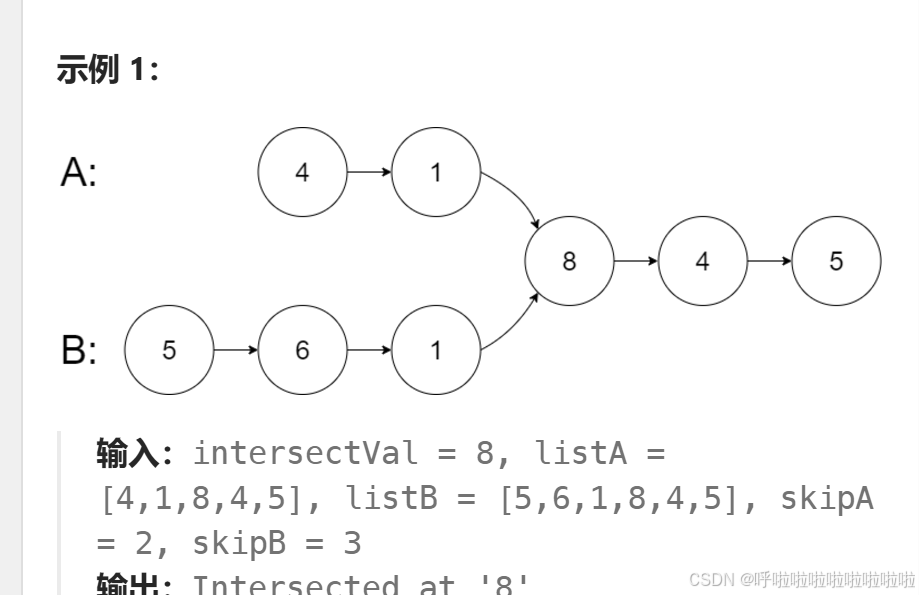
相交链表
题目分析:
暴力解法:
计算链表的长度: 首先我们需要知道链表 A 和链表 B 的长度。因为在开始比较两个链表是否相交之前,我们需要确保它们有相同的起始点。从长度上来说,两个链表的交点一定会出现在它们后续部分的某个地方。如果两个链表的长度不同,那么我们可以通过调整链表的头节点来使它们有相同的比较起点。
对齐链表的起始位置: 假设链表 A 比链表 B 长
len1 - len2个节点,那么我们可以让链表 A 从第len1 - len2个节点开始遍历;如果链表 B 比链表 A 长,那么我们让链表 B 从第len2 - len1个节点开始遍历。这样我们就确保了两个链表的后续部分从相同的节点开始比较。同时遍历两个链表: 在对齐了起始位置之后,我们就可以同步地遍历两个链表。如果两个链表在某个节点相遇,那么这个节点就是它们的交点。如果遍历结束后还没有相遇,就说明两个链表没有交点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode cur1 = headA;
ListNode cur2 = headB;
int len1 = 0, len2 = 0;
while (cur1 != null) {
len1++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != null) {
len2++;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
int len = len1-len2;
if(len < 0) {
ListNode tmp = headA;
headA = headB;
headB = tmp;
len = len2 - len1;
}
while(len != 0) {
headA = headA.next;
len--;
}
