shiro提供了完整的会话管理功能,不依赖底层容器,JavaSE应用和JavaEE应用都可以使用。SessionManager(会话管理器)管理着应用中所有Subject的会话,包括会话的创建、维护、删除、失效、验证等工作。
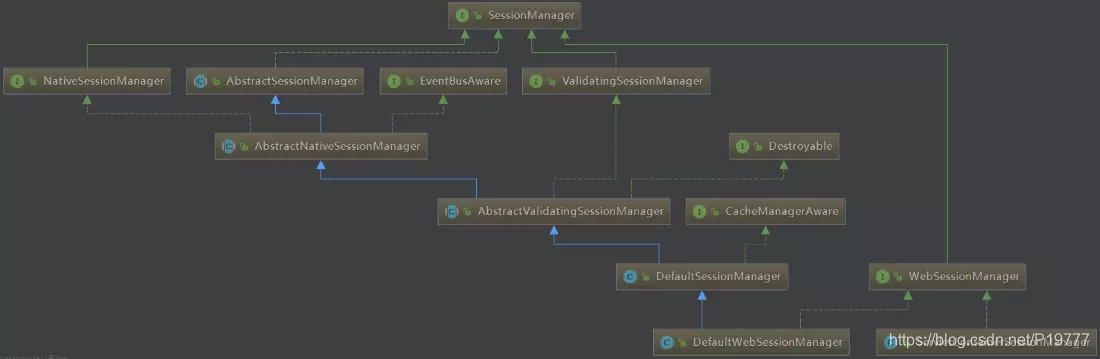
SessionManager继承结构
DefaultSecurityManager默认使用的SessionManager为DefaultSessionManager,用于JavaSE环境的session管理。
SessionManager 接口
SessionManager 接口是Shiro所有会话管理器的顶级接口。在此接口中声明了两个方法Session start(SessionContext context);和Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException;。
Session start(SessionContext context);方法,基于指定的上下文初始化数据启动新会话。
Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException; 根据指定的SessionKey检索会话,如果找不到则返回null。如果找到了会话,但会话但无效(已停止或已过期)则抛出SessionException异常。
扩展注意
如果要从新实现自己的会话管理器,建议扩展 AbstractValidationSessionManager 抽象类。
如果要在原有会话管理功能的基础上进行扩展,在桌面应用中建议扩展DefaultSessionManager,在Web环境下建议扩展DefaultWebSessionManager。
stat 方法 和 getSession 方法
需要重点说一下 getSession 方法,是因为大多数扩展中都是围绕它展开的。至于start方法,Shiro中自带的实现已经可以满足我们的需求。
Shiro 在三个地方对 start 进行了实现:
// AbstractNativeSessionManager 抽象类中的实现
public Session start(SessionContext context) {
Session session = createSession(context);
applyGlobalSessionTimeout(session);
onStart(session, context);
notifyStart(session);
//Don't expose the EIS-tier Session object to the client-tier:
return createExposedSession(session, context);
}
// ServletContainerSessionManager 中的实现
public Session start(SessionContext context) throws AuthorizationException {
return createSession(context);
}
// SessionsSecurityManager 中的实现
public Session start(SessionContext context) throws AuthorizationException {
return this.sessionManager.start(context);
}
由以上代码可知,SessionsSecurityManager中的实现其实没有实际的代码,而是直接调用的SessionManager对象的start方法(其实就是前两个实现中的一个)。两个有意义的start方法的实现在扩展中我们都无需要关心,直接继承就ok了。
Shiro 在同样在三个地方对getSession方法进行了实现:
// AbstractNativeSessionManager 抽象类中的实现
public Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException {
Session session = lookupSession(key);
return session != null ? createExposedSession(session, key) : null;
}
// ServletContainerSessionManager 中的实现
public Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException {
if (!WebUtils.isHttp(key)) {
String msg = "SessionKey must be an HTTP compatible implementation.";
throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg);
}
HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(key);
Session session = null;
HttpSession httpSession = request.getSession(false);
if (httpSession != null) {
session = createSession(httpSession, request.getRemoteHost());
}
return session;
}
// SessionsSecurityManager 中的实现
public Session getSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException {
return this.sessionManager.getSession(key);
}
同样的SessionsSecurityManager中的实现其实没有实际的代码,而是直接调用的SessionManager对象的getSession方法。由于ServletContainerSessionManager中直接使用了HttpServletSession,所以一般也不会对其进行扩展。我们扩展过程中需要关心的主要是AbstractNativeSessionManager中的getSession。
从上述源码中可以看到,lookupSession方法,才是用来获取Session的方法。
private Session lookupSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("SessionKey argument cannot be null.");
}
return doGetSession(key);
}
private Session lookupRequiredSession(SessionKey key) throws SessionException {
Session session = lookupSession(key);
if (session == null) {
