一、概念
单例模式就是一个类只能有一个实例,并且提供一个访问它的全局访问点。
通常通过私有化构造函数来实现只能通过类的内部创建实例。
二、饿汉式
饿汉式是单例模式中的一种,其特点为:在定义是就立即创建类的实例(真的饿了),但饿汉式是线程安全的,其核心代码如下:
class Singleton{
private:
Singleton(){}
static Singleton* m_instance;
public:
static Singleton* getInstance(){
return m_instance;
}
};
Singleton* Singleton::m_instance = new Singleton;
完整实例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Singleton {
static Singleton* singleton;
Singleton()
{
cout << "这是一个无参构造" << endl;
}
~Singleton()
{
cout << "这是析构" << endl;
}
public:
static Singleton* getinstence()
{
return singleton;
}
void show_info()
{
cout << this << endl;
}
//将编译器自动提供的拷贝构造与等号运算符重载移除掉
Singleton(const Singleton& other) = delete;
void operator=(const Singleton& other) = delete;
};
Singleton* Singleton::singleton = new Singleton;
int main()
{
Singleton* s1 = Singleton::getinstence();
s1->show_info();
Singleton* s2 = Singleton::getinstence();
s2->show_info();
Singleton* s3 = Singleton::getinstence();
s3->show_info();
return 0;
}
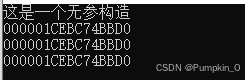
运行结果:
三、懒汉式
懒汉式也是单例模式的一种,其特点为:在需要用到的时候才会创建实例,具有懒加载的功能,其是线程不安全的,代码如下:
class Singleton{
private:
Singleton(){}
static Singleton* m_instance;
public:
static Singleton* getInstance(){
if(m_instance == nullptr){
m_instance = new Singleton;
}
return m_instance;
}
};
Singleton* Singleton::m_instance = nullptr;
完整示例如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Singleton {
static Singleton* singleton;
Singleton()
{
cout << "这是一个无参构造" << endl;
}
~Singleton()
{
cout << "这是析构" << endl;
}
public:
static Singleton* getinstence()
{
if (singleton == nullptr) {
singleton = new Singleton;
}
return singleton;
}
void show_info()
{
cout << this << endl;
}
//将编译器自动提供的拷贝构造与等号运算符重载移除掉
Singleton(const Singleton& other) = delete;
void operator=(const Singleton& other) = delete;
};
Singleton* Singleton::singleton = nullptr;
int main()
{
Singleton* s1 = Singleton::getinstence();
s1->show_info();
Singleton* s2 = Singleton::getinstence();
s2->show_info();
Singleton* s3 = Singleton::getinstence();
s3->show_info();
return 0;
}
运行结果为: