目录
1、引入
真实的生产环境都会经过exchange来发送消息,而不是直接发送到队列,交换机常用类型:
- Fanout:广播
- Direct:定向
- Topic:话题
为什么需要用到交换机:
我们上一篇文章案例中可以看到,消息发送者如果直接把消息发到队列中,消息就只能被一个消费者消费者,而生产环境下是存在一个消息发出去后,有好几个消费者都可以拿到这个消息去消费的~
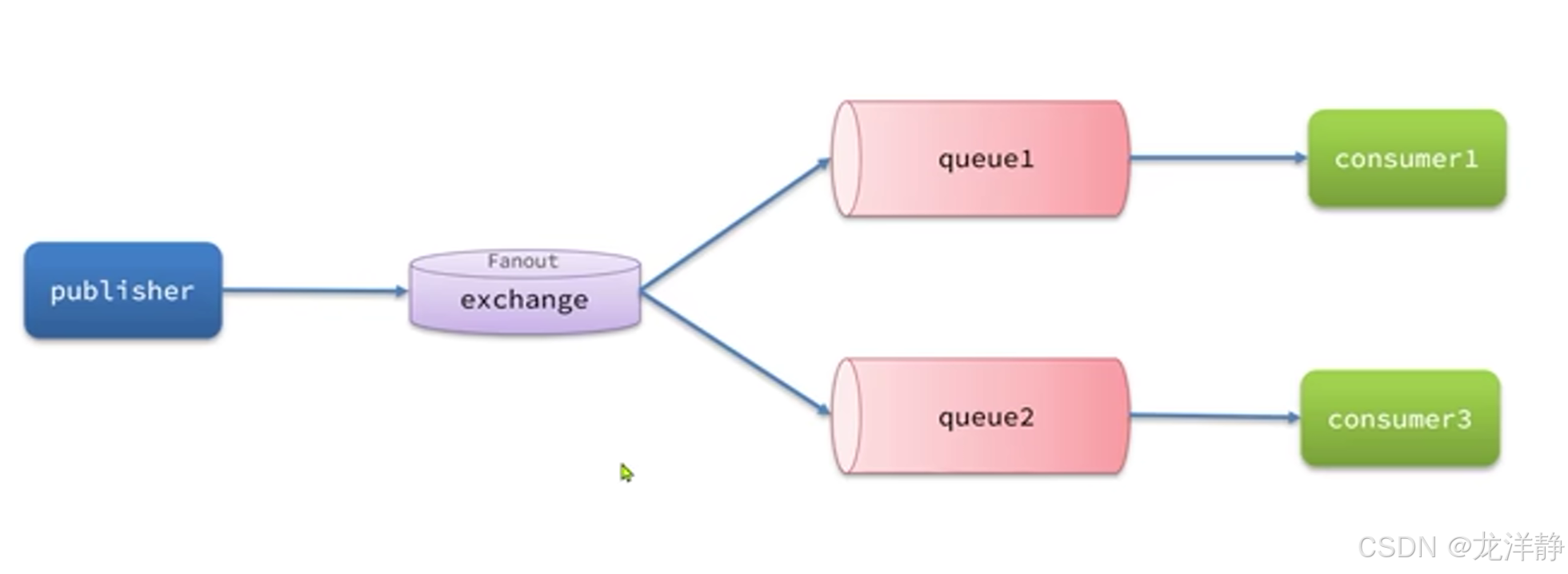
2、Fanout交换机
Fanout交换机 会将接收到的消息广播到每一个与其绑定的queue上
案例:利用SpringAMQP演示Fanout交换机的使用
需求:
- 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明队列fanout.queue1和fanout.queue2
- 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明交换机fan.fanout,将两个队列与其绑定
- 在consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听fanout.queue1和fanout.queue2
- 在publisher中编写测试方法,向fan.fanout发送消息
控制台中的操作就不说了,直接看代码:
consumer:
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void listenfan1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void listenfan2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("接收到消息:" + msg);
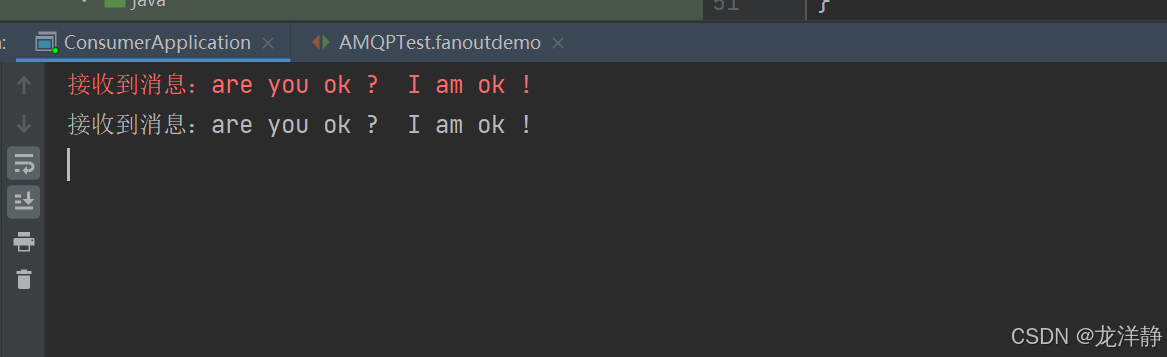
}publisher:
@Test
public void fanoutdemo(){
//交换机名
String exchangeName = "fan.fanout";
//消息
