}
//阻碍黑子连成五子 +1000
if (judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b))
{
score += 1000;
}
//白子连成活四 +200
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 4))
{
score += 200;
}
//阻碍黑子连成活四 +100
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 2, 4))
{
score += 100;
}
//白子连成死四 +50
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 4))
{
score += 50;
}
//阻碍黑子连成死四 +20
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 1, 4))
{
score += 20;
}
//白子连成活三 +30
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 3))
{
score += 30;
}
//阻碍黑子连成活三 +10
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 2, 3))
{
score += 10;
}
//白子连成死三 +8
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 3))
{
score += 8;
}
//阻碍黑子连成死三 +5
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 1, 3))
{
score += 5;
}
//白子连成活二 +2
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 2))
{
score += 2;
}
//阻碍黑子连成活二 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 2, 2))
{
score += 1;
}
//白子连成死二 +2
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 2))
{
score += 2;
}
//阻碍黑子连成死二 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 1, 2))
{
score += 1;
}
//白子连成活一 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 1))
{
score += 1;
}
//白子连成死一 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 1))
{
score += 1;
}
return score;
}
3.8 成品展示
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <conio.h>
#pragma comment(lib,"winmm.lib") //背景音乐
//游戏初始化
void initgame();
//人人游戏进行
void begingame();
//人机游戏进行
void rj_begingame();
//游戏结束释放资源
void gameover();
//游戏胜负的判定 返回1表示胜负已定 返回0表示胜负未分
int judge(COLORREF, int, int);
//人人模式游戏结束显示下棋顺序
void arraychess();
//人机模式游戏结束显示电脑下棋顺序
void rj_arraychess();
//人机模式游戏结束显示人下棋顺序
void rr_arraychess();
//创建一个人机判断 死几活几的通解 参数分别是 颜色, x坐标, y坐标, 死活判断(1代表死,2代表活), 死几或者活几 返回1代表成立,返回0代表不成立
int rj_judge(COLORREF , int , int , int , int );
//人机每一步分析可用棋子上的分数值,返回分数最高的就是落子点
int scorejudge(int, int);
//设置光标结构体类型
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
}post;
//设置人机结构体类型
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
int score;
}alph;
//设置光标
post xy;
//用一个数的奇偶性来判断产生棋子的黑白 偶数表示黑棋 当color == 225的时候表明平局
int color = 0;
//用一个开关来控制游戏的背景音乐; 奇数表示开
int bgm = 1;
//为了防止出现随意悔棋的情况 所以规定每个人只能悔当前下的棋 所以定义一个光标记录将要悔棋的地点
post huixy;
//人悔了一步棋,机器也要退回上一个的位置
alph rjhuixy;
//定义一个稍微大一点的结构体数组来存放每一步棋子顺序(人人)
post array[1000] = { 0 };
//定义一个稍微大一点的结构体数组来存放每一步棋子顺序(人机)
alph rjarray[1000] = { 0 };
int main()
{
initgame();
begingame();
gameover();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void initgame()
{
//设置窗口大小
initgraph(500, 750);
//让窗口名称变成不会五子棋
// 获得窗口句柄
HWND hWnd = GetHWnd();
// 使用 API 函数修改窗口名称
SetWindowText(hWnd, "不会五子棋");
B:;
//加载图片
IMAGE background;
loadimage(&background, "back.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &background);
//设置背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195,195,195)); //目的是为了让显示的文字看起来没有边框
//设置五张图片来显示出颜色动态效果
IMAGE ch1, ch2, ch3, ch4, ch5 ,ch6;
loadimage(&ch1, "1.jpg", 500, 750);
loadimage(&ch2, "2.jpg", 500, 750);
loadimage(&ch3, "3.jpg", 500, 750);
loadimage(&ch4, "4.jpg", 500, 750);
//游戏界面选择
MOUSEMSG m; // 定义鼠标消息
while (true)
{
// 获取鼠标消息
m = GetMouseMsg();
//清除鼠标缓存
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
//放置背景避免黑屏
putimage(0, 0, &background);
switch (m.uMsg)
{
case WM_MOUSEMOVE:
if (m.x >=0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) //(0,495)(220,545) 开始游戏
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch1);
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) // (275,495)(500,545) 人机对战
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch2);
}
if (m.x >= 0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (0,615)(220,665) 操作提示
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch3);
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (275,615)(500,665) 退出游戏
{
putimage(0, 0, &ch4);
}
break;
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN:
if (m.x >= 0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) //(0,495)(220,545) 开始游戏
{
goto A;
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 495 && m.y <= 545) // (275,495)(500,545) 人机对战