while(headA != null && headB!=null) {
if(headA == headB) {
return headA;
}
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}二.更优解
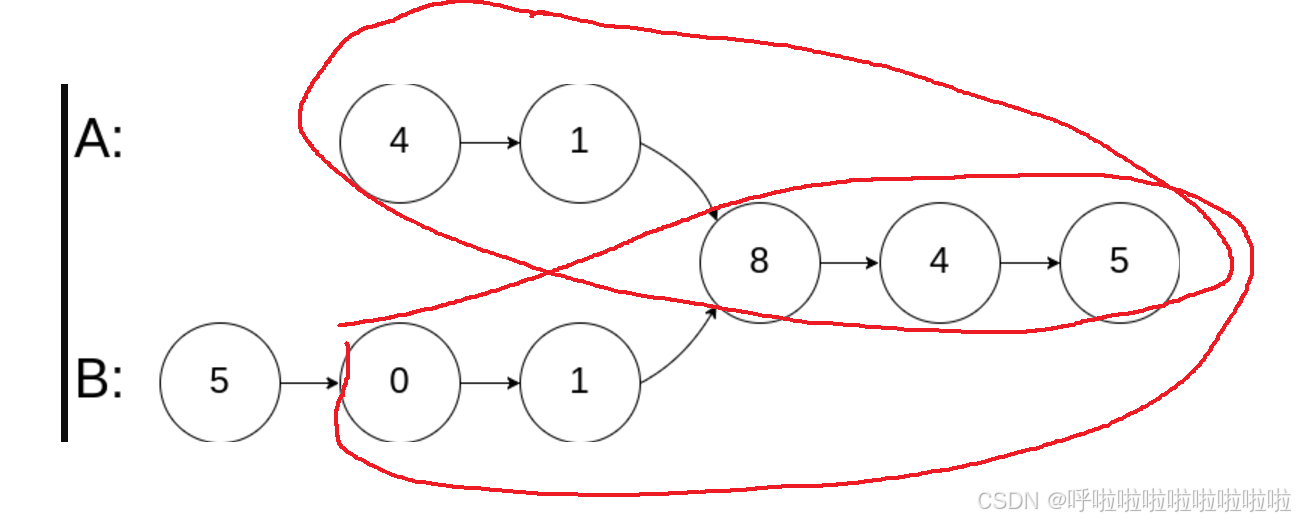
- 假设两个链表
A和B的长度分别为m和n,它们有交点时,交点之后的部分是相同的。- 双指针通过遍历两个链表,保证它们在遍历完各自链表后会同步开始从对方链表的头节点开始走。这样,两指针最终会在交点相遇。假如没有交点,它们会同时到达
null。- M+N = N+M
- 即使双方没有交点,最后也都返回了null
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode cur1 = headA;
ListNode cur2 = headB;
while(cur1 != cur2 ) {
cur1 = cur1 != null ? cur1.next : headB;
cur2 = cur2 != null ? cur2.next : headA;
}
return cur1;
}
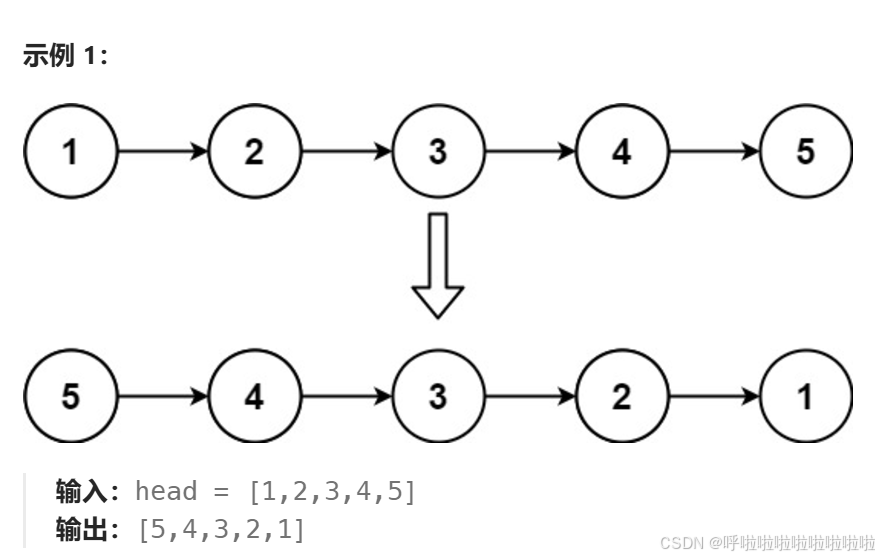
}反转链表
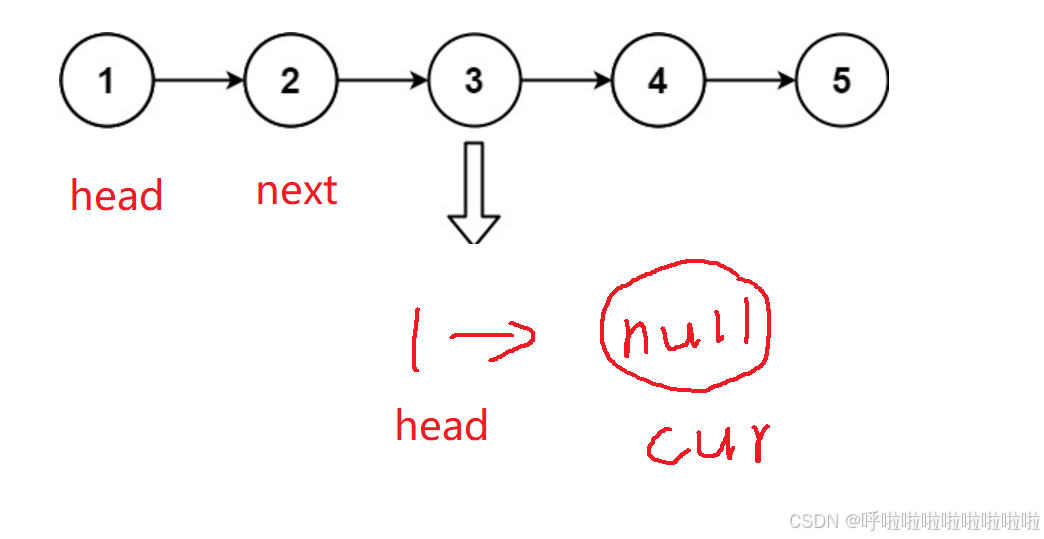
反转的过程可以分为以下几个步骤:
- 保存下一个节点next(防止丢失链表的剩余部分)。
- 改变当前节点的head 指针,指向cur。
- 更新
cur,表示反转后的链表的当前节点。- 更新head,指向next
- 继续遍历原链表,直到链表遍历完。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = null;
while(head != null) {
ListNode next= head.next;