String msg = "Unable to locate required Session instance based on SessionKey [" + key + "].";
throw new UnknownSessionException(msg);
}
return session;
}
protected abstract Session doGetSession(SessionKey key) throws InvalidSessionException;
lookupSession方法又把获取Session的操作交给了抽象方法doGetSession。而doGetSession仅有一个实现在AbstractValidatingSessionManager中如下:
@Override
protected final Session doGetSession(final SessionKey key) throws InvalidSessionException {
enableSessionValidationIfNecessary();
log.trace("Attempting to retrieve session with key {}", key);
Session s = retrieveSession(key);
if (s != null) {
validate(s, key);
}
return s;
}
protected abstract Session retrieveSession(SessionKey key) throws UnknownSessionException;
真是不让人省心,在doGetSession中又把获取Session的关键性操作交给了抽象方法retrieveSession。retrieveSession也仅有一个实现在DefaultSessionManager中,如下所示:
protected Session retrieveSession(SessionKey sessionKey) throws UnknownSessionException {
Serializable sessionId = getSessionId(sessionKey);
if (sessionId == null) {
log.debug("Unable to resolve session ID from SessionKey [{}]. Returning null to indicate a " +
"session could not be found.", sessionKey);
return null;
}
Session s = retrieveSessionFromDataSource(sessionId);
if (s == null) {
//session ID was provided, meaning one is expected to be found, but we couldn't find one:
String msg = "Could not find session with ID [" + sessionId + "]";
throw new UnknownSessionException(msg);
}
return s;
}
protected Serializable getSessionId(SessionKey sessionKey) {
return sessionKey.getSessionId();
}
protected Session retrieveSessionFromDataSource(Serializable sessionId) throws UnknownSessionException {
return sessionDAO.readSession(sessionId);
}
从上面的源码中,可以看出来获取Session的关键在于getSessionId方法。
其实对于DefaultSessionManager也没什么好扩展的。Shiro中的实现已经可以满足我们的大多数需求。真正需要扩展getSession方法功能的是在DefaultWebSessionManager中。在DefaultWebSessionManager没有getSession方法的实现,但它对getSessionId方法进行了重写:
@Override
public Serializable getSessionId(SessionKey key) {
Serializable id = super.getSessionId(key);
if (id == null && WebUtils.isWeb(key)) {
ServletRequest request = WebUtils.getRequest(key);
ServletResponse response = WebUtils.getResponse(key);
id = getSessionId(request, response);
}
return id;
}
在Web环境下,请求到来时的第一次Serializable id = super.getSessionId(key);得到的是null,因为这时是一个新的线程再处理请求。后续再调用super.getSessionId(key);时,就可以正常拿到SessionId了。
所以对SessionManager的扩展多数是在Web环境下才需要,一般也是继承DefaultWebSessionManager然后重写getSessionId方法。
扩展举例
比如我们在为App接口做Web应用时,想使用Session功能时。因为App端的请求一般不会设置Cookies,所以我们需要使用Token(一般存储的HTTP请求头中)来做SessionId。
这时我们可以继承DefaultWebSessionManager实现自己的SessionManager类,然后重写getSessionId方法如下:
public class MySessionManager extends DefaultWebSessionManager {
@Override
protected Serializable getSessionId(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
String id = WebUtils.toHttp(request).getHeader("token");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(id)) {
request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_SOURCE, "Stateless request");
request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID, id);
request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_IS_VALID, Boolean.TRUE);
return id;
} else {
//否则按默认规则从cookie取sessionId
return super.getSessionId(request, response);
}
}
}