list的认识与使用
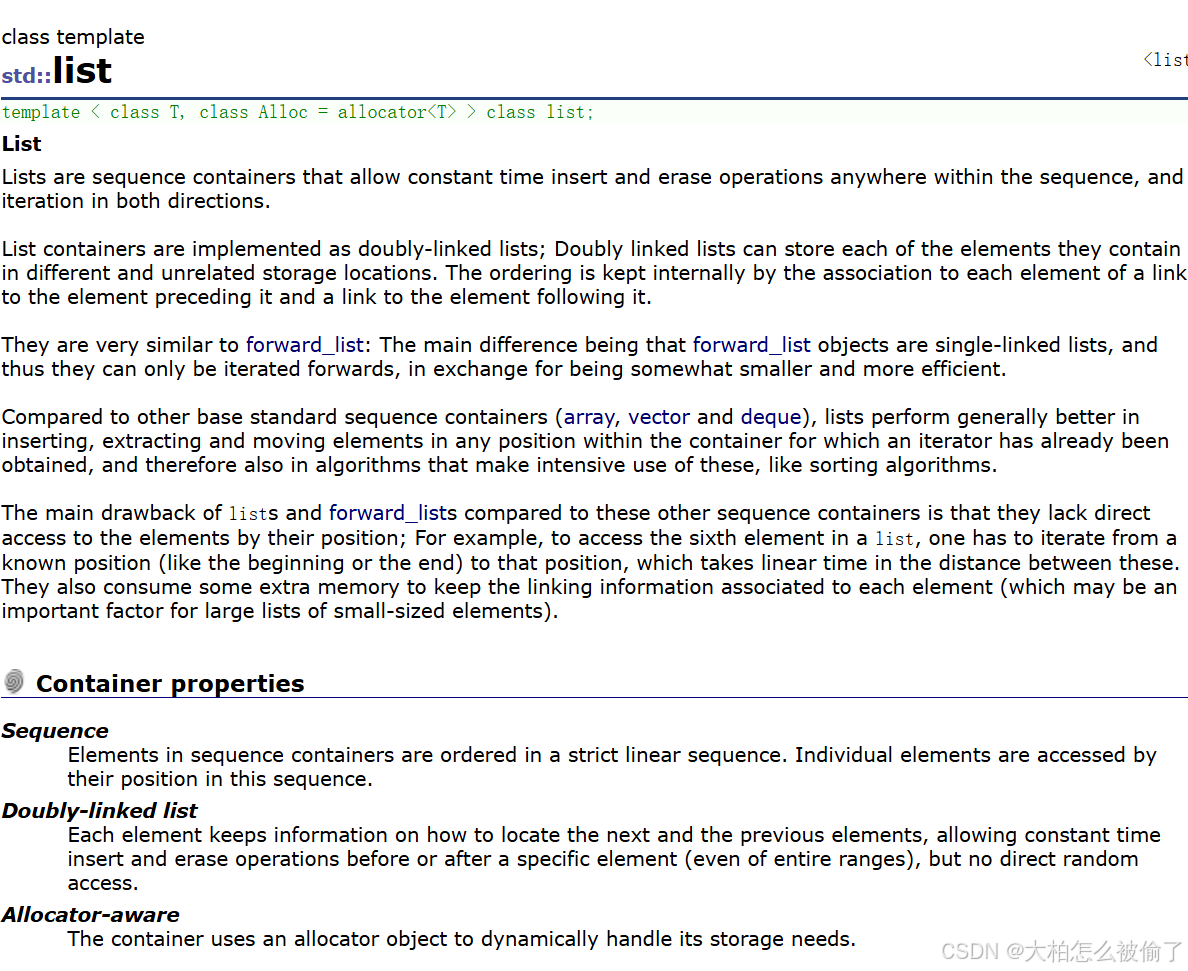
list的介绍
- std::list
- template < class T, class Alloc = allocator > class list;
1.list是可以在常数范围内可以在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
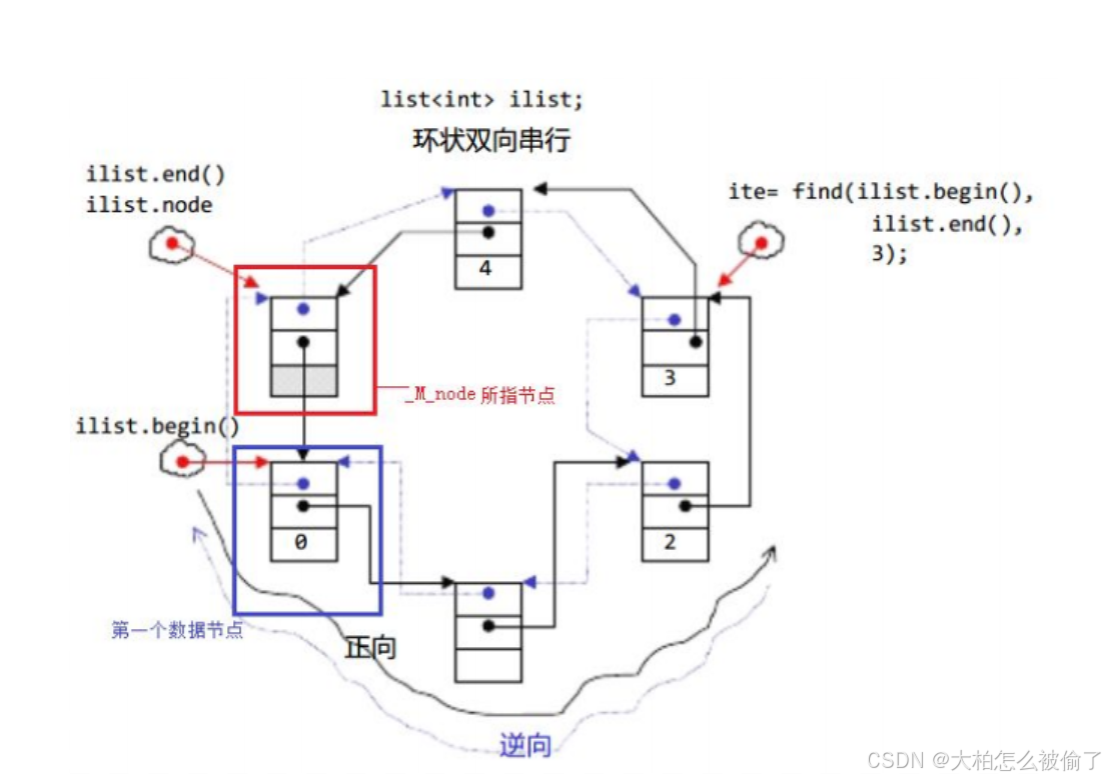
2.list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中的每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
3.list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,比起更加简单高效。
4.与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入,移除元素的执行效率更好。
5.与其他的序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)。
list的使用
Member functions(成员函数)
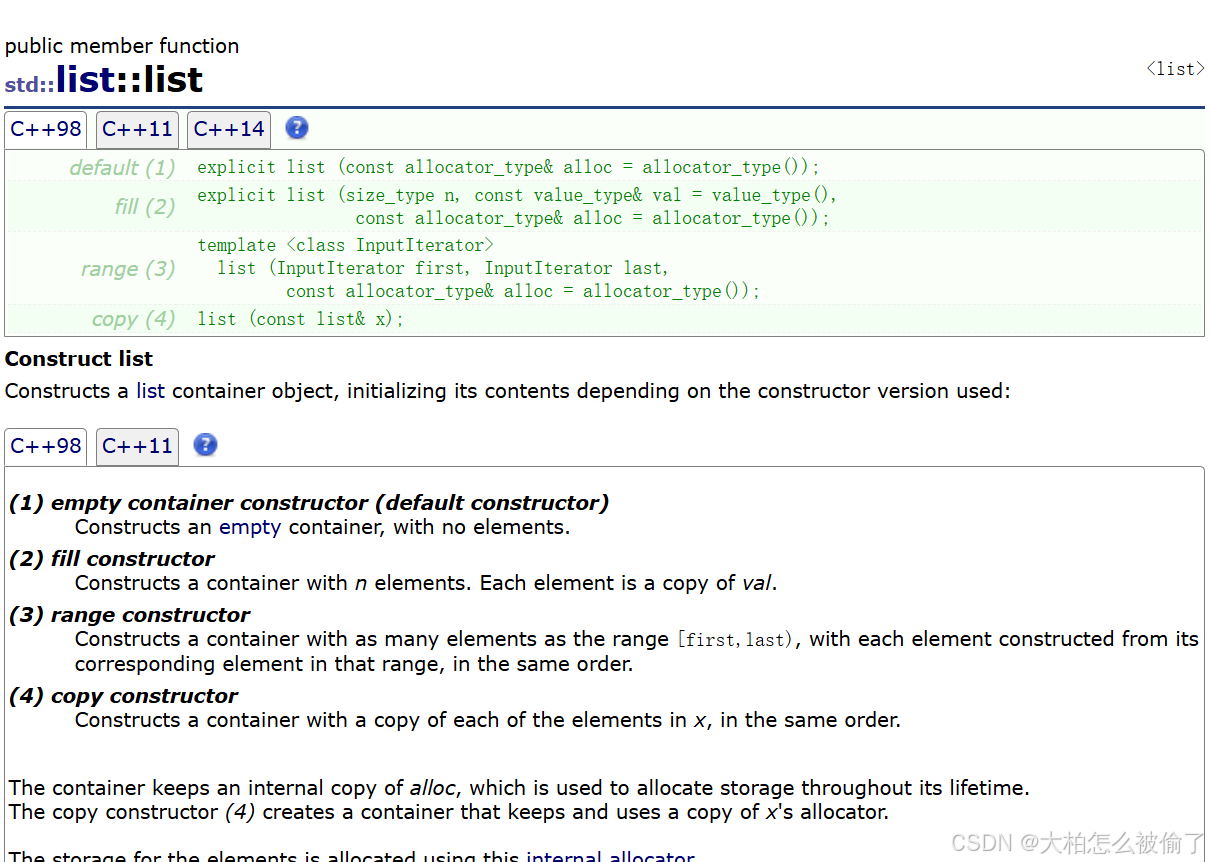
constuctor(构造函数)
- std::list::list
- 构造链表
- default (1)
explicit list (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