head.next = cur;
cur = head;
head = next;
}
return cur;
}
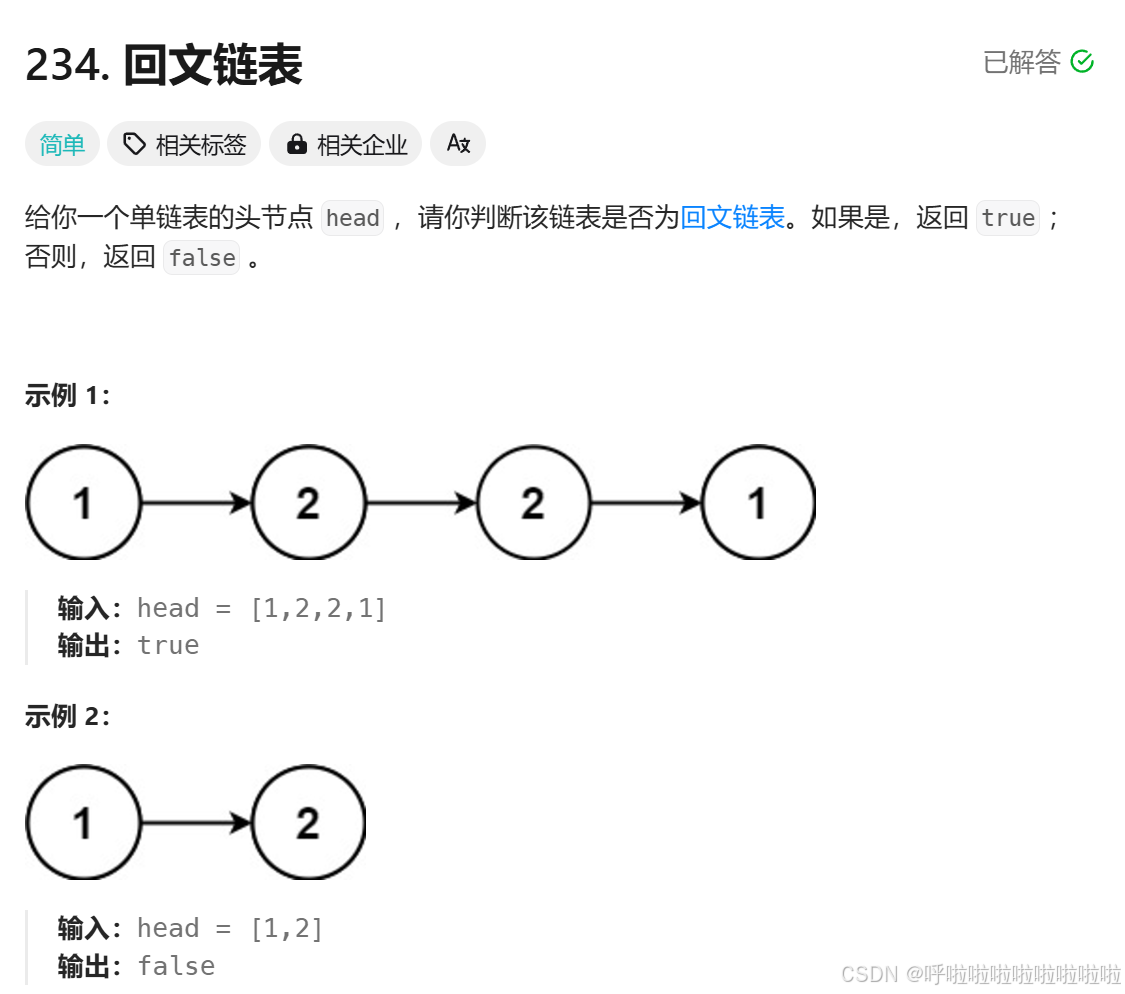
}回文链表

class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
//1.找到中间节点
while(fast !=null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//2.翻转后半部分链表 从slow开始
ListNode cur = null;
while(slow != null) {
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = cur;
cur = slow;
slow = next;
}
//3.从head 和 cur位置进行遍历
while(cur != null) {
if(head.val != cur.val) {
return false;
}else {
head = head.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return true;
}
}环形链表
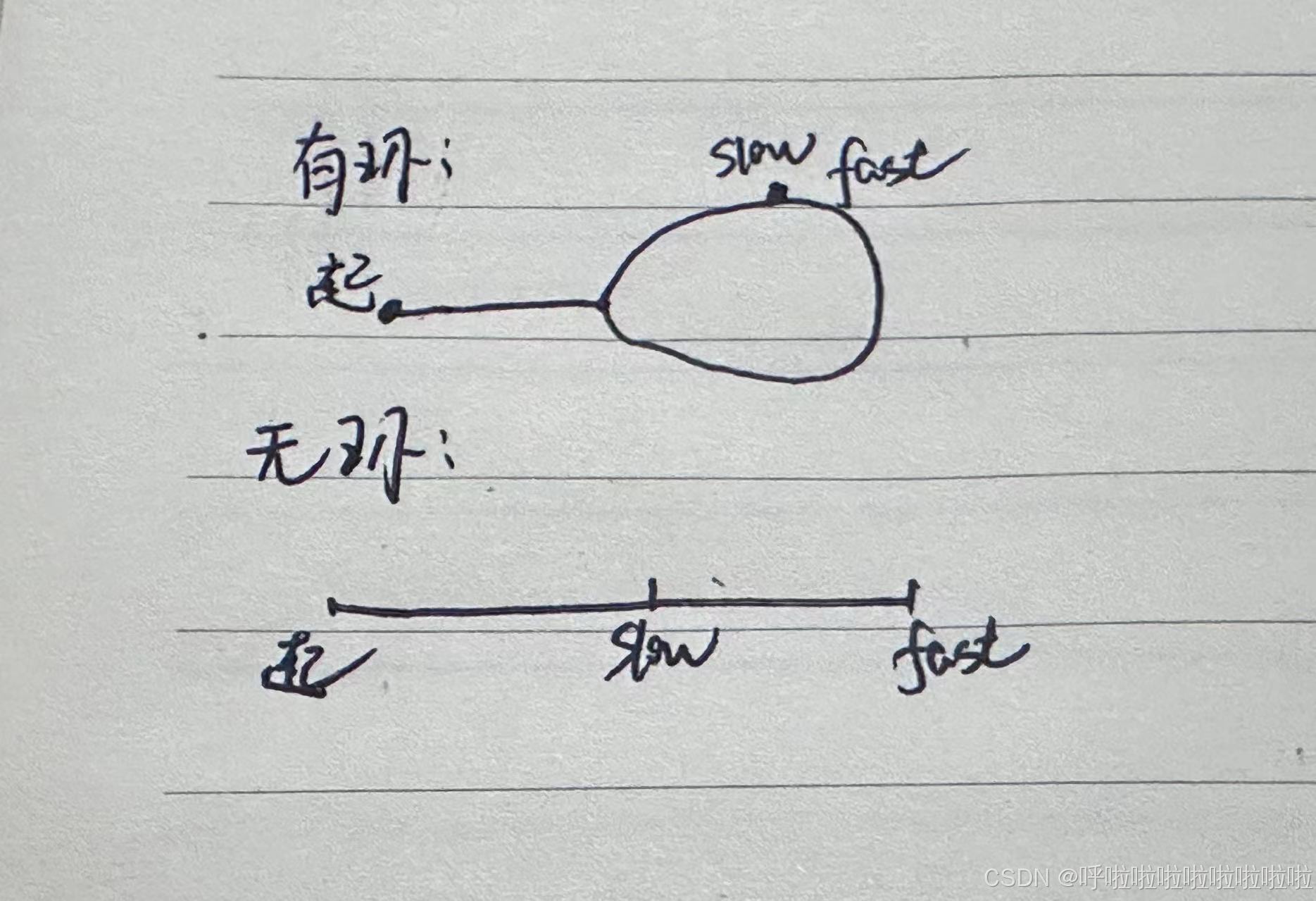
判断是否有环,执行一个快慢指针
当一个慢指针走一步,快指针走俩步,在一个圈里面,快指针将一定能追上慢指针
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}环形链表 II
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
fast = head;
while (true) {
if(slow == fast) {