{
rj_begingame();
}
if (m.x >= 0 && m.x <= 220 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (0,615)(220,665) 操作提示
{
IMAGE explain;
loadimage(&explain, "操作提示.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &explain);
system("pause");
goto B;
}
if (m.x >= 275 && m.x <= 500 && m.y >= 615 && m.y <= 665) // (275,615)(500,665) 退出游戏
{
//先释放资源
closegraph();
exit(0);
}
}
}
A:;
}
void begingame()
{
//加载背景音乐
mciSendString("open BGM1.mp3 alias bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
mciSendString("play bg repeat", NULL, 0, NULL);
C:
//显示背景音乐开关
IMAGE BGM;
loadimage(&BGM, "BGM.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &BGM);
//棋盘加载
setlinecolor(BLACK);
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID);
setfillcolor(RGB(223,200,158));
fillrectangle(25, 325, 425, 725); //计算而来的
for (int i = 1; i < 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < 15; j++)
{
rectangle(25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, 50 + j * 25, 350 + i * 25); //棋盘左上是50 350
}
}
//黑子先手 游戏开始光标默认在正中间
//绘制光标
xy.x = 225;
xy.y = 525; // 这个坐标是推出来的 就是最中心的坐标
setlinecolor(RED);
setlinestyle(PS_DOT);
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
//定义一个有225个元素的结构体数组来代表光标的所有分布的可能性
post master[225];
//填充电脑位置 //棋盘左上是50 350
int index = 0; //定义结构体数组的下标
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= 15; j++)
{
//25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, //棋盘左上是50 350
master[index].x = 25 + j * 25;
master[index].y = 325 + i * 25;
index++;
}
}
//清除上一下鼠标缓存
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
MOUSEMSG m; // 定义鼠标消息
while (true)
{
//按下esc返回游戏界面
if (_kbhit())
{
char key;
key = _getch();
switch (key)
{
case 27:
{
//重置color
color = 0;
//音乐暂停
mciSendString("close bg", NULL, 0, NULL); //竟然神奇的把pause改成close就可以消除按下esc会页面在点击开始游戏直接出来棋子的bug
main();
}
}
}
//清除上一下鼠标缓存让光标更加灵活
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
//获取一条鼠标消息
m = GetMouseMsg();
//是否暂停音乐
if (bgm % 2 == 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(25, 730, "背景音乐:OFF");
mciSendString("pause bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
else
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(25, 730, "背景音乐:O N");
mciSendString("resume bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
//显示提示黑子先手或者显示提示当前将要下的棋子颜色
if (color == 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "黑子先手");//
}
else if(color % 2 != 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "轮到棋子:");
//提示落子颜色
setfillcolor(WHITE);
setlinecolor(WHITE);
fillcircle(130, 310, 10);
}
else
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "轮到棋子:");
//提示落子颜色
setfillcolor(BLACK);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
fillcircle(130, 310, 10);
}
switch (m.uMsg)
{
case WM_MOUSEMOVE:
for (int i = 0; i < 225; i++)
{
if ( (m.x >= master[i].x - 10 && m.x <= master[i].x + 10) && (m.y >= master[i].y - 10 && m.y <= master[i].y + 10) ) // m.x == master[i].x && m.y == master[i].y
{
//(m.x >= master[i].x - 5 && m.x <= master[i].x + 5) && (m.y >= master[i].y - 5 && m.y <= master[i].y + 5)
setlinecolor(RGB(223,200,158));
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
xy.x = master[i].x;
xy.y = master[i].y;
setlinecolor(RED);
setlinestyle(PS_DOT);
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
}
}
break;
case WM_MBUTTONDOWN:
if (m.mkShift)
{
bgm++; // 如果按下中键同时按下shift就决定音乐是否暂停(先按住shift在按住鼠标中键)
Sleep(100);
break;
}
if (m.mkCtrl)
{
//如果按下中键同时按下ctrl就重新开始游戏
color = 0; //重置颜色
IMAGE background;
loadimage(&background, "back.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &background); //重置画面
goto C;
}
exit(0); //设置强制退出游戏功能
case WM_LBUTTONUP:
//通过getpixel实现不可重复下棋
if (getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) == RGB(0, 0, 0) || getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) == RGB(255, 255, 255))
{
break;
}
if (color % 2 == 0)
{
//把落子顺序保存在array数组里
array[color] = xy;
setfillcolor(BLACK);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
PlaySound("104.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
COLORREF hei = getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3);
