UE引擎的UWorld是什么,UWorld与GWorld的关系
UWorld有一些关于游戏的重要信息,比如(PersistentLevel,NetDriver,GameState),没有它,你不能做你想做的大部分事情。
GWorld是个全局指针变量,指向UWorld的指针(Global UWorld pointer)。
定义在文件:Engine\Source\Runtime\Engine\Classes\Engine\World.h
/** Global UWorld pointer. Use of this pointer should be avoided whenever possible. */
extern ENGINE_API class UWorldProxy GWorld; World 是代表地图或沙箱的顶级对象,Actor 和组件将存在于其中并进行渲染。
一个世界可以是一个单一的持久关卡,带有一个可选的流式关卡列表,这些关卡通过卷和蓝图函数加载和卸载或者它可以是使用 World Composition 组织的关卡集合。
在独立游戏中,通常只有一个世界存在,除非在无缝区域转换期间同时存在目的地和当前世界。
在编辑器中存在许多世界:正在编辑的关卡、每个 PIE 实例、每个具有交互式渲染视口的编辑器工具等等。
class UWorld : public UObject
{
public:
// ...
class ULevel* PersistentLevel;
class UNetDriver* NetDriver;
class AGameNetworkManager* NetworkManager;
// ...
class AGameStateBase* GameState;
// ...
class ULevel* CurrentLevel;
class UGameInstance* OwningGameInstance;
// ...
};UWorld代理类:
/** Proxy class that allows verification on GWorld accesses. */
class UWorldProxy
{
public:
UWorldProxy() :
World(NULL)
{}
inline UWorld* operator->()
{
// GWorld is changed often on the game thread when in PIE, accessing on any other thread is going to be a race condition
// In general, the rendering thread should not dereference UObjects, unless there is a mechanism in place to make it safe
checkSlow(IsInGameThread());
return World;
}
inline const UWorld* operator->() const
{
checkSlow(IsInGameThread());
return World;
}在内存中查看UWorld:
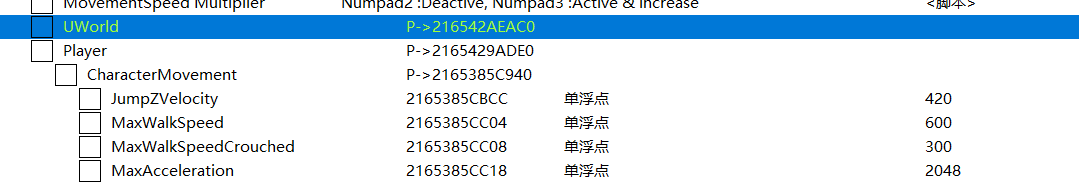
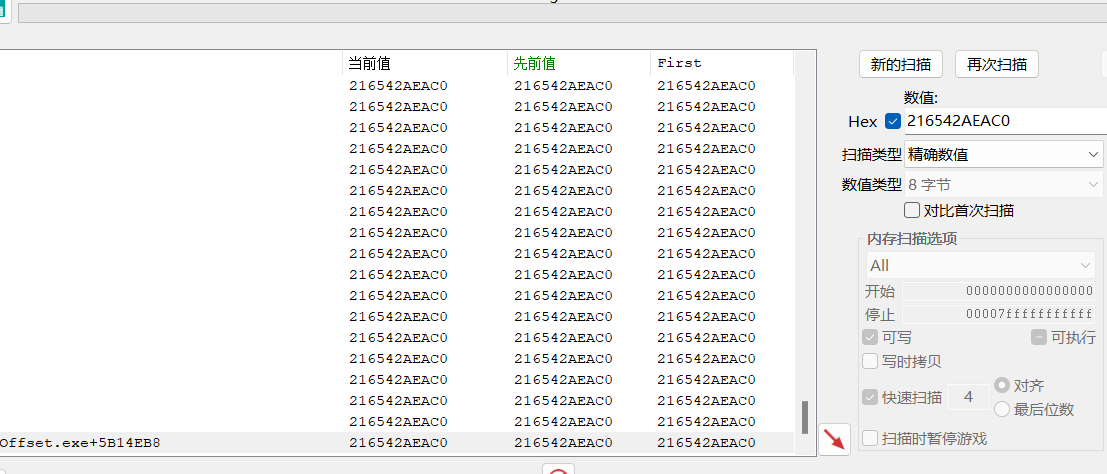
FirstPersonExampleMap 0x216542AEAC0 World
查看 UWorld偏移量:ExeModuleBase+0x5B14EB8
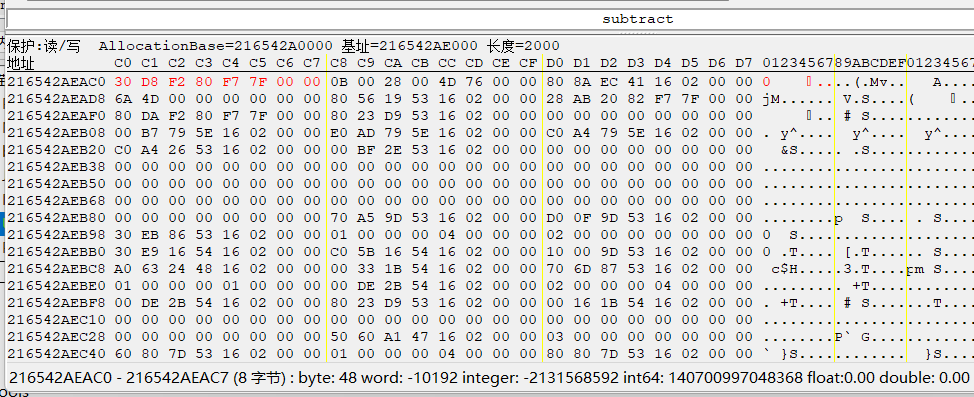
查看UWorld内存布局: