1、owner介绍
官网: https://owner.aeonbits.org/
github: https://github.com/lviggiano/owner
github中文翻译: https://github.com/cyfonly/owner-doc
OWNER API是一个Java库,其目标是在应用程序中最大程度地减少properties文件处理所需代码。在自动化测试中,需要处理Properties属性配置文件,使用owner使得整个开发过程变得更加流畅。
2、安装依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aeonbits.owner</groupId>
<artifactId>owner-java8</artifactId>
<version>1.0.12</version>
</dependency>
3、使用
映射规则
-
默认映射规则
定义的接口和配置文件名称需要相同,而且要在同一个包下,这样Owner才会自动关联他们; -
非默认映射规则
如果配置文件和接口不在一个包下,而且文件名也不一样,这时可以通过@Sources注解指定配置文件;这样配置文件和接口也会关联起来;
properties文件中定义的属性名也会自动和java类中相同名字的方法关联,如果属性名和方法名称不一样,可以通过@Key注解指定配置文件中的属性名;另外将会自动进行关联类型的转换。
常用注解:
@Sources中的参数为资源地址数组,可以选择多个,从多个文件中查找
@Sources支持的文件路径格式
| 格式 | 示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 类路径资源 | classpath:config.properties | 从项目的 src/main/resources 或 JAR 内加载。 |
| 文件系统路径 | file:/path/to/config.properties | 绝对路径或相对路径。 |
| URL 资源 | http://example.com/config.json | 支持 HTTP/HTTPS 协议。 |
| 系统属性 | system:properties | 读取 System.getProperties()。 |
| 环境变量 | env:variables | 读取 System.getenv()。 |
@LoadPolicy:指定加载策略。
- LoadType.FIRST:属性值只会从第一个被找到的文件中加载,一但有匹配的文件被加载,其它的都会被忽略;
- LoadType.MERGE:会加载所有的配置文件,但是属性值以第一个properties文件的为准;
@DefaultValue:指定默认值;
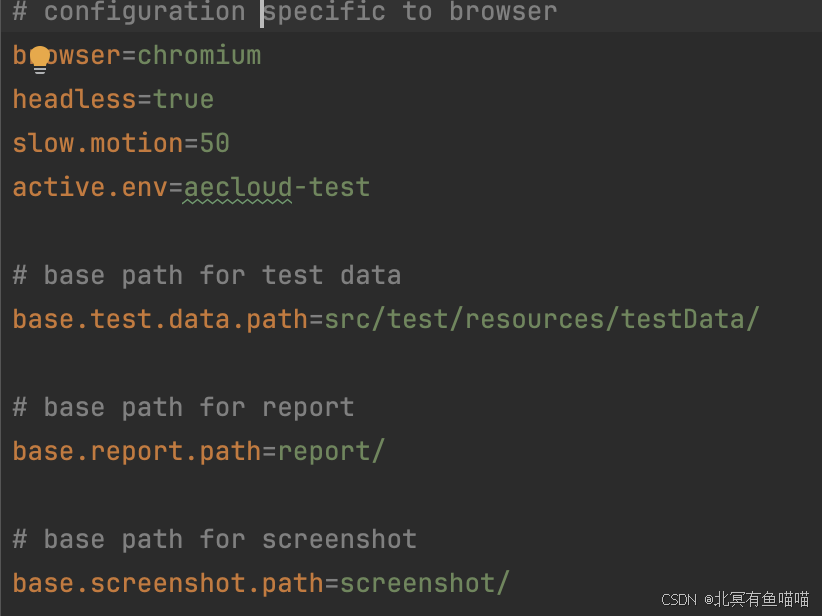
配置文件:
先定义一个与properties配置文件映射的接口。接口需要继承Config类。
@Config.LoadPolicy(Config.LoadType.MERGE)
@Config.Sources({
"classpath:config/general.properties",
"system:properties",
"system:env"
}
)
public interface Configuration extends Config {
/**
* @return a string containing the browser name
*/
@Key("browser")
String browser();
/**
* @return a boolean containing the choice whether the browser will run in headless mode
*/
@Key("headless")
Boolean headless();
/**
* @return an integer containing the slow motion value
*/
@Key("slow.motion")
int slowMotion();
/**
* @return a string containing active env setting
*/
@Key("active.env")
String activeEnv();
/**
* @return a string containing the base path to store all the test data
*/
@Key("base.test.data.path")
String baseTestDataPath();
/**
* @return a string containing the base path to store all the test reports
*/
@Key("base.report.path")
String baseReportPath();
/**
* @return a string containing the base path to store all the failed test screenshots
*/
@Key("base.screenshot.path")
String baseScreenshotPath();
}
public final class ConfigurationManager {
private ConfigurationManager() {}
/**
* @return an instance of Configuration class from an internal cache
* @see <a href="http://owner.aeonbits.org/docs/singleton">reference</a>
*/
public static Configuration configuration() {
// 顺序加载配置文件、系统属性、系统环境变量中的key-value键值对,使用时直接引用configuration()
return ConfigCache.getOrCreate(Configuration.class, System.getProperties(), System.getenv());
}
3.1、ConfigCache 和 ConfigFactory创建配置实例的区别
ConfigCache 和 ConfigFactory 都是 org.aeonbits.owner 库中用于创建配置实例的类,但它们有一些关键的区别和适用场景。下面是它们的区别和用法说明:
ConfigFactory
ConfigFactory 是用于创建新的配置实例的工厂类。每次调用 ConfigFactory.create 方法时,它都会创建一个新的配置实例。
优点
每次调用都会创建一个新的配置实例,适合需要不同配置实例的场景。
灵活性高,可以根据需要动态创建配置实例。
ConfigCache
ConfigCache 是用于缓存配置实例的类。使用 ConfigCache 创建的配置实例会被缓存,多次调用 ConfigCache.getOrCreate 方法会返回相同的配置实例。
优点
提供单例模式的配置实例,确保配置实例在整个应用程序生命周期内唯一。
提高性能,避免重复创建配置实例。
区别总结
实例创建方式:
ConfigFactory 每次调用都会创建一个新的配置实例。
ConfigCache 会缓存配置实例,多次调用会返回相同的实例。
适用场景:
ConfigFactory 适合需要多个不同配置实例的场景。
ConfigCache 适合需要单例配置实例,避免重复创建,提高性能的场景。
性能和资源利用:
ConfigFactory 每次创建新的实例,消耗资源更多。
ConfigCache 通过缓存实例,减少资源消耗,提高性能。