一、背景与具体实现功能。
在传统的 AGV 小车巡线作业场景中,诸如电磁导航、地面色带导航以及磁条导航等方式较为常见,它们通常需要在 AGV 小车的行进路面上进行特殊处理,如埋设金属线、铺设色带或磁条。
然而,这种依赖地面标识的导航手段存在明一些弊端:一方面,随着使用频次的增加,色带极易出现磨损,磁条也可能发生消磁状况,一旦出现此类问题,AGV 小车的导航精准度便会大打折扣,甚至完全失效;另一方面,倘若生产流程需要调整,或是物流布局有所变动,想要对这些地面导航标识进行变更,操作难度颇高,不仅耗时费力,还可能影响正常生产秩序。
鉴于此,我们可尝试利用天花板上的固有特征来实现 AGV 小车的巡线引导,选定天花板高低不平的交界线作为潜在的巡线轨迹,期望以此作为初步尝试,让 AGV 小车开启全新的巡线模式。
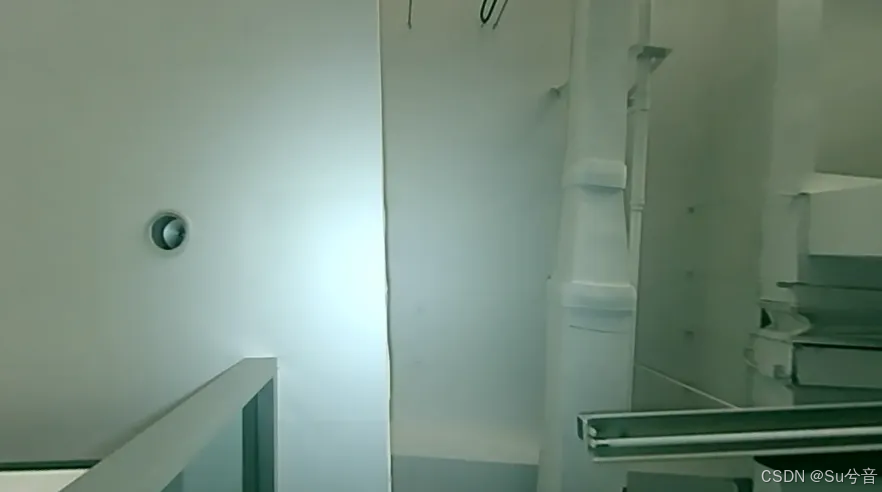
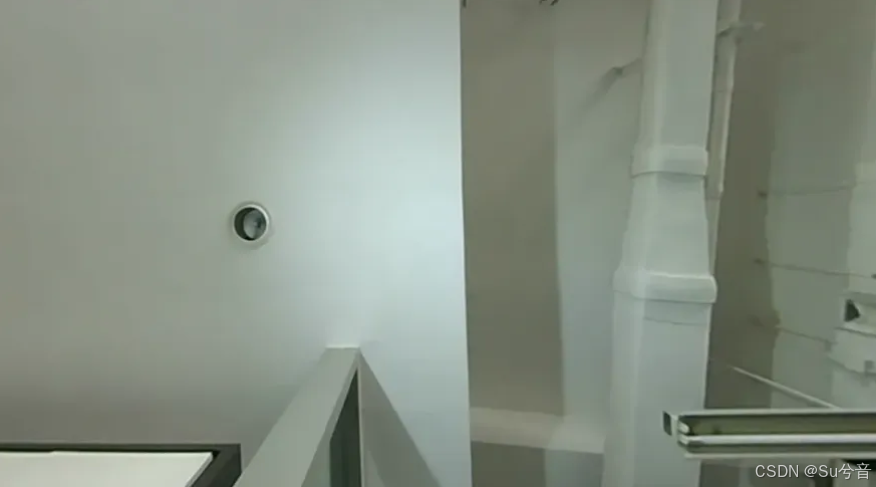
(如上图所示,初步采用识别红框中的天花板高度不一的交界线作为巡线轨迹)
二、基本物料。
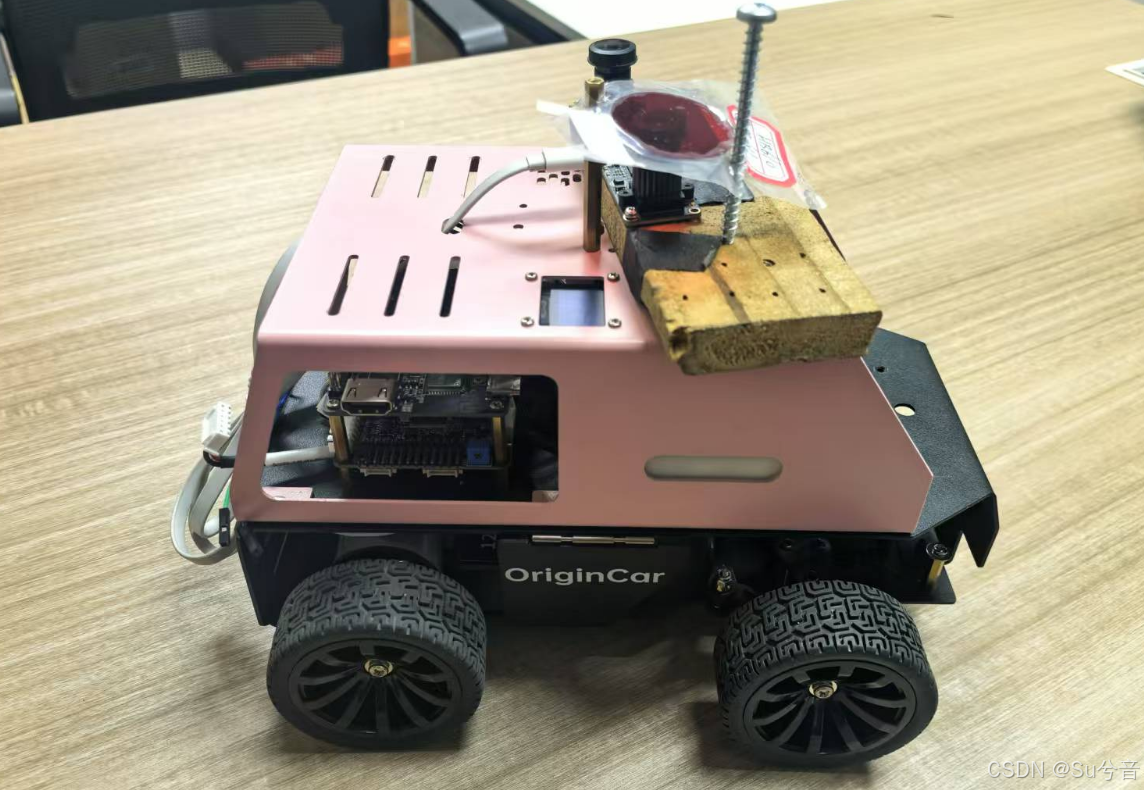
小车采用古月居的Origincar小车套件,自配双目鱼眼相机
1. 主控板:Origincar小车采用地平线RDK X3板,作为主控板;
2. 运动控制板:Origincar小车采用STM32F407VET6芯片,作为运动控制板;
3. 相机:自配双目鱼眼相机,但巡线使用时,实际只采用一个相机采集的图像;
三、基本功能实现流程。
1. 打开相机,拍摄天花板及天花板上的边缘线;
2. 识别图像中的边缘线,并根据边缘线识别特征点,绘制出巡线轨迹;
3. 沿着新绘制的线,发布机器人的运动指令,使机器人沿着线运动。
四、流程细节。
1. 打开相机/拍摄图像/图像矫正处理:
由于使用的是鱼眼相机,则需要对图像进行校正,此处选用桶形展开校正,本代码中是对本地图像进行校正,也可以直接从相机读取图像进行校正:
首先需要使用棋盘格图片对鱼眼相机采集的图像进行校正,得到光心坐标、相机的内参与畸变参数,再根据这些内容,来进行鱼眼图像的桶型矫正;
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
# 定义输入和输出文件夹路径
input_folder = '输入文件夹路径'
output_folder = '桶型矫正后输出文件夹路径'
# 确保输出文件夹存在
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 获取文件夹中的所有 .bmp 文件
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(input_folder) if f.endswith('.bmp')]
# 相机内参和畸变参数
K = np.array([[585.6065978157075, 0.0, 583.2996761313536],
[0.0, 583.7935461839306, 336.5316008144147],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
D = np.array([-0.17860062239081786, 0.004389935056111613, 0.023457691555598112, -0.011916211941152808])
# 定义光心坐标
cx, cy = 583.2996761313536, 336.5316008144147
# 处理每个图像文件
for image_file in image_files:
image_path = os.path.join(input_folder, image_file)
image = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
if image is None:
print(f"Image not found or cannot be read at path: {image_path}")
continue
# 图像尺寸
dim = image.shape[:2][::-1] # (width, height)
# 进行桶形畸变校正
map1, map2 = cv2.fisheye.initUndistortRectifyMap(K, D, np.eye(3), K, dim, cv2.CV_16SC2)
undistorted_image = cv2.remap(image, map1, map2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT)
# 在校正前后的图像中标记光心
marked_image = image.copy()
marked_undistorted_image = undistorted_image.copy()
cv2.circle(marked_image, (int(cx), int(cy)), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.circle(marked_undistorted_image, (int(cx), int(cy)), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 保存校正后的图像到本地
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, f"undistorted_{image_file}")
cv2.imwrite(output_path, undistorted_image)
print(f"Undistorted image saved to {output_path}")
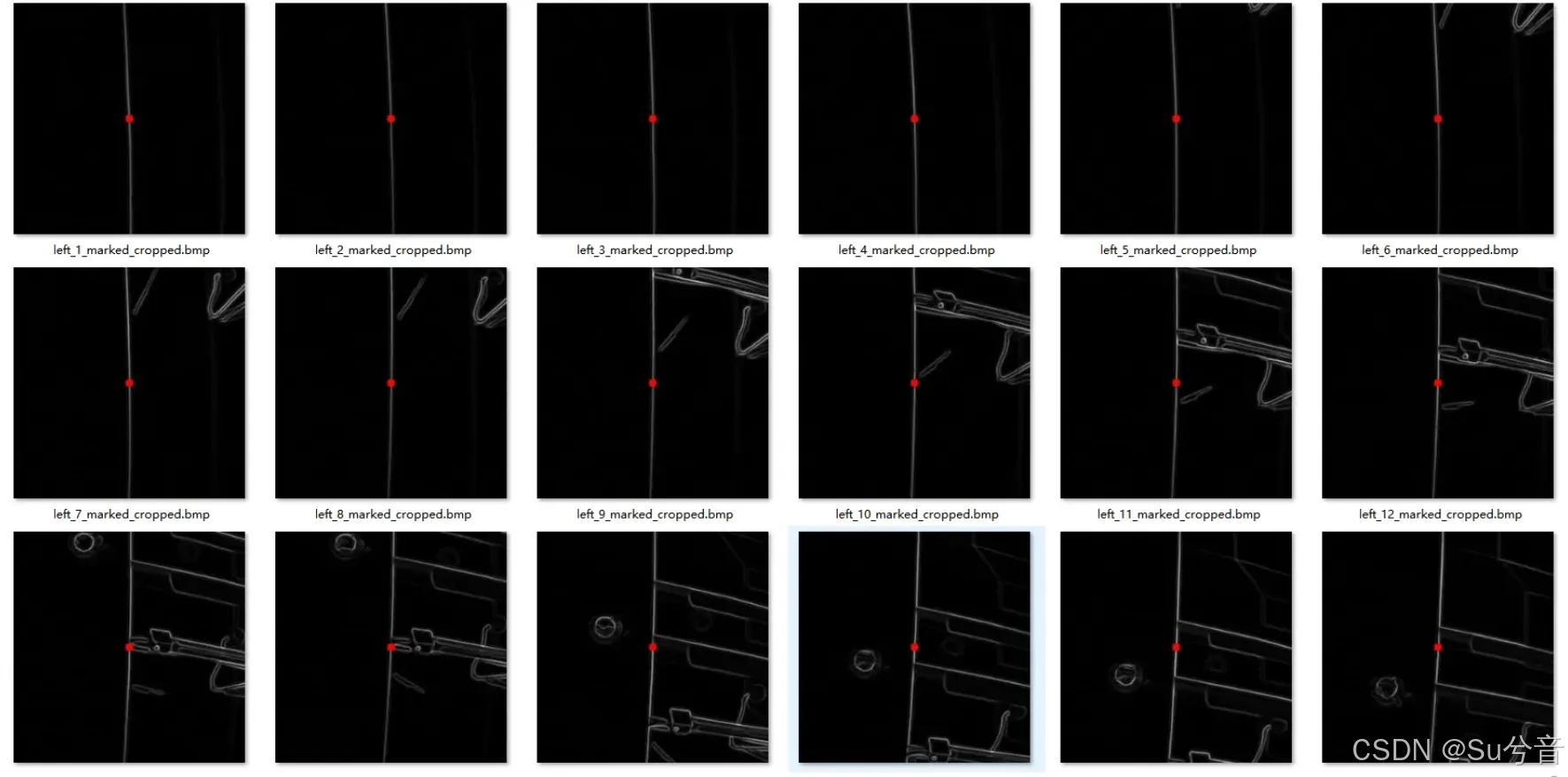
2.图像处理,找出梯度最高点并进行裁剪:
以相机的光心为中心,将梯度明显的部分计算提取出来,标记梯度最高的点并裁剪;
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
# 定义输入和输出文件夹路径
input_folder = '刚才保存的桶型矫正后输出文件夹路径'
