上一篇文档(SpringCloud从入门到精通之超详细文档一)已经对Springboot/SpringCloud做了简单的介绍以及应用讲解,下面将继续为大家介绍SpringCloud后续应用。
第12课:分布式锁
本达人课讲述的是基于 Spring Cloud 的分布式架构,那么也带来了线程安全问题,比如一个商城系统,下单过程可能由不同的微服务协作完成,在高并发的情况下如果不加锁就会有问题,而传统的加锁方式只针对单一架构,对于分布式架构是不适合的,这时就需要用到分布式锁。
实现分布式锁的方式有很多,本文结合我的实际项目和目前的技术趋势,通过实例实现几种较为流行的分布式锁方案,最后会对不同的方案进行比较。
基于 Redis 的分布式锁
利用 SETNX 和 SETEX
基本命令主要有:
- SETNX(SET If Not Exists):当且仅当 Key 不存在时,则可以设置,否则不做任何动作。
- SETEX:可以设置超时时间
其原理为:通过 SETNX 设置 Key-Value 来获得锁,随即进入死循环,每次循环判断,如果存在 Key 则继续循环,如果不存在 Key,则跳出循环,当前任务执行完成后,删除 Key 以释放锁。
这种方式可能会导致死锁,为了避免这种情况,需要设置超时时间。
下面,请看具体的实现步骤。
1.创建一个 Maven 工程并在 pom.xml 加入以下依赖:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 开启web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.创建启动类 Application.java:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
3.添加配置文件 application.yml:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
4.创建全局锁类 Lock.java:
/**
* 全局锁,包括锁的名称
*/
public class Lock {
private String name;
private String value;
public Lock(String name, String value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
5.创建分布式锁类 DistributedLockHandler.java:
@Component
public class DistributedLockHandler {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DistributedLockHandler.class);
private final static long LOCK_EXPIRE = 30 * 1000L;//单个业务持有锁的时间30s,防止死锁
private final static long LOCK_TRY_INTERVAL = 30L;//默认30ms尝试一次
private final static long LOCK_TRY_TIMEOUT = 20 * 1000L;//默认尝试20s
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate template;
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock) {
return getLock(lock, LOCK_TRY_TIMEOUT, LOCK_TRY_INTERVAL, LOCK_EXPIRE);
}
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取超时时间 单位ms
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock, long timeout) {
return getLock(lock, timeout, LOCK_TRY_INTERVAL, LOCK_EXPIRE);
}
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取锁的超时时间
* @param tryInterval 多少毫秒尝试获取一次
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock, long timeout, long tryInterval) {
return getLock(lock, timeout, tryInterval, LOCK_EXPIRE);
}
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取锁的超时时间
* @param tryInterval 多少毫秒尝试获取一次
* @param lockExpireTime 锁的过期
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock, long timeout, long tryInterval, long lockExpireTime) {
return getLock(lock, timeout, tryInterval, lockExpireTime);
}
/**
* 操作redis获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取的超时时间
* @param tryInterval 多少ms尝试一次
* @param lockExpireTime 获取成功后锁的过期时间
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean getLock(Lock lock, long timeout, long tryInterval, long lockExpireTime) {
try {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(lock.getName()) || StringUtils.isEmpty(lock.getValue())) {
return false;
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
do{
if (!template.hasKey(lock.getName())) {
ValueOperations<String, String> ops = template.opsForValue();
ops.set(lock.getName(), lock.getValue(), lockExpireTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return true;
} else {//存在锁
logger.debug("lock is exist!!!");
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime > timeout) {//尝试超过了设定值之后直接跳出循环
return false;
}
Thread.sleep(tryInterval);
}
while (template.hasKey(lock.getName())) ;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage());
return false;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 释放锁
*/
public void releaseLock(Lock lock) {
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(lock.getName())) {
template.delete(lock.getName());
}
}
}
6.最后创建 HelloController 来测试分布式锁。
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private DistributedLockHandler distributedLockHandler;
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index(){
Lock lock=new Lock("lynn","min");
if(distributedLockHandler.tryLock(lock)){
try {
//为了演示锁的效果,这里睡眠5000毫秒
System.out.println("执行方法");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
distributedLockHandler.releaseLock(lock);
}
return "hello world!";
}
}
7.测试。
启动 Application.java,连续访问两次浏览器:http://localhost:8080/index,控制台可以发现先打印了一次“执行方法”,说明后面一个线程被锁住了,5秒后又再次打印了“执行方法”,说明锁被成功释放。
通过这种方式创建的分布式锁存在以下问题:
- 高并发的情况下,如果两个线程同时进入循环,可能导致加锁失败。
- SETNX 是一个耗时操作,因为它需要判断 Key 是否存在,因为会存在性能问题。
因此,Redis 官方推荐 Redlock 来实现分布式锁。
利用 Redlock
通过 Redlock 实现分布式锁比其他算法更加可靠,继续改造上一例的代码。
1.pom.xml 增加以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
</dependency>
2.增加以下几个类:
/**
* 获取锁后需要处理的逻辑
*/
public interface AquiredLockWorker<T> {
T invokeAfterLockAquire() throws Exception;
}
/**
* 获取锁管理类
*/
public interface DistributedLocker {
/**
* 获取锁
* @param resourceName 锁的名称
* @param worker 获取锁后的处理类
* @param <T>
* @return 处理完具体的业务逻辑要返回的数据
* @throws UnableToAquireLockException
* @throws Exception
*/
<T> T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker<T> worker) throws UnableToAquireLockException, Exception;
<T> T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker<T> worker, int lockTime) throws UnableToAquireLockException, Exception;
}
/**
* 异常类
*/
public class UnableToAquireLockException extends RuntimeException {
public UnableToAquireLockException() {
}
public UnableToAquireLockException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public UnableToAquireLockException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}
/**
* 获取RedissonClient连接类
*/
@Component
public class RedissonConnector {
RedissonClient redisson;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
redisson = Redisson.create();
}
public RedissonClient getClient(){
return redisson;
}
}
@Component
public class RedisLocker implements DistributedLocker{
private final static String LOCKER_PREFIX = "lock:";
@Autowired
RedissonConnector redissonConnector;
@Override
public <T> T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker<T> worker) throws InterruptedException, UnableToAquireLockException, Exception {
return lock(resourceName, worker, 100);
}
@Override
public <T> T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker<T> worker, int lockTime) throws UnableToAquireLockException, Exception {
RedissonClient redisson= redissonConnector.getClient();
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(LOCKER_PREFIX + resourceName);
// Wait for 100 seconds seconds and automatically unlock it after lockTime seconds
boolean success = lock.tryLock(100, lockTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (success) {
try {
return worker.invokeAfterLockAquire();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
throw new UnableToAquireLockException();
}
}
3.修改 HelloController:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private DistributedLocker distributedLocker;
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index()throws Exception{
distributedLocker.lock("test",new AquiredLockWorker<Object>() {
@Override
public Object invokeAfterLockAquire() {
try {
System.out.println("执行方法!");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
});
return "hello world!";
}
}
4.按照上节的测试方法进行测试,我们发现分布式锁也生效了。
Redlock 是 Redis 官方推荐的一种方案,因此可靠性比较高。
基于数据库的分布式锁
基于数据库表
它的基本原理和 Redis 的 SETNX 类似,其实就是创建一个分布式锁表,加锁后,我们就在表增加一条记录,释放锁即把该数据删掉,具体实现,我这里就不再一一举出。
它同样存在一些问题:
- 没有失效时间,容易导致死锁;
- 依赖数据库的可用性,一旦数据库挂掉,锁就马上不可用;
- 这把锁只能是非阻塞的,因为数据的 insert 操作,一旦插入失败就会直接报错。没有获得锁的线程并不会进入排队队列,要想再次获得锁就要再次触发获得锁操作;
- 这把锁是非重入的,同一个线程在没有释放锁之前无法再次获得该锁。因为数据库中数据已经存在了。
乐观锁
基本原理为:乐观锁一般通过 version 来实现,也就是在数据库表创建一个 version 字段,每次更新成功,则 version+1,读取数据时,我们将 version 字段一并读出,每次更新时将会对版本号进行比较,如果一致则执行此操作,否则更新失败!
悲观锁(排他锁)
实现步骤见下面说明。
1.创建一张数据库表:
CREATE TABLE `methodLock` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`method_name` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '锁定的方法名',
`desc` varchar(1024) NOT NULL DEFAULT '备注信息',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '保存数据时间,自动生成',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uidx_method_name` (`method_name `) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='锁定中的方法';
2.通过数据库的排他锁来实现分布式锁。
基于 MySQL 的 InnoDB 引擎,可以使用以下方法来实现加锁操作:
public boolean lock(){
connection.setAutoCommit(false)
while(true){
try{
result = select * from methodLock where method_name=xxx for update;
if(result==null){
return true;
}
}catch(Exception e){
}
sleep(1000);
}
return false;
}
3.我们可以认为获得排它锁的线程即可获得分布式锁,当获取到锁之后,可以执行方法的业务逻辑,执行完方法之后,再通过以下方法解锁:
public void unlock(){
connection.commit();
}
基于 Zookeeper 的分布式锁
ZooKeeper 简介
ZooKeeper 是一个分布式的,开放源码的分布式应用程序协调服务,是 Google Chubby 的一个开源实现,是 Hadoop 和 Hbase 的重要组件。它是一个为分布式应用提供一致性服务的软件,提供的功能包括:配置维护、域名服务、分布式同步、组服务等。
分布式锁实现原理
实现原理为:
- 建立一个节点,假如名为 lock 。节点类型为持久节点(Persistent)
- 每当进程需要访问共享资源时,会调用分布式锁的 lock() 或 tryLock() 方法获得锁,这个时候会在第一步创建的 lock 节点下建立相应的顺序子节点,节点类型为临时顺序节点(
EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL),通过组成特定的名字 name+lock+顺序号。 - 在建立子节点后,对 lock 下面的所有以 name 开头的子节点进行排序,判断刚刚建立的子节点顺序号是否是最小的节点,假如是最小节点,则获得该锁对资源进行访问。
- 假如不是该节点,就获得该节点的上一顺序节点,并监测该节点是否存在注册监听事件。同时在这里阻塞。等待监听事件的发生,获得锁控制权。
- 当调用完共享资源后,调用 unlock() 方法,关闭 ZooKeeper,进而可以引发监听事件,释放该锁。
实现的分布式锁是严格的按照顺序访问的并发锁。
代码实现
我们继续改造本文的工程。
1.创建 DistributedLock 类:
public class DistributedLock implements Lock, Watcher{
private ZooKeeper zk;
private String root = "/locks";//根
private String lockName;//竞争资源的标志
private String waitNode;//等待前一个锁
private String myZnode;//当前锁
private CountDownLatch latch;//计数器
private CountDownLatch connectedSignal=new CountDownLatch(1);
private int sessionTimeout = 30000;
/**
* 创建分布式锁,使用前请确认config配置的zookeeper服务可用
* @param config localhost:2181
* @param lockName 竞争资源标志,lockName中不能包含单词_lock_
*/
public DistributedLock(String config, String lockName){
this.lockName = lockName;
// 创建一个与服务器的连接
try {
zk = new ZooKeeper(config, sessionTimeout, this);
connectedSignal.await();
Stat stat = zk.exists(root, false);//此去不执行 Watcher
if(stat == null){
// 创建根节点
zk.create(root, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (KeeperException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
}
}
/**
* zookeeper节点的监视器
*/
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
//建立连接用
if(event.getState()== Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected){
connectedSignal.countDown();
return;
}
//其他线程放弃锁的标志
if(this.latch != null) {
this.latch.countDown();
}
}
public void lock() {
try {
if(this.tryLock()){
System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " " +myZnode + " get lock true");
return;
}
else{
waitForLock(waitNode, sessionTimeout);//等待锁
}
} catch (KeeperException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
}
}
public boolean tryLock() {
try {
String splitStr = "_lock_";
if(lockName.contains(splitStr))
throw new LockException("lockName can not contains \\u000B");
//创建临时子节点
myZnode = zk.create(root + "/" + lockName + splitStr, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL);
System.out.println(myZnode + " is created ");
//取出所有子节点
List<String> subNodes = zk.getChildren(root, false);
//取出所有lockName的锁
List<String> lockObjNodes = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String node : subNodes) {
String _node = node.split(splitStr)[0];
if(_node.equals(lockName)){
lockObjNodes.add(node);
}
}
Collections.sort(lockObjNodes);
if(myZnode.equals(root+"/"+lockObjNodes.get(0))){
//如果是最小的节点,则表示取得锁
System.out.println(myZnode + "==" + lockObjNodes.get(0));
return true;
}
//如果不是最小的节点,找到比自己小1的节点
String subMyZnode = myZnode.substring(myZnode.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
waitNode = lockObjNodes.get(Collections.binarySearch(lockObjNodes, subMyZnode) - 1);//找到前一个子节点
} catch (KeeperException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
}
return false;
}
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) {
try {
if(this.tryLock()){
return true;
}
return waitForLock(waitNode,time);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
private boolean waitForLock(String lower, long waitTime) throws InterruptedException, KeeperException {
Stat stat = zk.exists(root + "/" + lower,true);//同时注册监听。
//判断比自己小一个数的节点是否存在,如果不存在则无需等待锁,同时注册监听
if(stat != null){
System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " waiting for " + root + "/" + lower);
this.latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.latch.await(waitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);//等待,这里应该一直等待其他线程释放锁
this.latch = null;
}
return true;
}
public void unlock() {
try {
System.out.println("unlock " + myZnode);
zk.delete(myZnode,-1);
myZnode = null;
zk.close();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeeperException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
this.lock();
}
public Condition newCondition() {
return null;
}
public class LockException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public LockException(String e){
super(e);
}
public LockException(Exception e){
super(e);
}
}
}
2.改造 HelloController.java:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index()throws Exception{
DistributedLock lock = new DistributedLock("localhost:2181","lock");
lock.lock();
//共享资源
if(lock != null){
System.out.println("执行方法");
Thread.sleep(5000);
lock.unlock();
}
return "hello world!";
}
}
3.按照本文 Redis 分布式锁的方法测试,我们发现同样成功加锁了。
总结
通过以上的实例可以得出以下结论:
- 通过数据库实现分布式锁是最不可靠的一种方式,对数据库依赖较大,性能较低,不利于处理高并发的场景。
- 通过 Redis 的 Redlock 和 ZooKeeper 来加锁,性能有了比较大的提升。
- 针对 Redlock,曾经有位大神对其实现的分布式锁提出了质疑,但是 Redis 官方却不认可其说法,所谓公说公有理婆说婆有理,对于分布式锁的解决方案,没有最好,只有最适合的,根据不同的项目采取不同方案才是最合理的。
第13课:分布式事务
首先我们应知道,事务是为了保证数据的一致性而产生的。那么分布式事务,顾名思义,就是我们要保证分布在不同数据库、不同服务器、不同应用之间的数据一致性。
为什么需要分布式事务?
