3D SLAM ->loam_velodyne论文与代码解析
一直做2D 的激光SLAM,最近终于接触到3D的了,想彻底的看透一个开源的3D 激光SLAM,选择了Loam_velodyne从论文到代码彻底看一下。论文:LOAM Lidar Odometry and Mapping in Real-time。
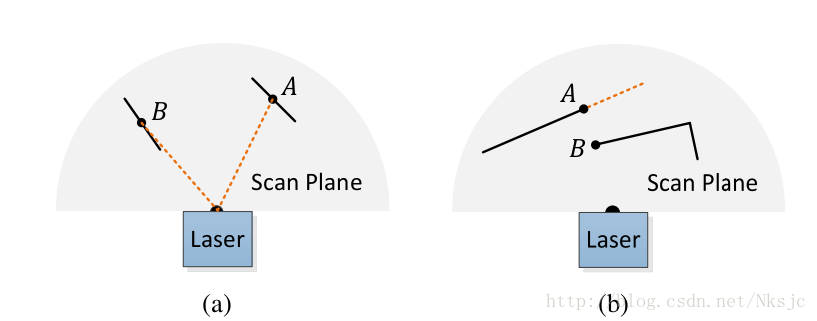
结构关系:订阅与发布节点关系
其中最终输出构建3D地图的点云是/laser_cloud_surround;需要更改的是最左侧输入、即订阅的/velodyne_points的topic名称。Remap成为需要订阅的主题。从图中可以看出scanRegister的工作是将源数据处理成/laser_cloud_sharp & /laser_cloud_flat等等,这些点云是具有特征信息的点云。
具体的操作为在论文中给出这样一幅图:
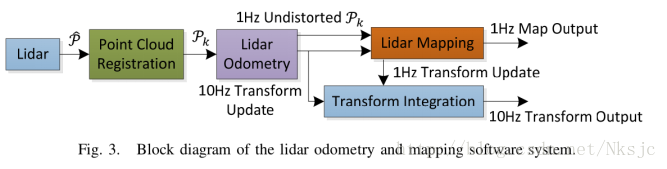
由此可以知道laserOdometry从特征点中估计运动(10HZ),然后整合数据发送给laserMapping(1HZ),在这个过程中,算是一种数据的降采样吧。也是为了保证运行online的时效性,以及节省内存占用的大小。
具体部分的实现思想
相对于其它直接匹配两个点云,loam是通过提取特征点匹配后计算坐标变换。
特征点提取
一次扫描的点通过曲率(c)值来分类,特征点是c的最大值点–边缘点;特征点是c的最小值点–平面点。为了使特征点均匀的分布在环境中,将一次扫描划分为4个独立的子区域。每个子区域最多提供2个边缘点和4个平面点,同时特征点的选择需要满足阈值的要求。
同时需要考虑特征点选择中的一些越是:比如如果一个点被其它特征点包围,那么就不被选择;以及一些点满足c的要求不过是不稳定的特征点,比如断点等。不稳定的点如下图:
代码部分:主要是在scanRegistration.cpp这个文件的任务是提取特征点,并且发布出去。
代码具体的阅读理解:
① 论文中存储每个点的曲率用的是数组,因此需要考虑数组的大小:
float cloudCurvature[80000];
int cloudSortInd[80000];
int cloudNeighborPicked[80000];
int cloudLabel[80000];前言:N_SCANS是将3D的激光点云按照激光的接受器做了个划分,比如N_SCANS是16表明是16线的激光(程序中的默认值,作者用过velodyne16)。
对于一堆点云并不是像LaserScan(二维的数据结构)那样按照角度给出个距离值,保证每次的扫描都能够有相同大小的数据量。PointCloud2接受到的点云的大小在变化,因此在数据到达需要一些运算来判断点的一些特性。例如下面这段通过计算pitch角度值将点划分到不同的“线”中。代码坑,point.x=laserCloudIn.points[i].y;做个迷惑的赋值。Pitch=atan(z/(x2+y2));和代码中只是形式的不同。
PointType point;
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<PointType> > laserCloudScans(N_SCANS);
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; i++) {
point.x = laserCloudIn.points[i].y;
point.y = laserCloudIn.points[i].z;
point.z = laserCloudIn.points[i].x;
float angle = atan(point.y / sqrt(point.x * point.x + point.z * point.z)) * 180 / M_PI;
int scanID;
int roundedAngle = int(angle + (angle<0.0?-0.5:+0.5));
if (roundedAngle > 0){
scanID = roundedAngle;
}
else {
scanID = roundedAngle + (N_SCANS - 1);
}
if (scanID > (N_SCANS - 1) || scanID < 0 ){
count--;
continue;
}算出scan ID后,又将intensity属性充分利用起来,整数部分:scan ID,小数部分:每个点扫描的时间(在startOri->endOri按照均匀划分)
float relTime = (ori - startOri) / (endOri - startOri);
point.intensity = scanID + scanPeriod * relTime;然后,将点压入到每个线中,同时更新总的点云laserCloud。
……
laserCloudScans[scanID].push_back(point);
}
cloudSize = count;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCANS; i++) {
*laserCloud += laserCloudScans[i];
}含义说明:cloudCurvature是存储每个点的曲率,由上面的laserCloud+=……,可以知道的是这个时候的点云是按照线的数据方式存储的,线的数量自己定义。作者给出的计算公式:
float diffX = laserCloud->points[i - 5].x + laserCloud->points[i - 4].x
+ laserCloud->points[i - 3].x + laserCloud->points[i - 2].x