output_folder = '新的处理后输出文件夹路径'
# 确保输出文件夹存在
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 获取文件夹中的所有 .bmp 文件
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(input_folder) if f.endswith('.bmp')]
# 定义光心坐标
cx, cy = 583.2996761313536, 336.5316008144147
# 定义搜索区域大小
search_radius = 50 # 可以根据需要调整搜索半径
# 处理每个图像文件
for image_file in image_files:
image_path = os.path.join(input_folder, image_file)
image = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
if image is None:
print(f"Image not found or cannot be read at path: {image_path}")
continue
# 计算梯度
grad_x = cv2.Sobel(image, cv2.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize=3)
grad_y = cv2.Sobel(image, cv2.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
# 计算梯度幅度
grad_magnitude = np.sqrt(grad_x**2 + grad_y**2)
# 将梯度幅度图像转换为 uint8 类型
grad_magnitude = (grad_magnitude / grad_magnitude.max() * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 在光心附近的区域内找到梯度最大的点
search_area = grad_magnitude[int(cy - search_radius):int(cy + search_radius), int(cx - search_radius):int(cx + search_radius)]
max_grad_index = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(search_area), search_area.shape)
max_grad_y, max_grad_x = max_grad_index[0] + int(cy - search_radius), max_grad_index[1] + int(cx - search_radius)
# 以最大梯度点为中心裁剪一张长300宽300像素的图像
crop_size = 300
half_crop_size = crop_size // 2
x_min = int(max_grad_x - half_crop_size)
y_min = int(max_grad_y - half_crop_size)
x_max = x_min + crop_size
y_max = y_min + crop_size
# 确保裁剪区域在图像范围内
if x_min < 0 or y_min < 0 or x_max > image.shape[1] or y_max > image.shape[0]:
print(f"Crop region out of bounds for image: {image_file}")
continue
cropped_image = grad_magnitude[y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max]
# 在裁剪后的图像中标记梯度最大的点
marked_cropped_image = cv2.cvtColor(cropped_image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
cv2.circle(marked_cropped_image, (half_crop_size, half_crop_size), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 保存标记后的裁剪图像
base_name = os.path.splitext(image_file)[0]
marked_cropped_output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, f'{base_name}_marked_cropped.bmp')
cv2.imwrite(marked_cropped_output_path, marked_cropped_image)
print(f"Marked cropped image saved to {marked_cropped_output_path}")为保证图像处理结果更加准确清晰,相机垂直仰拍天花板,并使用一盏白光灯进行补光;
初始时白光灯垂直仰视照射天花板,发现处理后的图像存在干扰,找出的特征点并不在需要巡线的轨迹上,于是将白光灯换到了图像左侧,由左向右进行打光;
(如上两幅图,为白光灯垂直仰视照射天花板的效果与处理效果,处理后的图像中,竖直的白色线条为处理后的天花板交界线,即为需要的巡线轨迹;红色点即为所需要识别出的特征点——梯度最高点,处理后的结果可看出部分找出的特征点并不在需要巡线的轨迹上)
(如上两幅图,为白光灯由左向右进行打光的效果与处理效果,处理后的图像中,红色点的特征点——梯度最高点均在需要巡线的轨迹上)
五、整体流程整理与运动控制。
以上流程走通后,对各部分代码进行整理,小车需要进行视觉巡线,目前已经得到所获取图像中梯度最高的点,那么可以得到梯度最高的点上方每隔五行、取一行,取出的那一行梯度最高的点,进行筛选与处理,形成一条路径,可以确定机器人的前进方向和角度。
1. 图像采集与处理代码整理:
在开启摄的像头、矫正、裁剪、找出初始的梯度最大点之后,再将初始的梯度最大点上方,每隔五行、取一行的梯度最大点取出,并判断这些梯度最大点:
如果它们和初始的梯度最大点,在x方向上的差值小于一定距离,则可将他们和初始的梯度最大点进行连接,拟合出一条线,标记出此条线(标记时可将线条适当加宽),以此作为小车的巡线轨迹;
最终将处理好的图像发布到话题中,为下一步处理做准备。
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from sensor_msgs.msg import CompressedImage
from cv_bridge import CvBridge
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import time
import datetime
class CameraProcessNode(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('camera_process_node')
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_V4L2)
if not self.cap.isOpened():
self.get_logger().error("Failed to open camera")
return
# 设置摄像头分辨率
self.width = 1280
self.height = 720
self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, self.width)
self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, self.height)
# 检查分辨率设置是否成功
actual_width = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
actual_height = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
self.get_logger().info(f"Set resolution to {self.width}x{self.height}, actual resolution is {actual_width}x{actual_height}")
self.publisher = self.create_publisher(CompressedImage, 'image/compressed', 5)
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.timer = self.create_timer(1.0 / 15, self.process_and_publish)
# 相机内参和畸变参数
self.K = np.array([[585.6065978157075, 0.0, 583.2996761313536],
[0.0, 583.7935461839306, 336.5316008144147],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
self.D = np.array([-0.17860062239081786, 0.004389935056111613, 0.023457691555598112, -0.11916211941152808])
self.cx, self.cy = 583.2996761313536 , 336.5316008144147
self.search_radius = 50
self.crop_width = 300
self.crop_height = 200
# 创建以当前时间戳命名的输出文件夹
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
self.output_folder = os.path.join('图像保存的本地路径', current_time)
os.makedirs(self.output_folder, exist_ok=True)
def process_and_publish(self):
ret, frame = self.cap.read()
if ret:
# 图像尺寸
dim = frame.shape[:2][::-1] # (width, height)
# 进行桶形畸变校正
map1, map2 = cv2.fisheye.initUndistortRectifyMap(self.K, self.D, np.eye(3), self.K, dim, cv2.CV_16SC2)
undistorted_image = cv2.remap(frame, map1, map2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT)
# 转换为灰度图
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(undistorted_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 计算梯度
grad_x = cv2.Sobel(gray_image, cv2.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize=3)
grad_y = cv2.Sobel(gray_image, cv2.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
# 计算梯度幅度
grad_magnitude = np.sqrt(grad_x ** 2 + grad_y ** 2)
# 将梯度幅度图像转换为 uint8 类型
grad_magnitude = (grad_magnitude / grad_magnitude.max() * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 在新的光心附近的区域内找到梯度最大的点