最传统的架构是单一架构,数据是存放在一个数据库上的,采用数据库的事务就能满足我们的要求。随着业务的不断扩张,数据的不断增加,单一数据库已经到达了一个瓶颈,因此我们需要对数据库进行分库分表。为了保证数据的一致性,可能需要不同的数据库之间的数据要么同时成功,要么同时失败,否则可能导致产生一些脏数据,也可能滋生 Bug。
在这种情况下,分布式事务思想应运而生。
应用场景
分布式事务的应用场景很广,我也无法一一举例,本文列举出比较常见的场景,以便于读者在实际项目中,在用到了一些场景时即可考虑分布式事务。
支付
最经典的场景就是支付了,一笔支付,是对买家账户进行扣款,同时对卖家账户进行加钱,这些操作必须在一个事务里执行,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。而对于买家账户属于买家中心,对应的是买家数据库,而卖家账户属于卖家中心,对应的是卖家数据库,对不同数据库的操作必然需要引入分布式事务。
在线下单
买家在电商平台下单,往往会涉及到两个动作,一个是扣库存,第二个是更新订单状态,库存和订单一般属于不同的数据库,需要使用分布式事务保证数据一致性。
银行转账
账户 A 转账到账户 B,实际操作是账户 A 减去相应金额,账户 B 增加相应金额,在分库分表的前提下,账户 A 和账户 B 可能分别存储在不同的数据库中,这时需要使用分布式事务保证数据库一致性。否则可能导致的后果是 A 扣了钱 B 却没有增加钱,或者 B 增加了钱 A 却没有扣钱。
SpringBoot 集成 Atomikos 实现分布式事务
Atomikos 简介
Atomikos 是一个为 Java 平台提供增值服务的开源类事务管理器。
以下是包括在这个开源版本中的一些功能:
- 全面崩溃 / 重启恢复;
- 兼容标准的 SUN 公司 JTA API;
- 嵌套事务;
- 为 XA 和非 XA 提供内置的 JDBC 适配器。
注释:XA 协议由 Tuxedo 首先提出的,并交给 X/Open 组织,作为资源管理器(数据库)与事务管理器的接口标准。目前,Oracle、Informix、DB2 和 Sybase 等各大数据库厂家都提供对 XA 的支持。XA 协议采用两阶段提交方式来管理分布式事务。XA 接口提供资源管理器与事务管理器之间进行通信的标准接口。XA 协议包括两套函数,以
xa_开头的及以ax_开头的。
具体实现
1.在本地创建两个数据库:test01,test02,并且创建相同的数据库表:
2.改造上篇的工程,在 pom.xml 增加以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.40</version>
</dependency>
3.修改配置文件 application.yml 如下:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
mysql:
datasource:
test1:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 1qaz2wsx
minPoolSize: 3
maxPoolSize: 25
maxLifetime: 20000
borrowConnectionTimeout: 30
loginTimeout: 30
maintenanceInterval: 60
maxIdleTime: 60
testQuery: select 1
test2:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 1qaz2wsx
minPoolSize: 3
maxPoolSize: 25
maxLifetime: 20000
borrowConnectionTimeout: 30
loginTimeout: 30
maintenanceInterval: 60
maxIdleTime: 60
testQuery: select 1
4.创建以下类:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mysql.datasource.test1")
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class DBConfig1 {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private int minPoolSize;
private int maxPoolSize;
private int maxLifetime;
private int borrowConnectionTimeout;
private int loginTimeout;
private int maintenanceInterval;
private int maxIdleTime;
private String testQuery;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getMinPoolSize() {
return minPoolSize;
}
public void setMinPoolSize(int minPoolSize) {
this.minPoolSize = minPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxPoolSize() {
return maxPoolSize;
}
public void setMaxPoolSize(int maxPoolSize) {
this.maxPoolSize = maxPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxLifetime() {
return maxLifetime;
}
public void setMaxLifetime(int maxLifetime) {
this.maxLifetime = maxLifetime;
}
public int getBorrowConnectionTimeout() {
return borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public void setBorrowConnectionTimeout(int borrowConnectionTimeout) {
this.borrowConnectionTimeout = borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public int getLoginTimeout() {
return loginTimeout;
}
public void setLoginTimeout(int loginTimeout) {
this.loginTimeout = loginTimeout;
}
public int getMaintenanceInterval() {
return maintenanceInterval;
}
public void setMaintenanceInterval(int maintenanceInterval) {
this.maintenanceInterval = maintenanceInterval;
}
public int getMaxIdleTime() {
return maxIdleTime;
}
public void setMaxIdleTime(int maxIdleTime) {
this.maxIdleTime = maxIdleTime;
}
public String getTestQuery() {
return testQuery;
}
public void setTestQuery(String testQuery) {
this.testQuery = testQuery;
}
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mysql.datasource.test2")
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class DBConfig2 {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private int minPoolSize;
private int maxPoolSize;
private int maxLifetime;
private int borrowConnectionTimeout;
private int loginTimeout;
private int maintenanceInterval;
private int maxIdleTime;
private String testQuery;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getMinPoolSize() {
return minPoolSize;
}
public void setMinPoolSize(int minPoolSize) {
this.minPoolSize = minPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxPoolSize() {
return maxPoolSize;
}
public void setMaxPoolSize(int maxPoolSize) {
this.maxPoolSize = maxPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxLifetime() {
return maxLifetime;
}
public void setMaxLifetime(int maxLifetime) {
this.maxLifetime = maxLifetime;
}
public int getBorrowConnectionTimeout() {
return borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public void setBorrowConnectionTimeout(int borrowConnectionTimeout) {
this.borrowConnectionTimeout = borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public int getLoginTimeout() {
return loginTimeout;
}
public void setLoginTimeout(int loginTimeout) {
this.loginTimeout = loginTimeout;
}
public int getMaintenanceInterval() {
return maintenanceInterval;
}
public void setMaintenanceInterval(int maintenanceInterval) {
this.maintenanceInterval = maintenanceInterval;
}
public int getMaxIdleTime() {
return maxIdleTime;
}
public void setMaxIdleTime(int maxIdleTime) {
this.maxIdleTime = maxIdleTime;
}
public String getTestQuery() {
return testQuery;
}
public void setTestQuery(String testQuery) {
this.testQuery = testQuery;
}
}
@SpringBootConfiguration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.lynn.demo.test01", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate")
public class MyBatisConfig1 {
// 配置数据源
@Primary
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DataSource dataSource(DBConfig1 config) throws SQLException {
MysqlXADataSource mysqlXaDataSource = new MysqlXADataSource();
mysqlXaDataSource.setUrl(config.getUrl());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
mysqlXaDataSource.setPassword(config.getPassword());
mysqlXaDataSource.setUser(config.getUsername());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
AtomikosDataSourceBean xaDataSource = new AtomikosDataSourceBean();
xaDataSource.setXaDataSource(mysqlXaDataSource);
xaDataSource.setUniqueResourceName("dataSource");
xaDataSource.setMinPoolSize(config.getMinPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(config.getMaxPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxLifetime(config.getMaxLifetime());
xaDataSource.setBorrowConnectionTimeout(config.getBorrowConnectionTimeout());
xaDataSource.setLoginTimeout(config.getLoginTimeout());
xaDataSource.setMaintenanceInterval(config.getMaintenanceInterval());
xaDataSource.setMaxIdleTime(config.getMaxIdleTime());
xaDataSource.setTestQuery(config.getTestQuery());
return xaDataSource;
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dataSource") DataSource dataSource)
throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return bean.getObject();
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(
@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
@SpringBootConfiguration
//basePackages 最好分开配置 如果放在同一个文件夹可能会报错
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.lynn.demo.test02", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate2")
public class MyBatisConfig2 {
// 配置数据源
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
public DataSource dataSource(DBConfig2 config) throws SQLException {
MysqlXADataSource mysqlXaDataSource = new MysqlXADataSource();
mysqlXaDataSource.setUrl(config.getUrl());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
mysqlXaDataSource.setPassword(config.getPassword());
mysqlXaDataSource.setUser(config.getUsername());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
AtomikosDataSourceBean xaDataSource = new AtomikosDataSourceBean();
xaDataSource.setXaDataSource(mysqlXaDataSource);
xaDataSource.setUniqueResourceName("dataSource2");
xaDataSource.setMinPoolSize(config.getMinPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(config.getMaxPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxLifetime(config.getMaxLifetime());
xaDataSource.setBorrowConnectionTimeout(config.getBorrowConnectionTimeout());
xaDataSource.setLoginTimeout(config.getLoginTimeout());
xaDataSource.setMaintenanceInterval(config.getMaintenanceInterval());
xaDataSource.setMaxIdleTime(config.getMaxIdleTime());
xaDataSource.setTestQuery(config.getTestQuery());
return xaDataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory2")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dataSource2") DataSource dataSource)
throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionTemplate2")
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(
@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory2") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
在 com.lynn.demo.test01 和 com.lynn.demo.test02 中分别创建以下 mapper:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper1 {
@Insert("insert into test_user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
void addUser(@Param("name")String name,@Param("age") int age);
}
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper2 {
@Insert("insert into test_user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
void addUser(@Param("name") String name,@Param("age") int age);
}
创建 service 类:
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper1 userMapper1;
@Autowired
private UserMapper2 userMapper2;
@Transactional
public void addUser(User user)throws Exception{
userMapper1.addUser(user.getName(),user.getAge());
userMapper2.addUser(user.getName(),user.getAge());
}
}
5.创建单元测试类进行测试:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class TestDB {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("lynn");
user.setAge(10);
try {
userService.addUser(user);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
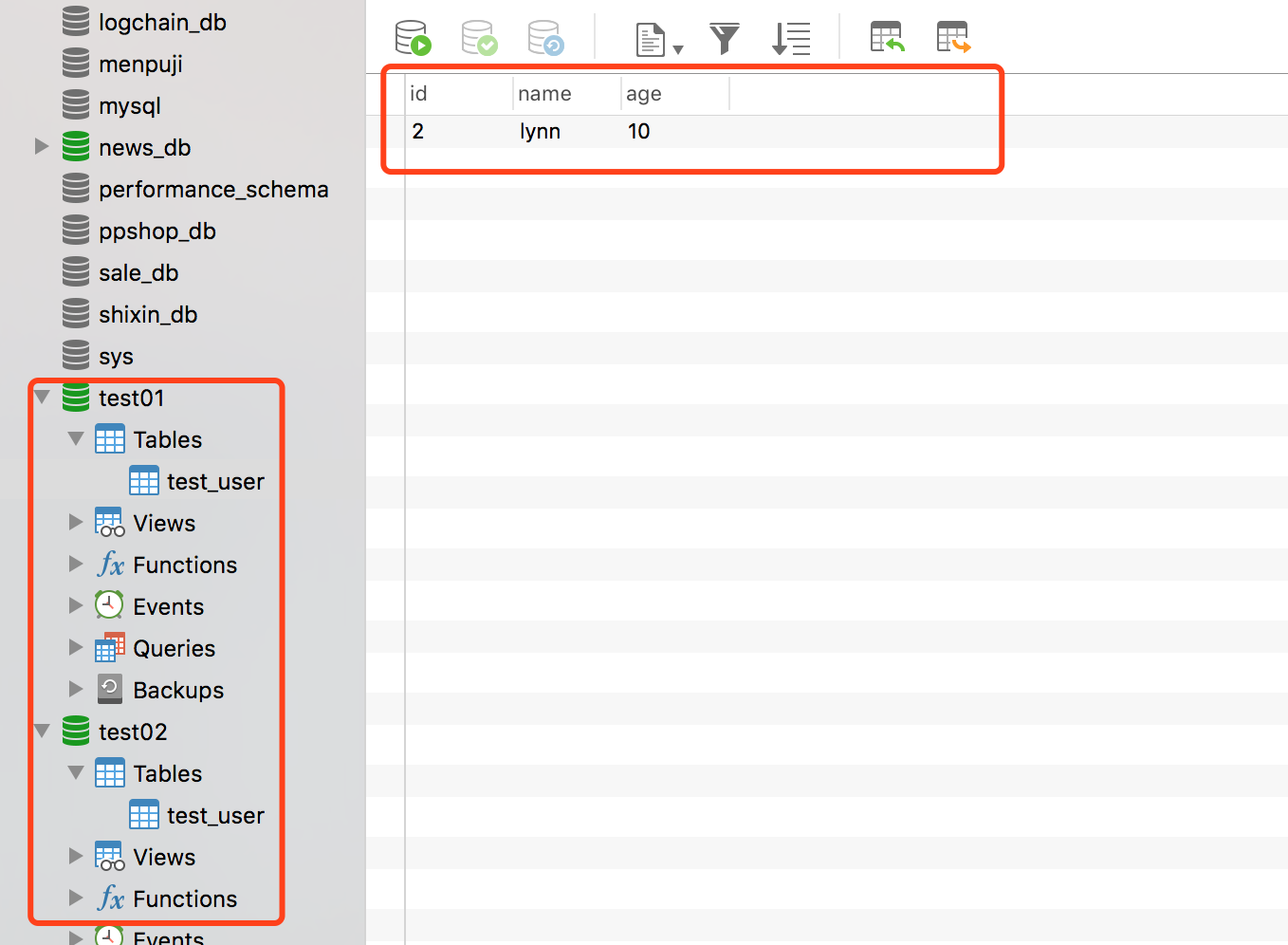
经过测试,如果没有报错,则数据被分别添加到两个数据库表中,如果有报错,则数据不会增加。
第14课:Spring Cloud 实例详解——基础框架搭建(一)