空容器构造函数(默认构造函数)
list<int> lt1;
- fill (2)
explicit list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type(),
const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
多参数构造函数
list<int> lt2(4, 100);
- range (3)
template < class InputIterator >
list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
范围构造函数
list<int> lt3(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
- copy (4)
list (const list& x);
拷贝构造函数
list<int> lt4(lt3);
destructor(析构函数)
- std::list::~list
- ~list();
- list的析构函数
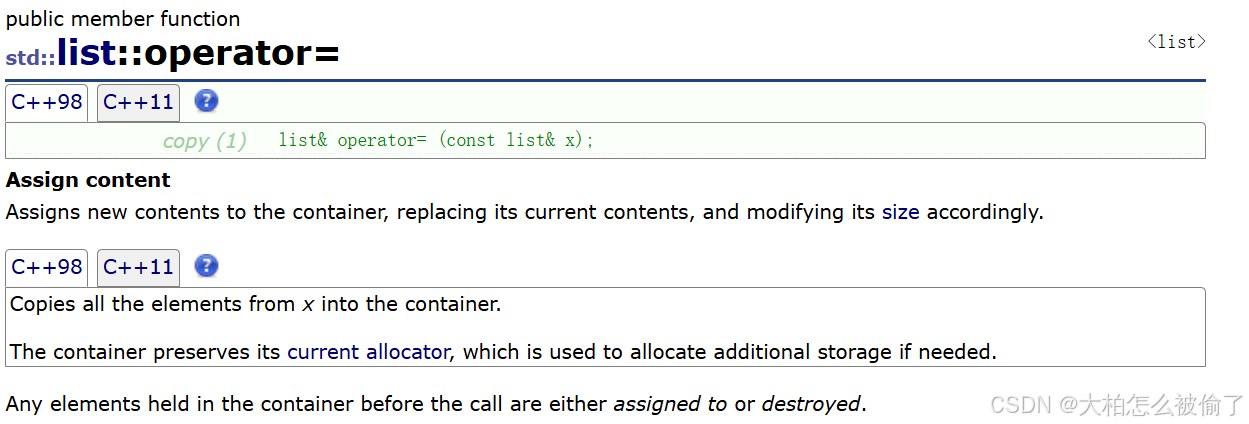
operator=(赋值构造)
-
std::list::operator=
-
copy (1)
list& operator= (const list& x); -
分配内容
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2(4, 100);
lt1 = lt2;
Iterators(迭代器)
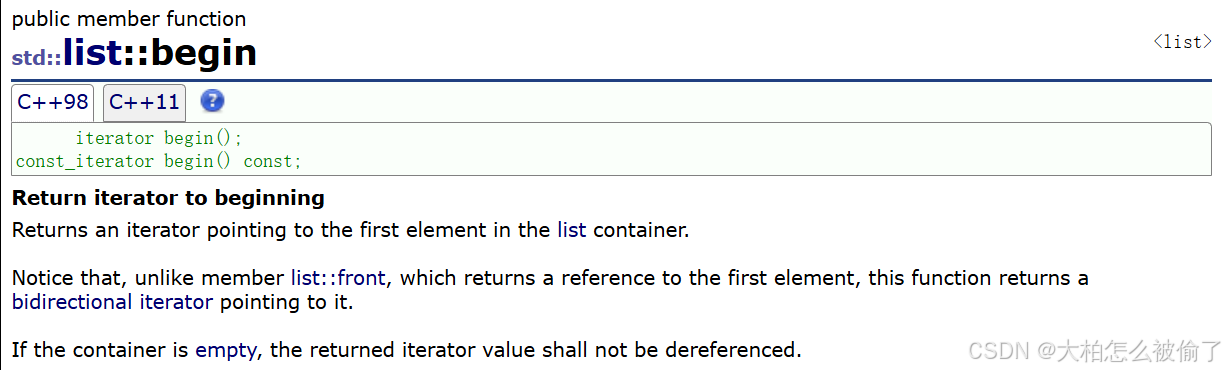
begin
-
