ArrayList顺序表(数据结构)
文章目录
👺 前言
ArrayList是一个动态类型的顺序表,即:在插入元素的过程中会自动扩容。 底层就像是一个数组,只不过会自动扩容。
一、顺序表的介绍及实现
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成
数据的增删查改。
模拟实现的顺序表有如下几个功能:
- 新增元素data(默认在数组最后新增)
- 在 pos 位置新增元素
- 判定是否包含某个元素
- 查找某个元素对应的位置
- 获取 pos 位置的元素
- 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
- 删除第一次出现的关键字key
- 获取顺序表长度
- 清空顺序表
接下来就是模拟实现的代码:
public class SeqList {
private int[] elem; //创建数组
private int usedSize; //记录当前数组中元素个数
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 5; //默认数组最大容量
public SeqList() { //无参构造,初始化数组大小为5;
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}
public boolean isFull(){ //判断数组是否满了
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){ //判断数组是否是为空
return usedSize == 0;
}
public void reSize(){ //给数组增容
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
public void add(int data) { // 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
if(isFull()){
reSize(); //增容
}
this.elem[usedSize] = data;
usedSize++;
}
public void add(int pos, int data) { // 在 pos 位置新增元素
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize-1){
throw new PosOutBoundsException("add 元素的时候,pos位置不合法!");
}
if(isFull()){
reSize();
}
for (int i = this.usedSize-1; i >= pos ; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
if(i == pos){
elem[pos] = data;
}
}
usedSize++;
}
public boolean contains(int toFind) { // 判定是否包含某个元素
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize-1; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int indexOf(int toFind) { // 查找某个元素对应的位置
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize-1; i++) {
if(elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public int get(int pos) { // 获取 pos 位置的元素
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize-1){
throw new PosOutBoundsException("get 元素的时候,pos位置不合法!");
}
return elem[pos];
}
public void set(int pos, int value) { // 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize - 1){
throw new PosOutBoundsException("get 元素的时候,pos位置不合法!");
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
public void remove(int toRemove) { //删除第一次出现的关键字key
if(isEmpty()){
return;
}
int index = indexOf(toRemove);
if(index == -1){
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize - 1 ; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
}
public int size() { // 获取顺序表长度
return this.usedSize;
}
public void clear() { // 清空顺序表
this.usedSize = 0;
}
// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i <= this.usedSize-1; i++) {
System.out.print(elem[i] + " ");
}
}
}
二、ArrayList使用
1、ArrayList的构造
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | 无参构造 |
| ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) | 利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList |
| ArrayList(int initialCapacity) | 指定顺序表初始容量 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造一个空的列表
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
// 构造一个具有10个容量的列表
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(10);
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
list2.add(3);
// 编译失败,List<Integer>已经限定了,list2中只能存储整形元素
list2.add("hello");
// list3构造好之后,与list2中的元素一致
ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>(list2);
// 避免省略类型,否则:任意类型的元素都可以存放,使用时将是一场灾难
List list4 = new ArrayList();
list4.add("111");
list4.add(100);
}
2、ArrayList常见操作
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中,返回(ture/false) |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
3、ArrayList的遍历
ArrayList 可以使用三方方式遍历:for循环+下标、foreach、使用迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
// 使用下标+for遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
// 借助foreach遍历
for (Integer integer : list) {
System.out.print(integer + " ");
}
//利用迭代器遍历
Iterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
4、ArrayList的扩容机制
以下是ArrayList源码中扩容方式:
Object[] elementData; // 存放元素的空间
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认空间
