内容概要
- 如何构建GET 与 POST request 请求消息
- 对 request 的header , query string, message body 定制化
- http header参数 content-type 的设置
- 分析request, response 消息数据
- 通过POST请求向服务器上传文件,,以及从服务器接收文件
- 请求与响应使用 json 格式
为什么推荐使用 requests 模块?
用 python 编写 http request 消息代码时,建议用requests库。因为requests比urllib内置库更为简捷,requests可以直接构造get,post请求并发送,而urllib.request只能先构造get,post请求消息内容,然后再发送。并且requests 模块提供了更友好的方法与属性来解析response消息内容。
1. 准备知识
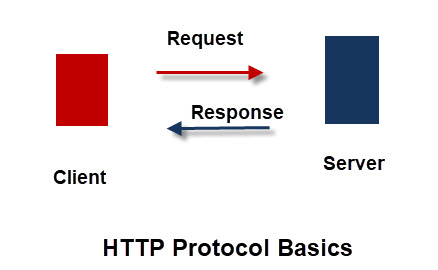
1.1 HTTP request 与 Response 通讯机制
http协议是基于1种客户机(client) – 服务器(server) 的通信模式,它的下层是TCP协议。
- 所有的请求request 都是由客户机发起的
- 服务器对客户请求做出响应response
- 每个request 都是独立于其它request消息,服务器不需要跟踪request消息的状态
1.2 Http Request 请求与响应消息
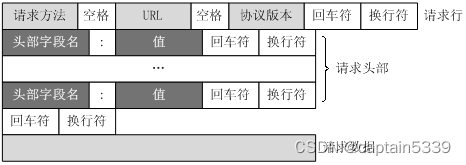
客户端发送一个HTTP请求到服务器的请求消息由四个部分组成
- 请求行(request line)
- 头部(header)、
- 空行(CLF)
- 报文主体(payload,或body)
下图给出了请求报文的一般格式。
上图中,可以看到。Request 请求行第1个字节为请求方法, 有时也称动词(verb), 常用的主要有4种方法:GET, POST, PUT, DELETE。
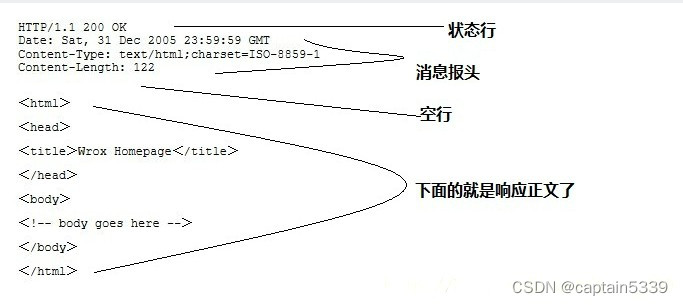
1.3 Http Response 响应消息
服务器的响应消息,也是由4部分组成
状态行、头部、空行和响应正文
请求消息与响应消息的头部都是由头部字段构成,它能起到传递额外重要信息的作用。 使用首部字段是为了给浏览器和服务器提供报文主体大小、所使用的语言、认证信息等内容。
头部字段的格式,如下
字段名: 字段值
如
Content-Type: text/html
就以上述示例来看,首部字段名为 Content-Type,字符串 text/html 是字段值。
另外,字段值对应单个 HTTP 首部字段可以有多个值,如下所示。
Keep-Alive: timeout=15, max=100
头部字段通常也用于携带用户身份信息,如访问知名站点时,对方通常会在响应的头部添加 set-cookie字段,其中包含用户id,token等加密后的数据。此后的请求的头部也会添加cookie 字段。
2. 安装 requests 模块
安装requests 模块非常简单,
pip install requests
3. 发送 GET 请求
3.1 request.get() 方法
get()方法用于准备并发送 http get 请求至指定url , 并返回response 对象
语法
requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs)