通过前面基础组件的学习,我们已经可以利用这些组件搭建一个比较完整的微服务架构,为了巩固我们前面学习的知识,从本文开始,将以一个实际的案例带领大家构建一个完整的微服务架构(本文代码已放在 Github 上)。
需求分析
本文要实现的一个产品是新闻门户网站,首先我们需要对其进行需求分析,本新闻门户网站包括的功能大概有以下几个:
- 注册登录
- 新闻列表
- 用户评论
产品设计
根据需求分析,就可以进行产品设计,主要是原型设计,我们先看看大致的原型设计图。
首页原型设计图
文章列表页原型设计图
文章详情页原型设计图
个人中心页原型设计图
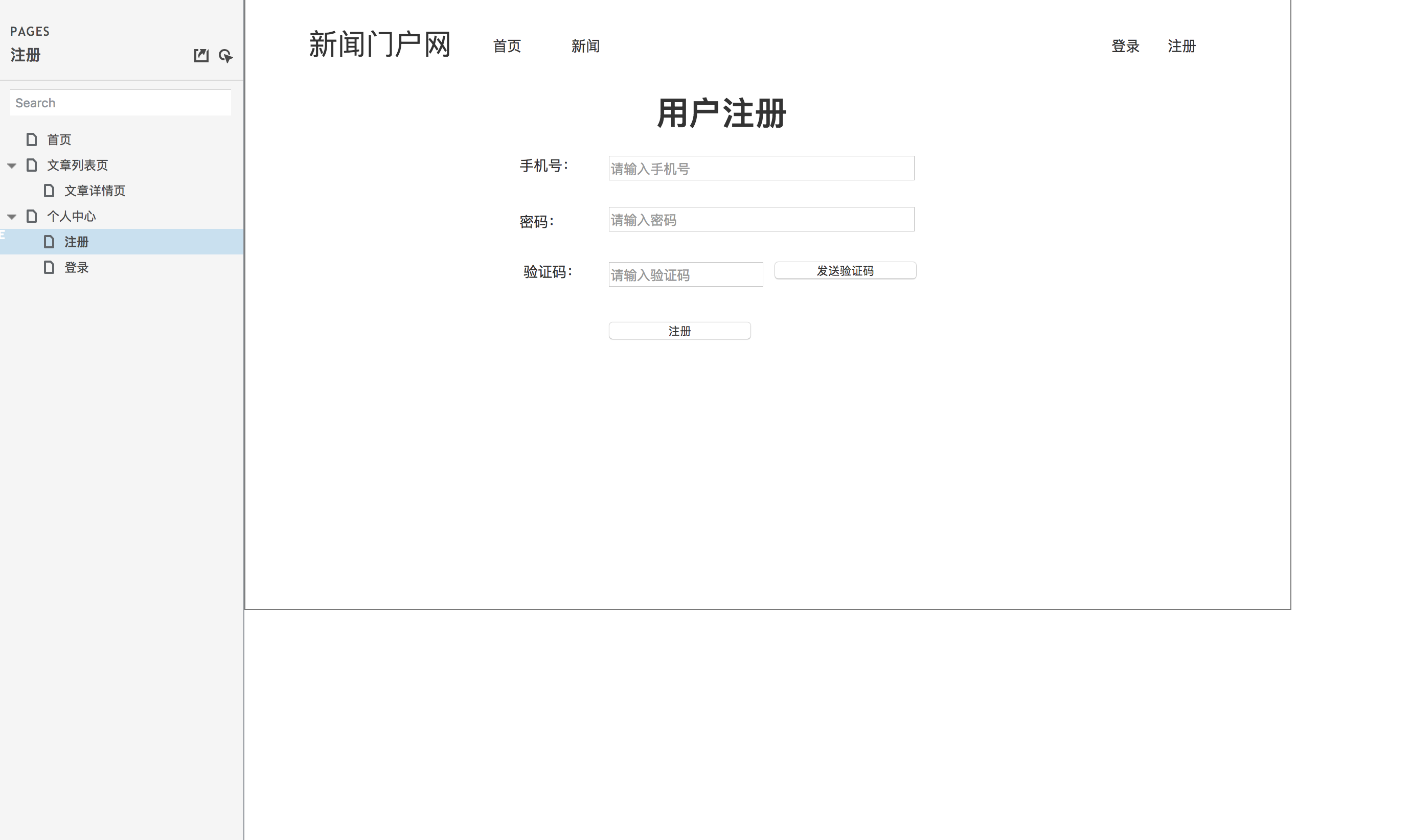
用户注册页原型设计图
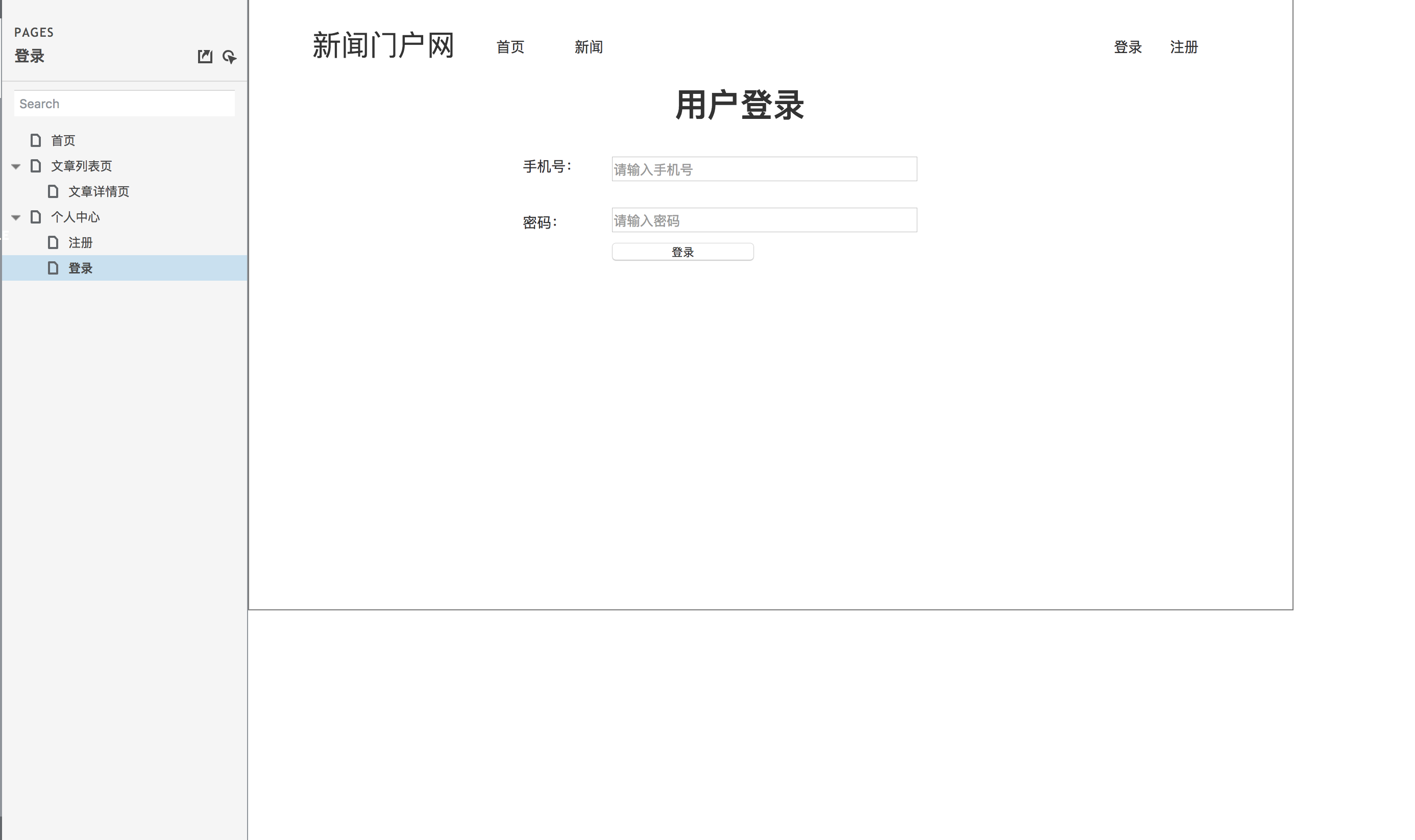
用户登录页原型设计图
数据库设计
根据原型设计图,我们可以分析出数据结构,从而设计数据库:
/*
Navicat Premium Data Transfer
Source Server : 本地
Source Server Type : MySQL
Source Server Version : 50709
Source Host : localhost:3306
Source Schema : news_db
Target Server Type : MySQL
Target Server Version : 50709
File Encoding : 65001
Date: 07/06/2018 21:15:58
*/
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_article
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_article`;
CREATE TABLE `news_article` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间',
`title` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '标题',
`summary` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '摘要',
`pic_url` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '图片',
`view_count` int(8) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '浏览数',
`source` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '来源',
`content` text COMMENT '文章内容',
`category_id` bigint(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '分类ID',
`is_recommend` tinyint(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '是否推荐',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_captcha
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_captcha`;
CREATE TABLE `news_captcha` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号',
`code` varchar(8) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '验证码',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_category
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_category`;
CREATE TABLE `news_category` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '分类名',
`parent_id` bigint(16) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '上级分类ID(0为顶级分类)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_comment
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_comment`;
CREATE TABLE `news_comment` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`article_id` bigint(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '文章ID',
`content` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '评论内容',
`parent_id` bigint(16) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '上级评论ID(0为顶级评论)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_user`;
CREATE TABLE `news_user` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号',
`password` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '密码(SHA1加密)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
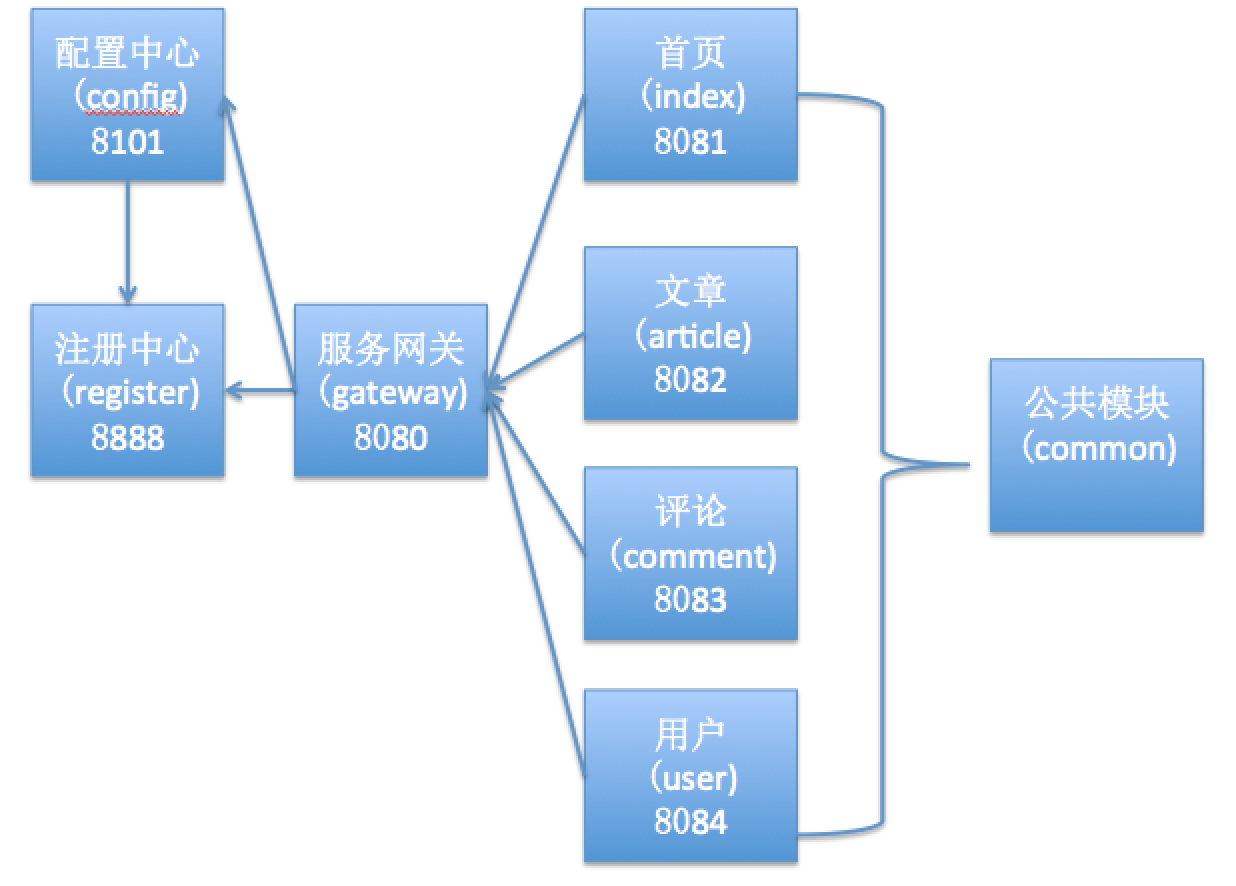
架构图设计
对于现代微服务架构来说,我们在搭建项目之前最好先设计架构图,因为微服务工程较多,关系比较复杂,有了架构图,更有利于我们进行架构设计,下面请看本实例的架构图:
框架搭建
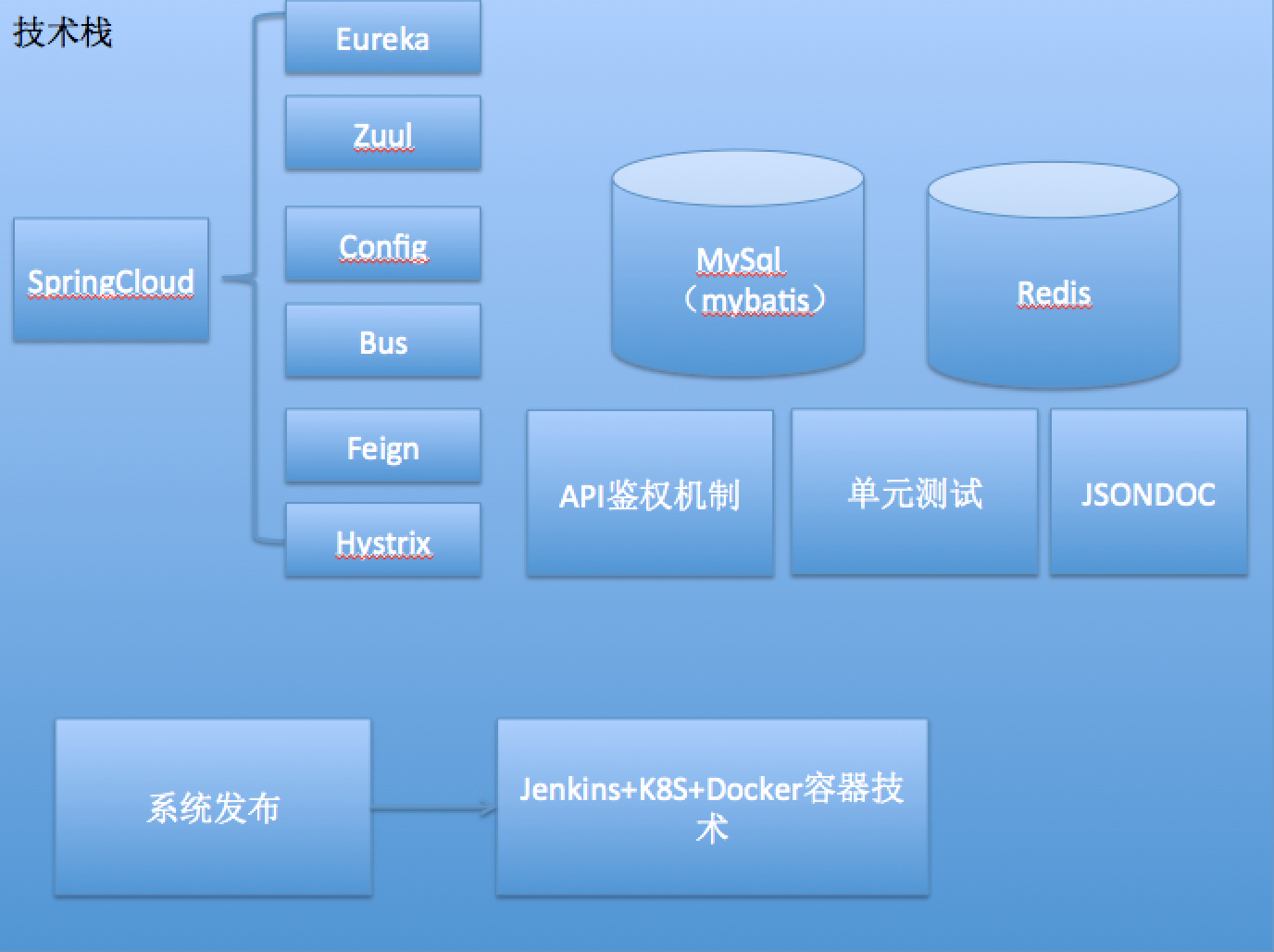
根据架构图,我们就可以开始搭建框架,首先要进行技术选型,也就是需要集成什么技术,本实例,我们将能够看到注册中心、配置中心、服务网关、Redis、MySQL、API 鉴权等技术,下面请看具体代码。
架构图截图:
我们知道,微服务架构其实是由多个工程组成的,根据架构图,我们就可以先把所有工程创建好:
其中,common 不是一个项目工程,而是公共类库,所有项目都依赖它,我们可以把公共代码放在 common 下,比如字符串的处理、日期处理、Redis 处理、JSON 处理等。
client 包括客户端工程,config 为配置中心,gateway 为服务网关,register 为注册中心。
本文我们先来搭建注册中心、配置中心和服务网关。
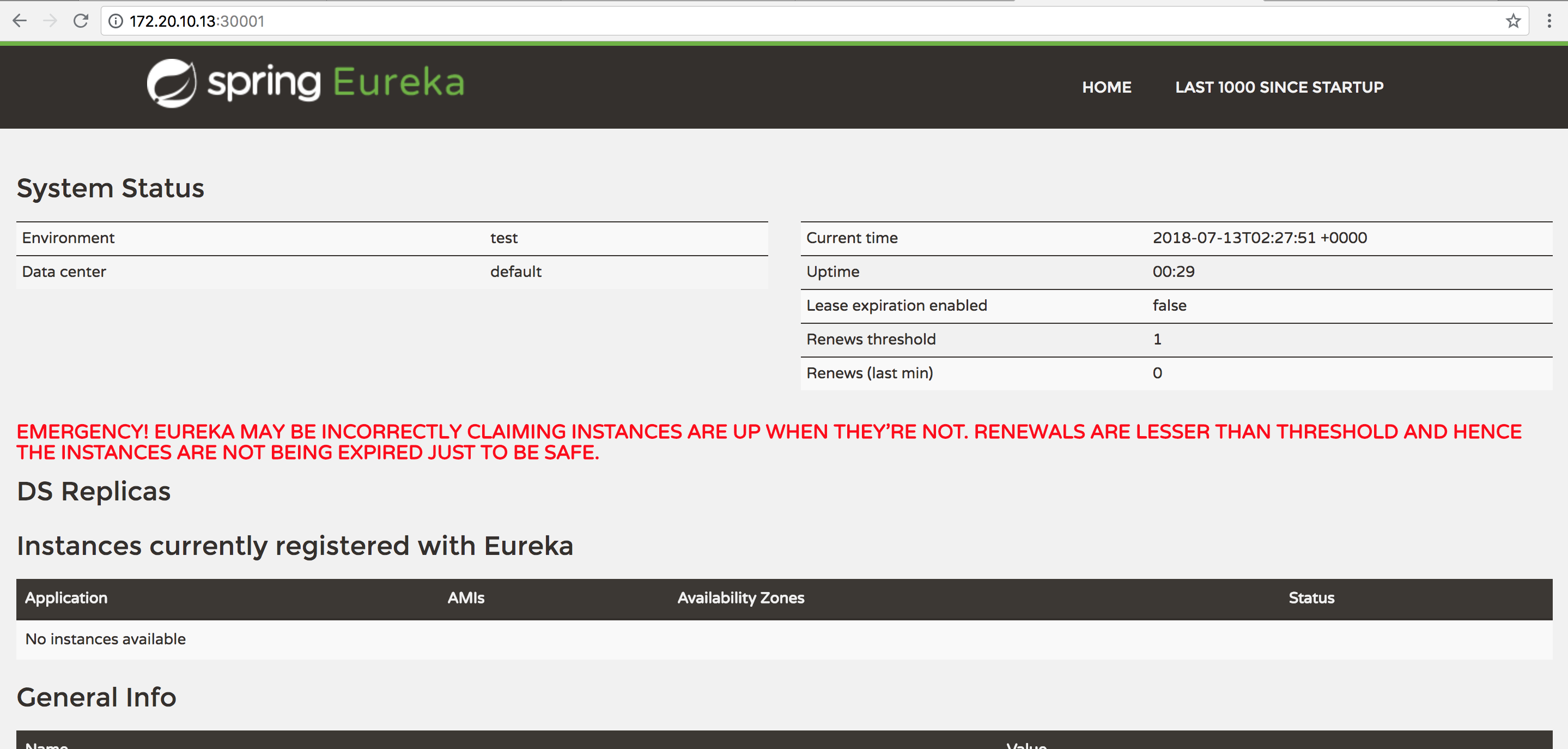
1.注册中心
首先创建启动类:
package com.lynn.register;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
然后创建 YAML 配置文件:
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: register
profiles:
active: dev
eureka:
server:
#开启自我保护
enable-self-preservation: true
instance:
#以IP地址注册
preferIpAddress: true
hostname: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}
instanceId: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}:${server.port}
client:
registerWithEureka: false
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
2.配置中心
创建启动类:
package com.lynn.config;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableConfigServer
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
创建 YAML 配置文件:
server:
port: 8101
spring:
application:
name: config
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/springcloudlynn/springcloudinactivity #配置git仓库地址
searchPaths: repo #配置仓库路径
username: springcloudlynn #访问git仓库的用户名
password: ly123456 #访问git仓库的用户密码
label: master #配置仓库的分支
eureka:
instance:
hostname: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}
instanceId: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}:${server.port}
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
3.服务网关
我们继续编写服务网关。
首先是启动类:
package com.lynn.gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy;
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableZuulProxy
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
服务网关的配置可以通过配置中心拉下来,下面是配置文件代码,此时配置文件名字为 bootstrap.yml:
spring:
application:
name: gateway
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
config:
name: gateway,eureka,key
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
serviceId: config
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
本文的基础框架就搭建到这里,后面将继续搭建基础框架。
第15课:Spring Cloud 实例详解——基础框架搭建(二)
接着上一篇,我们继续来搭建基础框架,本文我们将搭建客户端基础模块,集成熔断器,集成持久层框架 Mybatis。
在上一篇我们已经构建好了配置中心,因此,此后搭建的所有工程都是将配置文件放到 Git 上(点击这里获取本课程配置文件的 Git 仓库地址),通过配置中心将配置文件从 Git 仓库上拉取下来。
客户端基础模块
为了便于应用的可读性,我们在顶级工程下,先创建一个 packaging 为 pom 的工程,命名为 client,然后在 client 下创建我们的客户端模块,如图所示:
client 的 pom 内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>news</artifactId>
<groupId>com.lynn</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>client</artifactId>
<description>客户端</description>
<modules>
<module>index</module>
<module>article</module>
<module>comment</module>
<module>user</module>
</modules>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lynn</groupId>
<artifactId>common</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
接着继续创建客户端工程:index(首页)、article(文章)、comment(评论)、user(用户)。
我们首先在Git仓库下创建一些公有的 yaml 文件:eureka.yml,代码如下:
eureka:
instance:
hostname: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}
instanceId: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}:${server.port}
然后在每个客户端模块创建启动类,添加以下内容:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
最后在每个客户端工程下创建 bootstrap.yml 配置文件,在 Git 仓库创建每个客户端模块自己的配置项,并添加相应的内容。接下来,我们具体看下每个客户端下需要添加的代码内容。
- 首页
首页客户端下 bootstrap.yml 配置文件的代码如下:
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: index,eureka
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
serviceId: config
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
首页配置项 index.yml 中添加如下代码:
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: index
profiles:
active: dev
- 文章
文章客户端下 bootstrap.yml 配置文件的代码如下:
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: article,eureka
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
serviceId: config
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
文章配置项 article.yml 中添加如下代码:
server:
port: 8082
spring:
application:
name: article
profiles:
active: dev
- 评论
评论客户端下 bootstrap.yml 配置文件的代码如下:
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: comment,eureka
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
serviceId: config
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
评论配置项 comment.yml 中添加如下代码:
server:
port: 8083
spring:
application:
name: comment
profiles:
active: dev
- 用户
用户客户端下 bootstrap.yml 配置文件的代码如下:
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: user,eureka
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
serviceId: config
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
用户配置项 user.yml 中添加如下代码:
server:
port: 8084
spring:
application:
name: user
profiles:
active: dev
熔断器
熔断机制可以有效提升应用的健壮性,通过 Hystrix Dashboard 也可以监控 Feign 调用,便于我们随时观察服务的稳定性,因此集成熔断器是很有必要的,本实例将集成 Feign 和 Hystrix 框架。
首先,在 client 的 pom 中加入依赖(因为所有客户端都需要依赖它,所以在 client 中依赖即可),代码如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
接着,在每个客户端模块的启动类中加入注解,代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableHystrixDashboard
@EnableCircuitBreaker
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
我们随便启动一个客户端来看看效果。
依次启动 register、config 和 index,访问地址:http://localhost:8081/hystrix,即可看到如下图所示界面:
说明我们成功集成了 Hystrix Dashboard。
持久层框架 Mybatis
一个 Web 应用免不了数据库的操作,因此我们继续来集成数据库框架,本应用采取 Mybatis 框架,连接池使用阿里巴巴的 Druid 框架。
首先在 client 下加入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.40</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
然后在 Git 仓库创建配置文件 database.yml:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/news_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=true
username: root
password: ******
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
initial-size: 5
max-active: 20
min-idle: 5
max-wait: 60000
pool-prepared-statements: true
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 100
max-open-prepared-statements: 20
validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
validation-query-timeout: 30
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
test-while-idle: true
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
filters: stat,wall,log4j
filter:
stat:
log-slow-sql: true
slow-sql-millis: 2000
web-stat-filter:
enable: true
stat-view-servlet:
enabled: true
#druid控制台的用户名和密码
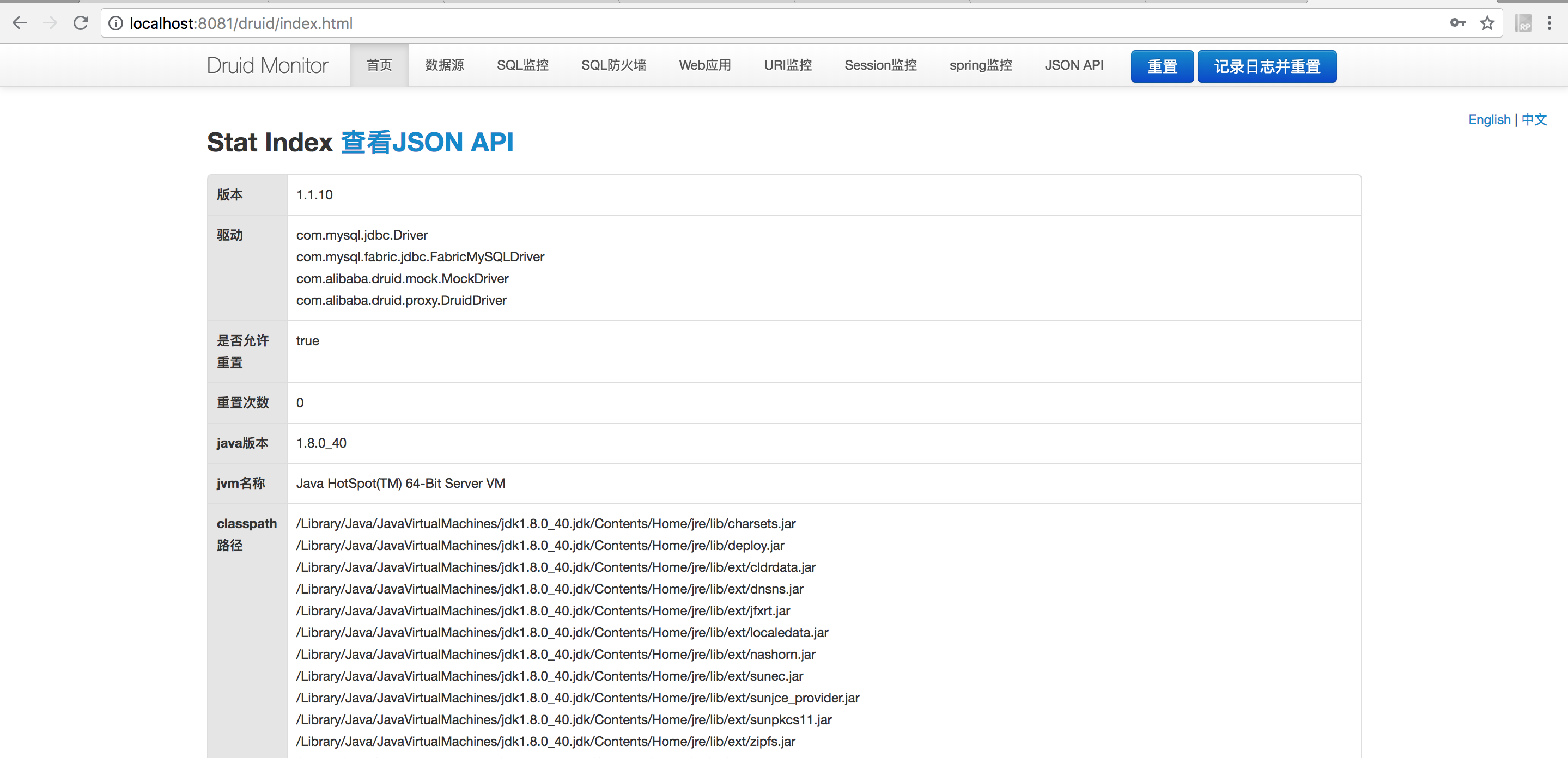
login-username: druid_admin
login-password: 123456
依次启动 register、config 和 index,然后访问:http://localhost:8081/druid,输入配置文件设置的用户名和密码,即可进入如下界面:
第16课:Spring Cloud 实例详解——基础框架搭建(三)
本文我们将集成 Redis,实现 API 鉴权机制。
Redis 的集成
Spring Boot 集成 Redis 相当简单,只需要在 pom 里加入如下依赖即可:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
由于每个模块都可能用到 Redis,因此我们可以考虑将 Redis 的依赖放到 common 工程下:
然后创建一个类实现基本的 Redis 操作:
@Component
public class Redis {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate template;
/**
* expire为过期时间,秒为单位
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param expire
*/
public void set(String key, String value, long expire) {
