// fields 格式为 {"类的属性名":"Excel表头字段名"}
public Class<?> addAnnotation(Map<String, String> fields, String className) throws CannotCompileException, NotFoundException {
// 获取导出类所有的属性名
List<String> fieldList = new ArrayList<>(fields.keySet());
// 单例模式初始化 ClassPool
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 可以取一个没有进行实例化的类。这里我们会从头生成一个符合导入要求的新类
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass(className);
// 给新生成的类添加 Serializable 接口
ctClass.addInterface(pool.get(Serializable.class.getName()));
ClassFile classFile = ctClass.getClassFile();
ConstPool constpool = classFile.getConstPool();
// 给新生成的类添加 @Data 注解和 @ExcelTarget(value = "新生成类的类名") 注解
// 这个地方的 @Data 其实并没有起到作用(待研究)
AnnotationsAttribute classAttr = new AnnotationsAttribute(constpool, AnnotationsAttribute.visibleTag);
Annotation annotation = new Annotation(Data.class.getCanonicalName(), constpool);
AnnotationsAttribute classAttr1 = new AnnotationsAttribute(constpool, AnnotationsAttribute.visibleTag);
Annotation annotation1 = new Annotation(ExcelTarget.class.getCanonicalName(), constpool);
annotation1.addMemberValue("value", new StringMemberValue(className.substring(className.lastIndexOf('.') + 1), constpool));
Annotation[] annotations = new Annotation[]{annotation, annotation1};
classAttr.setAnnotations(annotations);
ctClass.getClassFile().addAttribute(classAttr);
// 给新生成的类添加字段
for (int i = 0; i < fieldList.size(); i++) {
// 增加字段
CtField field = new CtField(pool.get(String.class.getCanonicalName()),fieldList.get(i),ctClass);
field.setModifiers(Modifier.PRIVATE);
FieldInfo fieldInfo = field.getFieldInfo();
ctClass.addField(field);
//创建要添加的注解
Annotation fieldAnnotation = new Annotation(Excel.class.getCanonicalName(), constpool);
//设置注解中的属性和值,目标格式为 @Excel(name = "Excel表头字段名")
fieldAnnotation.addMemberValue("name", new StringMemberValue(fields.get(fieldList.get(i)), constpool));
//添加getter setter方法
ctClass.addMethod(CtNewMethod.setter("set" + UpFirst(fieldList.get(i)), field));
ctClass.addMethod(CtNewMethod.getter("get" + UpFirst(fieldList.get(i)), field));
AnnotationsAttribute annotationsAttribute = new AnnotationsAttribute(constpool, AnnotationsAttribute.visibleTag);
annotationsAttribute.addAnnotation(fieldAnnotation);
field.getFieldInfo().addAttribute(annotationsAttribute);
}
// 这里重新 new 一个 ClassLoader, 是为了防止一个类加载器加载两个相同的类导致报错
Class<?> res = ctClass.toClass(new ClassLoader() {
@Override
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return super.loadClass(name);
}
});
// 如果CtClass通过writeFile(),toClass(),toBytecode()转换了类文件,javassist冻结了CtClass对象。以后是不允许修改这个 CtClass对象。这是为了警告开发人员当他们试图修改一个类文件时,已经被JVM载入的类不允许被重新载入。这里我们为了可以多次修改类文件,所以进行手动解冻
// ctClass.writeFile("E:/workspace/annotation"); 可以将新生成的类的 class 文件持久化在本地。
if (ctClass.isFrozen()){
ctClass.defrost();
}
return res;
}
// 将 set/get 方法的属性名首字母大写
private static String UpFirst(String str){
return str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + str.substring(1);
}
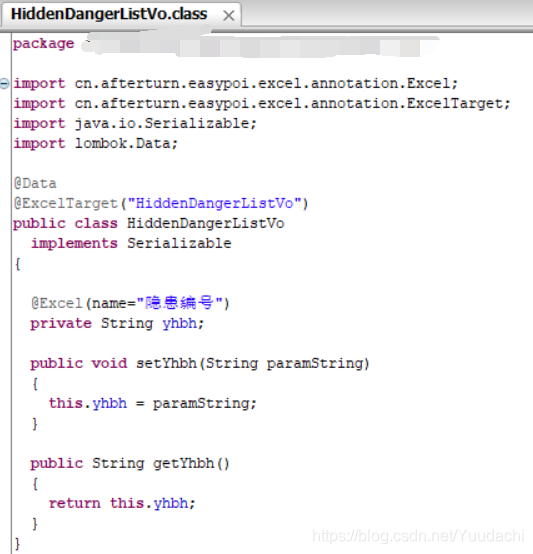
我们将 CtClass.writeFile 保存的 class 文件进行反编译,可以看到如下代码:
调用我们的 addAnnotation 方法获得新生成的类,并进行 Excel 导出
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Map<String, String> fields = new HashMap();
fields.put("name","姓名");
fields.put("age", "年龄");
Class<?> annotatedClass = addAnnotation(fields, xxx.class.getName());
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
// xxxService.list() 从数据库查询完整数据
for (Xxx xxx : xxxService.list()) {
Object target = annotatedClass.newInstance();
// 将其中部分数据的值复制到我们新生成的类上面
BeanUtil.copyProperties(xxx, target);
list.add(target);
}
// EasyPoi 导出
List<EasyPoiUtil.SheetConfig> configList = new ArrayList<>();
EasyPoiUtil.SheetConfig sheetConfig = new EasyPoiUtil.SheetConfig();
sheetConfig.setName("Excel表名");
sheetConfig.setData(list);
configList.add(sheetConfig);
String fileName = "Excel文件名.xlsx";
try {
EasyPoiUtil.exportExcel(configList, fileName, annotatedClass, true, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}