注:本文分析的内容,针对的是Spring 2.5.6的版本
ApplicationContext是spring IoC容器的顶级接口,其类结构图如下:
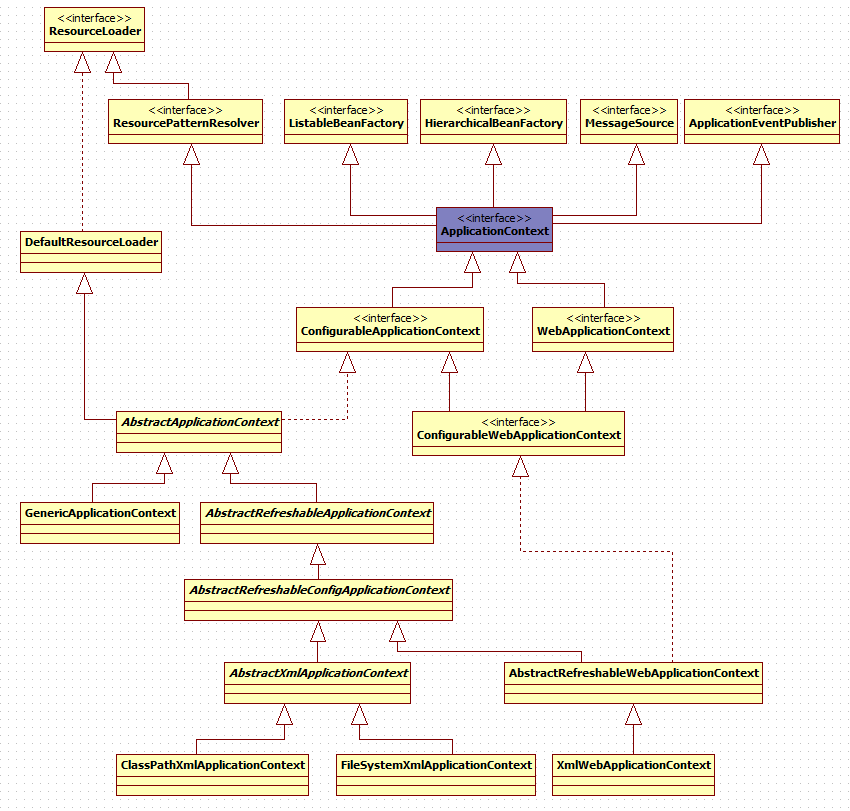
从上面的类图中可以看出, ApplicationContext继承了ResourceLoader接口,便于获取外部资源;也间接继承了 BeanFactory接口,这样可以在Spring容器中创建Bean对象;同时也继承了ApplicationEventPublisher接口,用于发送一些事件消息。
通常我们使用这样的一行代码来创建并启动Spring容器:
1、prepareRefresh()
该方法所做的事情相对比较简单:记录容器启动的时间,并设置容器处于活跃状态。
2、obtainFreshBeanFactory()
该方法的作用:创建BeanFactory实例,并解析Spring的xml配置文件。beanFactory的实现类是:ConfigurableListableBeanFactory。方法的实现如下:
ApplicationContext是spring IoC容器的顶级接口,其类结构图如下:

从上面的类图中可以看出, ApplicationContext继承了ResourceLoader接口,便于获取外部资源;也间接继承了 BeanFactory接口,这样可以在Spring容器中创建Bean对象;同时也继承了ApplicationEventPublisher接口,用于发送一些事件消息。
通常我们使用这样的一行代码来创建并启动Spring容器:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//1、 Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
//2、 Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//3、 Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//4、 Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//5、 Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//6、 Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//7、 Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
//8、 Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//9、 Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
//10、 Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
//11、 Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//12、 Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
beanFactory.destroySingletons();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}1、prepareRefresh()
该方法所做的事情相对比较简单:记录容器启动的时间,并设置容器处于活跃状态。
2、obtainFreshBeanFactory()
该方法的作用:创建BeanFactory实例,并解析Spring的xml配置文件。beanFactory的实现类是:ConfigurableListableBeanFactory。方法的实现如下:
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Bean factory for application context [" &#