template.opsForValue().set(key, value, expire, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public void set(String key, String value) {
template.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
public Object get(String key) {
return template.opsForValue().get(key);
}
public void delete(String key) {
template.delete(key);
}
}
如果具体的模块需要操作 Redis 还需要在配置文件配置 Redis 的连接信息,这里我们在 Git 仓库创建一个 yaml 文件 redis.yaml,并加入以下内容:
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
password:
最后在需要操作 Redis 的工程的 bootstrap.yml 文件中加上 Redis 配置文件名即可,如下:
spring:
cloud:
config:
#这里加入redis
name: user,eureka,feign,database,redis,key
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
serviceId: config
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
这样在工程想操作 Redis 的地方注入 Redis 类:
@Autowired
private Redis redis;
但这样启动工程会报错,原因是 CommonScan 默认从工程根目录开始扫描,我们工程的根包名是:com.lynn.xxx(其中 xxx 为工程名),而 Redis 类在 com.lynn.common 下,因此我们需要手动指定开始扫描的包名,我们发现二者都有 com.lynn,所以指定为 comm.lynn 即可。
在每个工程的 Application 类加入如下注解:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableHystrixDashboard
@EnableCircuitBreaker
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.lynn")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
API 鉴权
互联网发展至今,已由传统的前后端统一架构演变为如今的前后端分离架构,最初的前端网页大多由 JSP、ASP、PHP 等动态网页技术生成,前后端十分耦合,也不利于扩展。现在的前端分支很多,如 Web 前端、Android 端、iOS 端,甚至还有物联网等。前后端分离的好处就是后端只需要实现一套界面,所有前端即可通用。
前后端的传输通过 HTTP 进行传输,也带来了一些安全问题,如果抓包、模拟请求、洪水攻击、参数劫持、网络爬虫等等。如何对非法请求进行有效拦截,保护合法请求的权益是这篇文章需要讨论的。
我依据多年互联网后端开发经验,总结出了以下提升网络安全的方式:
- 采用 HTTPS 协议;
- 密钥存储到服务端而非客户端,客户端应从服务端动态获取密钥;
- 请求隐私接口,利用 Token 机制校验其合法性;
- 对请求参数进行合法性校验;
- 对请求参数进行签名认证,防止参数被篡改;
- 对输入输出参数进行加密,客户端加密输入参数,服务端加密输出参数。
接下来,将对以上方式展开做详细说明。
HTTP VS HTTPS
普通的 HTTP 协议是以明文形式进行传输,不提供任何方式的数据加密,很容易解读传输报文。而 HTTPS 协议在 HTTP 基础上加入了 SSL 层,而 SSL 层通过证书来验证服务器的身份,并为浏览器和服务器之间的通信加密,保护了传输过程中的数据安全。
动态密钥的获取
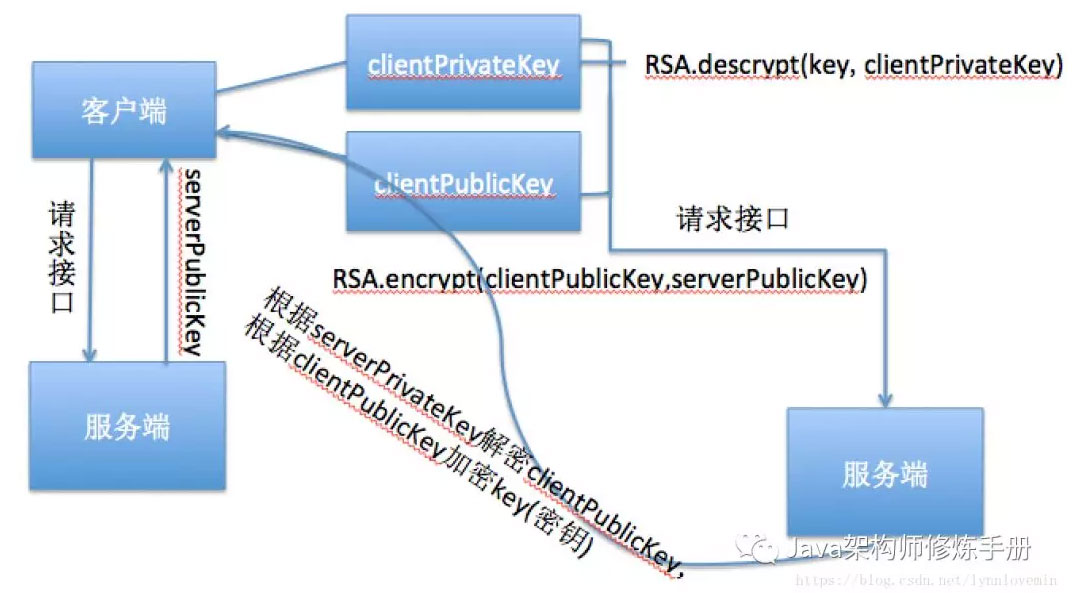
对于可逆加密算法,是需要通过密钥进行加解密,如果直接放到客户端,那么很容易反编译后拿到密钥,这是相当不安全的做法,因此考虑将密钥放到服务端,由服务端提供接口,让客户端动态获取密钥,具体做法如下:
- 客户端先通过 RSA 算法生成一套客户端的公私钥对(clientPublicKey 和 clientPrivateKey);
- 调用 getRSA 接口,服务端会返回 serverPublicKey;
- 客户端拿到 serverPublicKey 后,用 serverPublicKey 作为公钥,clientPublicKey 作为明文对 clientPublicKey 进行 RSA 加密,调用 getKey 接口,将加密后的 clientPublicKey 传给服务端,服务端接收到请求后会传给客户端 RSA 加密后的密钥;
- 客户端拿到后以 clientPrivateKey 为私钥对其解密,得到最终的密钥,此流程结束。
注: 上述提到数据均不能保存到文件里,必须保存到内存中,因为只有保存到内存中,黑客才拿不到这些核心数据,所以每次使用获取的密钥前先判断内存中的密钥是否存在,不存在,则需要获取。
为了便于理解,我画了一个简单的流程图:
那么具体是如何实现的呢,请看下面的代码(同样地,我们将这些公用方法放到 common 类库下)。
全局密钥配置,故加密算法统一密钥
api:
encrypt:
key: d7b85c6e414dbcda
此配置的公司钥信息为测试数据,不能直接使用,请自行重新生成公私钥。
rsa:
publicKey: MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQCcZlkHaSN0fw3CWGgzcuPeOKPdNKHdc2nR6KLXazhhzFhe78NqMrhsyNTf3651acS2lADK3CzASzH4T0bT+GnJ77joDOP+0SqubHKwAIv850lT0QxS+deuUHg2+uHYhdhIw5NCmZ0SkNalw8igP1yS+2TEIYan3lakPBvZISqRswIDAQAB
privateKey: MIICeAIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQeFAcSCAmIwggJeAgEAAoGBAJxmWQdpI3R/DcJYaDNy4944o900od1zadHootdrOGHMWF7vw2oyuGzI1N/frmxoVLaUAMrcLMBLMfhPRtP4acnvuOgM4/7RKq5scrAAi/znSVPRDFL5165QeDb64diF2EjDk0KZnRKQ1qXDyKA/XJL7ZMQhhqfeVqQ8G9khKpGzAgMBAAECgYEAj+5AkGlZj6Q9bVUez/ozahaF9tSxAbNs9xg4hDbQNHByAyxzkhALWVGZVk3rnyiEjWG3OPlW1cBdxD5w2DIMZ6oeyNPA4nehYrf42duk6AI//vd3GsdJa6Dtf2has1R+0uFrq9MRhfRunAf0w6Z9zNbiPNSd9VzKjjSvcX7OTsECQQD20kekMToC6LZaZPr1p05TLUTzXHvTcCllSeXWLsjVyn0AAME17FJRcL9VXQuSUK7PQ5Lf5+OpjrCRYsIvuZg9AkEAojdC6k3SqGnbtftLfGHMDn1fe0nTJmL05emwXgJvwToUBdytvgbTtqs0MsnuaOxMIMrBtpbhS6JiB5Idb7GArwJAfKTkmP5jFWT/8dZdBgFfhJGv6FakEjrqLMSM1QT7VzvStFWtPNYDHC2b8jfyyAkGvpSZb4ljZxUwBbuh5QgM4QJBAJDrV7+lOP62W9APqdd8M2X6gbPON3JC09EW3jaObLKupTa7eQicZsX5249IMdLQ0A43tanez3XXo0ZqNhwT8wcCQQDUubpNLwgAwN2X7kW1btQtvZW47o9CbCv+zFKJYms5WLrVpotjkrCgPeuloDAjxeHNARX8ZTVDxls6KrjLH3lT
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codec</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
public class AesEncryptUtils {
private static final String KEY = "d7585fde114abcda";
private static final String ALGORITHMSTR = "AES/CBC/NoPadding"; public static String base64Encode(byte[] bytes) { return Base64.encodeBase64String(bytes);
} public static byte[] base64Decode(String base64Code) throws Exception { return Base64.decodeBase64(base64Code);
} public static byte[] aesEncryptToBytes(String content, String encryptKey) throws Exception {
KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
kgen.init(128);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHMSTR);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(encryptKey.getBytes(), "AES")); return cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes("utf-8"));
} public static String aesEncrypt(String content, String encryptKey) throws Exception { return base64Encode(aesEncryptToBytes(content, encryptKey));
} public static String aesDecryptByBytes(byte[] encryptBytes, String decryptKey) throws Exception {
KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
kgen.init(128);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHMSTR);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(decryptKey.getBytes(), "AES")); byte[] decryptBytes = cipher.doFinal(encryptBytes); return new String(decryptBytes);
} public static String aesDecrypt(String encryptStr, String decryptKey) throws Exception { return aesDecryptByBytes(base64Decode(encryptStr), decryptKey);
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String content = "{name:\"lynn\",id:1}";
System.out.println("加密前:" + content);
String encrypt = aesEncrypt(content, KEY);
System.out.println(encrypt.length() + ":加密后:" + encrypt);
String decrypt = aesDecrypt("H9pGuDMV+iJoS8YSfJ2Vx0NYN7v7YR0tMm1ze5zp0WvNEFXQPM7K0k3IDUbYr5ZIckTkTHcIX5Va/cstIPrYEK3KjfCwtOG19l82u+x6soa9FzAtdL4EW5HAFMmpVJVyG3wz/XUysIRCwvoJ20ruEwk07RB3ojc1Vtns8t4kKZE=", "d7b85f6e214abcda");
System.out.println("解密后:" + decrypt);
}
}public class RSAUtils {
public static final String CHARSET = "UTF-8"; public static final String RSA_ALGORITHM = "RSA"; public static Map<String, String> createKeys(int keySize){ //为RSA算法创建一个KeyPairGenerator对象
KeyPairGenerator kpg; try{
kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
}catch(NoSuchAlgorithmException e){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("No such algorithm-->[" + RSA_ALGORITHM + "]");
} //初始化KeyPairGenerator对象,密钥长度
kpg.initialize(keySize); //生成密匙对
KeyPair keyPair = kpg.generateKeyPair(); //得到公钥
Key publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
String publicKeyStr = Base64.encodeBase64String(publicKey.getEncoded()); //得到私钥
Key privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
String privateKeyStr = Base64.encodeBase64String(privateKey.getEncoded());
Map<String, String> keyPairMap = new HashMap<>(2);
keyPairMap.put("publicKey", publicKeyStr);
keyPairMap.put("privateKey", privateKeyStr); return keyPairMap;
} /**
* 得到公钥
* @param publicKey 密钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static RSAPublicKey getPublicKey(String publicKey) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException { //通过X509编码的Key指令获得公钥对象
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(Base64.decodeBase64(publicKey));
RSAPublicKey key = (RSAPublicKey) keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec); return key;
} /**
* 得到私钥
* @param privateKey 密钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static RSAPrivateKey getPrivateKey(String privateKey) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException { //通过PKCS#8编码的Key指令获得私钥对象
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(Base64.decodeBase64(privateKey));
RSAPrivateKey key = (RSAPrivateKey) keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec); return key;
} /**
* 公钥加密
* @param data
* @param publicKey
* @return
*/
public static String publicEncrypt(String data, RSAPublicKey publicKey){ try{
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); return Base64.encodeBase64String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, data.getBytes(CHARSET), publicKey.getModulus().bitLength()));
}catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("加密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常", e);
}
} /**
* 私钥解密
* @param data
* @param privateKey
* @return
*/
public static String privateDecrypt(String data, RSAPrivateKey privateKey){ try{
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); return new String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, Base64.decodeBase64(data), privateKey.getModulus().bitLength()), CHARSET);
}catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("解密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常", e);
}
} /**
* 私钥加密
* @param data
* @param privateKey
* @return
*/
public static String privateEncrypt(String data, RSAPrivateKey privateKey){ try{
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey); return Base64.encodeBase64String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, data.getBytes(CHARSET), privateKey.getModulus().bitLength()));
}catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("加密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常", e);
}
} /**
* 公钥解密
* @param data
* @param publicKey
* @return
*/
public static String publicDecrypt(String data, RSAPublicKey publicKey){ try{
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey); return new String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, Base64.decodeBase64(data), publicKey.getModulus().bitLength()), CHARSET);
}catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("解密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常", e);
}
} private static byte[] rsaSplitCodec(Cipher cipher, int opmode, byte[] datas, int keySize){ int maxBlock = 0; if(opmode == Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE){
maxBlock = keySize / 8;
}else{
maxBlock = keySize / 8 - 11;
}
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); int offSet = 0; byte[] buff; int i = 0; try{ while(datas.length > offSet){ if(datas.length-offSet > maxBlock){