std::list::begin
-
iterator begin();
-
const_iterator begin() const;
-
返回指向开始的迭代器
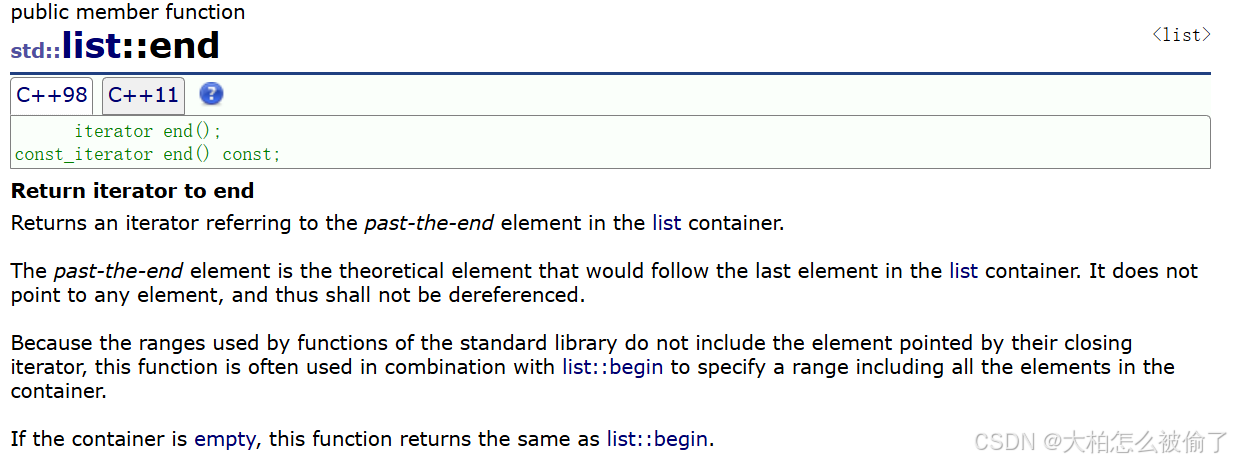
end
- std::list::end
- iterator end();
- const_iterator end() const;
- 返回指向结尾的迭代器
list<int> lt(4, 100);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
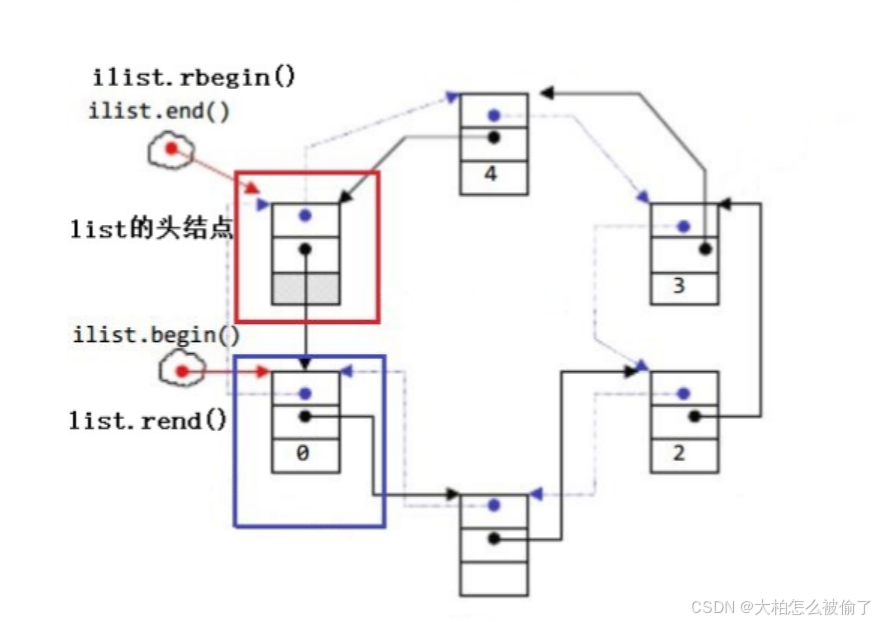
rbegin
- std::list::rbegin
- reverse_iterator rbegin();
- const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
- 返回指向反向开始的反向迭代器
rend
- std::list::rend
- reverse_iterator rend();
- const_reverse_iterator rend() const;
- 返回指向反向结尾的反向迭代器
list<int> lt(4, 100);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.end();
while (it != lt.begin())
{
cout << *it << " ";
--it;
}
cout << endl;
【注意】
1.begin与end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动。