search_area = grad_magnitude[int(self.cy - self.search_radius):int(self.cy + self.search_radius),
int(self.cx - self.search_radius):int(self.cx + self.search_radius)]
max_grad_index = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(search_area), search_area.shape)
max_grad_y, max_grad_x = max_grad_index[0] + int(self.cy - self.search_radius), max_grad_index[1] + int(self.cx - self.search_radius)
# 以最大梯度点为中心裁剪一张长100宽300像素的图像
half_crop_width = self.crop_width // 2
half_crop_height = self.crop_height // 2
x_min = int(max_grad_x - half_crop_width)
y_min = int(max_grad_y - half_crop_height)
x_max = x_min + self.crop_width
y_max = y_min + self.crop_height
# 确保裁剪区域在图像范围内
if x_min < 0 or y_min < 0 or x_max > gray_image.shape[1] or y_max > gray_image.shape[0]:
self.get_logger().warn("Crop region out of bounds")
return
cropped_image = grad_magnitude[y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max]
# 在裁剪后的图像中标记梯度最大的点
marked_cropped_image = cv2.cvtColor(cropped_image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
cv2.circle(marked_cropped_image, (half_crop_width, half_crop_height), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 找出梯度最高的点上方每隔5行的一行梯度最高的点
step = 5
points = []
for y in range(0, half_crop_height, step):
line = cropped_image[y, :]
max_val_index = np.argmax(line)
points.append((max_val_index, y))
# 以第一个梯度最高的点为基准,依次连接这些梯度最高的点
base_point = (half_crop_width, half_crop_height)
for point in points:
dist = abs(point[0] - base_point[0])
if dist <= 10: # 如果平移距离小于等于10列,则连接这两个点
cv2.line(marked_cropped_image, (base_point[0], base_point[1]), (point[0], point[1]), (0, 0, 255), 30)
# 保存处理后的图像,按顺序编号保存
file_index = 1
output_path = os.path.join(self.output_folder, f'processed_{file_index}.jpg')
while os.path.exists(output_path):
file_index += 1
output_path = os.path.join(self.output_folder, f'processed_{file_index}.jpg')
cv2.imwrite(output_path, marked_cropped_image)
# 压缩图像并发布
compressed_msg = self.bridge.cv2_to_compressed_imgmsg(marked_cropped_image, "jpeg")
self.publisher.publish(compressed_msg)
else:
self.get_logger().warn("Failed to capture frame")
def destroy_node(self):
self.cap.release()
self.get_logger().info("Camera released")
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
camera_node = CameraProcessNode()
try:
rclpy.spin(camera_node)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
camera_node.get_logger().info("Shutting down")
finally:
camera_node.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
处理结果如下图,红色线即为小车巡线所需轨迹:
2. 运动控制部分:
订阅图像采集与处理代码中发布的话题,并对话题中的图像信息进行接收和解析,裁剪后识别图中的红色部分;
将红色部分的重心,和裁剪后整个图像的中心进行重合,来控制小车的巡线运动;
(此时线速度为固定给出,角速度根据红色部分的重心,与整个图像的中心的偏移量计算得出)
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import cv2
import numpy as np
import rclpy
import time
from rclpy.node import Node