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, maxBlock);
}else{
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, datas.length-offSet);
}
out.write(buff, 0, buff.length);
i++;
offSet = i * maxBlock;
}
}catch(Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException("加解密阀值为["+maxBlock+"]的数据时发生异常", e);
} byte[] resultDatas = out.toByteArray();
IOUtils.closeQuietly(out); return resultDatas;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Map<String, String> keyMap = RSAUtils.createKeys(1024);
String publicKey = keyMap.get("publicKey");
String privateKey = "MIICeAIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCAmIwggJeAgEAAoGBAJxmWQdpI3R/DcJYaDNy4944o900od1zadHootdrOGHMWF7vw2oyuGzI1N/frmxoVLaUAMrcLMBLMfhPRtP4acnvuOgM4/7RKq5scrAAi/znSVPRDFL5165QeDb64diF2EjDk0KZnRKQ1qXDyKA/XJL7ZMQhhqfeVqQ8G9khKpGzAgMBAAECgYEAj+5AkGlZj6Q9bVUez/ozahaF9tSxAbNs9xg4hDbQNHByAyxzkhALWVGZVk3rnyiEjWG3OPlW1cBdxD5w2DIMZ6oeyNPA4nehYrf42duk6AI//vd3GsdJa6Dtf2has1R+0uFrq9MRhfRunAf0w6Z9zNbiPNSd9VzKjjSvcX7OTsECQQD20kekMToC6LZaZPr1p05TLUTzXHvTcCllSeXWLsjVyn0AAME17FJRcL9VXQuSUK7PQ5Lf5+OpjrCRYsIvuZg9AkEAojdC6k3SqGnbtftLfGHMDn1fe0nTJmL05emwXgJvwToUBdytvgbTtqs0MsnuaOxMIMrBtpbhS6JiB5Idb7GArwJAfKTkmP5jFWT/8dZdBgFfhJGv6FYkEjrqLMSM1QT7VzvStFWtPNYDHC2b8jfyyAkGvpSZb4ljZxUwBbuh5QgM4QJBAJDrV7+lOP62W9APqdd8M2X6gbPON3JC09EW3jaObLKupTa7eQicZsX5249IMdLQ0A43tanez3XXo0ZqNhwT8wcCQQDUubpNLwgAwN2X7kW1btQtvZW47o9CbCv+zFKJYms5WLrVpotjkrCgPeuloDAjxeHNARX8ZTVDxls6KrjLH3lT";
System.out.println("公钥: \n\r" + publicKey);
System.out.println("私钥: \n\r" + privateKey);
System.out.println("公钥加密——私钥解密");
String str = "站在大明门前守卫的禁卫军,事先没有接到\n" + "有关的命令,但看到大批盛装的官员来临,也就\n" + "以为确系举行大典,因而未加询问。进大明门即\n" + "为皇城。文武百官看到端门午门之前气氛平静,\n" + "城楼上下也无朝会的迹象,既无几案,站队点名\n" + "的御史和御前侍卫“大汉将军”也不见踪影,不免\n" + "心中揣测,互相询问:所谓午朝是否讹传?";
System.out.println("\r明文:\r\n" + str);
System.out.println("\r明文大小:\r\n" + str.getBytes().length);
String encodedData = RSAUtils.publicEncrypt(str, RSAUtils.getPublicKey(publicKey));
System.out.println("密文:\r\n" + encodedData);
String decodedData = RSAUtils.privateDecrypt("X4hHPa9NjPd5QJGPus+4+hWmOzbWg7oCJ1+Vc+7dHW81nEhkYnJpFyV5xcDkg70N2Mym+YAJ1PvYY9sQWf9/EkUE61TpUKBmDaGWLjEr3A1f9cKIelqLKLsJGdXEOr7Z55k4vYFvA7N3Vf5KQo3NrouvIT4wR+SjH4tDQ8tNh3JH8BvXLtXqGa2TCK2z1AzHNgYzcLCrqDasd7UDHRPZPiW4thktM/whjBn0tU9B/kKjAjLuYttKLEmy5nT7v7u16aZ6ehkk+kzvuCXF%2B3RsqraISDPbsTki2agJyqsycRx3w7CvKRyUbZhFaNcWigOwmcbZVoiom+ldh7Vh6HYqDA==", RSAUtils.getPrivateKey(privateKey));
System.out.println("解密后文字: \r\n" + decodedData);
}
}/**
* 私钥输入参数(其实就是客户端通过服务端返回的公钥加密后的客户端自己生成的公钥)
*/public class KeyRequest {
/**
* 客户端自己生成的加密后公钥
*/
@NotNull
private String clientEncryptPublicKey; public String getClientEncryptPublicKey() { return clientEncryptPublicKey;
} public void setClientEncryptPublicKey(String clientEncryptPublicKey) { this.clientEncryptPublicKey = clientEncryptPublicKey;
}
}/**
* RSA生成的公私钥输出参数
*/public class RSAResponse extends BaseResponse{
private String serverPublicKey; private String serverPrivateKey; public static class Builder{
private String serverPublicKey; private String serverPrivateKey; public Builder setServerPublicKey(String serverPublicKey){ this.serverPublicKey = serverPublicKey; return this;
} public Builder setServerPrivateKey(String serverPrivateKey){ this.serverPrivateKey = serverPrivateKey; return this;
} public RSAResponse build(){ return new RSAResponse(this);
}
} public static Builder options(){ return new Builder();
} public RSAResponse(Builder builder){ this.serverPrivateKey = builder.serverPrivateKey; this.serverPublicKey = builder.serverPublicKey;
} public String getServerPrivateKey() { return serverPrivateKey;
} public String getServerPublicKey() { return serverPublicKey;
}
}/**
* 私钥输出参数
*/public class KeyResponse extends BaseResponse{
/**
* 整个系统所有加密算法共用的密钥
*/
private String key; public static class Builder{
private String key; public Builder setKey(String key){ this.key = key; return this;
} public KeyResponse build(){ return new KeyResponse(this);
}
} public static Builder options(){ return new Builder();
} private KeyResponse(Builder builder){ this.key = builder.key;
} public String getKey() { return key;
}
}/**
* API传输加解密相关接口
*/public interface EncryptOpenService {
/**
* 生成RSA公私钥
* @return
*/
SingleResult<RSAResponse> getRSA(); /**
* 获得加解密用的密钥
* @param request
* @return
*/
SingleResult<KeyResponse> getKey(KeyRequest request) throws Exception;
}
@Servicepublic class EncryptOpenServiceImpl implements EncryptOpenService{
@Value("${rsa.publicKey}") private String publicKey; @Value("${rsa.privateKey}") private String privateKey; @Value("${api.encrypt.key}") private String key; @Override
public SingleResult<RSAResponse> getRSA() {
RSAResponse response = RSAResponse.options()
.setServerPublicKey(publicKey)
.build(); return SingleResult.buildSuccess(response);
} @Override
public SingleResult<KeyResponse> getKey(KeyRequest request)throws Exception {
String clientPublicKey = RSAUtils.privateDecrypt(request.getClientEncryptPublicKey(), RSAUtils.getPrivateKey(privateKey));
String encryptKey = RSAUtils.publicEncrypt(key,RSAUtils.getPublicKey(clientPublicKey));
KeyResponse response = KeyResponse.options()
.setKey(encryptKey)
.build(); return SingleResult.buildSuccess(response);
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("open/encrypt")
public class EncryptController {
@Autowired
private EncryptOpenService encryptOpenService;
@RequestMapping(value = "getRSA",method = RequestMethod.POST) //@DisabledEncrypt
public SingleResult<RSAResponse> getRSA(){
return encryptOpenService.getRSA();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "getKey",method = RequestMethod.POST) //@DisabledEncrypt
public SingleResult<KeyResponse> getKey(@Valid @RequestBody KeyRequest request)throws Exception{
return encryptOpenService.getKey(request);
}
}
接口请求的合法性校验
对于一些隐私接口(即必须要登录才能调用的接口),我们需要校验其合法性,即只有登录用户才能成功调用,具体思路如下:
- 调用登录或注册接口成功后,服务端会返回 Token(设置较短有效时间)和 refreshToken(设定较长有效时间);
- 隐私接口每次请求接口在请求头带上 Token,如 header(“token”,token),若服务端 返回403错误,则调用 refreshToken 接口获取新的 Token 重新调用接口,若 refreshToken 接口继续返回403,则跳转到登录界面。
这种算法较为简单,这里就不写出具体实现了。
输入参数的合法性校验
一般情况下,客户端会进行参数的合法性校验,这个只是为了减轻服务端的压力,针对于普通用户做的校验,如果黑客通过直接调用接口地址,就可绕过客户端的校验,这时要求我们服务端也应该做同样的校验。
SpringMVC 提供了专门用于校验的注解,我们通过 AOP 即可实现统一的参数校验,下面请看代码:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Aspect
@Component
public class WebExceptionAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WebExceptionAspect.class); //凡是注解了RequestMapping的方法都被拦截
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping)") private void webPointcut() {
} /**
* 拦截web层异常,记录异常日志,并返回友好信息到前端 目前只拦截Exception,是否要拦截Error需再做考虑
*
* @param e
* 异常对象
*/
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "webPointcut()", throwing = "e") public void handleThrowing(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
logger.error("发现异常!" + e.getMessage());
logger.error(JSON.toJSONString(e.getStackTrace())); try { if(StringUtils.isEmpty(e.getMessage())){
writeContent(JSON.toJSONString(SingleResult.buildFailure()));
}else {
writeContent(JSON.toJSONString(SingleResult.buildFailure(Code.ERROR,e.getMessage())));
}
}catch (Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* 将内容输出到浏览器
*
* @param content
* 输出内容
*/
private void writeContent(String content)throws Exception {
HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())
.getResponse();
response.reset();
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
response.setHeader("icop-content-type", "exception");
response.getWriter().print(content);
response.getWriter().close();
}
}
在controller提供共有方法:
protected void validate(BindingResult result){
if(result.hasFieldErrors()){
List<FieldError> errorList = result.getFieldErrors();
errorList.stream().forEach(item -> Assert.isTrue(false,item.getDefaultMessage()));
}
}
每个接口的输入参数都需要加上 @Valid 注解,并且在参数后面加上 BindResult 类:
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public SingleResult<String> hello(@Valid @RequestBody TestRequest request, BindingResult result){
validate(result); r
eturn "name="+name;
public class TestRequest{
@NotNull(message = "name不能为空") private String name; public String getName() { return name;
} public void setName(String name) { this.name = name;
}
}
输入参数签名认证
我们请求的接口是通过 HTTP/HTTPS 传输的,一旦参数被拦截,很有可能被黑客篡改,并传回给服务端,为了防止这种情况发生,我们需要对参数进行签名认证,保证传回的参数是合法性,具体思路如下。
请求接口前,将 Token、Timstamp 和接口需要的参数按照 ASCII 升序排列,拼接成 url=key1=value1&key2=value2,如 name=xxx×tamp=xxx&token=xxx,进行 MD5(url+salt),得到 Signature,将 Token、Signature、Timestamp 放到请求头传给服务端,如 header(“token”,token)、header(“timestamp”,timestamp),header(“signature”,signature)。
注: salt 即为动态获取的密钥。
下面请看具体的实现,应该在拦截器里统一处理:
public class ApiInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ApiInterceptor.class); private String salt="ed4ffcd453efab32"; @Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o) throws Exception {
logger.info("进入拦截器");
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
StringBuilder urlBuilder = getUrlAuthenticationApi(request); //这里是MD5加密算法
String sign = MD5(urlBuilder.toString() + salt);
String signature = request.getHeader("signature");
logger.info("加密前传入的签名" + signature);
logger.info("后端加密后的签名" + sign); if(sign.equals(signature)){ return true;
}else { //签名错误
response.getWriter().print("签名错误");
response.getWriter().close(); return false;
}
} private StringBuilder getUrlAuthenticationApi(HttpServletRequest request) {
Enumeration<String> paramesNames = request.getParameterNames();
List<String> nameList = new ArrayList<>();
nameList.add("token");
nameList.add("timestamp"); while (paramesNames.hasMoreElements()){
nameList.add(paramesNames.nextElement());
}
StringBuilder urlBuilder = new StringBuilder();
nameList.stream().sorted().forEach(name -> { if ("token".equals(name) || "timestamp".equals(name)){ if("token".equals(name) && null ==request.getHeader(name)){ return;