- url: 拟获取页面的url链接
- params: url中的额外参数,字典或字节流格式,可选
**kwargs: 可选参数.
url 完整格式
最终发送的完整url, 是将输入url 与parameters 拼接形成,格式如下:
url格式:http://host_ip:port/path/add?key1=value1&key2=value2
3.2 GET 方法的请求参数 QueryParameters
get方法的请求参数是通过 params来传递的。 其类型为字典,
params={ key1: value1, key2: value2 }
response = requests.get(
'https://api.github.com/search/repositories',
params={'name': 'Jack','type':'display'},
)
requests 模块会将url与parameters 拼接成完整的请求消息
ttps://api.github.com/search/repositories?name=Jack&type=display
可能遇到的问题 : 如果GET请求参数中包含汉字,常会遇到编码错误
主要原因:http协议对URL参数的编码要求是ASCII字符集,而汉字是UTF-8。在发送时要进行两次编码才能将汉字转为ASCII字节码:
- 第1次编码, 用 UTF-8 字符集,每个汉字占3个字节。
- 第2次编码,可以用 iso-8859-1,然后再转为ASCII,也可以用其它字符集来转ASCII。
同样,接收方也要进行两次解码,才能正确地还原汉字。
还好,python 内置库urllib 提供了1条命令,1次就可以将汉字转为ASCII编码。
编码: urllib.parse.urlencode(dic)
解码: urllib.parse.unquote(dic or str)
示例代码
keyword = "天气预报"
param_list = urllib.parse.urlencode( { 'q' : keyword } ) #包含汉字
header = {'user-Agent':’haha‘}
url = 'http://www.baidu.com/s/'
response = request.get( url, params=param_list, headers = header )
3.3 get()方法的可选参数
get()方法的可选参数 **kwargs部分,常见的参数主要有:
- headers 设置头部参数,字典类型
- cookies 设置cookie,也是字典类型。
- auth, tupe类型,用于基本鉴权
- proxies 设置代理服务器
- stream, 为bool类型,如果请求二进制文件,图片等应设置为True
- timeout, 超时时间,为秒
headers = {
'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1',
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=UTF-8'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers,timeout=10)
3.4 Response 对象常用属性及方法
查看响应消息内容
响应内容的文本格式:response.text>>> r = requests.get('https://api.github.com/events')
>>> r.text
'[{"repository":{"open_issues":0,"url":"https://github.com/...
响应内容的二进制格式: response.content
>>>r.content
b'[{"repository":{"open_issues":0,"url":"https://github.com/...
如果响应内 容是json格式,可以用Response.json()方法转换成 dict类型
>>> r = requests.get('https://api.github.com/events')
>>> r.json()
[{'repository': {'open_issues': 0, 'url': 'https://github.com/...
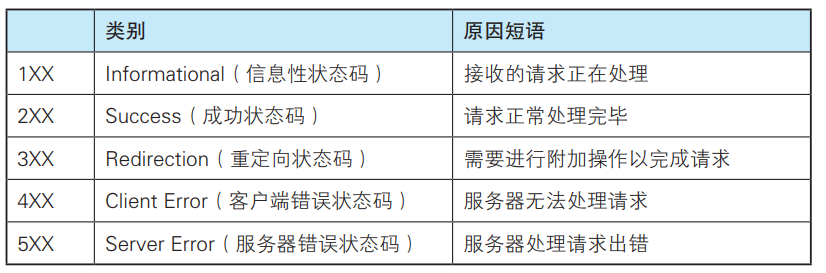
分析status_code
收到response后,需要分析响应状态码status_code,有必要可以对404, 500等出错响应进行特殊处理。import requests
from requests.exceptions import HTTPError
for url in ['https://api.github.com', 'https://api.github.com/invalid']:
try:
response = requests.get(url)
# If the response was successful, no Exception will be raised
response.raise_for_status()
except HTTPError as http_err:
print(f'HTTP error occurred: {http_err}') # Python 3.6
except Exception as err:
print(f'Other error occurred: {err}') # Python 3.6
else:
print('Success!')
