一、 IoU概述
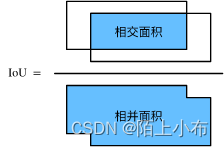
IoU的全称为交并比(Intersection over Union),是目标检测中使用的一个概念,IoU计算的是“预测的边框”和“真实的边框”的交叠率-,即它们的交集和并集的比值。最理想情况是完全重叠,即比值为1。
二、IoU计算
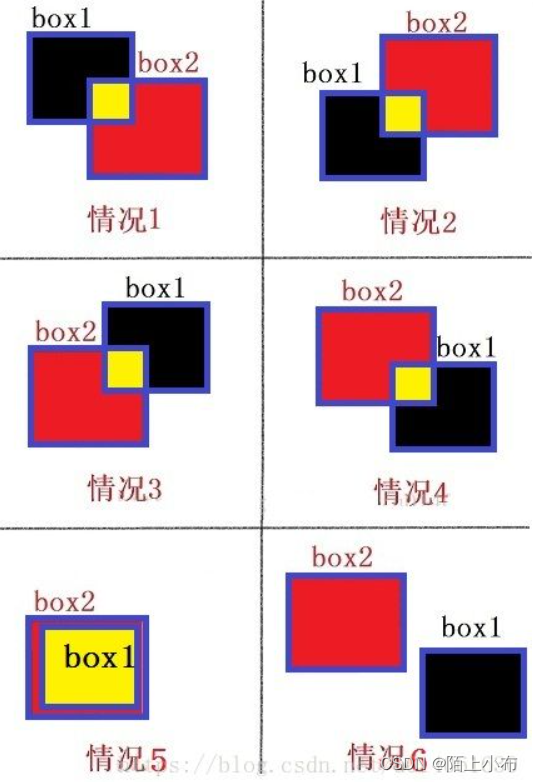
六种情况:
计算相交的面积和上个问题类似,只需计算出相交框的w与h如果没有相交,就是0。由上图可以发现以下规律:如果相交时
- xmin =max(xmin1, xmin2)#相交框xmin是两个框的左上角x坐标的最大值;
ymin =max(ymin1, ymin2)#相交框ymin是两个框的左上角y坐标的最大值;
xmax =min(xmax1, xmax2)#相交框xmax是两个框的右下角x坐标的最大值;
ymax =min(ymax1, ymax2)#相交框ymax是两个框的右下角y坐标的最大值;
最后处理一下不想交的情况即可,可以发现当不想交时,就会至少出现一下情况的一种:
xmax<=xmin or ymax<ymin
所以处理方法很简单:出现任一情况,w or h就会有一个等于0,使得计算出的面积也为0
w =max(0, xmax - xmin)
h =max(0, ymax - ymin)
所以整体代码就挥之欲出了,是不是也挺简单的:)
三、IoU代码实现
代码如下:
def intersection_over_union(boxA, boxB):
# determine the (x, y)-coordinates of the intersection rectangle
xA = max(boxA[0], boxB[0])
yA = max(boxA[1], boxB[1])
xB = min(boxA[2], boxB[2])
yB = min(boxA[3], boxB[3])
# compute the area of intersection rectangle
w = max(0, (xB - xA + 1))
h = max(0, (yB - yA + 1))
interArea = w * h
# compute the area of both the prediction and ground-truth
# rectangles
boxAArea = (boxA[2] - boxA[0] +1) * (boxA[3] - boxA[1] +1)
boxBArea = (boxB[2] - boxB[0] +1) * (boxB[3] - boxB[1] +1)
# compute the intersection over union by taking the intersection
# area and dividing it by the sum of prediction + ground-truth
# areas - the interesection area
iou = interArea / float(boxAArea + boxBArea - interArea)
# return the intersection over union value
return iou