}
urlBuilder.append('&');
urlBuilder.append(name).append('=').append(request.getHeader(name));
} else {
urlBuilder.append('&');
urlBuilder.append(name).append('=').append(request.getParameter(name));
}
});
urlBuilder.deleteCharAt(0);
logger.info("url : " + urlBuilder.toString()); return urlBuilder;
} @Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
} @Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) throws Exception {
}
}
输入输出参数加密
为了保护数据,比如说防爬虫,需要对输入输出参数进行加密,客户端加密输入参数传回服务端,服务端解密输入参数执行请求;服务端返回数据时对其加密,客户端拿到数据后解密数据,获取最终的数据。这样,即便别人知道了参数地址,也无法模拟请求数据。
至此,基础框架就已经搭建完成,下篇我们将开始实现具体的需求。
第17课:Spring Cloud 实例详解——业务代码实现
本文开始,我们将实现具体的业务,由于篇幅问题,本文将贴出部分实例代码,其余会提供一般思路。
公共模块
我们的接口会分别放在不同的工程下,其中会有公共代码,在此我们考虑将公共代码抽象出来放到公共模块 common 下。
Bean
我们提供的接口分为输入参数(request)和输出参数(response),输入参数为客户端请求时传入,输出参数为后端接口返回的数据。我们在定义接口时最好将输入参数和输出参数放到 request 和 response 包下,在定义的 Bean 下抽象出 Base 类来,如下代码:
package com.lynn.common.model;
public abstract class BaseModel {
private Long id;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
package com.lynn.common.model.response;
import com.lynn.common.model.BaseModel;
public abstract class BaseResponse extends BaseModel{
}
package com.lynn.common.model.request;
public abstract class BaseRequest {
}
Service和Controller
同样地,我们也可以定义出 BaseService 和 BaseController,在 BaseService 中实现公共方法:
package com.lynn.common.service;
import com.lynn.common.encryption.Algorithm;
import com.lynn.common.encryption.MessageDigestUtils;
public abstract class BaseService {
/**
* 密码加密算法
* @param password
* @return
*/
protected String encryptPassword(String password){
return MessageDigestUtils.encrypt(password, Algorithm.SHA1);
}
/**
* 生成API鉴权的Token
* @param mobile
* @param password
* @return
*/
protected String getToken(String mobile,String password){
return MessageDigestUtils.encrypt(mobile+password, Algorithm.SHA1);
}
}
我们也可以在 BaseController 里写公共方法:
package com.lynn.common.controller;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import java.util.List;
public abstract class BaseController {
/**
* 接口输入参数合法性校验
*
* @param result
*/
protected void validate(BindingResult result){
if(result.hasFieldErrors()){
List<FieldError> errorList = result.getFieldErrors();
errorList.stream().forEach(item -> Assert.isTrue(false,item.getDefaultMessage()));
}
}
}
接下来,我们就可以来实现具体的业务了。
用户模块
根据第14课提供的原型设计图,我们可以分析出,用户模块大概有如下几个接口:
- 登录
- 注册
- 获得用户评论
接下来我们来实现具体的业务(以登录为例),首先是 Bean:
package com.lynn.user.model.bean;
import com.lynn.common.model.BaseModel;
public class UserBean extends BaseModel{
private String mobile;
private String password;
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
package com.lynn.user.model.request;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
public class LoginRequest {
@NotEmpty
private String mobile;
@NotEmpty
private String password;
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
其次是 Mapper(框架采用 Mybatis 的注解方式):
package com.lynn.user.mapper;
import com.lynn.user.model.bean.UserBean;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select id,mobile,password from news_user where mobile = #{mobile} and password = #{password}")
List<UserBean> selectUser(String mobile,String password);
}
然后是 Service(具体的业务实现):
package com.lynn.user.service;
import com.lynn.common.result.Code;
import com.lynn.common.result.SingleResult;
import com.lynn.common.service.BaseService;
import com.lynn.user.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.lynn.user.model.bean.UserBean;
import com.lynn.user.model.request.LoginRequest;
import com.lynn.user.model.response.TokenResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
@Service
public class UserService extends BaseService{
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public SingleResult<TokenResponse> login(LoginRequest request){
List<UserBean> userList = userMapper.selectUser(request.getMobile(),request.getPassword());
if(null != userList && userList.size() > 0){
String token = getToken(request.getMobile(),request.getPassword());
TokenResponse response = new TokenResponse();
response.setToken(token);
return SingleResult.buildSuccess(response);
}else {
return SingleResult.buildFailure(Code.ERROR,"手机号或密码输入不正确!");
}
}
我们写的接口要提供给客户端调用,因此最后还需要添加 Controller:
package com.lynn.user.controller;
import com.lynn.common.controller.BaseController;
import com.lynn.common.result.SingleResult;
import com.lynn.user.model.request.LoginRequest;
import com.lynn.user.model.response.TokenResponse;
import com.lynn.user.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.validation.Valid;
@RequestMapping("user")
@RestController
public class UserController extends BaseController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("login")
public SingleResult<TokenResponse> login(@Valid @RequestBody LoginRequest request, BindingResult result){
//必须要调用validate方法才能实现输入参数的合法性校验
validate(result);
return userService.login(request);
}
}
这样一个完整的登录接口就写完了。
为了校验我们写的接口是否有问题可以通过 JUnit 来进行单元测试:
package com.lynn.user.test;
import com.lynn.user.Application;
import com.lynn.user.model.request.LoginRequest;
import com.lynn.user.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class TestDB {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test(){
try {
LoginRequest request = new LoginRequest();
request.setMobile("13800138000");
request.setPassword("1");
System.out.println(userService.login(request));
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
总结
在定义接口之前首先应该分析该接口的输入参数和输出参数,分别定义到 request 和 response 里,在 request 里添加校验的注解,如 NotNull(不能为 null)、NotEmpty(不能为空)等等。
在定义具体的接口,参数为对应的 request,返回值为 SingleResult<Response> 或 MultiResult<Response>,根据具体的业务实现具体的逻辑。
最后添加 Controller,就是调用 Service 的代码,方法参数需要加上 @Valid,这样参数校验才会生效,在调 Service 之前调用 validate(BindResult) 方法会抛出参数不合法的异常。最后,我们通过 JUnit 进行单元测试。
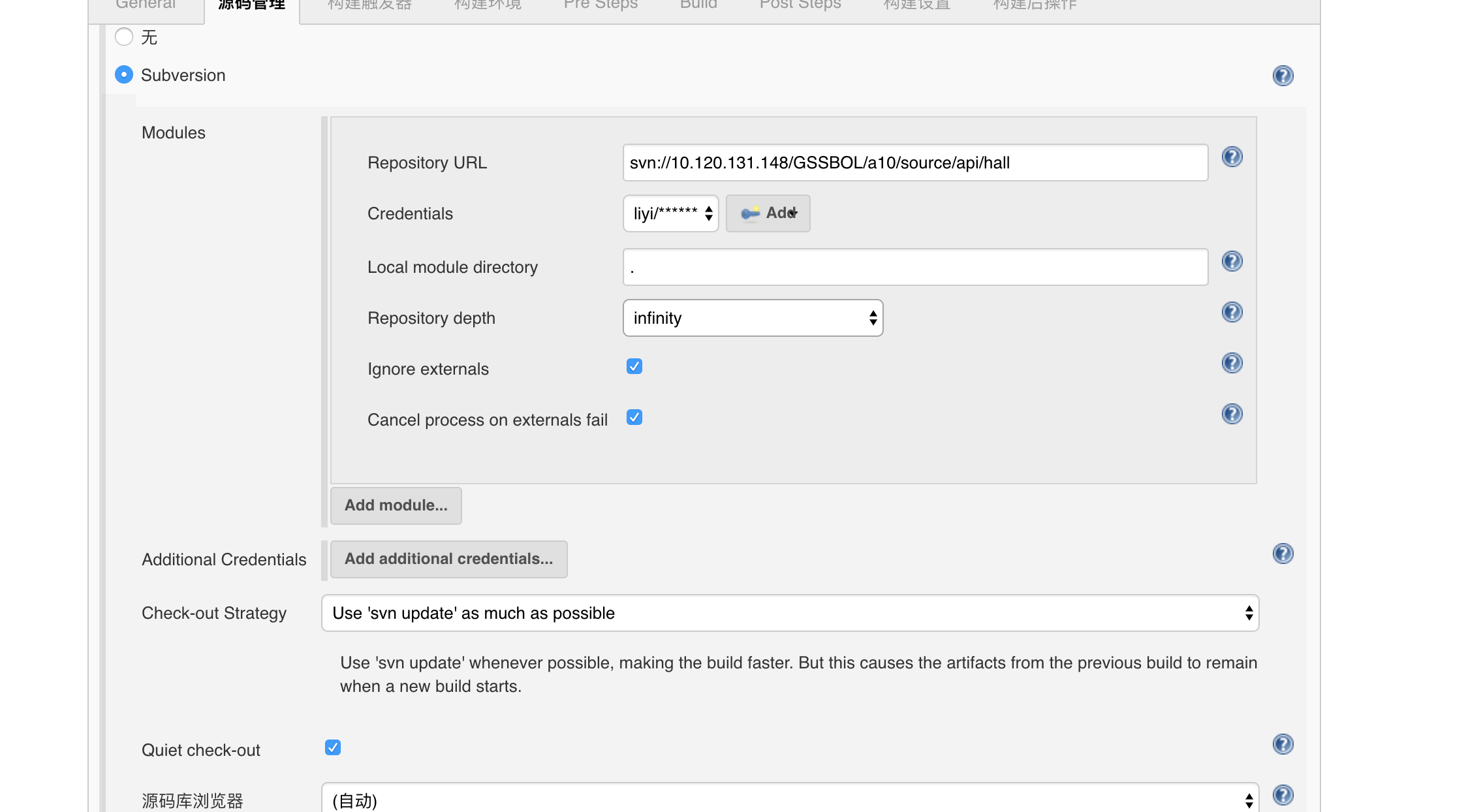
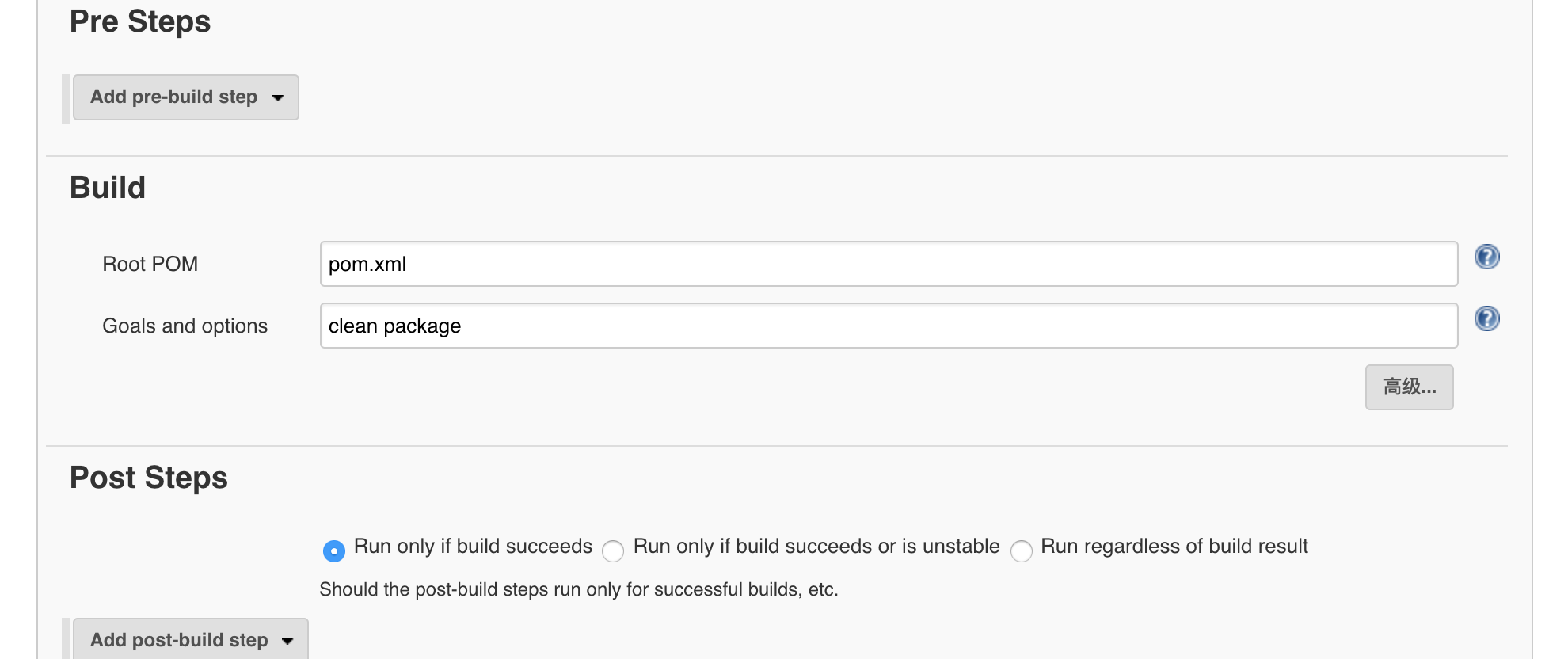
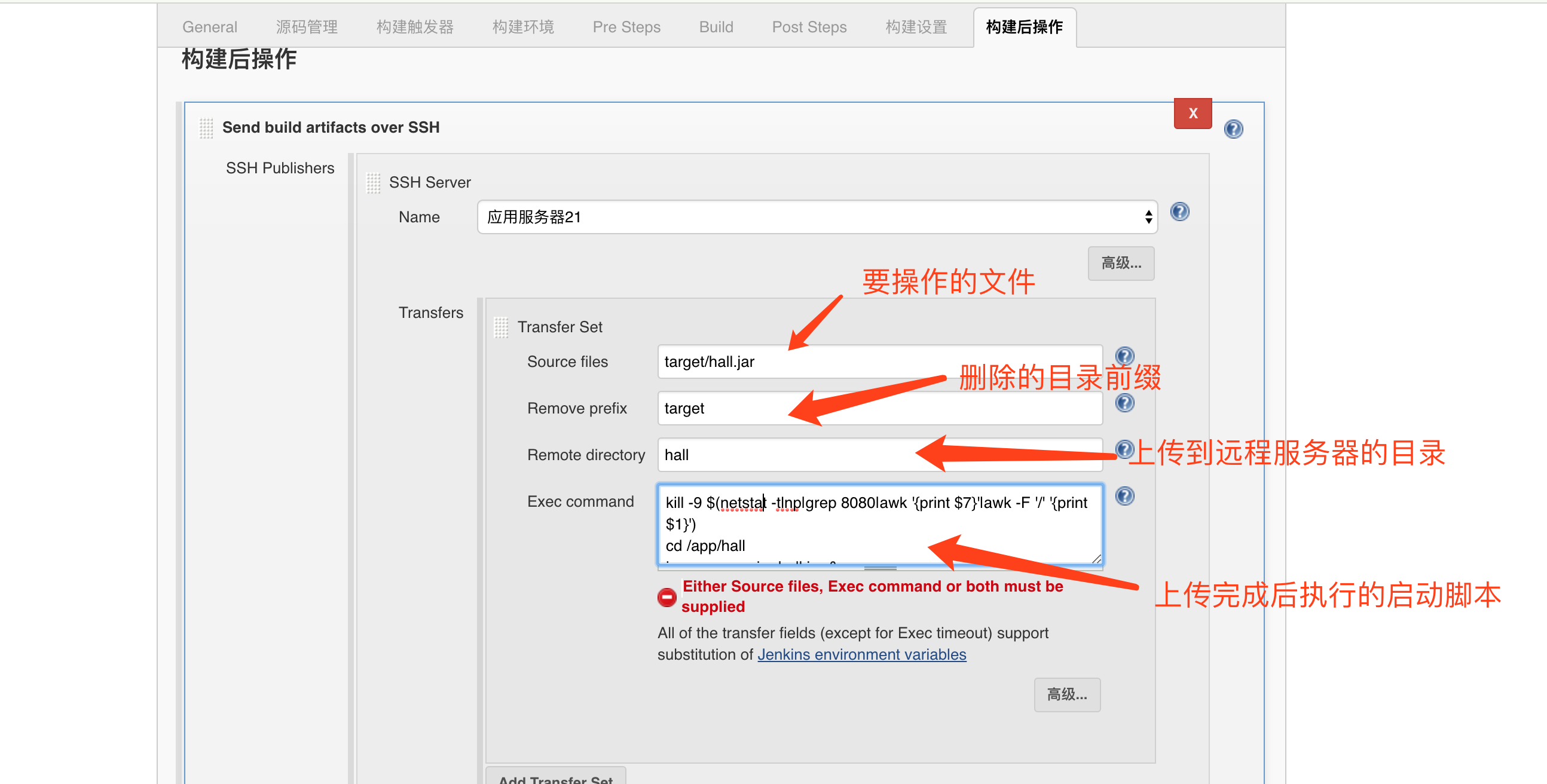
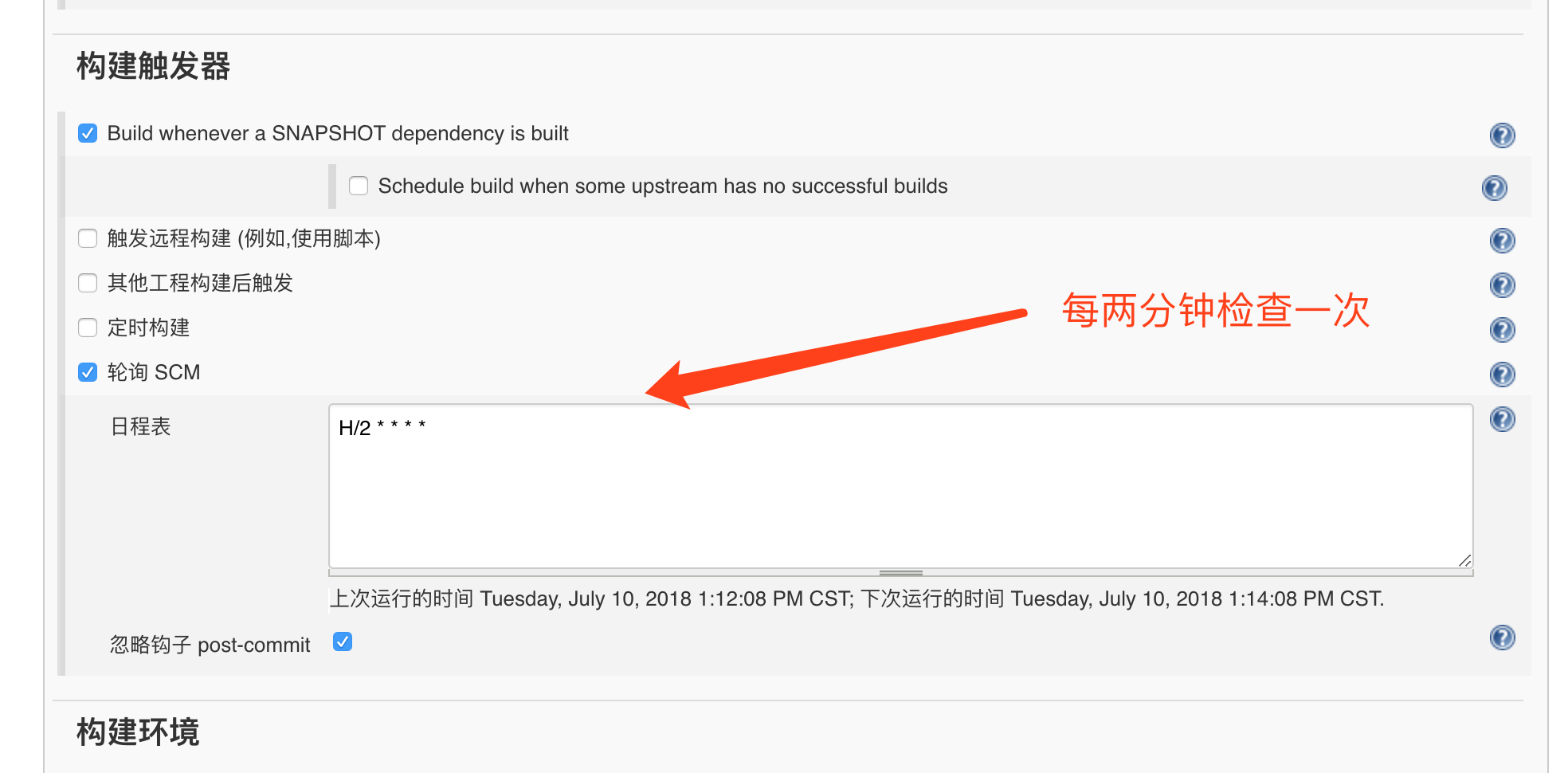
第18课:Spring Cloud 实例详解——系统发布
接口开发完成并且测试通过后,就可以进行发布,系统发布可以有很多方式,本文将目前主要的发布方式一一列举出来,供大家参考。
Java 命令行启动
这种方式比较简单,由于 Spring Boot 默认内置了 Tomcat,我们只需要打包成 Jar,即可通过 Java 命令启动 Jar 包,即我们的应用程序。
首先,news 下面的每个子工程都加上(Client 除外):
<packaging>jar</packaging>
此表示我们打包成 Jar 包。
其次,我们在每个 Jar 工程(除去 Commmon)的 pom.xml 中都加入以下内容:
<build>
<!-- jar包名字,一般和我们的工程名相同 -->
<finalName>user</finalName>
<sourceDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/java</sourceDirectory>
<testSourceDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/test/java</testSourceDirectory>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
<mainClass>com.lynn.${project.build.finalName}.Application</mainClass>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<useDefaultDelimiters>true</useDefaultDelimiters>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.18.1</version>
<configuration>
<skipTests>true</skipTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
<executions>
<!-- 替换会被 maven 特别处理的 default-compile -->
<execution>
<id>default-compile</id>
<phase>none</phase>
</execution>
<!-- 替换会被 maven 特别处理的 default-testCompile -->
<execution>
<id>default-testCompile</id>
<phase>none</phase>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>java-compile</id>
<phase>compile</phase>
<goals> <goal>compile</goal> </goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>java-test-compile</id>
<phase>test-compile</phase>
<goals> <goal>testCompile</goal> </goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
然后执行 maven clean package 命名打包:
第一次运行可能需要花点时间,因为需要从 Maven 仓库下载所有依赖包,以后打包就会比较快,等一段时间后,打包完成:
最后,我们将 Jar 包上传到服务器,依次启动 register.jar、config.jar、gateway.jar、article.jar、comment.jar、index.jar、user.jar 即可,启动命令是:
nohup java -server -jar xxx.jar &
用 nohup 命令启动 Jar 才能使 Jar 在后台运行,否则 shell 界面退出后,程序会自动退出。
Tomcat 启动
除了 Spring Boot 自带的 Tomcat,我们同样可以自己安装 Tomcat 来部署。
首先改造工程,将所有 <packaging>jar</packaging> 改为 <packaging>war</packaging>,去掉内置的 Tomcat:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
修改 build:
<build>
<!-- 文件名 -->
<finalName>register</finalName>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.18.1</version>
<configuration>
<skipTests>true</skipTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
然后修改启动类 Application.java:
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
}
这样打包后就会生成 War 包,打包方式同上。
我们将 War 上传到服务器的 Tomcat 上即可通过 Tomcat 启动项目。
Jenkins 自动化部署
我们搭建的是一套微服务架构,真实环境可能有成百上千个工程,如果都这样手动打包、上传、发布,工作量无疑是巨大的。这时,我们就需要考虑自动化部署了。
Jenkins 走进了我们的视野,它是一个开源软件项目,是基于 Java 开发的一种持续集成工具,用于监控持续重复的工作,旨在提供一个开放易用的软件平台,使软件的持续集成变成可能。
下面,我们就来看看如果通过 Jenkins 实现系统的自动化部署。
安装
Jenkins 的安装方式请自行百度,本文不做详细说明。
注: 安装好后,至少需要安装 Maven、SSH、Git、SVN 插件。
创建任务
安装好后,访问 Jenkins,登录后,即可看到如下界面:
(1)点击系统管理 -> 系统设置,添加服务器 SSH 信息:
(2)点击系统管理 -> 全局工具配置,配置好 JDK 和 Maven:
(3)点击新建任务,输入任务名,选择构建一个 Maven 风格的软件:
(4)点击确定,进入下一步:
这里以 SVN 为例说明(如果代码在 Git上,操作类似),将源码的 SVN 地址、SVN 账号信息依次填入文本框。
Build 下面填入 Maven 的构建命令。
在“构建后操作”里按要求填入如图所示内容:
其中,启动脚本示例如下:
kill -9 $(netstat -tlnp|grep 8080|awk '{print $7}'|awk -F '/' '{print $1}')
cd /app/hall
java -server -jar hall.jar &
点击保存。
手动构建
任务创建好后,点击“立即构建”即可自动构建并启动我们的应用程序,并且能够实时看到构建日志:
自动构建
我们每次都手动点击“立即构建”也挺麻烦,程序猿的最高进阶是看谁更懒,我都不想点那个按钮了,就想我提交了代码能自动构建,怎么做呢?很简单,进入任务配置界面,找到构建触发器选项:
保存后,Jenkins 会每隔两分钟对比一下 SVN,如果有改动,则自动构建。
总结
系统发布方式很多,我们可以根据自身项目特点选择适合自己的方式,当然还有很多方式,比如 K8S、Docker 等等,这里就不再赘述了 ,关于 K8S+Docker 的方式,我会在第20课讲解。
第19课:Spring Cloud 源码解析
Spring Cloud 集成了很多第三方框架,把它的全部源码拿出来解析几本书都讲不完,也不太现实,本文带领读者分析其中一小部分源码(其余源码读者有兴趣可以继续跟进),包括 Eureka-Server、Config、Zuul 的 starter 部分,分析其启动原理。
如果我们开发出一套框架,要和 Spring Boot 集成,就需要放到它的 starter 里。因此我们分析启动原理,直接从每个框架的 starter 开始分析即可。
Eureka-Server 源码解析
我们知道,要实现注册与发现,需要在启动类加上 @EnableEurekaServer 注解,我们进入其源码:
@EnableDiscoveryClient//表示eurekaserver也是一个客户端服务
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableEurekaServer {
}
注意看 @Import 注解,这个注解导入了 EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration 类,继续跟进这个类:
/**
* Responsible for adding in a marker bean to activate
* {@link EurekaServerAutoConfiguration}
*
* @author Biju Kunjummen
*/
@Configuration
public class EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration {
@Bean
public Marker eurekaServerMarkerBean() {
return new Marker();
}
class Marker {
}
}
通过上面的注释,我们继续查看 EurekaServerAutoConfiguration 类的源码:
@Configuration
@Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class,
InstanceRegistryProperties.class })
@PropertySource("classpath:/eureka/server.properties")
public class EurekaServerAutoConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* List of packages containing Jersey resources required by the Eureka server
*/
private static String[] EUREKA_PACKAGES = new String[] { "com.netflix.discovery",
"com.netflix.eureka" };
@Autowired
private ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager;
@Autowired
private EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig;
@Autowired
private EurekaClientConfig eurekaClientConfig;
@Autowired
private EurekaClient eurekaClient;
@Autowired
private InstanceRegistryProperties instanceRegistryProperties;
public static final CloudJacksonJson JACKSON_JSON = new CloudJacksonJson();
@Bean
public HasFeatures eurekaServerFeature() {
return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Eureka Server",
EurekaServerAutoConfiguration.class);
}
//如果eureka.client.registerWithEureka=true,则把自己注册进去
@Configuration
protected static class EurekaServerConfigBeanConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig(EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) {
EurekaServerConfigBean server = new EurekaServerConfigBean();
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
// Set a sensible default if we are supposed to replicate
server.setRegistrySyncRetries(5);
}
return server;
}
}
//实例化eureka-server的界面
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "eureka.dashboard", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public EurekaController eurekaController() {
return new EurekaController(this.applicationInfoManager);
}
static {
CodecWrappers.registerWrapper(JACKSON_JSON);
EurekaJacksonCodec.setInstance(JACKSON_JSON.getCodec());
}
@Bean
public ServerCodecs serverCodecs() {
return new CloudServerCodecs(this.eurekaServerConfig);
}
private static CodecWrapper getFullJson(EurekaServerConfig serverConfig) {
CodecWrapper codec = CodecWrappers.getCodec(serverConfig.getJsonCodecName());
return codec == null ? CodecWrappers.getCodec(JACKSON_JSON.codecName()) : codec;
}
private static CodecWrapper getFullXml(EurekaServerConfig serverConfig) {
CodecWrapper codec = CodecWrappers.getCodec(serverConfig.getXmlCodecName());
return codec == null ? CodecWrappers.getCodec(CodecWrappers.XStreamXml.class)
: codec;
}
class CloudServerCodecs extends DefaultServerCodecs {
public CloudServerCodecs(EurekaServerConfig serverConfig) {
super(getFullJson(serverConfig),
CodecWrappers.getCodec(CodecWrappers.JacksonJsonMini.class),
getFullXml(serverConfig),
CodecWrappers.getCodec(CodecWrappers.JacksonXmlMini.class));
}
}
@Bean
public PeerAwareInstanceRegistry peerAwareInstanceRegistry(
ServerCodecs serverCodecs) {
this.eurekaClient.getApplications(); // force initialization
return new InstanceRegistry(this.eurekaServerConfig, this.eurekaClientConfig,
serverCodecs, this.eurekaClient,
this.instanceRegistryProperties.getExpectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin(),
this.instanceRegistryProperties.getDefaultOpenForTrafficCount());
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes(PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry,
ServerCodecs serverCodecs) {
return new PeerEurekaNodes(registry, this.eurekaServerConfig,
this.eurekaClientConfig, serverCodecs, this.applicationInfoManager);
}
@Bean
public EurekaServerContext eurekaServerContext(ServerCodecs serverCodecs,
PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes) {
return new DefaultEurekaServerContext(this.eurekaServerConfig, serverCodecs,
registry, peerEurekaNodes, this.applicationInfoManager);
}
@Bean
public EurekaServerBootstrap eurekaServerBootstrap(PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry,
EurekaServerContext serverContext) {
return new EurekaServerBootstrap(this.applicationInfoManager,
this.eurekaClientConfig, this.eurekaServerConfig, registry,
serverContext);
}
/**
* Register the Jersey filter
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean jerseyFilterRegistration(
javax.ws.rs.core.Application eurekaJerseyApp) {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new ServletContainer(eurekaJerseyApp));
bean.setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE);
bean.setUrlPatterns(
Collections.singletonList(EurekaConstants.DEFAULT_PREFIX + "/*"));
return bean;
}
/**
* Construct a Jersey {@link javax.ws.rs.core.Application} with all the resources
* required by the Eureka server.
*/
@Bean
public javax.ws.rs.core.Application jerseyApplication(Environment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider provider = new ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider(
false, environment);
// Filter to include only classes that have a particular annotation.
//
provider.addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Path.class));
provider.addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Provider.class));
// Find classes in Eureka packages (or subpackages)
//
Set<Class<?>> classes = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
for (String basePackage : EUREKA_PACKAGES) {
Set<BeanDefinition> beans = provider.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition bd : beans) {
Class<?> cls = ClassUtils.resolveClassName(bd.getBeanClassName(),
resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
classes.add(cls);
}
}
// Construct the Jersey ResourceConfig
//
Map<String, Object> propsAndFeatures = new HashMap<String, Object>();
propsAndFeatures.put(
// Skip static content used by the webapp
ServletContainer.PROPERTY_WEB_PAGE_CONTENT_REGEX,
EurekaConstants.DEFAULT_PREFIX + "/(fonts|images|css|js)/.*");
DefaultResourceConfig rc = new DefaultResourceConfig(classes);
rc.setPropertiesAndFeatures(propsAndFeatures);
return rc;
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean traceFilterRegistration(
@Qualifier("webRequestLoggingFilter") Filter filter) {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(filter);
bean.setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10);
return bean;
}
}
这个类上有一个注解:@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class),这后面指定的类就是刚才那个类,而 @ConditionalOnBean 这个注解的作用是:仅仅在当前上下文中存在某个对象时,才会实例化一个 Bean。
因此,启动时就会实例化 EurekaServerAutoConfiguration 这个类。
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class,
InstanceRegistryProperties.class })
这个注解就是定义了一些 Eureka 的配置项。
Config 源码解析
通过上面的方法,我们找到了 ConfigServerAutoConfiguration 类:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnBean(ConfigServerConfiguration.Marker.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ConfigServerProperties.class)
@Import({ EnvironmentRepositoryConfiguration.class, CompositeConfiguration.class, ResourceRepositoryConfiguration.class,
ConfigServerEncryptionConfiguration.class, ConfigServerMvcConfiguration.class, TransportConfiguration.class })
public class ConfigServerAutoConfiguration {
}
可以发现这个类是空的,只是多了几个注解, @EnableConfigurationProperties(ConfigServerProperties.class) 表示开启 Config 配置属性。
最核心的注解是:@Import,它将其他一些配置类导入这个类,其中, EnvironmentRepositoryConfiguration 为环境配置类,内置了以下几种环境配置。
1. Native
@Configuration
@Profile("native")
protected static class NativeRepositoryConfiguration {
@Autowired
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
@Bean
public NativeEnvironmentRepository nativeEnvironmentRepository() {
return new NativeEnvironmentRepository(this.environment);
}
}
2. git
@Configuration
@Profile("git")
protected static class GitRepositoryConfiguration extends DefaultRepositoryConfiguration {}
3. subversion
@Configuration
@Profile("subversion")
protected static class SvnRepositoryConfiguration {
@Autowired
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
@Autowired
private ConfigServerProperties server;
@Bean
public SvnKitEnvironmentRepository svnKitEnvironmentRepository() {
SvnKitEnvironmentRepository repository = new SvnKitEnvironmentRepository(this.environment);
if (this.server.getDefaultLabel()!=null) {
repository.setDefaultLabel(this.server.getDefaultLabel());
}
return repository;
}
}
4.vault
@Configuration
@Profile("subversion")
protected static class SvnRepositoryConfiguration {
@Autowired
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
@Autowired
private ConfigServerProperties server;
@Bean
public SvnKitEnvironmentRepository svnKitEnvironmentRepository() {
SvnKitEnvironmentRepository repository = new SvnKitEnvironmentRepository(this.environment);
if (this.server.getDefaultLabel()!=null) {
repository.setDefaultLabel(this.server.getDefaultLabel());
}
return repository;
}
}
从代码可以看到 Git 是配置中心默认环境。
@Bean
public MultipleJGitEnvironmentRepository defaultEnvironmentRepository() {
MultipleJGitEnvironmentRepository repository = new MultipleJGitEnvironmentRepository(this.environment);
repository.setTransportConfigCallback(this.transportConfigCallback);
if (this.server.getDefaultLabel()!=null) {
repository.setDefaultLabel(this.server.getDefaultLabel());
}
return repository;
}
我们进入 MultipleJGitEnvironmentRepository 类:
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.cloud.config.server.git")
public class MultipleJGitEnvironmentRepository extends JGitEnvironmentRepository {
}
这个类表示可以支持配置多个 Git 仓库,它继承自 JGitEnvironmentRepository 类:
public class JGitEnvironmentRepository extends AbstractScmEnvironmentRepository
implements EnvironmentRepository, SearchPathLocator, InitializingBean {
/**
* Get the working directory ready.
*/
public String refresh(String label) {
Git git = null;
try {
git = createGitClient();
if (shouldPull(git)) {
fetch(git, label);
// checkout after fetch so we can get any new branches, tags,
// ect.
checkout(git, label);
if (isBranch(git, label)) {
// merge results from fetch
merge(git, label);
if (!isClean(git)) {
logger.warn("The local repository is dirty. Resetting it to origin/" + label + ".");
resetHard(git, label, "refs/remotes/origin/" + label);
}
}
} else {
// nothing to update so just checkout
checkout(git, label);
}
// always return what is currently HEAD as the version
return git.getRepository().getRef("HEAD").getObjectId().getName();
} catch (RefNotFoundException e) {
throw new NoSuchLabelException("No such label: " + label, e);
} catch (NoRemoteRepositoryException e) {
throw new NoSuchRepositoryException("No such repository: " + getUri(), e);
} catch (GitAPIException e) {
throw new NoSuchRepositoryException("Cannot clone or checkout repository: " + getUri(), e);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot load environment", e);
} finally {
try {
if (git != null) {
git.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
this.logger.warn("Could not close git repository", e);
}
}
}
}
refresh 方法的作用就是 ConfigServer 会从我们配置的 Git 仓库拉取配置下来。
Zuul 源码解析
同理,我们找到 Zuul 的配置类 ZuulProxyAutoConfiguration:
@Configuration
@Import({ RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration.RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class,
RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration.OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class,
RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration.HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class })
@ConditionalOnBean(ZuulProxyMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class)
public class ZuulProxyAutoConfiguration extends ZuulServerAutoConfiguration {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonRequestCustomizer> requestCustomizers = Collections.emptyList();
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discovery;
@Autowired
private ServiceRouteMapper serviceRouteMapper;
@Override
public HasFeatures zuulFeature() {
return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Zuul (Discovery)", ZuulProxyAutoConfiguration.class);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DiscoveryClientRouteLocator.class)
public DiscoveryClientRouteLocator discoveryRouteLocator() {
return new DiscoveryClientRouteLocator(this.server.getServletPrefix(), this.discovery, this.zuulProperties,
this.serviceRouteMapper);
}
//以下是过滤器,也就是之前zuul提到的实现的ZuulFilter接口
// pre filters
//路由之前
@Bean
public PreDecorationFilter preDecorationFilter(RouteLocator routeLocator, ProxyRequestHelper proxyRequestHelper) {
return new PreDecorationFilter(routeLocator, this.server.getServletPrefix(), this.zuulProperties,
proxyRequestHelper);
}
// route filters
// 路由时
@Bean
public RibbonRoutingFilter ribbonRoutingFilter(ProxyRequestHelper helper,
RibbonCommandFactory<?> ribbonCommandFactory) {
RibbonRoutingFilter filter = new RibbonRoutingFilter(helper, ribbonCommandFactory, this.requestCustomizers);
return filter;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(SimpleHostRoutingFilter.class)
public SimpleHostRoutingFilter simpleHostRoutingFilter(ProxyRequestHelper helper, ZuulProperties zuulProperties) {
return new SimpleHostRoutingFilter(helper, zuulProperties);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> zuulDiscoveryRefreshRoutesListener() {
return new ZuulDiscoveryRefreshListener();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ServiceRouteMapper.class)
public ServiceRouteMapper serviceRouteMapper() {
return new SimpleServiceRouteMapper();
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.Endpoint")
protected static class NoActuatorConfiguration {
@Bean
public ProxyRequestHelper proxyRequestHelper(ZuulProperties zuulProperties) {
ProxyRequestHelper helper = new ProxyRequestHelper();
helper.setIgnoredHeaders(zuulProperties.getIgnoredHeaders());
helper.setTraceRequestBody(zuulProperties.isTraceRequestBody());
return helper;
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(Endpoint.class)
protected static class RoutesEndpointConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private TraceRepository traces;
@Bean
public RoutesEndpoint zuulEndpoint(RouteLocator routeLocator) {
return new RoutesEndpoint(routeLocator);
}
@Bean
public RoutesMvcEndpoint zuulMvcEndpoint(RouteLocator routeLocator, RoutesEndpoint endpoint) {
return new RoutesMvcEndpoint(endpoint, routeLocator);
}
@Bean
public ProxyRequestHelper proxyRequestHelper(ZuulProperties zuulProperties) {
TraceProxyRequestHelper helper = new TraceProxyRequestHelper();
if (this.traces != null) {
helper.setTraces(this.traces);
}
helper.setIgnoredHeaders(zuulProperties.getIgnoredHeaders());
helper.setTraceRequestBody(zuulProperties.isTraceRequestBody());
return helper;
}
}
private static class ZuulDiscoveryRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
private HeartbeatMonitor monitor = new HeartbeatMonitor();
@Autowired
private ZuulHandlerMapping zuulHandlerMapping;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof InstanceRegisteredEvent) {
reset();
}
else if (event instanceof ParentHeartbeatEvent) {
ParentHeartbeatEvent e = (ParentHeartbeatEvent) event;
resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
}
else if (event instanceof HeartbeatEvent) {
HeartbeatEvent e = (HeartbeatEvent) event;
resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
}
}
private void resetIfNeeded(Object value) {
if (this.monitor.update(value)) {
reset();
}
}
private void reset() {
this.zuulHandlerMapping.setDirty(true);
}
}
}
通过 @Import 注解可以找到几个类:
- RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration.RestClientRibbonConfiguration
- RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration.OkHttpRibbonConfiguration
- RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration.HttpClientRibbonConfiguration
我们知道 Zuul 提供网关能力,通过上面这几个类就能分析到,它内部其实也是通过接口请求,找到每个服务提供的接口地址。
进入 RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration 类:
public class RibbonCommandFactoryConfiguration {
//以下提供了3个不同的请求模式
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient
protected static class RestClientRibbonConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private Set<ZuulFallbackProvider> zuulFallbackProviders = Collections.emptySet();
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RibbonCommandFactory<?> ribbonCommandFactory(
SpringClientFactory clientFactory, ZuulProperties zuulProperties) {
return new RestClientRibbonCommandFactory(clientFactory, zuulProperties,
zuulFallbackProviders);
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnRibbonOkHttpClient
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "okhttp3.OkHttpClient")
protected static class OkHttpRibbonConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private Set<ZuulFallbackProvider> zuulFallbackProviders = Collections.emptySet();
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RibbonCommandFactory<?> ribbonCommandFactory(
SpringClientFactory clientFactory, ZuulProperties zuulProperties) {
return new OkHttpRibbonCommandFactory(clientFactory, zuulProperties,
zuulFallbackProviders);
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnRibbonHttpClient
protected static class HttpClientRibbonConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private Set<ZuulFallbackProvider> zuulFallbackProviders = Collections.emptySet();
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RibbonCommandFactory<?> ribbonCommandFactory(
SpringClientFactory clientFactory, ZuulProperties zuulProperties) {
return new HttpClientRibbonCommandFactory(clientFactory, zuulProperties, zuulFallbackProviders);
}
}
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnRibbonHttpClientCondition.class)
@interface ConditionalOnRibbonHttpClient { }
private static class OnRibbonHttpClientCondition extends AnyNestedCondition {
public OnRibbonHttpClientCondition() {
super(ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
}
@Deprecated //remove in Edgware"
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "zuul.ribbon.httpclient.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
static class ZuulProperty {}
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "ribbon.httpclient.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
static class RibbonProperty {}
}
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnRibbonOkHttpClientCondition.class)
@interface ConditionalOnRibbonOkHttpClient { }
private static class OnRibbonOkHttpClientCondition extends AnyNestedCondition {
public OnRibbonOkHttpClientCondition() {
super(ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
}
@Deprecated //remove in Edgware"
@ConditionalOnProperty("zuul.ribbon.okhttp.enabled")
static class ZuulProperty {}
@ConditionalOnProperty("ribbon.okhttp.enabled")
static class RibbonProperty {}
}
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnRibbonRestClientCondition.class)
@interface ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient { }
private static class OnRibbonRestClientCondition extends AnyNestedCondition {
public OnRibbonRestClientCondition() {
super(ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
}
@Deprecated //remove in Edgware"
@ConditionalOnProperty("zuul.ribbon.restclient.enabled")
static class ZuulProperty {}
@ConditionalOnProperty("ribbon.restclient.enabled")
static class RibbonProperty {}
}
}
总结
前面带领大家分析了一小段源码,Spring Cloud 很庞大,不可能一一分析,本文的主要目的就是教大家如何分析源码,从何处下手,以便大家可以按照这种思路继续跟踪下去。
第20课:K8S+Docker 部署 Spring Cloud 集群
在一个实际的大型系统中,微服务架构可能由成百上千个服务组成,我们发布一个系统如果都单纯的通过打包上传,再发布,工作量无疑是巨大的,也是不可取的,前面我们知道了可以通过 Jenkins 帮我们自动化完成发布任务。
但是,我们知道一个 Java 应用其实是比较占用资源的,每个服务都发布到物理宿主机上面,资源开销也是巨大的,而且每扩展一台服务器,都需要重复部署相同的软件,这种方式显然是不可取的。
容器技术的出现带给了我们新的思路,我们将服务打包成镜像,放到容器中,通过容器来运行我们的服务,这样我们可以很方便进行分布式的管理,同样的服务也可以很方便进行水平扩展。
Docker 是容器技术方便的佼佼者,它是一个开源容器。而 Kubernetes(以下简称 K8S),是一个分布式集群方案的平台,它天生就是和 Docker 一对,通过 K8S 和 Docker 的配合,我们很容易搭建分布式集群环境。
下面,我们就来看看 K8S 和 Docker 的吸引之处。
集群环境搭建
本文用一台虚拟机模拟集群环境。
操作系统:CentOS7 64位
配置:内存2GB,硬盘40GB。
注:真正的分布式环境搭建方案类似,可以参考博文:Kubernetes学习2——集群部署与搭建》。
下面开始搭建集群环境。
1. 关闭防火墙:
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
2. 安装 etcd:
yum install -y etcd
安装完成后启动 etcd:
systemctl start etcd
systemctl enable etcd
启动后,我们可以检查 etcd 健康状况:
etcdctl -C http://localhost:2379 cluster-health
出现下面信息说明 etcd 目前是稳定的:
member 8e9e05c52164694d is healthy: got healthy result from http://localhost:2379
cluster is healthy
3. 安装 Docker:
yum install docker -y
完成后启动 Docker:
chkconfig docker on
service docker start
4. 安装 Kubernetes:
yum install kubernetes -y
安装完成后修改配置文件 /etc/kubernetes/apiserver:
vi /etc/kubernetes/apiserver
把 KUBE_ADMISSION_CONTROL 后面的 ServiceAccount 删掉,如:
KUBE_ADMISSION_CONTROL="--admission-control=NamespaceLifecycle,NamespaceExists,LimitRanger,SecurityContextDeny,ResourceQuota"
然后依次启动 kubernetes-server:
systemctl enable kube-apiserver
systemctl start kube-apiserver
systemctl enable kube-controller-manager
systemctl start kube-controller-manager
systemctl enable kube-scheduler
systemctl start kube-scheduler
再依次启动 kubernetes-client:
systemctl enable kubelet
systemctl start kubelet
systemctl enable kube-proxy
systemctl start kube-proxy
我们查看集群状态:
kubectl get no
可以看到以下信息:
NAME STATUS AGE
127.0.0.1 Ready 1h
至此,我们基于 K8S 的集群环境就搭建完成了,但是我们发布到 Docker 去外部是无法访问的,还要安装 Flannel 以覆盖网络。
执行以下命令安装 Flannel:
yum install flannel -y
安装完成后修改配置文件 /etc/sysconfig/flanneld:
vim /etc/sysconfig/flanneld
内容如下:
# Flanneld configuration options
# etcd url location. Point this to the server where etcd runs
FLANNEL_ETCD_ENDPOINTS="http://127.0.0.1:2379"
# etcd config key. This is the configuration key that flannel queries
# For address range assignment
FLANNEL_ETCD_PREFIX="/atomic.io/network"
# Any additional options that you want to pass
FLANNEL_OPTIONS="--logtostderr=false --log_dir=/var/log/k8s/flannel/ --etcd-prefix=/atomic.io/network --etcd-endpoints=http://localhost:2379 --iface=enp0s3"
其中,enp0s3 为网卡名字,通过 ifconfig 可以查看。
然后配置 etcd 中关于 Flannel 的 key:
etcdctl mk /atomic.io/network/config '{ "Network": "10.0.0.0/16" }'
其中 /atomic.io/network 要和配置文件中配置的一致。
最后启动 Flannel 并重启 Kubernetes:
systemctl enable flanneld
systemctl start flanneld
systemctl enable flanneld
service docker restart
systemctl restart kube-apiserver
systemctl restart kube-controller-manager
systemctl restart kube-scheduler
systemctl restart kubelet
systemctl restart kube-proxy
这样,一个完整的基于 K8S+Docker 的集群环境搭建完成了,后面我们就可以在这上面部署分布式系统。
本文只是做演示,不会真正的发布一套系统,因此我们以注册中心 register 为例,演示如何发布一套分布式系统。
创建 Docker 镜像
我们首先将 register 本地打包成 Jar 上传到虚拟机上,然后通过 Dockerfile 来创建 register 的镜像,Dockerfile 内容如下:
#下载java8的镜像
FROM java:8
#将本地文件挂到到/tmp目录
VOLUME /tmp
#复制文件到容器
ADD register.jar /registar.jar
#暴露8888端口
EXPOSE 8888
#配置启动容器后执行的命令
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/register.jar"]
通过 docker build 构建镜像:
docker build -t register.jar:0.0.1 .
执行该命令后,会打印以下信息:
Sending build context to Docker daemon 48.72 MB
Step 1/6 : FROM java:8
Trying to pull repository docker.io/library/java ...
apiVersion: v1
8: Pulling from docker.io/library/java
5040bd298390: Pull complete
fce5728aad85: Pull complete
76610ec20bf5: Pull complete
60170fec2151: Pull complete
e98f73de8f0d: Pull complete
11f7af24ed9c: Pull complete
49e2d6393f32: Pull complete
bb9cdec9c7f3: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:c1ff613e8ba25833d2e1940da0940c3824f03f802c449f3d1815a66b7f8c0e9d
Status: Downloaded newer image for docker.io/java:8
---> d23bdf5b1b1b
Step 2/6 : VOLUME /tmp
---> Running in f6f284cf34f2
---> bf70efe7bea0
Removing intermediate container f6f284cf34f2
Step 3/6 : ADD register.jar registar.jar
---> 91d6f5aa9db3
Removing intermediate container e4dd67f5acc2
Step 4/6 : RUN bash -c 'touch /register.jar'
---> Running in 3b6d5f4ed216
---> 70381c5e0b5d
Removing intermediate container 3b6d5f4ed216
Step 5/6 : EXPOSE 8888
---> Running in b87b788ff362
---> 912e4f8e3004
Removing intermediate container b87b788ff362
Step 6/6 : ENTRYPOINT java -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom jar /register.jar
---> Running in 1bc65e0bfbea
---> 1aec9d5e9c70
Removing intermediate container 1bc65e0bfbea
Successfully built 1aec9d5e9c70
这时通过 docker images 命令就可以看到我们刚构建的镜像:
[root@localhost ~]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
register.jar 0.0.1 1aec9d5e9c70 2 minutes ago 692 MB
docker.io/registry 2 b2b03e9146e1 5 days ago 33.3 MB
docker.io/java 8 d23bdf5b1b1b 18 months ago 643 MB
系统发布
我们本地虚拟机有了镜像就可以通过 K8S 发布了。
1. 创建 register-rc.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController
metadata:
name: register
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
app: register
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: register
spec:
containers:
- name: register
#镜像名
image: register
#本地有镜像就不会去仓库拉取
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 8888
执行命令:
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl create -f register-rc.yaml
replicationcontroller "register" created
提示创建成功后,我们可以查看 pod:
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
register-4l088 1/1 Running 0 10s
如果 STATUS 显示为 Running,说明运行成功,否则可以通过以下命令来查看日志:
kubectl describe po register-4l088
然后我们通过 docker ps 命令来查看当前运行的容器:
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
dd8c05ae4432 register "java -jar /app.jar" 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes k8s_register.892502b2_register-4l088_default_4580c447-8640-11e8-bba0-080027607861_5bf71ba9
3b5ae8575079 registry.access.redhat.com/rhel7/pod-infrastructure:latest "/usr/bin/pod" 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes k8s_POD.43570bb9_register-4l088_default_4580c447-8640-11e8-bba0-080027607861_1f38e064
可以看到容器已经在运行了,但是这样外部还是无法访问,因为 K8S 分配的是虚拟 IP,要通过宿主机访问,还需要创建 Service。
编写 register-svc.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: register
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8888
targetPort: 8888
节点暴露给外部的端口(范围必须为30000-32767)
nodePort: 30001
selector:
app: register
然后执行命令:
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl create -f register-svc.yaml
service "register" created
我们可以查看创建的 Service:
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get svc
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes 10.254.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 20h
register 10.254.228.248 <nodes> 8888:30001/TCP 37s
这时就可以通过 IP:30001 访问 register 了,如果访问不了需要先运行命令:
iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
访问 http://172.20.10.13:30001,如图:
至此,我们的注册中心就可以通过 K8S 部署了,现在看起来比较麻烦,但是在一个大的集群环境中是很爽的,我们可以在结合前面提到的 Jenkins,把刚才一系列手动的操作交给 Jenkins 做。