+ laserCloud->points[i - 1].x - 10 * laserCloud->points[i].x
+ laserCloud->points[i + 1].x + laserCloud->points[i + 2].x
+ laserCloud->points[i + 3].x + laserCloud->points[i + 4].x
+ laserCloud->points[i + 5].x;
float diffY = laserCloud->points[i - 5].y + laserCloud->points[i - 4].y
+ laserCloud->points[i - 3].y + laserCloud->points[i - 2].y
+ laserCloud->points[i - 1].y - 10 * laserCloud->points[i].y
+ laserCloud->points[i + 1].y + laserCloud->points[i + 2].y
+ laserCloud->points[i + 3].y + laserCloud->points[i + 4].y
+ laserCloud->points[i + 5].y;
float diffZ = laserCloud->points[i - 5].z + laserCloud->points[i - 4].z
+ laserCloud->points[i - 3].z + laserCloud->points[i - 2].z
+ laserCloud->points[i - 1].z - 10 * laserCloud->points[i].z
+ laserCloud->points[i + 1].z + laserCloud->points[i + 2].z
+ laserCloud->points[i + 3].z + laserCloud->points[i + 4].z
+ laserCloud->points[i + 5].z;
//jc : cloudCurvature calculate
cloudCurvature[i] = diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ;因为是按照线的序列存储,因此接下来能够得到起始和终止的index;在这里滤除前五个和后五个。
if (int(laserCloud->points[i].intensity) != scanCount) {
scanCount = int(laserCloud->points[i].intensity);
//N_SCANS is 16
if (scanCount > 0 && scanCount < N_SCANS) {
//std::vector<int> scanStartInd(N_SCANS, 0);
//std::vector<int> scanEndInd(N_SCANS, 0);
scanStartInd[scanCount] = i + 5;
scanEndInd[scanCount - 1] = i - 5;
}
}cloudSortInd是对曲率排序得到的序列:这里作者将每一线划分为等间距的6段分别处理,在每一段升序排列。 变量说明sp startPoint;ep endPoint.
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCANS; i++) {
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr surfPointsLessFlatScan(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>);
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
int sp = (scanStartInd[i] * (6 - j) + scanEndInd[i] * j) / 6;
int ep = (scanStartInd[i] * (5 - j) + scanEndInd[i] * (j + 1)) / 6 - 1;
for (int k = sp + 1; k <= ep; k++) {
for (int l = k; l >= sp + 1; l--) {
if (cloudCurvature[cloudSortInd[l]] < cloudCurvature[cloudSortInd[l - 1]]) {
int temp = cloudSortInd[l - 1];
cloudSortInd[l - 1] = cloudSortInd[l];
cloudSortInd[l] = temp;
}
}
}cloudNeighborPicked是考虑一个特征点的周围不能再设置成特征点约束的判断标志位。
cloudLabel按照如下计算,选择最大曲率的作为sharp和lessSharp,因为是按照升序排列的cloudSortInd,因此从ep->sp逐个选择:
int largestPickedNum = 0;
for (int k = ep; k >= sp; k--) {
int ind = cloudSortInd[k];
// jc : in cloudNeighborPicked array 1 is nerighbor and 0 is alone
// jc : if it 's alone and the curudCurvature is bigger then 0.1,
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] ==