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默认容量大小
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// 获取旧空间大小
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 预计按照1.5倍方式扩容
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 如果用户需要扩容大小 超过 原空间1.5倍,按照用户所需大小扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果需要扩容大小超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新计算容量大小
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 调用copyOf扩容
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 如果minCapacity小于0,抛出OutOfMemoryError异常
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
【总结】
-
检测是否真正需要扩容,如果是调用grow准备扩容
-
预估需要库容的大小
- 初步预估按照1.5倍大小扩容
- 如果用户所需大小超过预估1.5倍大小,则按照用户所需大小扩容
- 真正扩容之前检测是否能扩容成功,防止太大导致扩容失败
-
使用copyOf进行扩容
三、ArrayList具体的使用
1、简单的洗牌算法
Card类
public class Card {
private String suit ;
private int rank;
public Card(String suit, int rank) {
this.suit = suit;
this.rank = rank;
}
public String getSuit() {
return suit;
}
public void setSuit(String suit) {
this.suit = suit;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
public void setRank(int rank) {
this.rank = rank;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return suit + " " + rank;
}
}
Test类
public class Test { //简单的洗牌算法
public static final String[] SUIT = {"♠","♣","♦","♥"};
//买一副扑克
public static List<Card> buyCard(){
List<Card> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < SUIT.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {
Card card = new Card(SUIT[i], j);
list.add(card);
}
}
return list;
}
//洗牌,将所有牌打乱。
public static void shuffle(List<Card> cards){
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = cards.size() - 1; i > 0 ; i--) {
int j = random.nextInt(i);
Card temp = cards.get(i);
cards.set(i, cards.get(j));
cards.set(j, temp);
}
}
// 三个人,每个人轮流抓 5 张牌
public static void playCards(){
List<Card> cards = buyCard();
List<Card> hand1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Card>> hand = new ArrayList<>();
hand.add(hand1);
hand.add(hand2);
hand.add(hand3);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Card card = cards.remove(0);
hand.get(j).add(card);
}
}
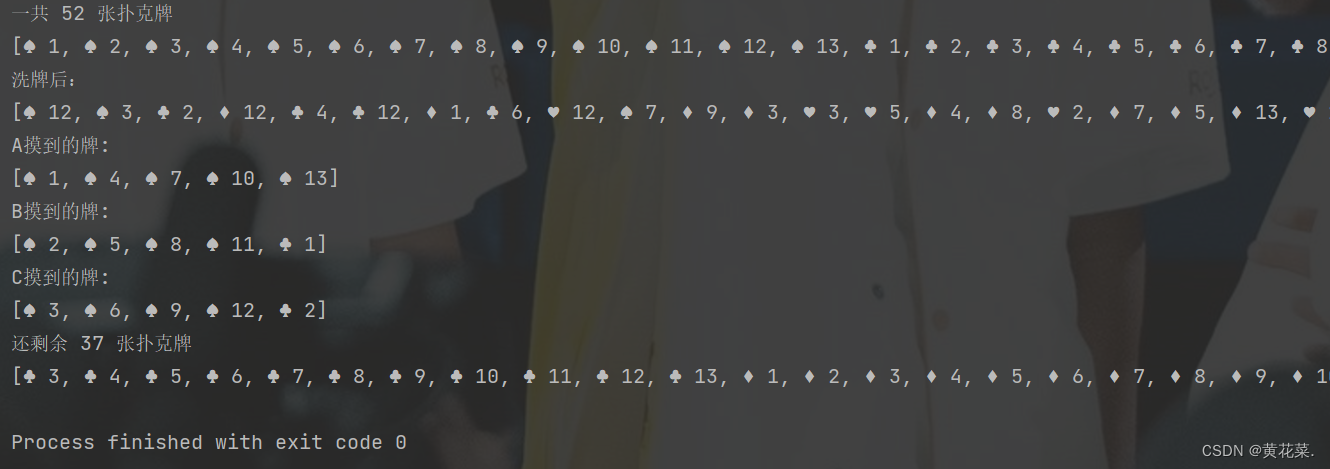
System.out.println("A摸到的牌: ");
System.out.println(hand1);
System.out.println("B摸到的牌: ");
System.out.println(hand2);
System.out.println("C摸到的牌: ");
System.out.println(hand3);
System.out.println("还剩余 " + cards.size() + " 张扑克牌");
System.out.println(cards);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Card> cards = buyCard();
System.out.println("一共 " + cards.size() + " 张扑克牌");
System.out.println(cards);
System.out.println("洗牌后:");
shuffle(cards);
System.out.println(cards);
playCards();
}
}
结果展示:
2、 杨辉三角 - 力扣(LeetCode)
核心思想:a[i] [j] = a[i - 1] [j] + a[i - 1] [j -1] ,类似与二维数组, 因此在使用ArrayList的时候要注意尖括号里面的接受值。
List<List> ret = new ArrayList<>();
直接上代码:
public class Test { //力扣的 杨辉三角形
public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
ret.add(list);
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> curRows = new ArrayList<>();
curRows.add(1);
//[i][j] = [i-1][j] + [i][j-1]
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
curRows.add(ret.get(i - 1).get(j) + ret.get(i - 1).get(j - 1));
}
curRows.add(1);
ret.add(curRows);
}
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ret = generate(5);
System.out.println(ret);
System.out.println("====");
}
}
四、ArrayList的问题及思考
优点:
- 根据指定下表(索引)去查找元素,效率非常高!时间复杂度:O(1)
- 更新元素也很快:更新指定下表的元素!!!!
缺点:
- 每次插入数据,都需要移动元素,极端情况下,如果插入到0下标,那么移动的元素复杂度为O(n)
- 每次删除数据的时候,都需要移动元素,极端情况下,删除0下标的元素:O(N)
- 当满了之后,进行扩容,1.5倍扩容。然后只放了1个元素,可能会有浪费空间!!!!!!
总结:顺序表适合用于 经常进行查找元素或者更新元素的场景下 才推荐使用
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Z0qb8TRk-1680971516614)(C:\Users\28779\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230409002220529.png)]](/image/aHR0cHM6Ly9pLWJsb2cuY3NkbmltZy5jbi9ibG9nX21pZ3JhdGUvY2NiZTM5NDM2N2UzZDBkY2FhNmY5MmNmZDY1ZjkyMWQucG5n)
