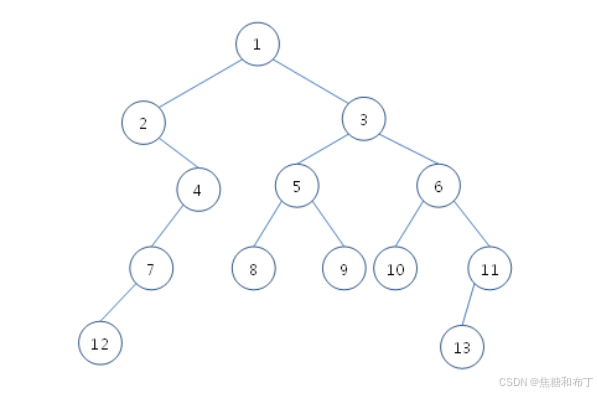
- You are to find the closest common ancestor of two vertices in a binary tree. For example, the common ancestors of vertices 8 and 13 in the figure below are vertices 3 and 1. Among them, vertex 3 is the closest to the vertex 8 and 13. And the size of sub-tree (the number of vertices in the sub-tree) rooted by vertex 3 is 8.
-
[Input]
You are given 10 test cases. Each test case has two lines, so the total number of lines is 20. In each test case, the first line consists of four integers, V (the number of vertices in the tree), E (the number of edges), and the indices of two vertices. E edges are listed in the next line. Each edge is represented by two vertices; the index of the parent vertex always precedes the index of the child. For example, the edge connecting vertices 5 and 8 is represented by “5 8”, not by “8 5.” There is no order in which the edges are given. Every consecutive integer in the input is separated by a space.
-
13 12 8 13 ← Start of the first input
1 2 1 3 2 4 3 5 3 6 4 7 7 12 5 9 5 8 6 10 6 11 11 13
10 9 1 10 ← Start of the second input
1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 10
...
#1 3 8
#2 1 10
...
思路:把每个节点的父节点保存在数组,父节点和它的子节点保存在map。
-
public class Solution { /** * 13 12 8 13 ← Start of the first input * 1 2 1 3 2 4 3 5 3 6 4 7 7 12 5 9 5 8 6 10 6 11 11 13 * * #1 3 8 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int T; T = sc.nextInt(); for(int t = 1; t <= T; t++) { sc.nextLine(); String line1 = sc.nextLine(); String line2 = sc.nextLine(); int[] res = commonAncestor(line1, line2); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("#").append(t).append(" ").append(res[0]).append(" ").append(res[1]); System.out.println(sb); } sc.close(); } public static int[] commonAncestor(String line1, String line2) { String[] parts1 = line1.split(" "); int v = Integer.parseInt(parts1[0]); int e = Integer.parseInt(parts1[1]); int n1 = Integer.parseInt(parts1[2]); int n2 = Integer.parseInt(parts1[3]); int[] parentNode = new int[v + 1]; // 存放每个节点的父节点 Arrays.fill(parentNode, -1); String[] edges = line2.split(" "); Map<Integer, List<Integer>> edgeMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i += 2) { int x = Integer.parseInt(edges[i]); // 边的第一个端点 int y = Integer.parseInt(edges[i + 1]); // 边的第二个端点 parentNode[y] = x; edgeMap.computeIfAbsent(x, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(y); // 父节点和它的子节点 -- 1:[2,3] } List<Integer> r1List = new ArrayList<>(); int t = n1; while (parentNode[t] != -1) { r1List.add(parentNode[t]); // 5-3-1 t = parentNode[t]; } List<Integer> r2List = new ArrayList<>(); t = n2; while (parentNode[t] != -1) { r2List.add(parentNode[t]); // 11-6-3-1 t = parentNode[t]; } if (r1List.isEmpty() || r2List.isEmpty()) { return new int[]{1, v}; } int root = -1; // 公共父节点 for (int n : r2List) { if (r1List.contains(n)) { root = n; break; } } if (root == -1) { return new int[]{1, v}; // 如果没有共同的祖先,返回root为1,size为v } Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int total = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); total += size; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { int p = queue.poll(); if (edgeMap.containsKey(p)) { queue.addAll(edgeMap.get(p)); } } } return new int[]{root, total}; } }