当调用 .raise_for_status(), 对特定的status_code将产生1个 HTTPError 异常
Status_code
收到响应状态码301重定向
如果收到的status_code 为301,可以从response.url中获取新的url.
response = requests.get("http://192.168.3.100/demo/")
new_url = response.url
异常 response 消息
如果发出request后,收到异常的response, 可以用下面的数据检查 :
>>> response = requests.post('https://httpbin.org/post', json={'key':'value'})
>>> response.request.headers['Content-Type']
'application/json'
>>> response.request.url
'https://httpbin.org/post'
>>> response.request.body
b'{"key": "value"}'
或将所有头部字段打印出来:
resp = requests.get(url, headers=header)
for head in resp.headers:
print(head, ":", resp.headers[head])
output类似于:
Date : Thu, 13 Jul 2023 05:00:49 GMT
Server : WSGIServer/0.2 CPython/3.9.4
Content-Type : text/html; charset=utf-8
X-Frame-Options : DENY
Content-Length : 3669
X-Content-Type-Options : nosniff
Referrer-Policy : same-origin
4. 发送 POST 请求
4.1 requests.post()方法的使用
与GET请求不同的是, POST 请求参数是放在 request body 里发送的,
post() 语法
requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
POST请求参数使用data, 或json传入。data的数据类型可以是dict,tuple, list等, json也就是json。
返回类型为 response类型。
# 请求参数以字典方式坆
post_dict = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
# 以元组方式传入
post_tuple = (('key1', 'value1'), ('key1', 'value2'))
# 用json格式
post_json = { "some": "data" }
headers = { "Content-Type": "application/json" }
r1 = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=post_dict)
r2 = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=post_tuple)
r3 = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", json=post_json, headers=headers)
收到 Response。 Response对象主要属性与方法,请参考上一节内容。
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 19
Content-Type: application/json
{"success":"true"}
4.2 POST 消息设置 cookie, header
import requests
# 请求数据
url = 'http://api.shein.com/v2/member/login'
cookie = "token=code_space;"
header = {
"cookie": cookie,
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate, br",
"Accept-Language": "zh-CN,zh;q=0.9",
"Connection": "keep-alive",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) "
"AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.159 Safari/537.36"
}
data = {
'user_id': '123456',
'email': '[email protected]'
}
timeout = 0.5
resp = requests.post(url, headers=header, data=data, timeout=timeout)
print(resp.text)
print(type(resp.json()))
4.3 用 POST请求向服务器上传文件
客户端可通过POST请求,向服务器上传文件
#形式1
url = 'http://httpbin.org/post'
#定义文件对象
files = {"files":open('test.xls', 'rb')}
response = requests.post(url,files = files)
print(response.text)
#形式2
url ='http://httpbin.org/post'
files = {'file': ('t.xls', open('t.xls', 'rb'), 'application/vnd.ms-excel', {'Expires': '0'})}
r = requests.post(url, files=files)
r.text
#形式3, 发送多个文件
url = 'http://httpbin.org/post'
files = {'file': ('t.csv', 'bb.csv')}
response = requests.post(url, files=files)
response.text
4.4 从服务器接收文件
向服务器请求1个2进制文件时,stream设置为True.
r = requests.get('https://api.github.com/events', stream=True)
print(r.raw.read(10))
r.raw 是文件原始内容,可以用文件的方式读取,如 r.raw.read(10)。 如果尺寸不大,可直接保存到文件。如果收到的内容比较大,用response的 iter_content()方法来分块保存,以避免内存溢出等风险
with open(filename, 'wb') as fd:
for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=128):
fd.write(chunk)
4.5 基本鉴权
当服务器web应用的认证采用的是基本鉴权(Basic authentication) 时,使用auth参数传入username与password。 get(), post() 均支持。
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
requests.post(url, auth=HTTPBasicAuth("username", "password"))
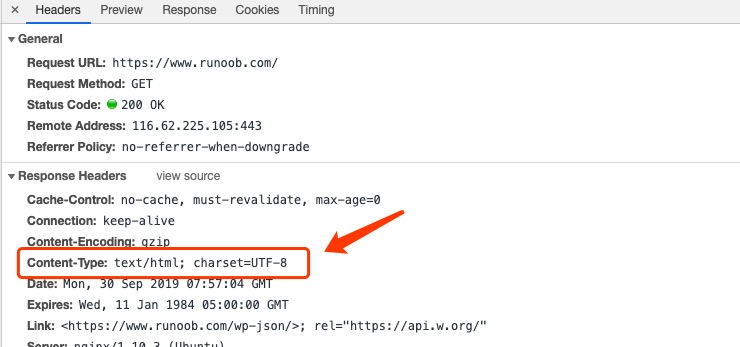
5、请求与响应头部的 content-type 参数说明
上一切,发送json格式请求参数时,要设置头部参数"Content-Type": “application/json”,
Content-Type 参数用于告诉服务器或浏览器,http 消息所包含资源的类型。这个参数在request 与 response消息中都可能包含,是 response 消息头部非常关键1个参数,也是开发者应该掌握的1个知识点。其内容格式是 IETF’s RFC 6838 标准中的 MIME Type(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions).