//胜负判断
int a = judge(hei, xy.x, xy.y);
if (a == 1)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(120, 200, "恭喜黑棋获胜");
outtextxy(80, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
char str[30];
sprintf_s(str, "战了%d回合", color / 2 + 1);
outtextxy(120, 230, str);
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示落子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//加入平局的判断
if (a == 0 && color == 224) //color最大值是224
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(250, 200, "平局");
outtextxy(65, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
}
else
{
//把落子保存在array数组里
array[color] = xy;
setfillcolor(WHITE);
setlinecolor(WHITE);
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
PlaySound("104.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
COLORREF bai = getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3);
//胜负判断
int b = judge(bai, xy.x, xy.y);
if (b == 1)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(120, 200, "恭喜白棋获胜");
outtextxy(80, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
char str[30];
sprintf_s(str, "大战了%d回合!", color / 2 + 1);
outtextxy(120, 230, str);
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//加入平局的判断
if (b == 0 && color == 224)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(105, 200, "平局");
outtextxy(65, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
}
//把当前下的棋保存在huixy中
huixy.x = xy.x;
huixy.y = xy.y;
color++;
Sleep(100);
break;
case WM_RBUTTONDOWN:
//设置悔棋功能
//保证是悔的上一颗的棋
if (huixy.x == xy.x && huixy.y == xy.y && getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) != RGB(223,200,158))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(223,200,158));
setlinecolor(RGB(223,200,158));
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
for (int i = 1; i < 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < 15; j++)
{
rectangle(25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, 50 + j * 25, 350 + i * 25);
}
}
color--;
break;
}
}
//重新检查防止主要是让白棋中心出现黑线
for (int i = 0; i < 255; i++)
{
if (getpixel(master[i].x - 3, master[i].y - 3) == RGB(0, 0, 0))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
setlinecolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
fillcircle(master[i].x, master[i].y, 10);
}
if (getpixel(master[i].x - 3, master[i].y - 3) == RGB(255, 255, 255))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
setlinecolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
fillcircle(master[i].x, master[i].y, 10);
}
}
}
}
void rj_begingame()
{
//加载背景音乐
mciSendString("open BGM.mp3 alias bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
mciSendString("play bg repeat", NULL, 0, NULL);
C:
//显示背景音乐开关
IMAGE BGM;
loadimage(&BGM, "BGM.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &BGM);
// 棋盘加载
setlinecolor(BLACK);
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID);
setfillcolor(RGB(223,200,158));
fillrectangle(25, 325, 425, 725);
for (int i = 1; i < 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < 15; j++)
{
rectangle(25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, 50 + j * 25, 350 + i * 25); //棋盘左上是50 350
}
}
//黑子先手 游戏开始光标默认在正中间
//绘制光标
xy.x = 225;
xy.y = 525;
setlinecolor(RED);
setlinestyle(PS_DOT);
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
//初始化人机阿尔法猫
//加载每个点并且把分数设为0
alph alphcat[225];
//填充电脑位置
//棋盘左上是50 350
int inde = 0; //定义结构体数组的下标
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= 15; j++)
{
//25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25,
alphcat[inde].x = 25 + j * 25;
alphcat[inde].y = 325 + i * 25;
alphcat[inde].score = 0;
inde++;
}
}
//定义一个有225个元素的结构体数组来代表光标的所有分布的可能性
post master[225];
//填充电脑位置
int index = 0; //定义结构体数组的下标
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= 15; j++)
{
//25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25,
master[index].x = 25 + j * 25;
master[index].y = 325 + i * 25;
index++;
}
}
//清除上一下鼠标缓存
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
MOUSEMSG m; // 定义鼠标消息
while (true)
{
//按下esc返回游戏界面
if (_kbhit())
{
char key;
key = _getch();
switch (key)
{
case 27:
{
//重置color
color = 0;
//音乐暂停
mciSendString("close bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
main();
}
}
}
//清除上一下鼠标缓存,让光标更加灵活
FlushMouseMsgBuffer();
//获取一条鼠标消息
m = GetMouseMsg();
//是否暂停音乐
if (bgm % 2 == 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(25, 730, "背景音乐:OFF");
mciSendString("pause bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
else
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(25, 730, "背景音乐:O N");
mciSendString("resume bg", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
//显示提示黑子先手或者显示提示当前将要下的棋子颜色
if (color == 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "黑子先手");
}
else if (color % 2 != 0)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "轮到棋子:");
//提示落子颜色
setfillcolor(WHITE);
setlinecolor(WHITE);
fillcircle(130, 310, 10);
}
else
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(20, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(30, 300, "轮到棋子:");
//提示落子颜色
setfillcolor(BLACK);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
fillcircle(130, 310, 10);
}
switch (m.uMsg)
{
case WM_MOUSEMOVE:
for (int i = 0; i < 225; i++)
{
if ((m.x >= master[i].x - 10 && m.x <= master[i].x + 10) && (m.y >= master[i].y - 10 && m.y <= master[i].y + 10))
{
setlinecolor(RGB(223,200,158));
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
xy.x = master[i].x;
xy.y = master[i].y;
setlinecolor(RED);
setlinestyle(PS_DOT);
rectangle(xy.x - 15, xy.y - 15, xy.x + 15, xy.y + 15);
}
}
break;
case WM_MBUTTONDOWN:
if (m.mkShift)
{
bgm++; //按下中键同时按下shift就决定音乐是否暂停(先按住shift在按住鼠标中键)
Sleep(100);
break;
}
if (m.mkCtrl)
{
//如果按下中键同时按下ctrl就重新开始游戏
color = 0; //重置颜色
IMAGE background;
loadimage(&background, "back.jpg", 500, 750);
putimage(0, 0, &background); //重置画面
goto C;
}
exit(0); //设置强制退出游戏功能
case WM_LBUTTONUP:
{
//通过getpixel函数防止重复下棋
if (getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) == RGB(0, 0, 0) || getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) == RGB(255, 255, 255))
{
break;
}
//把落子顺序保存在array数组里
array[color] = xy;
setfillcolor(BLACK);
setlinecolor(BLACK);
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
PlaySound("104.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
COLORREF hei = getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3);
//胜负判断
int a = judge(hei, xy.x, xy.y);
if (a == 1)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(120, 200, "恭喜你打败电脑");
outtextxy(80, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
char str[30];
sprintf_s(str, "战了%d回合", color / 2 + 1);
outtextxy(120, 230, str);
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
rr_arraychess();//人
rj_arraychess();//电脑
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//加入平局的判断
if (a == 0 && color == 224) //因为color最大值是224
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(80, 200, "平局");
outtextxy(65, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
rr_arraychess();
rj_arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//把当前下的棋保存在huixy中
huixy.x = xy.x;
huixy.y = xy.y;
color++;
Sleep(100);
}
case 1:
{
for (int i = 0; i < 225; i++)
{
if (RGB(0, 0, 0) != getpixel(alphcat[i].x - 3, alphcat[i].y - 3) && RGB(255, 255, 255) != getpixel(alphcat[i].x - 3, alphcat[i].y - 3)
/*当前落棋点没有落棋 (这个点的颜色是背景色)*/)
{
//RGB(255, 255, 255) != getpixel(alphcat[i].x - 3, alphcat[i].y - 3)
alphcat[i].score = scorejudge(alphcat[i].x, alphcat[i].y);
}
}
//再来选出一个得分最大的,如果得分一样就随机从最大的一个选一个
alph alphmax;
alphmax.score = alphcat[0].score;
for (int i = 1; i < 225; i++)
{
if (alphcat[i].score >= alphmax.score)
{
alphmax = alphcat[i];
}
}
// 把落子顺序保存在array数组里
rjarray[color] = alphmax;
//根据这个点画白棋
setfillcolor(WHITE);
setlinecolor(WHITE);
fillcircle(alphmax.x, alphmax.y, 10);
PlaySound("104.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
for (int i = 0; i < 225; i++)
{
alphcat[i].score = 0;
}
COLORREF bai = getpixel(alphmax.x - 3, alphmax.y - 3);
//胜负判断
int b = judge(bai, alphmax.x, alphmax.y);
if (b == 1)
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(120, 200, "恭喜电脑获胜");
outtextxy(80, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
char str[30];
sprintf_s(str, "战了%d回合", color / 2 + 1);