2.rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动。
Capacity(容量)
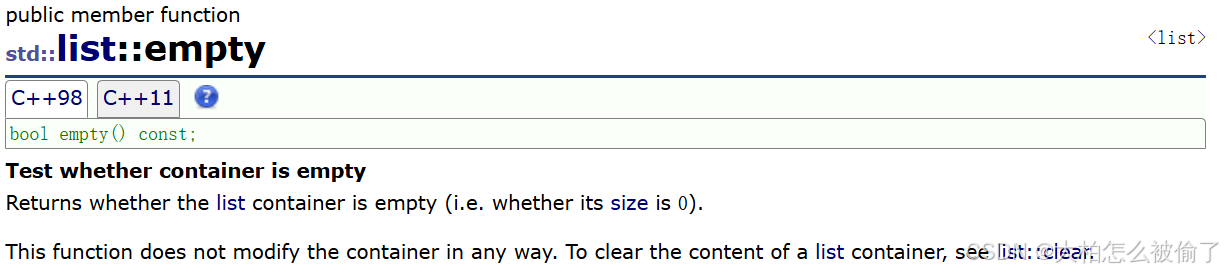
empty
- std::list::empty
- bool empty() const;
- 检测容器是否为空
list<int> lt(2, 5);
cout << lt.empty() << endl;
size
- std::list::size
- size_type size() const;
- 返回list中有效节点的个数
list<int> lt(2, 5);
cout << lt.size() << endl;
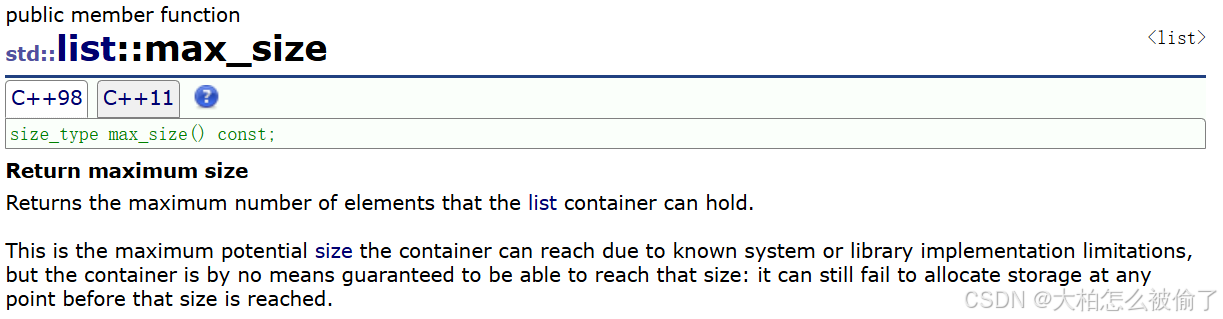
max_size
- std::list::max_size
- size_type max_size() const;
- 返回容器最大字节
list<int> lt;
cout << lt.max_size() << endl;
Element access(元素访问)
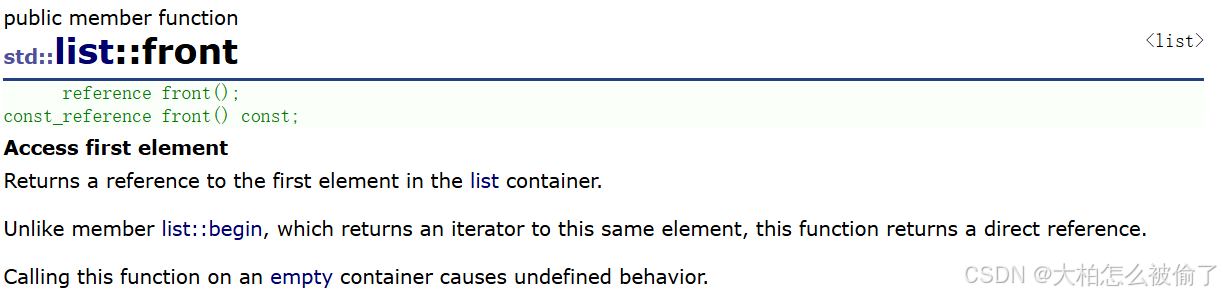
front
- std::list::front
- reference front();
- const_reference front() const;
- 返回list的第一个节点中值的引用
list<int> lt(5, 20);
cout << lt.front() << endl;
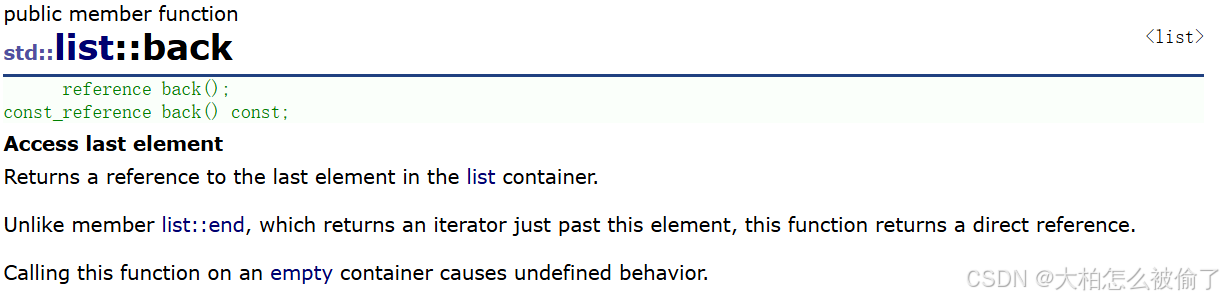
back
- std::list::back
- reference back();
- const_reference back() const;
- 返回list的最后一个节点中值的引用
list<int> lt(5, 20);
cout << lt.back() << endl;
Modifiers(修饰符)
assign
- std::list::assign
- range (1)
template < class InputIterator >
void assign (InputIterator first, InputIterator last); - fill (2)
void assign (size_type n, const value_type& val); - 分配新的内容给容器
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2;
lt1.assign(4, 12);
lt2.assign(lt1.begin(), lt1.end());
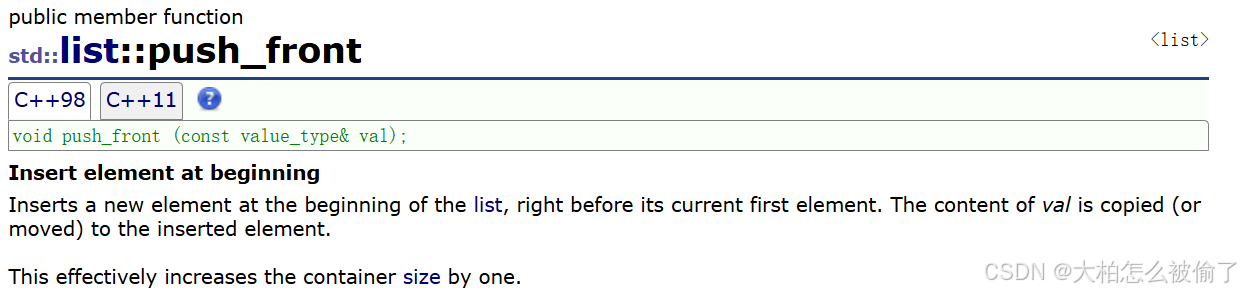
push_front
- std::list::push_front
- void push_front (const value_type& val);
- 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素
list<int> lt1;
lt1.assign(4, 12);
lt1.push_front(1);
for (auto t : lt1)
{
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;
pop_front
- std::list::pop_front
- void pop_front();
- 删除list中第一个元素
list<int> lt1;
lt1.assign(4, 12);
lt1.pop_back();
for (auto t : lt1)
{
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;
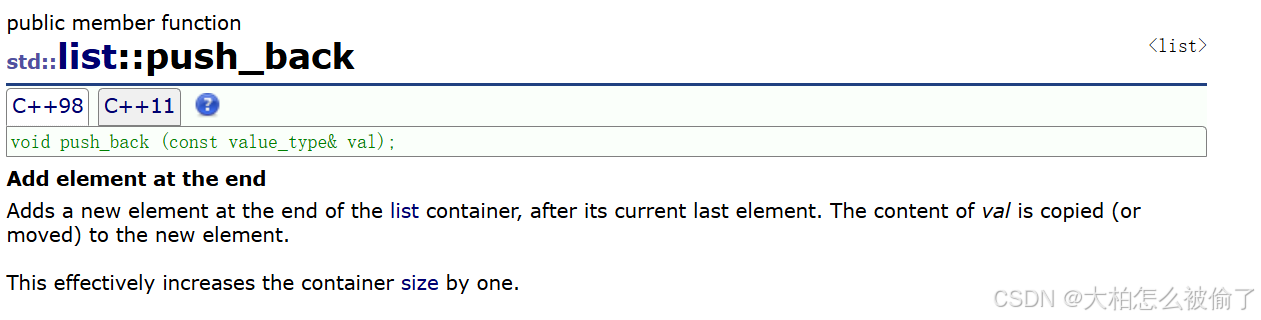
push_back
- std::list::push_back
- void push_back (const value_type& val);
- 在list尾部插入值为val的元素
list<int> lt1;
lt1.assign(4, 12);
lt1.push_back(1);
for (auto t : lt1)
{
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;
pop_back
- std::list::pop_front
- void pop_front();
- 删除list中最后一个元素
list<int> lt1;
lt1.assign(4, 12);
lt1.pop_front();
for (auto t : lt1)
{
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;
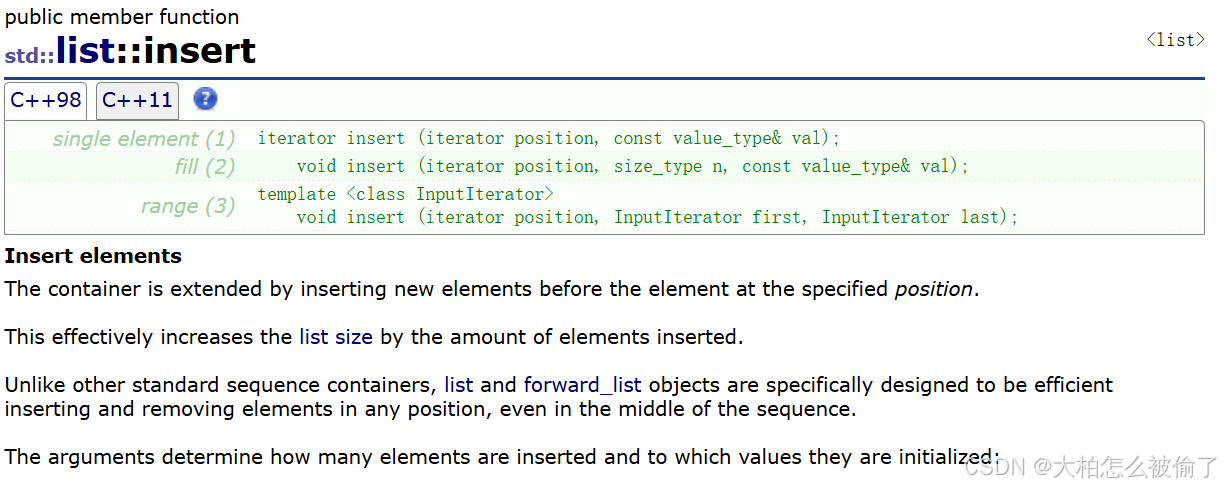
insert
- std::list::insert
- single element (1)
