✨✨谢谢大家捧场,祝屏幕前的小伙伴们每天都有好运相伴左右,一定要天天开心哦!✨✨
🎈🎈作者主页: 🎈丠丠64-CSDN博客🎈
✨✨ 帅哥美女们,我们共同加油!一起进步!✨✨
目录
一、前言
在 Java 中,异常处理是一种重要的编程概念,用于处理程序执行过程中可能出现的错误或异常情况。异常是程序中的一些错误,但并不是所有的错误都是异常,并且错误有时候是可以避免的。
二、Exception 类的层次
所有的异常类是从 java.lang.Exception 类继承的子类
- Throwable:是异常体系的顶层类,其派生出两个重要的子类, Error 和 Exception
- Error:错误指的是Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题
- Exception:异常产生后程序员可以通过代码进行处理,使程序继续执行

三、异常的分类
1.编译时异常
public class Test {
private String name;
private String gender;
int age;
@Override
public Test clone() {
return (Test)super.clone();
}
}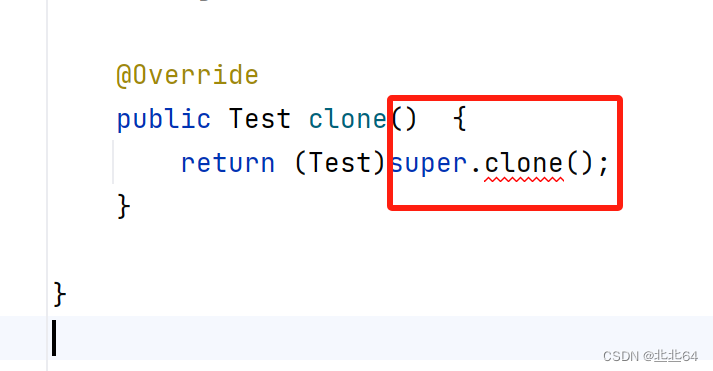
像这样在没有编译之前就报错 提醒的称为编译时异常,不包括语法错误!
2.运行时异常
System.out.println(10 / 0); //算数异常
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; //数组越界异常
System.out.println(arr[100]);
int[] arr = null; //空指针异常
System.out.println(arr.length);
这些在编译时没问题,运行时有问题的称为异常时处理
四、异常的处理
如果本方法中没有合适的处理异常的方式, 就会沿着调用栈向上传递,如果向上一直传递都没有合适的方法处理异常, 最终就会交给 JVM 处理, 程序就会异常终止
1.异常的抛出throw
throw new XXXException ( " 异常产生的原因 " );
int a = 0;
if(a == 0){
throw new ArithmeticException("异常为 a = 0");
}
2.异常声明throws
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名 ( 参数列表 ) throws 异常类型 1 ,异常类型 2 ...{}
抛出运行时异常是不需要处理的;但是如果是一个编译性异常,我们需要处理这个异常,最简单的方式就是通过throws处理(一搬放在方法声明的地方)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0;
if(a == 0){
throw new CloneNotSupportedException("异常为 a = 0");
}
}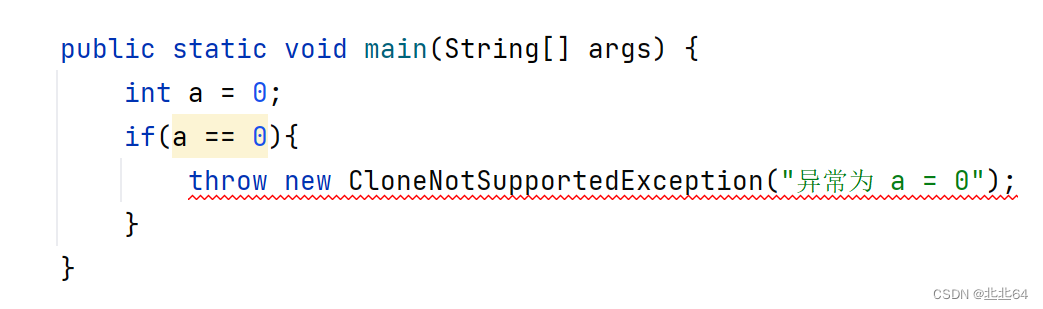
加上throws CloneNotSupportedException后,错误消失

public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
public static void test() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
int a = 0;
if(a == 0){
throw new CloneNotSupportedException("异常为 a = 0");
}
}
我们发现Test问题向上抛给main处理,但main没有处理继续向上抛,所以报错,解决方案有两种
- 一种是异常再声明声明一下 throws