outtextxy(120, 230, str);
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
rr_arraychess();
rj_arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//加入平局的判断
if (b == 0 && color == 224) //因为color最大值是224
{
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(30, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(250, 200, "平局");
outtextxy(65, 170, "(请按任意键继续游戏)");
PlaySound("ying.wav", NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
//显示棋子顺序
rr_arraychess();
rj_arraychess();
//重置color
color = 0;
system("pause");
goto C;
}
//把当前下的棋保存在rjhuixy中
rjhuixy.x = alphmax.x;
rjhuixy.y = alphmax.y;
color++;
Sleep(100);
break;
}
case WM_RBUTTONDOWN: //设置悔棋功能
//保证是悔的上一颗的棋
if (huixy.x == xy.x && huixy.y == xy.y && getpixel(xy.x - 3, xy.y - 3) != RGB(223,200,158))
{
//悔自己的黑棋
setfillcolor(RGB(223,200,158));
setlinecolor(RGB(223,200,158));
fillcircle(xy.x, xy.y, 10);
//机器也要悔一步棋
setfillcolor(RGB(223,200,158));
setlinecolor(RGB(223,200,158));
fillcircle(rjhuixy.x, rjhuixy.y, 10);
//重新画棋盘
setlinecolor(BLACK);
for (int i = 1; i < 15; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < 15; j++)
{
rectangle(25 + j * 25, 325 + i * 25, 50 + j * 25, 350 + i * 25);
}
}
color -= 2;
break;
}
}
//来一个重新检查 主要是让白棋不存在中心有黑线的情况
for (int i = 0; i < 255; i++)
{
if (getpixel(master[i].x - 3, master[i].y - 3) == RGB(0, 0, 0))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
setlinecolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
fillcircle(master[i].x, master[i].y, 10);
}
if (getpixel(master[i].x - 3, master[i].y - 3) == RGB(255, 255, 255))
{
setfillcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
setlinecolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
fillcircle(master[i].x, master[i].y, 10);
}
}
}
}
void gameover()
{
//游戏结束释放资源
_getch();
closegraph();
}
int judge(COLORREF cl, int x, int y)
{
int a, b;
//定义上下总个数
int i = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
/*x = xy.x;
y = xy.y;*/
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 - 25))
{
i++;
b -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 + 25))
{
i++;
b += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (i >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
//定义左右总个数
int j = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查左面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (j >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
//定义'\'总个数
int k = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
k++;
a -= 25;
b -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
k++;
a += 25;
b += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (k >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
//定义'/'总个数
int l = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
l++;
a += 25;
b -= 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
l++;
a -= 25;
b += 25;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (l >= 4)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void arraychess()
{
//主要实现的功能是在黑色的棋上显示白色顺序 在白色棋子上显示黑色的顺序
for (int i = 0; i <= color; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
setbkcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%-2d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(array[i].x - 7, array[i].y - 7, arr);
}
else
{
setbkcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%-2d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(array[i].x - 7, array[i].y - 7, arr);
}
}
//恢复了背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195,195,195));
}
void rj_arraychess()
{
// 在白色棋子上显示黑色的顺序
for (int i = 0; i <= color; i++)
{
if (i % 2 != 0)
{
setbkcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(rjarray[i].x - 7, rjarray[i].y - 7, arr);
}
}
//恢复背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195,195,195));
}
void rr_arraychess()
{
// 在黑色棋子上显示白色的顺序
for (int i = 0; i <= color; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
setbkcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
char arr[10];
sprintf_s(arr, "%2d", i + 1);
settextcolor(RGB(255, 255, 255));
settextstyle(15, 0, "楷体");
outtextxy(array[i].x - 7, array[i].y - 7, arr);
}
}