iterator insert (iterator position, const value_type& val); - fill (2)
void insert (iterator position, size_type n, const value_type& val); - range (3)
template < class InputIterator>
void insert (iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last); - 在list position位置插入值为val的元素
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
++it;
lt1.insert(it, 19);
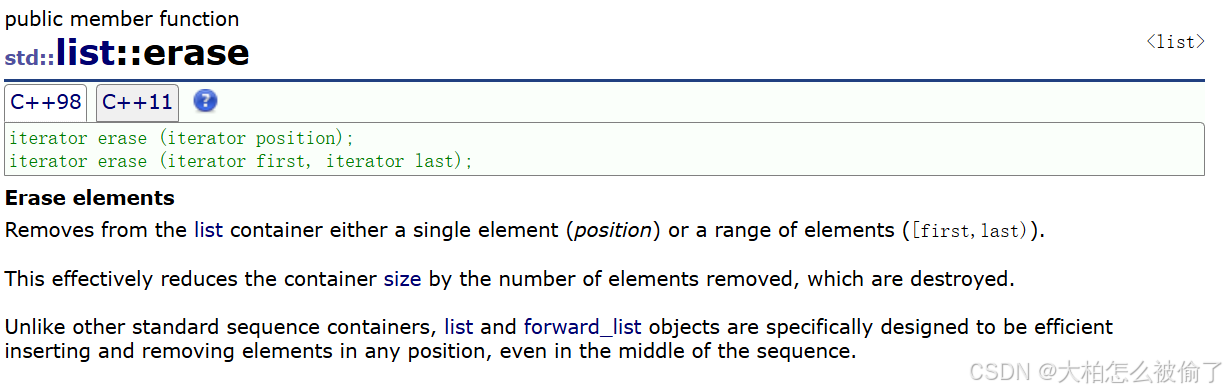
erase
- std::list::erase
- iterator erase (iterator position);
- iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last);
- 删除list position位置中插入值为val的元素
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
++it;
lt1.erase(it);
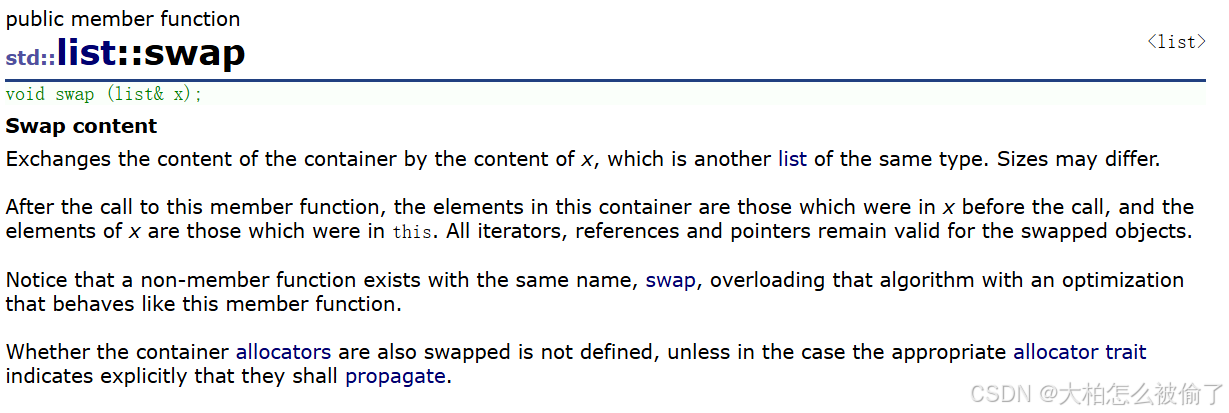
swap
- std::list::swap
- void swap (list& x);
- 交换list中的有效元素
list<int> lt1(3, 5);
list<int> lt2(4, 2);
lt1.swap(lt2)
resize