3.try-catch捕获并处理
- 第二种使用try-catch捕获并处理

语法格式:try {// 将可能出现异常的代码放在这里} catch ( 要捕获的异常类型 e ){// 如果 try 中的代码抛出异常了,此处 catch 捕获时异常类型与 try 中抛出的异常类型一致时,或者是 try 中抛出异常的基类时,就会被捕获到// 对异常就可以正常处理,处理完成后,跳出 try-catch 结构,继续执行后序代码} catch ( 异常类型 e ){// 对异常进行处理} finally {// 此处代码一定会被执行到}
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
int a = 10 / 0;
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("捕获到了异常");
}
System.out.println("后续的代码");
}异常成功捕获,由程序员处理,退出代码为0

try {
int a = 10 / 0;
}catch (NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("捕获到了异常");
}
System.out.println("后续的代码");
}
异常捕获失败,异常类型不匹配,也就不会被处理,继续往外抛,直到JVM收到后中断程序,退出代码为1

try {
int a = 10 / 0;
System.out.println("66666666");
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("捕获到了异常");
}
System.out.println("后续的代码");我们发现当异常抛出后,异常后面代码将不会执行

try 中可能会抛出多个不同的异常对象,则必须用多个 catch 来捕获,但是只能抛出一个异常
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
int a = 10 / 0;
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("捕获到了异常111");
}catch (NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("捕获到了异常222");
}
System.out.println("后续的代码");
}
如果异常之间具有父子关系,一定是子类异常在前catch,父类异常在后catch,否则则会报错
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
int a = 10 / 0;
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("捕获到了异常111");
}catch (NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("捕获到了异常222");
}
System.out.println("后续的代码");
}Exception 是所有异常的父类,所以报错

4.finally
语法格式:try {// 可能会发生异常的代码} catch ( 异常类型 e ){// 对捕获到的异常进行处理} finally {// 此处的语句无论是否发生异常,都会被执行到}// 如果没有抛出异常,或者异常被捕获处理了,这里的代码也会执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int a = 10 / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到了异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally代码");
}
System.out.println("后续的代码");
} 
五、自定义异常类
public class LogIn {
private String userName = "admin";
private String password = "123456";
public void loginInfo(String userName, String password) {
if (!this.userName.equals(userName)) {
System.out.println("名字错误");
}
if (!this.password.equals(password)) {
System.out.println("密码错误");
}
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}
public void main(String[] args) {
LogIn logIn = new LogIn();
logIn.loginInfo("admin", "123456");
}
}- 继承自 Exception 的异常默认是受查异常
- 继承自 RuntimeException 的异常默认是非受查异常
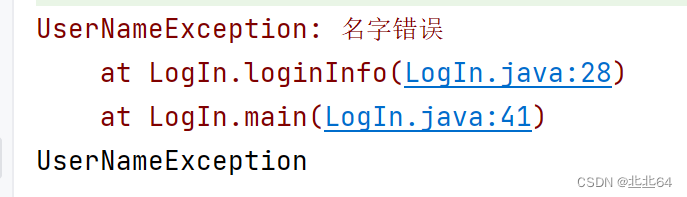
class UserNameException extends RuntimeException {
public UserNameException() {
}
public UserNameException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}class PasswordException extends Exception {
public PasswordException() {
}
public PasswordException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}public class LogIn {
private String userName = "admin";
private String password = "123456";
public void loginInfo(String userName, String password) throws UserNameException,PasswordException{
if (!this.userName.equals(userName)) {
//System.out.println("名字错误");
throw new UserNameException("名字错误");
}
if (!this.password.equals(password)) {
//System.out.println("密码错误");
throw new PasswordException("密码错误");
}
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LogIn logIn = new LogIn();
try{
logIn.loginInfo("admin1", "123456");
} catch (PasswordException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("PasswordException");
}catch (UserNameException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("UserNameException");
}
}
}
这样就实现了自定义异常,使我们查找错误会特别方便
希望对你有帮助