下载了libc的源码,现在就开始libc源码的学习,最近了解到了linux动态库的相关知识,那么就从linux动态库加载函数dlopen进行梳理学习吧。
如果还没下载libc源码,可通过
https://blog.csdn.net/SweeNeil/article/details/83744069
来查看自己需要的libc版本并进行下载。在这里我使用的是glibc-2.15
一、glibc/dlfcn/dlopen.c
解压源代码,首先进入glibc/dlfcn目录下,我们看到在该目录下有很多的dlxxx文件
其中dlopen.c就是我们需要分析的dlopen函数的定义地址,进入到dlopen.c中
dlopen函数如下:
void *
dlopen (const char *file, int mode)
{
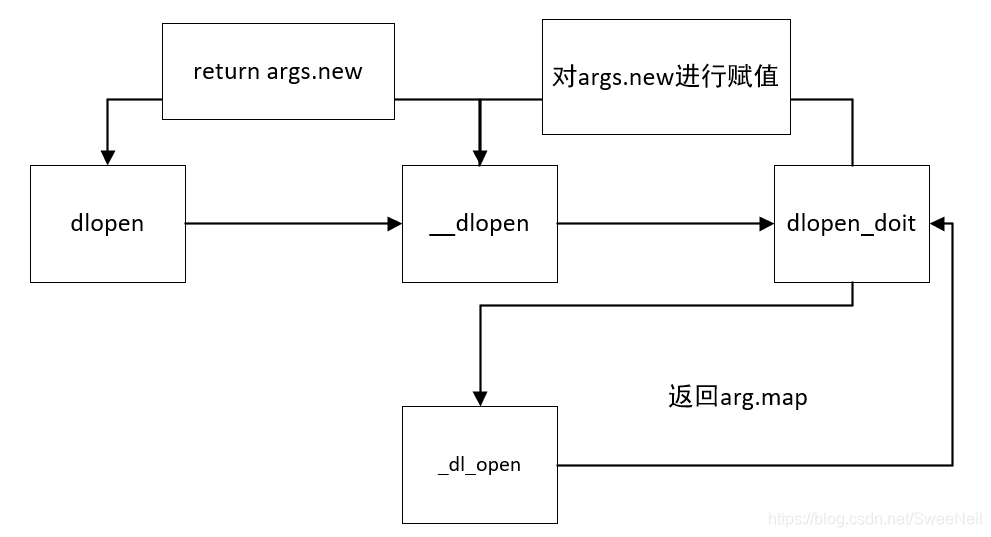
return __dlopen (file, mode, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
}它实际上是调用了__dlopen函数,我们在进入到__dlopen函数中
void *
__dlopen (const char *file, int mode DL_CALLER_DECL)
{
# ifdef SHARED
if (__builtin_expect (_dlfcn_hook != NULL, 0))
return _dlfcn_hook->dlopen (file, mode, DL_CALLER);
# endif
struct dlopen_args args;
args.file = file;
args.mode = mode;
args.caller = DL_CALLER;
# ifdef SHARED
return _dlerror_run (dlopen_doit, &args) ? NULL : args.new;
# else
if (_dlerror_run (dlopen_doit, &args))
return NULL;
__libc_register_dl_open_hook ((struct link_map *) args.new);
__libc_register_dlfcn_hook ((struct link_map *) args.new);
return args.new;
# endif
}该函数主要对args进行了赋值,比较关键的就是args.new,它作为了返回值被返回,而这个args.new是通过dlopen_doit函数进行赋值的。
先来了解一个这个args到底是什么
struct dlopen_args
{
/* The arguments for dlopen_doit. */
const char *file;
int mode;
/* The return value of dlopen_doit. */
void *new;
/* Address of the caller. */
const void *caller;
};它由上述所示的四个字段组成,这个void *new就是最终的返回值,它在dlopen_doit中被返回到__dlopen。进入到dlopen_doit函数中
static void
dlopen_doit (void *a)
{
struct dlopen_args *args = (struct dlopen_args *) a;
if (args->mode & ~(RTLD_BINDING_MASK | RTLD_NOLOAD | RTLD_DEEPBIND
| RTLD_GLOBAL | RTLD_LOCAL | RTLD_NODELETE
| __RTLD_SPROF))
GLRO(dl_signal_error) (0, NULL, NULL, _("invalid mode parameter"));
args->new = GLRO(dl_open) (args->file ?: "", args->mode | __RTLD_DLOPEN,
args->caller,
args->file == NULL ? LM_ID_BASE : NS,
__dlfcn_argc, __dlfcn_argv, __environ);
}上述代码主要是对args->new进行赋值,不过是通过_dl_open函数来进行的,这个GLRO(dl_open)实际上就是_dl_open函数,因此下一步又需要去查看_dl_open函数,此时_dl_open函数就已经不再是定义在dlopen.c中了,而是dl-open.c中。
暂且将dlopen.c文件中的调用关系称为第一层调用吧,其具体图示如下所示:
二、glibc/elf/dl-open.c
在dl-open.c下也有着大量的关于dl-xxx的具体实现
我们需要了解的是其中的dl-open,打开dl-open文件,里面有_dl_open函数的具体实现,省略号部分表示省略了部分代码。
void *
_dl_open (const char *file, int mode, const void *caller_dlopen, Lmid_t nsid,
int argc, char *argv[], char *env[])
{
……
……
/* Never allow loading a DSO in a namespace which is empty. Such
direct placements is only causing problems. Also don't allow
loading into a namespace used for auditing. */
else if (__builtin_expect (nsid != LM_ID_BASE && nsid != __LM_ID_CALLER, 0)
