记录学习阅读ROS Navigation源码的理解,本文为Base Local Planner局部规划源码学习记录,以文字总结、绘制结构图说明、代码注释为主。仍在学习过程中,有错误欢迎指正,共同进步。
Movebase使用的局部规划器默认为TrajectoryPlannerROS,它循环检查是否到达目标点位置(给定位置误差范围内),若未到达,则调用TrajectoryPlanner类函数来进行局部路径规划,得到下一步速度,反馈给Movebase;若已到达,则检查是否到达目标姿态,若未到达,先给机器人降速至阈值内,再使它原地旋转,直至达到目标姿态(给定姿态误差范围内),至此局部规划器完成任务。
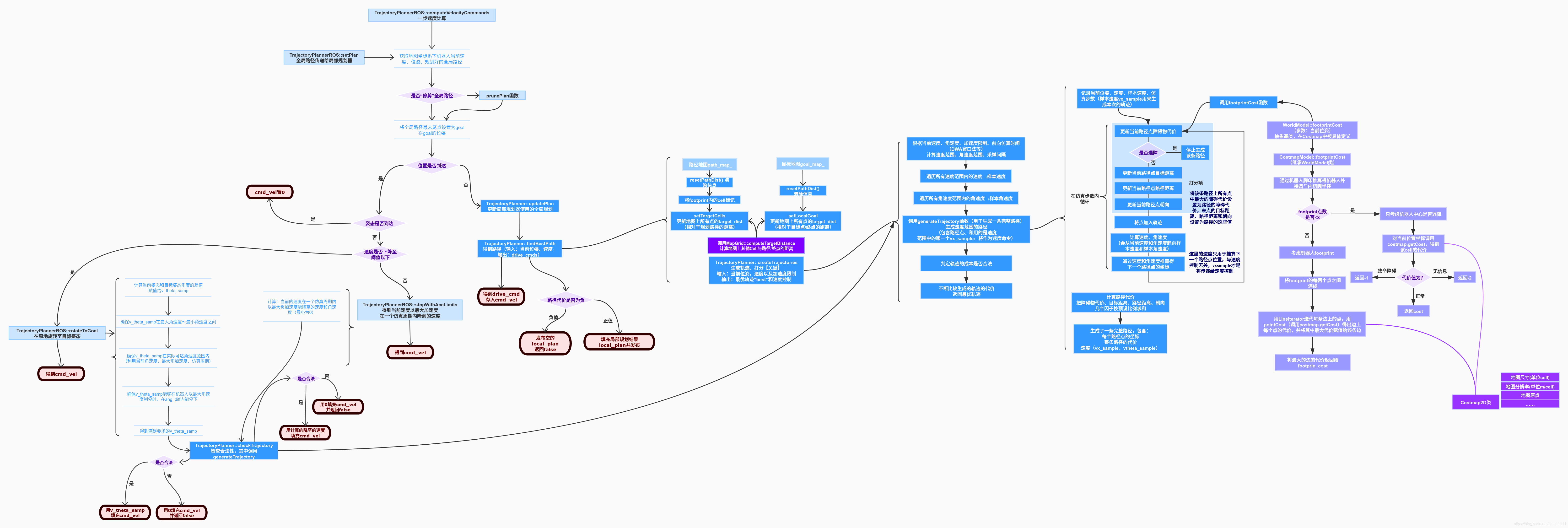
【结构示意图】
【相关文件】
- base_local_planner/src/trajectory_planner_ros.cpp
- base_local_planner/src/trajectory_planner.cpp
- base_local_planner/src/map_grid.cpp
- base_local_planner/src/map_cell.cpp
- base_local_planner/src/costmap_model.cpp
trajectory_planner_ros.cpp中定义了TrajectoryPlannerROS类,trajectory_planner.cpp中定义了TrajectoryPlanner类,MapGrid和MapCell类用于局部规划的计算,costmap_model.cpp中定义了CostmapModel类,它派生自WorldModel类,在TrajectoryPlanner中被使用,承担局部规划器与局部规划Costmap之间的桥梁工作。
本篇记录对TrajectoryPlannerROS类的阅读和理解。
【代码分析】
trajectory_planner_ros.cpp
–目录–
准备工作 TrajectoryPlannerROS::initialize | 初始化本地规划器
传入全局规划 TrajectoryPlannerROS::setPlan | 用全局规划结果给本地规划器赋值参数
核心函数 TrajectoryPlannerROS::computeVelocityCommands | 一步速度计算
降速 TrajectoryPlannerROS::stopWithAccLimits | 以最大加速度“刹车”
旋转 TrajectoryPlannerROS::rotateToGoal | 原地旋转至目标姿态
前两个函数属于准备工作;后两个函数作为局部规划的情形之一,在核心函数computeVelocityCommands中被调用,即当已处于目标位置时的情况。
<1> 准备工作 TrajectoryPlannerROS::initialize
Movebase在初始化了局部规划器-TrajectoryPlannerROS类实例后即调用了initialize函数,这个函数的主要工作是从参数服务器下载参数值给局部规划器赋参,首先设置全局和本地规划结果的发布,并用传入的参数costmap_ros(格式为Costmap2DROS:ROS的地图封装类,它整合了静态层、障碍层、膨胀层地图,具体理解在该部分详述)来初始化本地规划器用到的代价地图。
void TrajectoryPlannerROS::initialize(
std::string name,
tf::TransformListener* tf,
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS* costmap_ros){
if (! isInitialized()) {
ros::NodeHandle private_nh("~/" + name);
//发布全局规划在~/本地规划器名称/global_plan话题上
g_plan_pub_ = private_nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("global_plan", 1);
//发布本地规划在~/本地规划器名称/local_plan话题上
l_plan_pub_ = private_nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("local_plan", 1);
//初始化tf、局部代价地图
tf_ = tf;
costmap_ros_ = costmap_ros;
rot_stopped_velocity_ = 1e-2;
trans_stopped_velocity_ = 1e-2;
double sim_time, sim_granularity, angular_sim_granularity;
int vx_samples, vtheta_samples;