//恢复了背景颜色
setbkcolor(RGB(195,195,195));
}
int rj_judge(COLORREF cl, int x, int y, int q, int p)
{
//用一个K来体现某一个方向的下一个是背景而不是有另外颜色的(活) K = 1 表示下一个为背景色
int K = 0;
int a, b;
//定义上下总个数
int i = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 - 25))
{
i++;
b -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 - 25) == RGB(223,200,158) && b - 25 > 350)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 + 25))
{
i++;
b += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3, b - 3 + 25) == RGB(223,200,158) && b + 35 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (i == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
//重置K
K = 0;
//定义左右总个数
int j = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查左面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3) == RGB(223,200,158) && a - 35 > 50)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3))
{
j++;
a += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3) == RGB(223,200,158) && a + 35 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (j == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
//重置K
K = 0;
//定义'\'总个数
int k = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
k++;
a -= 25;
b -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 - 25) == RGB(223,200,158) && a - 25 > 50 && b - 25 > 350)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
k++;
a += 25;
b += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 + 25) == RGB(223,200,158) && a + 25 < 400 && b + 25 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (k == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
//重置K
K = 0;
//定义'/'总个数
int l = 0;
a = x;
b = y;
//先检查上面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 - 25))
{
l++;
a += 25;
b -= 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 + 25, b - 3 - 25) == RGB(223,200,158) && a + 25 < 400 && b - 25 > 350)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
//再检查下面的
while (cl == getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 + 25))
{
l++;
a -= 25;
b += 25;
}
//检查是否下一个是背景色
if (getpixel(a - 3 - 25, b - 3 + 25) == RGB(223,200,158) && a - 25 > 50 && b + 25 < 700)
{
K++;
}
//还原落子位置
a = x;
b = y;
if (l == p - 1 && K == q)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int scorejudge(int x, int y)
{
/*主要思想(来自https://blog.csdn.net/ChinaJane163/article/details/52599787)
电脑白子 自己黑子
白子连成五子 +10000 阻碍黑子连成五子 +1000
白子连成活四 +200 阻碍黑子连成活四 +100
白子连成死四 +50 阻碍黑子连成死四 +20
白子连成活三 +30 阻碍黑子连成活三 +10
白子连成死三 +8 阻碍黑子连成死三 +5
白子连成活二 +2 阻碍黑子连成活二 +1
白子连成死二 +2 阻碍黑子连成死二 +1
白子连成活一 +1 阻碍黑子连成活一 +0
白子连成死一 +1 阻碍黑子连成死一 +0
*/
int a = x;
int b = y;
//定义一个得分
int score = 0;
//白子连成五子 +10000
if (judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b)) //这个函数只是i的值与k的值不一样 所以可以加两个变量在函数里面
{
score += 10000;
}
//阻碍黑子连成五子 +1000
if (judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b))
{
score += 1000;
}
//白子连成活四 +200
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 4))
{
score += 200;
}
//阻碍黑子连成活四 +100
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 2, 4))
{
score += 100;
}
//白子连成死四 +50
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 4))
{
score += 50;
}
//阻碍黑子连成死四 +20
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 1, 4))
{
score += 20;
}
//白子连成活三 +30
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 3))
{
score += 30;
}
//阻碍黑子连成活三 +10
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 2, 3))
{
score += 10;
}
//白子连成死三 +8
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 3))
{
score += 8;
}
//阻碍黑子连成死三 +5
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 1, 3))
{
score += 5;
}
//白子连成活二 +2
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 2))
{
score += 2;
}
//阻碍黑子连成活二 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 2, 2))
{
score += 1;
}
//白子连成死二 +2
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 2))
{
score += 2;
}
//阻碍黑子连成死二 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(0, 0, 0), a, b, 1, 2))
{
score += 1;
}
//白子连成活一 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 2, 1))
{
score += 1;
}
//白子连成死一 +1
if (rj_judge(RGB(255, 255, 255), a, b, 1, 1))
{
score += 1;
}
return score;
}