&& (GL(dl_ns)[nsid]._ns_nloaded == 0
|| GL(dl_ns)[nsid]._ns_loaded->l_auditing))
_dl_signal_error (EINVAL, file, NULL,
N_("invalid target namespace in dlmopen()"));
#ifndef SHARED
else if ((nsid == LM_ID_BASE || nsid == __LM_ID_CALLER)
&& GL(dl_ns)[LM_ID_BASE]._ns_loaded == NULL
&& GL(dl_nns) == 0)
GL(dl_nns) = 1;
#endif
struct dl_open_args args;
args.file = file;
args.mode = mode;
args.caller_dlopen = caller_dlopen;
args.caller_dl_open = RETURN_ADDRESS (0);
args.map = NULL;
args.nsid = nsid;
args.argc = argc;
args.argv = argv;
args.env = env;
const char *objname;
const char *errstring;
bool malloced;
int errcode = _dl_catch_error (&objname, &errstring, &malloced,
dl_open_worker, &args);
#ifndef MAP_COPY
/* We must munmap() the cache file. */
_dl_unload_cache ();
#endif
/* See if an error occurred during loading. */
if (__builtin_expect (errstring != NULL, 0))
{
/* Remove the object from memory. It may be in an inconsistent
state if relocation failed, for example. */
if (args.map)
{
/* Maybe some of the modules which were loaded use TLS.
Since it will be removed in the following _dl_close call
we have to mark the dtv array as having gaps to fill the
holes. This is a pessimistic assumption which won't hurt
if not true. There is no need to do this when we are
loading the auditing DSOs since TLS has not yet been set
up. */
if ((mode & __RTLD_AUDIT) == 0)
GL(dl_tls_dtv_gaps) = true;
_dl_close_worker (args.map);
}
assert (_dl_debug_initialize (0, args.nsid)->r_state == RT_CONSISTENT);
/* Release the lock. */
__rtld_lock_unlock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock));
/* Make a local copy of the error string so that we can release the
memory allocated for it. */
size_t len_errstring = strlen (errstring) + 1;
char *local_errstring;
if (objname == errstring + len_errstring)
{
size_t total_len = len_errstring + strlen (objname) + 1;
local_errstring = alloca (total_len);
memcpy (local_errstring, errstring, total_len);
objname = local_errstring + len_errstring;
}
else
{
local_errstring = alloca (len_errstring);
memcpy (local_errstring, errstring, len_errstring);
}
if (malloced)
free ((char *) errstring);
/* Reraise the error. */
_dl_signal_error (errcode, objname, NULL, local_errstring);
}
assert (_dl_debug_initialize (0, args.nsid)->r_state == RT_CONSISTENT);
/* Release the lock. */
__rtld_lock_unlock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock));
#ifndef SHARED
DL_STATIC_INIT (args.map);
#endif
return args.map;
}在_dl_open函数中定义了一个新的结构体dl_open_args,并且_dl_open中实际上是调用