String message = "are you ok ? I am ok !";
//发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,null, message);
}结果:两个消费者都收到了
3、Direct交换机
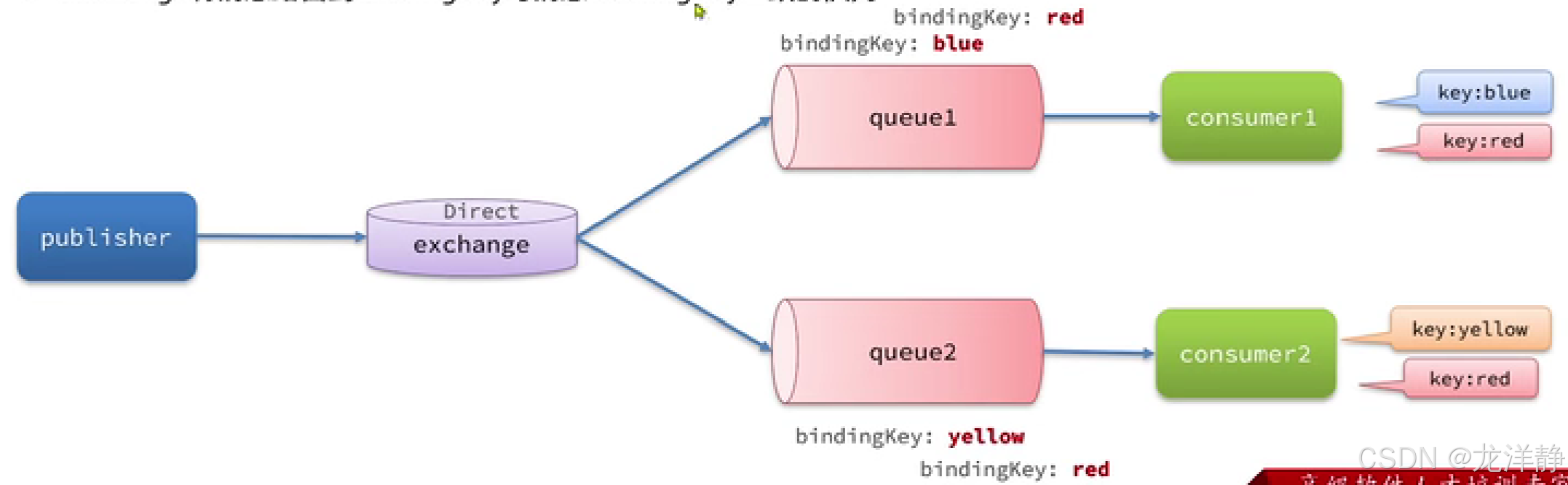
Direct交换机 会将接收到的消息根据规则路由到指定的Queue,因此成为定向路由:
- 每一个Queue都与Exchange设置一个BindingKey
- 发布者发送消息时,指定消息的RoutingKey
- Exchang将消息路由到BindingKey与消息RoutingKey一致的队列
举例:
现在有一个支付服务,要求支付成功后,给用户发送一条短信。此时支付服务会把支付结果发送到交换机中,而短信服务就会去监听这个交换机,但是交换机不会把所有的消息都路由给短信服务,而只把支付成功的消息路由给这个短信服务。这种情况下,就需要使用到这个Direct交换机,短信服务下的队列和这个交换机设置一个key(例如:success),支付服务发消息时,支付成功RoutingKey设为success,失败为fail,交换机就会只把key为success的消息路由给短信服务了~
如下:
上图中,就是,key为blue,消费者1去消费;key为yellow,消费者1去消费;key为red,两个消费者都能拿到这个消息一起去消息~
案例:利用SpringAMQP演示Direct交换机的使用
需求:
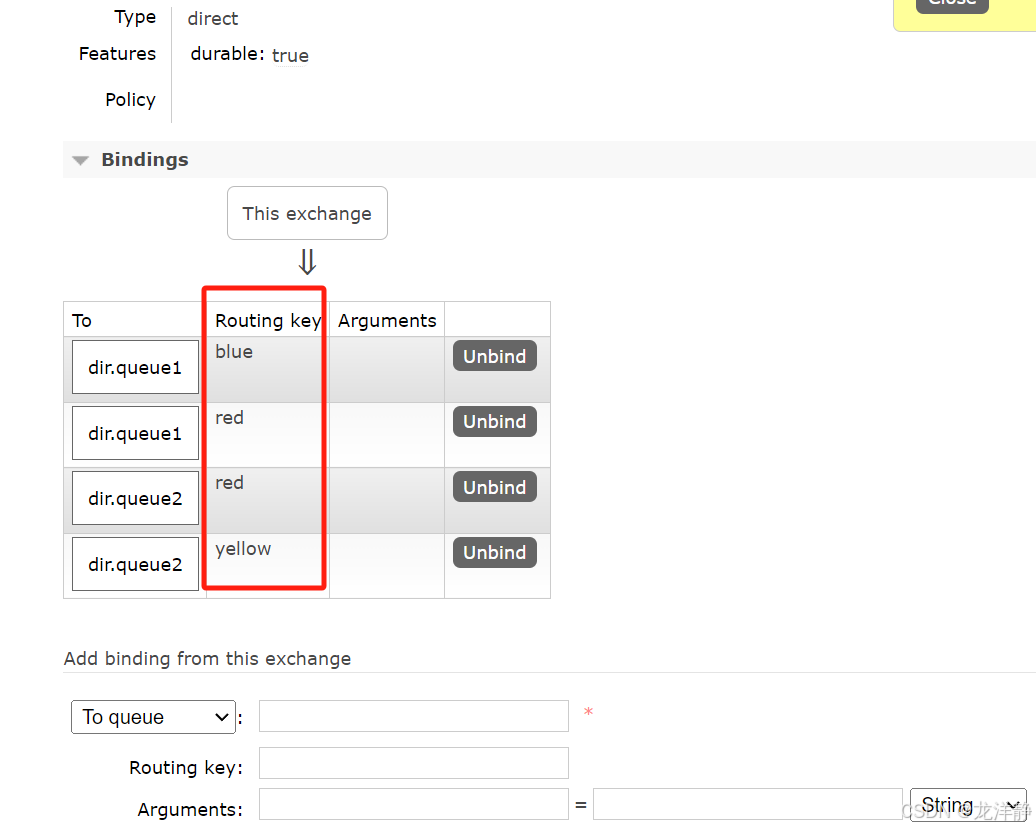
- 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明队列dir.queue1和dir.queue2
- 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明交换机dir.direct,将两个队列与其绑定
- 在consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听dir.queue1和dir.queue2
- 在publisher中编写测试方法,向dir.direct发送消息