double pdist_scale, gdist_scale, occdist_scale, heading_lookahead, oscillation_reset_dist, escape_reset_dist, escape_reset_theta;
bool holonomic_robot, dwa, simple_attractor, heading_scoring;
double heading_scoring_timestep;
double max_vel_x, min_vel_x;
double backup_vel;
double stop_time_buffer;
std::string world_model_type;
rotating_to_goal_ = false;
//复制一个代价地图供本地规划器使用
costmap_ = costmap_ros_->getCostmap();
//地图坐标系
global_frame_ = costmap_ros_->getGlobalFrameID();
//机器人底盘坐标系
robot_base_frame_ = costmap_ros_->getBaseFrameID();
上面声明了局部变量,接下来从参数服务器下载参数,并用它们来创建TrajectoryPlanner类实例,它完成实际的速度计算工作;sim_time、sim_granularity、angular_sim_granularity与一步计算的仿真时间有关;vx_samples、vtheta_samples是速度计算时在线速度和角速度范围内生成的样本数,pdist_scale、gdist_scale、occdist_scale是在计算局部路线cost时将路线、目标、障碍因子对应的加和比例;max_vel_x、 min_vel_x是机器人行动时的速度阈值。
private_nh.param("prune_plan", prune_plan_, true);
private_nh.param("yaw_goal_tolerance", yaw_goal_tolerance_, 0.05);//角速度误差范围
private_nh.param("xy_goal_tolerance", xy_goal_tolerance_, 0.10);//线速度误差范围
private_nh.param("acc_lim_x", acc_lim_x_, 2.5);//线加速度阈值
private_nh.param("acc_lim_y", acc_lim_y_, 2.5);//y向线加速度阈值,非柔性机器人用不到,没有y方向速度
private_nh.param("acc_lim_theta", acc_lim_theta_, 3.2);//角加速度阈值
private_nh.param("stop_time_buffer", stop_time_buffer, 0.2);
private_nh.param("latch_xy_goal_tolerance", latch_xy_goal_tolerance_, false);
if(private_nh.hasParam("acc_limit_x"))
ROS_ERROR("You are using acc_limit_x where you should be using acc_lim_x. Please change your configuration files appropriately. The documentation used to be wrong on this, sorry for any confusion.");
if(private_nh.hasParam("acc_limit_y"))
ROS_ERROR("You are using acc_limit_y where you should be using acc_lim_y. Please change your configuration files appropriately. The documentation used to be wrong on this, sorry for any confusion.");
if(private_nh.hasParam("acc_limit_th"))
ROS_ERROR("You are using acc_limit_th where you should be using acc_lim_th. Please change your configuration files appropriately. The documentation used to be wrong on this, sorry for any confusion.");
//Assuming this planner is being run within the navigation stack, we can
//just do an upward search for the frequency at which its being run. This
//also allows the frequency to be overwritten locally.
std::string controller_frequency_param_name;
if(!private_nh.searchParam("controller_frequency", controller_frequency_param_name))
sim_period_ = 0.05;
else
{
double controller_frequency = 0;
private_nh.param(controller_frequency_param_name, controller_frequency, 20.0);
if(controller_frequency > 0)
sim_period_ = 1.0 / controller_frequency;
else
{
ROS_WARN("A controller_frequency less than 0 has been set. Ignoring the parameter, assuming a rate of 20Hz");
sim_period_ = 0.05;
}
}
ROS_INFO("Sim period is set to %.2f", sim_period_);
private_nh.param("sim_time", sim_time, 1.0);
private_nh.param("sim_granularity", sim_granularity, 0.025);
private_nh.param("angular_sim_granularity", angular_sim_granularity, sim_granularity);
private_nh.param("vx_samples", vx_samples, 3);
private_nh.param("vtheta_samples", vtheta_samples, 20);
private_nh.param("path_distance_bias", pdist_scale, 0.6);
private_nh.param("goal_distance_bias", gdist_scale, 0.8);
private_nh.param("occdist_scale", occdist_scale, 0.01);
接下来同样是在获取参数服务器上的参数值,如果未设置,则赋值为默认值,局部规划器用到的参数非常多,有很多种选项可以产生不同的规划行为,在具体路径和速度生成用到的时候再提。
bool meter_scoring;
if ( ! private_nh.hasParam("meter_scoring")) {
ROS_WARN("Trajectory Rollout planner initialized with param meter_scoring not set. Set it to true to make your settins robust against changes of costmap resolution.");
} else {
private_nh.param("meter_scoring", meter_scoring, false);
if(meter_scoring) {
//如果我们使用meter scoring,我们将局部路径打分的比例因子×代价地图的分辨率
double resolution = costmap_->getResolution();
gdist_scale *= resolution;
pdist_scale *= resolution;
occdist_scale *= resolution;
} else {
ROS_WARN("Trajectory Rollout planner initialized with param meter_scoring set to false. Set it to true to make your settins robust against changes of costmap resolution.");
}
}
private_nh.param("heading_lookahead", heading_lookahead, 0.325);
private_nh.param("oscillation_reset_dist", oscillation_reset_dist, 0.05);
private_nh.param("escape_reset_dist", escape_reset_dist, 0.10);
private_nh.param("escape_reset_theta", escape_reset_theta, M_PI_4);
private_nh.param("holonomic_robot", holonomic_robot, true);
private_nh.param("max_vel_x", max_vel_x, 0.5);
private_nh.param("min_vel_x", min_vel_x, 0.1);
double max_rotational_vel;
private_nh.param("max_rotational_vel", max_rotational_vel, 1.0);
max_vel_th_ = max_rotational_vel;
min_vel_th_ = -1.0 * max_rotational_vel;
private_nh.param("min_in_place_rotational_vel", min_in_place_vel_th_, 0.4);
reached_goal_ = false;
backup_vel = -0.1;
if(private_nh.getParam("backup_vel", backup_vel))
ROS_WARN("The backup_vel parameter has been deprecated in favor of the escape_vel parameter. To switch, just change the parameter name in your configuration files.");
//if both backup_vel and escape_vel are set... we'll use escape_vel
private_nh.getParam("escape_vel", backup_vel);
if(backup_vel >= 0.0)
ROS_WARN("You've specified a positive escape velocity. This is probably not what you want and will cause the robot to move forward instead of backward. You should probably change your escape_vel parameter to be negative");
private_nh.param("world_model", world_model_type, std::string("costmap"));
private_nh.param("dwa", dwa, true);
private_nh.param("heading_scoring", heading_scoring, false);
private_nh.param("heading_scoring_timestep", heading_scoring_timestep, 0.8);
simple_attractor = false;
在初始化world_model_时,用的是CostmapModel类,它是WorldModel的派生类。
//parameters for using the freespace controller
double min_pt_separation, max_obstacle_height, grid_resolution;
private_nh.param("point_grid/max_sensor_range", max_sensor_range_, 2.0);
private_nh.param("point_grid/min_pt_separation", min_pt_separation, 0.01);
private_nh.param("point_grid/max_obstacle_height", max_obstacle_height, 2.0);
private_nh.param("point_grid/grid_resolution", grid_resolution, 0.2);
ROS_ASSERT_MSG(world_model_type == "costmap", "At this time, only costmap world models are supported by this controller");
world_model_ = new CostmapModel(*costmap_);
std::vector<double> y_vels = loadYVels(private_nh);
footprint_spec_ = costmap_ros_->getRobotFootprint();
接下来创建TrajectoryPlanner类实例,它是TrajectoryPlannerROS类的成员,并开启动态参数配置服务。
//用从参数服务器获取的参数来初始化TrajectoryPlanner的实例tc_
tc_ = new TrajectoryPlanner(*world_model_, *costmap_, footprint_spec_,
acc_lim_x_, acc_lim_y_, acc_lim_theta_, sim_time, sim_granularity, vx_samples, vtheta_samples, pdist_scale,
gdist_scale, occdist_scale, heading_lookahead, oscillation_reset_dist, escape_reset_dist, escape_reset_theta, holonomic_robot,
max_vel_x, min_vel_x, max_vel_th_, min_vel_th_, min_in_place_vel_th_, backup_vel,
dwa, heading_scoring, heading_scoring_timestep, meter_scoring, simple_attractor, y_vels, stop_time_buffer, sim_period_, angular_sim_granularity);
map_viz_.initialize(name, global_frame_, boost::bind(&TrajectoryPlanner::getCellCosts, tc_, _1, _2, _3, _4, _5, _6));
initialized_ = true;
dsrv_ = new dynamic_reconfigure::Server<BaseLocalPlannerConfig>(private_nh);
dynamic_reconfigure::Server<BaseLocalPlannerConfig>::CallbackType cb = boost::bind(&TrajectoryPlannerROS::reconfigureCB, this, _1, _2);
dsrv_->setCallback(cb);
} else {
ROS_WARN("This planner has already been initialized, doing nothing");
}
}
<2> 传入全局规划 TrajectoryPlannerROS::setPlan
Movebase通过调用这个函数传入先前针对当前位置和目标点间规划好的全局路径,与全局路径的贴合程度将作为局部规划路线的一个打分项。
bool TrajectoryPlannerROS::setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& orig_global_plan){ //base_local_planner的核心:计算机器人实际运行速度、发布局部路径规划
if (! isInitialized()) {
ROS_ERROR("This planner has not been initialized, please call initialize() before using this planner");
return false;
}
//reset the global plan
global_plan_.clear();
global_plan_ = orig_global_plan;
//when we get a new plan, we also want to clear any latch we may have on goal tolerances
xy_tolerance_latch_ = false;
//reset the at goal flag
reached_goal_ = false;
return true;
}
<3> 核心函数 TrajectoryPlannerROS::computeVelocityCommands
该函数在Movebase的executeCycle函数中被调用,executeCycle函数本身是被循环执行的,所以能够不断进行局部速度规划,从而获得连续的速度指令,控制机器人行动。
首先,获取global系的当前位姿(使用从底盘到global的转换),它可以用来判断是否行进到目标点。
并将全局规划结果global_plan_从地图系转换到global系,得到transformed_plan,这里调用的transformGlobalPlan函数来自goal_functions.cpp,这个文件中定义了一些辅助函数。transformGlobalPlan函数除了通过tf完成坐标转换,还对转换后的路径点做了一些筛选处理,与主体关系不大,这里略过。
这样,得到了global系的当前位姿和全局规划transformed_plan。
bool TrajectoryPlannerROS::computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist& cmd_vel){
//检查是否初始化
if (! isInitialized()) {
ROS_ERROR("This planner has not been initialized, please call initialize() before using this planner");
return false;
}
//声明本地规划结果
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> local_plan;
//声明global系上的位姿
tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> global_pose;
//将机器人的姿态转换,从底盘(原点)到global
if (!costmap_ros_->getRobotPose(global_pose)) {
return false;
}
//将全局路径规划转换到global系,得到transformed plan
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> transformed_plan;
if (!transformGlobalPlan(*tf_, global_plan_, global_pose, *costmap_, global_frame_, transformed_plan)) {
ROS_WARN("Could not transform the global plan to the frame of the controller");
return false;
}
prune_plan_是初始化函数中从参数服务器上下载的值,这里对它进行判断,看是否要“修剪”全局规划,“修剪”是指在机器人前进的过程中,将一定阈值外的走过的路径点从global_plan_和transformed_plan中去掉。该函数同样定义在goal_functions中。
if(prune_plan_)
prunePlan(global_pose, transformed_plan, global_plan_);
//tf格式速度控制,坐标系是机器人底盘坐标系
tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> drive_cmds;
drive_cmds.frame_id_ = robot_base_frame_;
//机器人当前速度
tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> robot_vel;
odom_helper_.getRobotVel(robot_vel);
/* For timing uncomment
struct timeval start, end;
double start_t, end_t, t_diff;
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
*/
//如果全局规划为空,返回false
if(transformed_plan.empty())
return false;
接下来,认为全局规划的最后一个路径点即为目标点,获取它,得到目标x、y坐标及朝向。
//tf格式,目标点
tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> goal_point;
//将全局规划的目标点存储在goal_point
tf::poseStampedMsgToTF(transformed_plan.back(), goal_point);
double goal_x = goal_point.getOrigin().getX();
double goal_y = goal_point.getOrigin().getY();
double yaw = tf::getYaw(goal_point.getRotation());
double goal_th = yaw;
接下来判断当前机器人是否到达目标周围(误差范围内),若是,则进行接下来的判断:
① 若当前姿态朝向同样满足目标姿态(误差范围内),认为完成任务,设置0速,准备制停机器人;
//检查是否到达目标“位置”
if (xy_tolerance_latch_ || (getGoalPositionDistance(global_pose, goal_x, goal_y) <= xy_goal_tolerance_)) {
if (latch_xy_goal_tolerance_) {
xy_tolerance_latch_ = true;
}
//检查是否到达目标“朝向、姿态”
//获取当前朝向和目标姿态的差值
double angle = getGoalOrientationAngleDifference(global_pose, goal_th);
//到达目标位置,如果差值小于容忍度
if (fabs(angle) <= yaw_goal_tolerance_) {
//到达位置且如果朝向和姿态小于容忍度,设置速度为0,停下
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.0;
cmd_vel.linear.y = 0.0;
cmd_vel.angular.z = 0.0;
rotating_to_goal_ = false;
xy_tolerance_latch_ = false;
reached_goal_ = true;
} else {
② 若未达到姿态要求,调用TrajectoryPlanner类的findBestPath函数(它完成局部规划的实际工作)
有个疑问,这里调用它的作用是什么?既然位置到了,只有姿态未达到,那么下面两步-降速、旋转就足够了,这里何必再调用findBestPath做局部规划?并且,局部规划器与Movebase的速度接口是cmd_vel,后面对速度的设置都放进了cmd_vel中返还给Movebase发布,而这里的计算结果drive_cmds也没有放进cmd_vel中,那么这里的调用是用来做什么?
接下来进行两步,降速、旋转:
- 如果选项“rotating to goal”为假,且base_local_planner::stopped返回假(它是goal_functions.cpp中定义的判断机器人是否停止的函数)
这表示机器人还未停止,调用类内stopWithAccLimits函数,给机器人降速,直到降至降至一个极小值范围内,表示机器人停止,跳出该层判断,执行下一步; - 当机器人停止了,调用类内rotateToGoal函数,让机器人旋转至目标姿态。
当机器人位置、姿态均符合要求,则进入上面的①,发布零速,停止。
//如果到达位置,但朝向和姿态没达到目标要求
//将全局路径拷贝进来,并认为全局路径的最后一个点就是终点
tc_->updatePlan(transformed_plan);
//给定当前机器人的位置和朝向,计算机器人应该跟随的“best”轨迹,存储在drive_cmds中
Trajectory path = tc_->findBestPath(global_pose, robot_vel, drive_cmds);
//发布代价地图点云
map_viz_.publishCostCloud(costmap_);
//得到里程计信息
nav_msgs::Odometry base_odom;
odom_helper_.getOdom(base_odom);
//如果“到达目标后旋转到姿态满足”为假且“调用base_local_planner::stopped 判断是否机器人是否停止”返回假
//即到达了目标,姿态还不满足,还未旋转过去,且线速度还没降到阈值以下
//那让机器人减速
if ( ! rotating_to_goal_ && !base_local_planner::stopped(base_odom, rot_stopped_velocity_, trans_stopped_velocity_)) {
//如果用最大负加速度使机器人从当前速度降到的速度,不合法
if ( ! stopWithAccLimits(global_pose, robot_vel, cmd_vel)) {
//返回false
return false;
}
}
//否则,线速度降到了阈值以下,可以等同与线速度降到了0
//那么rotating_to_goal_置真,开始原地旋转
else{
rotating_to_goal_ = true;
//旋转至目标姿态
if(!rotateToGoal(global_pose, robot_vel, goal_th, cmd_vel)) {
return false;
}
}
}
publishPlan(transformed_plan, g_plan_pub_);
publishPlan(local_plan, l_plan_pub_);
//we don't actually want to run the controller when we're just rotating to goal
return true;
}
若未到达目标点误差范围内,调用TrajectoryPlanner类的updatePlan函数,将global系下的全局规划传入,再调用findBestPath函数,进行局部规划,速度结果填充在drive_cmds中,并得到局部路线plan。
再将drive_cmds的结果存储进cmd_vel,返还给Movebase发布,完成对机器人的运动控制。
//如果没到目标“位置”,更新全局规划
tc_->updatePlan(transformed_plan);
//用当前机器人位姿和速度,计算速度控制命令
//【核心:TrajectoryPlanner的findBestPath函数】
Trajectory path = tc_->findBestPath(global_pose, robot_vel, drive_cmds);
//发布代价地图点云
map_viz_.publishCostCloud(costmap_);
/* For timing uncomment
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
start_t = start.tv_sec + double(start.tv_usec) / 1e6;
end_t = end.tv_sec + double(end.tv_usec) / 1e6;
t_diff = end_t - start_t;
ROS_INFO("Cycle time: %.9f", t_diff);
*/
//速度控制存储进cmd_vel
cmd_vel.linear.x = drive_cmds.getOrigin().getX();
cmd_vel.linear.y = drive_cmds.getOrigin().getY();
cmd_vel.angular.z = tf::getYaw(drive_cmds.getRotation());
接下来对生成路径path的代价进行判断,若为负,说明是无效路径,返回false;若为正,说明找到有效路径,将其进行格式转换后通过话题发布,便于对局部规划结果可视化。
//如果路径代价<0,说明没找到合法的路径,对于所有模拟路径,机器人的足迹都在振荡
if (path.cost_ < 0) {
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("trajectory_planner_ros",
"The rollout planner failed to find a valid plan. This means that the footprint of the robot was in collision for all simulated trajectories.");
local_plan.clear();
publishPlan(transformed_plan, g_plan_pub_);
publishPlan(local_plan, l_plan_pub_);
return false;
}
//如果路径代价正常,代表找到了有效路径
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("trajectory_planner_ros", "A valid velocity command of (%.2f, %.2f, %.2f) was found for this cycle.",