from sensor_msgs.msg import CompressedImage
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile
import cv_bridge
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
import os
import datetime
# 红色的HSV范围
col_red = (0, 100, 80, 10, 255, 255)
class Follower(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('follower')
self.bridge = cv_bridge.CvBridge()
qos = QoSProfile(depth=10)
self.image_sub = self.create_subscription(
CompressedImage,
'image/compressed',
self.image_callback,
qos)
self.cmd_vel_pub = self.create_publisher(Twist, 'cmd_vel', qos)
self.twist = Twist()
self.last_erro = 0
self.image_count = 0
# 创建以当前时间戳命名的输出文件夹
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
self.save_path = os.path.join('输出图像文件夹', current_time)
os.makedirs(self.save_path, exist_ok=True)
def image_callback(self, msg):
# 解压图像消息为OpenCV图像
image = self.bridge.compressed_imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, desired_encoding='bgr8')
h, w, d = image.shape
# 截取图像的上半部分
image_top_half = image[:h // 2, :]
# 将截取的图像转换为HSV颜色空间
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image_top_half, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# 使用固定的红色HSV范围
lowerbH, lowerbS, lowerbV = col_red[:3]
upperbH, upperbS, upperbV = col_red[3:]
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, (lowerbH, lowerbS, lowerbV), (upperbH, upperbS, upperbV))
masked = cv2.bitwise_and(image_top_half, image_top_half, mask=mask)
# 计算mask图像的重心
M = cv2.moments(mask)
if M['m00'] > 0:
cx = int(M['m10'] / M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01'] / M['m00'])
# 计算目标重心与图像中心的偏移量
erro = cx - w // 2
d_erro = erro - self.last_erro
# 控制机器人的线速度和角速度
self.twist.linear.x = 0.11
self.twist.angular.z = -(float(erro) * 0.0011 - float(d_erro) * 0.0000)
self.last_erro = erro
# 在图像上标记重心
cv2.circle(image_top_half, (cx, cy), 10, (0, 255, 0), -1)
self.get_logger().info(f"Marked center at ({cx}, {cy + h // 2})")
else:
self.twist.linear.x = 0.0
self.twist.angular.z = 0.0
self.get_logger().info("No red object detected")
# 发布速度命令
self.cmd_vel_pub.publish(self.twist)
# 显示调试图像
cv2.imshow("Adjust_hsv", mask)
cv2.imshow("Image with Center Marked", image_top_half)
# 保存图像,按顺序编号保存
file_index = 1
filename = os.path.join(self.save_path, f'center_marked_image_{file_index}.jpg')
while os.path.exists(filename):
file_index += 1
filename = os.path.join(self.save_path, f'center_marked_image_{file_index}.jpg')
cv2.imwrite(filename, image_top_half)
def destroy_node(self):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
super().destroy_node()
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
print('start patrolling')
follower = Follower()
while rclpy.ok():
rclpy.spin_once(follower)
time.sleep(0.2)