控制台中的操作,注意:
直接看代码:
consumer:
@RabbitListener(queues = "dir.queue1")
public void listendir1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("接收到" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "dir.queue2")
public void listendir2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("接收到" + msg);
}publisher:
@Test
public void directdemo(){
//交换机名
String exchangeName = "dir.direct";
//发送消息
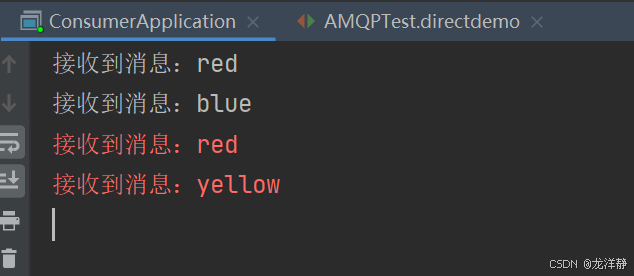
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"red", "消息:red");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"blue","消息:blue");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"yellow","消息:yellow");
}结果:red都能收到,blue、yellow指定的queue才能收到
4、Topic交换机
Topic交换机与Direct交换机类似,区别在于RoutingKey可以是多个单词的列表,并且以 . 分割
Queue与交换机指定BindingKey时可以使用通配符:
- # : 代指0个或多个单词
- * : 代指一个单词
案例:利用SpringAMQP演示Topic交换机的使用
需求:
- 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明队列topic.queue1和topic.queue2
- 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明交换机topic.topic,将两个队列与其绑定
- 在consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听topic.queue1和topic.queue2
- 在publisher中编写测试方法,利用不同的RoutingKey向topic.topic发送消息
控制台中的操作,注意:
consumer:
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue1")
public void listentopic1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("接收到" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue2")
public void listentopic2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("接收到" + msg);
}publisher:
@Test
public void topicdemo(){
//交换机名
String exchangeName = "topic.topic";
//发送消息
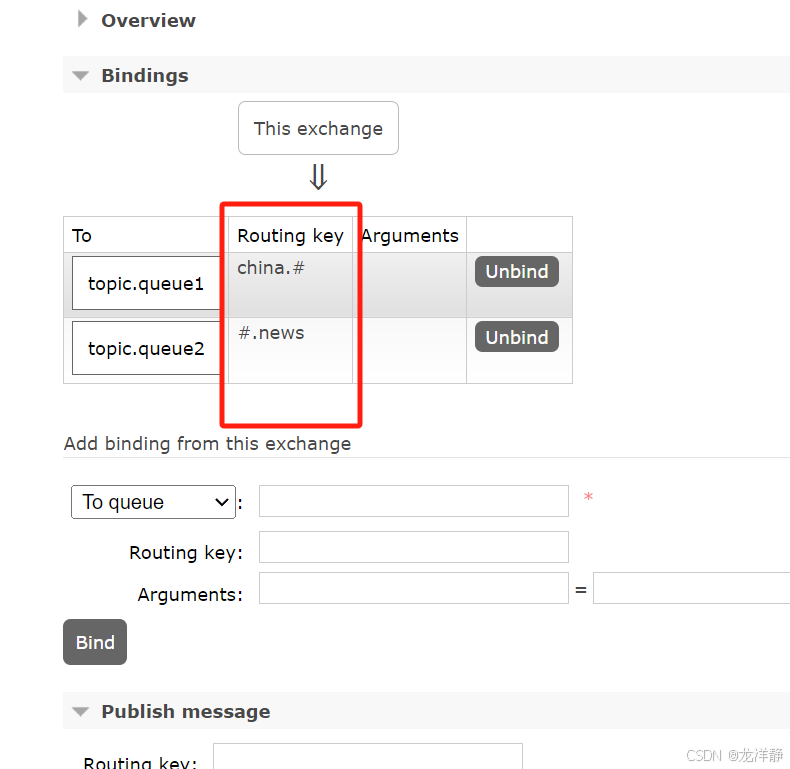
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"china.whether", "消息:中国天气预报");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"china.news","消息:中国新闻");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"LD.whether","消息:外国天气预报");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"LD.news","消息:外国新闻");
}结果:
一个只能接到新闻,一个只能接到和中国相关的消息~