- std::list::resize
- void resize (size_type n, value_type val = value_type());
- 改变大小
list<int> lt1(3, 5);
lt1.resize(10, 1);
clear
- std::list::clear
- void clear();
- 清空list中的有效元素
list<int> lt1(3, 5);
lt1.clear();
Operations(操作)
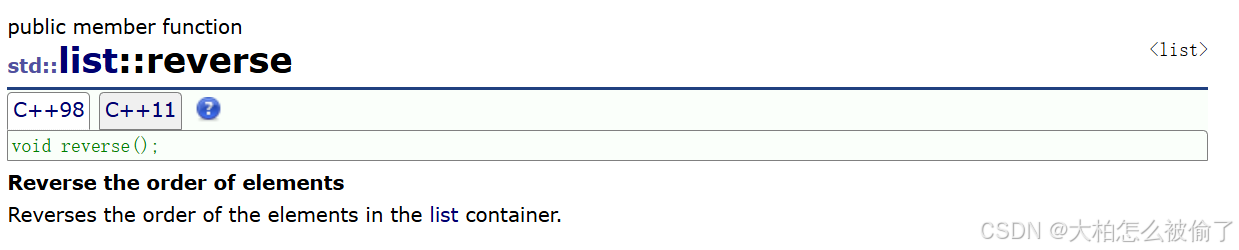
reverse
- std::list::reverse
- void reverse();
- 翻转列表
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(4);
lt1.reverse();
for (auto t : lt1)
{
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;
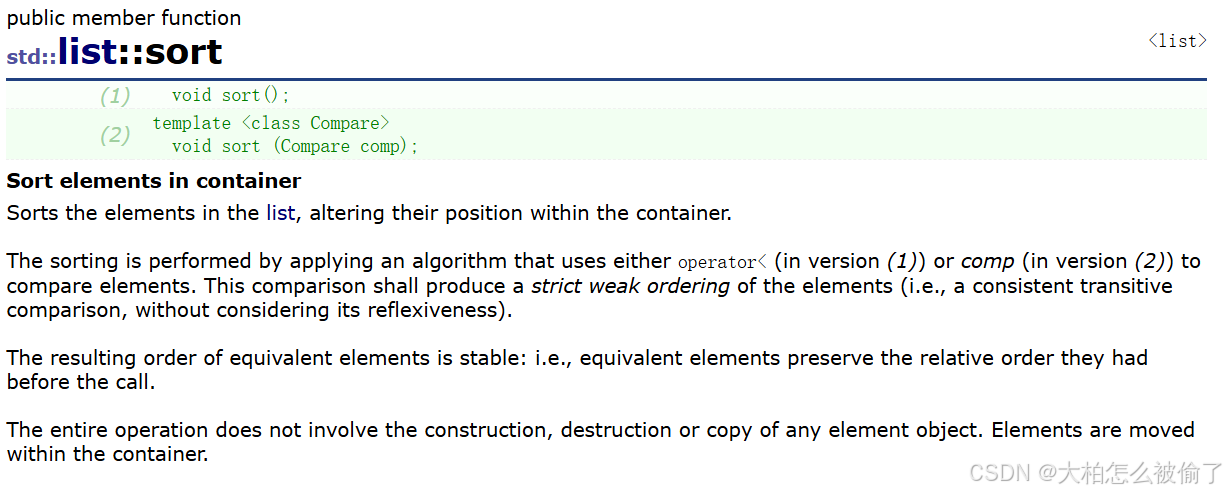
sort
- std::list::sort
- (1) void sort();
- (2) template < class Compare >
void sort (Compare comp); - 排序
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(4);
lt1.sort();
for (auto t : lt1)
{
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;