follower.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()处理结果如下图,红色线即为小车巡线所需轨迹,绿色为红色部分的重心:
3. 一键启动:
(1)大致逻辑:使用一条命令,就可启动小车底盘、启动处理代码、启动巡线代码;
(2)目前小车巡线功能的代码分成了多个文件,需要将这些文件进行一键启动,方便操作,则计划更改小车启动方式为:1个启动文件,使用1条命令进行启动,这条命令将同时启动图像处理,外加小车巡线节点;
以上,则需要:①总体启动代码、②图像处理代码、③小车巡线代码;其中②、③已有,差一个总体启动代码可命名为【xxxx.launch.py】;
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
photo2_node = Node(
package='功能包名',
executable='可执行文件名1',
name='节点名1',
output='screen'
)
sport_node = Node(
package='功能包名',
executable='可执行文件名2',
name='节点名2',
output='screen'
)
return LaunchDescription([
节点1,
节点2
])
4. 将多个代码整合成一个代码,可不使用.launch.py文件:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from sensor_msgs.msg import CompressedImage
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from cv_bridge import CvBridge
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import datetime
import time
class ImageProcessorAndFollower(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('image_processor_and_follower')
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_V4L2)
if not self.cap.isOpened():
self.get_logger().error("Failed to open camera")
return
# 设置摄像头分辨率
self.width = 1280
self.height = 720
self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, self.width)
self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, self.height)
# 检查分辨率设置是否成功
actual_width = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
actual_height = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
self.get_logger().info(f"Set resolution to {self.width}x{self.height}, actual resolution is {actual_width}x{actual_height}")
self.publisher = self.create_publisher(CompressedImage, 'image/compressed', 5)
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.cmd_vel_pub = self.create_publisher(Twist, 'cmd_vel', 5)
self.twist = Twist()
self.last_error = 0
self.image_count = 0
# 相机内参和畸变参数
self.K = np.array([[585.6065978157075, 0.0, 583.2996761313536],
[0.0, 583.7935461839306, 336.5316008144147],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
self.D = np.array([-0.17860062239081786, 0.004389935056111613, 0.023457691555598112, -0.11916211941152808])
self.cx, self.cy = 583.2996761313536 , 336.5316008144147
self.search_radius = 50
self.crop_width = 300
self.crop_height = 200
# 创建以当前时间戳命名的输出文件夹
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
self.output_folder = os.path.join('图像输出路径', current_time)
os.makedirs(self.output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 为不同类型的图像创建子文件夹
self.processed_images_folder = os.path.join(self.output_folder, 'processed_images')
self.center_marked_images_folder = os.path.join(self.output_folder, 'center_marked_images')
os.makedirs(self.processed_images_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(self.center_marked_images_folder, exist_ok=True)