return fast;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}合并两个有序链表
初始化: 伪头节点 dum ,节点 cur 指向 dum 。
循环合并: 当 l1 或 l2 为空时跳出。当 l1 .val<l 2 .val 时: cur 的后继节点指定为 l1,并 l1向前走一步。
当 l1 .val≥l 2 .val 时: cur 的后继节点指定为 l2 ,并 l2 向前走一步 。
节点 cur 向前走一步,即 cur=cur.next 。
合并剩余尾部: 跳出时有两种情况,即 l1为空 或 l2为空。
若 l1=null : 将 l1添加至节点 cur 之后。
否则: 将 l2添加至节点 cur 之后。
返回值:合并链表在伪头节点 dum 之后,因此返回 dum.next 即可。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dum = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dum ;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val >= list2.val) {
cur.next = list2;
cur = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
} else {
cur.next = list1;
cur = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
}
if (list1 != null) {
cur.next = list1;
}
if (list2 != null) {
cur.next = list2;
}
return dum .next;
}
}递归方法:
- 终止条件:两条链表分别名为 l1 和 l2,当 l1 为空或 l2 为空时结束
- 返回值:每一层调用都返回排序好的链表头
- 本级递归内容:如果 l1 的 val 值更小,则将 l1.next 与排序好的链表头相接,l2 同理
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null) return list2;
if(list2 == null) return list1;
if(list1.val < list2.val) {
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}else {
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}两数相加
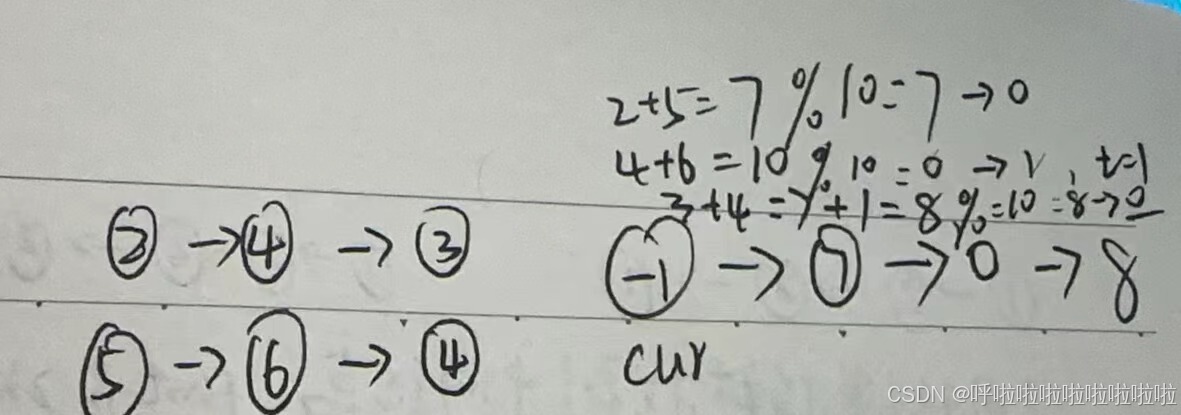
- 通过
l1和l2按位相加,处理每个节点。- 用
t记录当前位的和,并处理进位(t % 10存入当前节点,t / 10作为进位传递到下一位)。- 当所有节点处理完毕,并且没有进位时,结束循环。
- 返回结果链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = newHead;
int t = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null || t !=0 ) {
if(l1 != null) {
t += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if(l2 != null) {
t+= l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur.next = new ListNode(t%10);
cur = cur.next;
t /=10;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}