cmd_vel.linear.x, cmd_vel.linear.y, cmd_vel.angular.z);
//填充本地路径local_plan,把path中的点存放到tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>的实例p中,再转换成msg格式,用pose存储,一个个添加到local_plan中
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < path.getPointsSize(); ++i) {
double p_x, p_y, p_th;
path.getPoint(i, p_x, p_y, p_th);
tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> p =
tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>(tf::Pose(
tf::createQuaternionFromYaw(p_th),
tf::Point(p_x, p_y, 0.0)),
ros::Time::now(),
global_frame_);
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose;
tf::poseStampedTFToMsg(p, pose);
local_plan.push_back(pose);
}
//发布全局规划和已填充好的本地规划,用于“可视化”
publishPlan(transformed_plan, g_plan_pub_);
publishPlan(local_plan, l_plan_pub_);
return true;
}
<4> 降速 TrajectoryPlannerROS::stopWithAccLimits
该函数的作用是,机器人已达目标附近范围而姿态未达姿态要求时,在调整姿态前,将机器人速度降至阈值以下。将下一步速度设置为当前速度以最大反向加速度在一个仿真周期sim_period_内降至的速度,角速度同理。注意在计算中防止越过0界。
bool TrajectoryPlannerROS::stopWithAccLimits(const tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>& global_pose, const tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>& robot_vel, geometry_msgs::Twist& cmd_vel){
//slow down with the maximum possible acceleration... we should really use the frequency that we're running at to determine what is feasible
//but we'll use a tenth of a second to be consistent with the implementation of the local planner.
//x方向速度=(当前x向速度符号)× max(0,当前x向速度绝对值-最大加速度×仿真周期)
double vx = sign(robot_vel.getOrigin().x()) * std::max(0.0, (fabs(robot_vel.getOrigin().x()) - acc_lim_x_ * sim_period_));
double vy = sign(robot_vel.getOrigin().y()) * std::max(0.0, (fabs(robot_vel.getOrigin().y()) - acc_lim_y_ * sim_period_));
//角速度,同上
double vel_yaw = tf::getYaw(robot_vel.getRotation());
double vth = sign(vel_yaw) * std::max(0.0, (fabs(vel_yaw) - acc_lim_theta_ * sim_period_));
得到下一步速度后,对其调用TrajectoryPlanner类的checkTrajectory函数,检查该采样速度能否生成有效路径,若可以,则将下一步速度储存在cmd_vel,否则,速度置0。
//用上述计算出的速度、角速度、和当前位姿,调用checkTrajectory,检查速度命令是否合法
double yaw = tf::getYaw(global_pose.getRotation());
bool valid_cmd = tc_->checkTrajectory(global_pose.getOrigin().getX(), global_pose.getOrigin().getY(), yaw,
robot_vel.getOrigin().getX(), robot_vel.getOrigin().getY(), vel_yaw, vx, vy, vth);
//上述计算的如果合法,把降到的速度存放到cmd_vel
if(valid_cmd){
ROS_DEBUG("Slowing down... using vx, vy, vth: %.2f, %.2f, %.2f", vx, vy, vth);
cmd_vel.linear.x = vx;
cmd_vel.linear.y = vy;
cmd_vel.angular.z = vth;
return true;
}
//如果不合法,全部置0
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.0;
cmd_vel.linear.y = 0.0;
cmd_vel.angular.z = 0.0;
return false;
}
<5> 旋转 TrajectoryPlannerROS::rotateToGoal
在达到目标点误差范围内,且速度降至极小后,最后一步的工作是原地旋转至目标姿态。它采用一种类似“反馈控制”的思想,通过计算当前姿态与目标姿态的差值,通过这个差值来控制下一步的角速度。
bool TrajectoryPlannerROS::rotateToGoal(const tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>& global_pose, const tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>& robot_vel, double goal_th, geometry_msgs::Twist& cmd_vel){
//机器人姿态的偏角yaw
double yaw = tf::getYaw(global_pose.getRotation());
//机器人速度的航偏角vel_yaw
double vel_yaw = tf::getYaw(robot_vel.getRotation());
//初始化cmd_vel为0
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0;
cmd_vel.linear.y = 0;
//计算机器人当前位姿角度和目标角度的差值ang_diff
double ang_diff = angles::shortest_angular_distance(yaw, goal_th);
在差值计算完成后,需要用几个条件对它进行限制。
① 首先,最直接的限制,下一步的角速度要在预先设置的角速度允许范围内。
/***********************角速度范围************************/
//计算用来生成采样的角速度(范围)
//若角度差值为正,角速度=min(最大角速度,max(最小角速度,角度差))
//↑也就是,如果角度差小于最小角速度,用最小角速度;角度差位于最大最小角速度之间,用角度差;角度差大于最大角速度用最大角速度
//若角度差值为负,角速度=max(最小角速度,min(-1×最小角速度,角度差))
double v_theta_samp = ang_diff > 0.0 ? std::min(max_vel_th_,
std::max(min_in_place_vel_th_, ang_diff)) : std::max(min_vel_th_,
std::min(-1.0 * min_in_place_vel_th_, ang_diff));
/********************************************************/
② 然后,由于有角加速度的限制,需要保证下一步的角速度能够由当前角加速度在规定角加速度范围内达到。
/********************实际可达角速度范围*********************/
//考虑机器人的加速度限制
//实际最大角速度=当前角速度+最大角加速度×1个仿真周期
double max_acc_vel = fabs(vel_yaw) + acc_lim_theta_ * sim_period_;
//实际最小角速度=当前角速度-最大角加速度×1个仿真周期
double min_acc_vel = fabs(vel_yaw) - acc_lim_theta_ * sim_period_;
/********************************************************/
/**********用可达角速度和停止所限制的最大速度更新角速度范围************/
//角速度=角速度符号× min(max(角速度绝对值,实际最小角速度),实际最大角速度)
v_theta_samp = sign(v_theta_samp) * std::min(std::max(fabs(v_theta_samp), min_acc_vel), max_acc_vel);
③ 下一步,由起始状态0速的运动公式 v^2 = 2ax,最大角加速度和角度差给定,若角速度超过√(2×角加速度×角度差),则当机器人旋转到目标姿态时角速度无法降至0,会“转过头”,所以角速度不能超过这个范围。
double max_speed_to_stop = sqrt(2 * acc_lim_theta_ * fabs(ang_diff));
//角速度=角速度符号× min(max_speed_to_stop,角速度绝对值)
v_theta_samp = sign(v_theta_samp) * std::min(max_speed_to_stop, fabs(v_theta_samp));
/**************************************************************/
④ 重复第①步,再次用预设角速度范围来限制下一步的角速度。
/***再次用min_in_place_vel_th_来加强限制,这比加速度限制更加重要***/
v_theta_samp = v_theta_samp > 0.0
? std::min( max_vel_th_, std::max( min_in_place_vel_th_, v_theta_samp ))
: std::max( min_vel_th_, std::min( -1.0 * min_in_place_vel_th_, v_theta_samp ));
/***********************************************************/
和降速过程同样,最后都要检查计算出来的下一步速度生成的路径是否合法,同样调用TrajectoryPlanner的checkTrajectory函数,若有效,则用它填充cmd_vel,否则填充0角速度。
//检查合法性
bool valid_cmd = tc_->checkTrajectory(global_pose.getOrigin().getX(), global_pose.getOrigin().getY(), yaw,
robot_vel.getOrigin().getX(), robot_vel.getOrigin().getY(), vel_yaw, 0.0, 0.0, v_theta_samp);
ROS_DEBUG("Moving to desired goal orientation, th cmd: %.2f, valid_cmd: %d", v_theta_samp, valid_cmd);
//如果动作合法,把计算出的角速度填充进去
if(valid_cmd){
cmd_vel.angular.z = v_theta_samp;
return true;
}
cmd_vel.angular.z = 0.0;
return false;
}
Neo 2020.3