先看1个实际消息示例 :
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=something
content-type 参数的语法格式:
type/subtype
- type 代表数据资源的大类,如 text (文本类型), video(视频类型)等
- subtype 是资源子类,如,对于 text类,subtype 可能是 plain(纯文本),csv 或者html等。
content-type还可以附加参数
type/subtype;parameter=value
常见情形:当type是 text类型,文本内容是中文,需添加charset参数,指定编码类型:
Content-Type: text/html;charset=UTF-8
在http协议以及行业内,有很多通用的建议值,最常见的:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded, 这是提交表单默认的content-type设置, 对应form属性为 enctype=“application/x-www-form-urlencoded”。multipart/form-data, 用于 form 上传文件application/json传json数据text/html传网页text/plain text/xml传文本image/jpeg传图片video/mp4传MP4视频
等。
注:
- 对于"application/x-www-form-urlencoded" 编码,如果两端都是用request编程,则不需要编解码,request 模块会自动完成。
下面是 content-type 可能用到的 type/subtype 列表:
| Type | Subtype |
|---|---|
| Application | application/javascript application/pdf application/xhtml+xml application/json application/ld+json application/xml application/zip application/x-www-form-urlencoded application/octet-stream : 二进制流数据(如常见的文件下载) |
| Audio | audio/mpeg audio/x-ms-wma |audio audio/x-wav |
| Image | image/gif image/jpeg image/png image/tiff i mage/vnd.microsoft.icon image/x-icon image/vnd.djvu image/svg+xml |
| Multipart | multipart/mixed multipart/alternative multipart/related (using by MHTML (HTML mail).) multipart/form-data |
| Text | text/css text/csv text/html text/plain text/xml |
| Video | video/mpeg video/mp4 video/quicktime video/x-ms-wmv video/x-msvideo video/x-flv video/webm |
| VND | application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.text application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.spreadsheet application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.presentation application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.graphics application/vnd.ms-excel application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet application/vnd.ms-powerpoint application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation application/msword application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document application/vnd.mozilla.xul+xml |
6. 用 json 做 payload
payload 就是通过http Post,get发送的数据,包括请求参数,文件,图片等, 发送方可以将用json类型来准备这些数据,接收方用json解开。
这在Header 里约定好。如下, 但注意,header 不能是json格式。
import json
import requests
url = "http://www.example.com"
payload = {'data': 12345, }
rep = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload))
print(rep.text.json())
用 data 参数提交数据时, request.body 的内容则为 a=1&b=2 的这种形式,
用 json 参数提交数据时, request.body 的内容则为’“a”: 1, “b”: 2’ 的这种形式
如
POST /echo/post/json HTTP/1.1
Host: reqbin.com
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 52
{
"Id": 12345
}
检查响应消息response头部参数’content-type’,如果为 “application/json”,表示内容为 json 格式. 可使用response对象内置方法json()查看响应消息的内容
>>> r.headers['content-type']
'application/json; charset=utf8'
>>> r.json()
{"success": "true", "data": { "TotalOrders": 100 } }
7. 其它requests 方法
其它请求消息, PUT与PATCH与 POST类似。 DELETE, HEAD与GET类似。
>>> requests.put('https://httpbin.org/put', data={'key':'value'})
>>> requests.delete('https://httpbin.org/delete')
>>> requests.head('https://httpbin.org/get')
>>> requests.patch('https://httpbin.org/patch', data={'key':'value'})
>>> requests.options('https://httpbin.org/get')