self.timer = self.create_timer(1.0 / 15, self.process_and_follow)
def process_and_follow(self):
ret, frame = self.cap.read()
if ret:
dim = frame.shape[:2][::-1]
# 进行桶形畸变校正
map1, map2 = cv2.fisheye.initUndistortRectifyMap(self.K, self.D, np.eye(3), self.K, dim, cv2.CV_16SC2)
undistorted_image = cv2.remap(frame, map1, map2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT)
# 第一次处理:裁剪并标记梯度最高的点
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(undistorted_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
grad_x = cv2.Sobel(gray_image, cv2.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize=3)
grad_y = cv2.Sobel(gray_image, cv2.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=3)
grad_magnitude = np.sqrt(grad_x ** 2 + grad_y ** 2)
grad_magnitude = (grad_magnitude / grad_magnitude.max() * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 在新的光心附近的区域内找到梯度最大的点
search_area = grad_magnitude[int(self.cy - self.search_radius):int(self.cy + self.search_radius),
int(self.cx - self.search_radius):int(self.cx + self.search_radius)]
max_grad_index = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(search_area), search_area.shape)
max_grad_y, max_grad_x = max_grad_index[0] + int(self.cy - self.search_radius), max_grad_index[1] + int(self.cx - self.search_radius)
# 裁剪
half_crop_width = self.crop_width // 2
half_crop_height = self.crop_height // 2
x_min = int(max_grad_x - half_crop_width)
y_min = int(max_grad_y - half_crop_height)
x_max = x_min + self.crop_width
y_max = y_min + self.crop_height
if x_min < 0 or y_min < 0 or x_max > gray_image.shape[1] or y_max > gray_image.shape[0]:
self.get_logger().warn("Crop region out of bounds")
return
cropped_image = grad_magnitude[y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max]
marked_cropped_image = cv2.cvtColor(cropped_image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
cv2.circle(marked_cropped_image, (half_crop_width, half_crop_height), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# 找出梯度最高的点上方每隔5行的一行梯度最高的点
step = 5
points = []
for y in range(0, half_crop_height, step):
line = cropped_image[y, :]
max_val_index = np.argmax(line)
points.append((max_val_index, y))
# 连接这些梯度最高的点
base_point = (half_crop_width, half_crop_height)
for point in points:
dist = abs(point[0] - base_point[0])
if dist <= 10:
cv2.line(marked_cropped_image, (base_point[0], base_point[1]), (point[0], point[1]), (0, 0, 255), 30)
# 保存处理后的图像
processed_file_index = self.image_count + 1
processed_output_path = os.path.join(self.processed_images_folder, f'processed_{processed_file_index}.jpg')
cv2.imwrite(processed_output_path, marked_cropped_image)
# 第二次处理:识别红色物体并计算重心
# 使用第一次处理后的中间结果
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(marked_cropped_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
lower_red = np.array([0, 100, 80])
upper_red = np.array([10, 255, 255])
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, lower_red, upper_red)
masked = cv2.bitwise_and(marked_cropped_image, marked_cropped_image, mask=mask)
# 计算mask图像的重心
M = cv2.moments(mask)
if M['m00'] > 0:
cx = int(M['m10'] / M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01'] / M['m00'])
error = cx - self.crop_width // 2
d_error = error - self.last_error
# 控制机器人的线速度和角速度
self.twist.linear.x = 0.11
self.twist.angular.z = -(float(error) * 0.0011 - float(d_error) * 0.0000)
self.last_error = error
# 在图像上标记重心
cv2.circle(marked_cropped_image, (cx, cy), 10, (0, 255, 0), -1)
else:
self.twist.linear.x = 0.0
self.twist.angular.z = 0.0
# 发布速度命令
self.cmd_vel_pub.publish(self.twist)
# 保存带有重心标记的图像
center_marked_file_index = self.image_count + 1
center_marked_filename = os.path.join(self.center_marked_images_folder, f'center_marked_image_{center_marked_file_index}.jpg')
cv2.imwrite(center_marked_filename, marked_cropped_image)
# 压缩图像并发布
compressed_msg = self.bridge.cv2_to_compressed_imgmsg(marked_cropped_image, "jpeg")
self.publisher.publish(compressed_msg)
self.image_count += 1
else:
self.get_logger().warn("Failed to capture frame")
def destroy_node(self):
self.cap.release()
self.get_logger().info("Camera released")
super().destroy_node()
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
node = ImageProcessorAndFollower()
try:
rclpy.spin(node)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
node.get_logger().info("Shutting down")
finally:
node.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()六、其他。
1. 可能用到代码-文件重命名排序代码:
import os
import re
def rename_bmp_files(folder_path):
# 获取文件夹中所有的文件
files = os.listdir(folder_path)
# 过滤出.bmp文件
bmp_files = [file for file in files if file.endswith('.bmp')]
# 按照文件名中的数字进行排序
def sort_key(filename):
match = re.search(r'\d+', filename)
if match:
return int(match.group())
return 0
bmp_files.sort(key=sort_key)
# 重新命名文件
for index, bmp_file in enumerate(bmp_files, start=1):
# 提取文件名和扩展名
filename_without_ext, ext = os.path.splitext(bmp_file)
# 构造新的文件名
new_filename = f"{index}{ext}"
# 构造完整的文件路径
old_file = os.path.join(folder_path, bmp_file)
new_file = os.path.join(folder_path, new_filename)
# 重命名文件
os.rename(old_file, new_file)
print(f"Renamed '{bmp_file}' to '{new_filename}'")
# 使用示例
# 请将'your_folder_path'替换为你的文件夹路径
folder_path = 'your_folder_path' # 假设你的.bmp文件在这个路径
rename_bmp_files(folder_path)2. 问题-摄像头连接虚拟机,虚拟机无法识别:
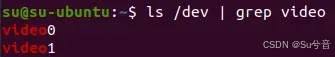
(1)首先接入摄像头,将摄像头连接入虚拟机:
(2)输入命令 ls /dev/video* 或命令 ls /dev | grep video 可列出当前所有的视频设备文件,一般默认摄像头是 video0,可根据摄像头编号修改代码中摄像头接口内容:
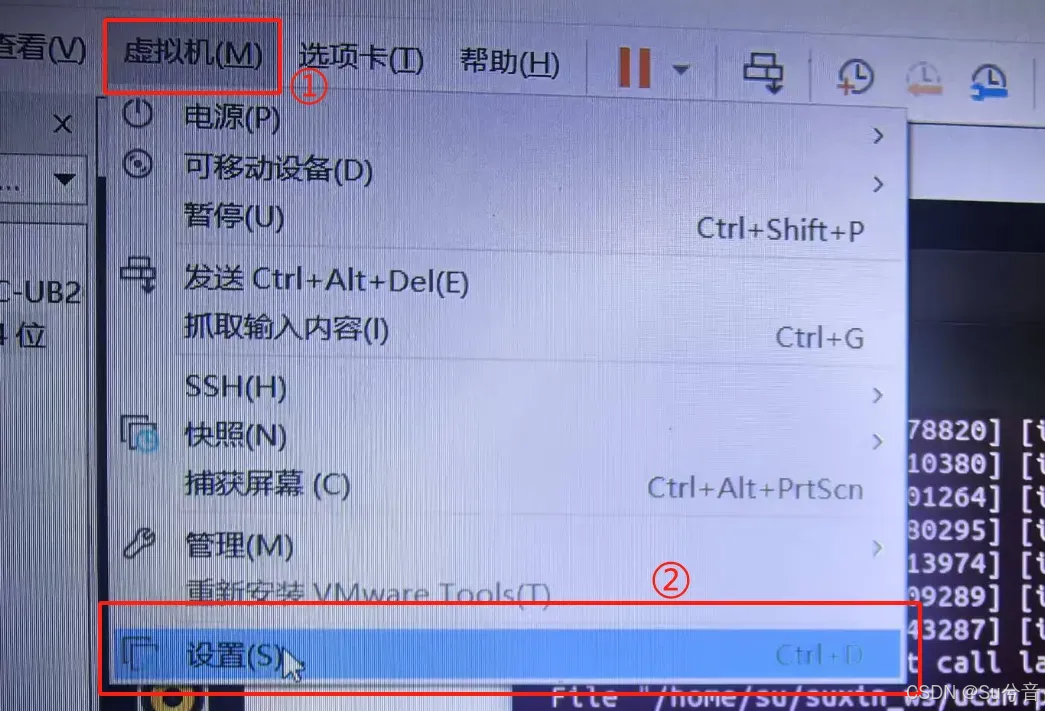
(3)打开【虚拟机→设置→USB控制器】,其中 USB2.0 和 USB3.1都可以尝试,看哪个能正常打开摄像头