读取文件夹,将json文件转化为txt文件
一 样例1 json文件只有一个样本
1 json文件内容
{
"version": "4.5.7",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "car",
"points": [
[
737.3076923076923,
244.8461538461538
],
[
1028.076923076923,
555.6153846153846
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {}
}
],
"imagePath": "..\\..\\images\\train2017\\000001.jpg",
"imageData": "/9j/4AAQSkZJR"
2 代码转化
读取文件夹,将json文件转化为txt文件,即将JSON的关键数据读出
import os
import json
json_dir = 'C:/Users/YourName/Desktop/coco128/labels/train2017/' # json文件路径
out_dir = 'C:/Users/YourName/Desktop/output/' # 输出的 txt 文件路径
def get_json(json_file, filename):
# 读取 json 文件数据
with open(json_file, 'r') as load_f:
content = json.load(load_f)
# # 循环处理
tmp = filename
filename_txt = out_dir + tmp + '.txt'
#创建txt文件
fp = open(filename_txt, mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
#将数据写入文件
# 计算 yolo 数据格式所需要的中心点的 相对 x, y 坐标, w,h 的值
x = (content["shapes"][0])["points"][0][0]
y = (content["shapes"][0])["points"][0][1]
w = (content["shapes"][0])["points"][1][0] - (content["shapes"][0])["points"][0][0]
h = (content["shapes"][0])["points"][1][1] - (content["shapes"][0])["points"][0][1]
fp = open(filename_txt, mode="r+", encoding="utf-8")
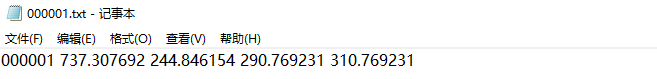
file_str = str(filename) + ' ' + str(round(x, 6)) + ' ' + str(round(y, 6)) + ' ' + str(round(w, 6)) + \
' ' + str(round(h, 6))
line_data = fp.readlines()
if len(line_data) != 0:
fp.write('\n' + file_str)
else:
fp.write(file_str)
fp.close()
def main():
files= os.listdir(json_dir) #得到文件夹下的所有文件名称
s = []
for file in files: #遍历文件夹
filename = file.split('.')[0]
# print(tmp)
get_json(json_dir+file, filename)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3 效果图
原:
改后:
txt内容:
二 样例2 json文件中有多个样本
1 json文件内容
{
"version": "3.16.2",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "00000001",
"line_color": null,
"fill_color": null,
"points": [
[
167.0,
114.0
],
[
146.0,
142.0
],
[
177.0,
145.0
],
[
214.0,
129.0
],
[
210.0,
102.0
],
[
185.0,
107.0
]
],
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "00004702",
"line_color": null,
"fill_color": null,
"points": [
[
306.0,
71.0
],
[
289.0,
109.0
],
[
321.0,
112.0
],
[
359.0,
78.0
],
[
329.0,
57.0
]
],
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {}
}
],
"lineColor": [
0,
255,
0,
128
],
"fillColor": [
255,
0,
0,
128
],
"imagePath": "048.jpg",
"imageData": "/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wBDAAgGBgcGBQgHBwcJCQgKDBQNDAsLDBkSEw8UHRofHh0a"
}
2 代码转化
import os
import json
json_dir = 'C:/Users/YourName/Desktop/coco/jsonDir/' # json文件路径
out_dir = 'C:/Users/YourName/Desktop/coco/outputDir/' # 输出的 txt 文件路径
def get_json(json_file, filename):
# 读取 json 文件数据
with open(json_file, 'r') as load_f:
content = json.load(load_f)
# # 循环处理
tmp = filename
filename_txt = out_dir + tmp + '.txt'
#创建txt文件
fp = open(filename_txt, mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
#将数据写入文件
str_tmp = "" #存储字符串内容
#1.获取version、flags数据
version = content["version"]
flags = content["flags"]
#暂存内容
str_tmp = str(version)+"\n"+str(flags)+"\n"
#2. 获取shapes数组中的数据
#循环读取 shapes中的每一组数据,json文件中有2组数据,循环则是2个 [0,1]
for i in range(2):
label = (content["shapes"][i])["label"]
line_color = (content["shapes"][i])["line_color"]
fill_color = (content["shapes"][i])["fill_color"]
str_tmp += str(label) + "\n" + str(line_color) + "\n" + str(fill_color) + "\n" ##暂存内容
#读取points中的数据,有6组数据
points_size = len((content["shapes"][i])["points"])
for j in range(points_size):
x = (content["shapes"][i])["points"][j][0]
y = (content["shapes"][i])["points"][j][1]
str_tmp += str(x) + " " + str(y) + "\n" ##暂存内容
#读取shape_type,flags
shape_type = (content["shapes"][i])["shape_type"]
flags = (content["shapes"][i])["flags"]
str_tmp += str(shape_type) + " " + str(flags) + "\n" ##暂存内容
#3. 获取lineColor、fillColor、imagePath、imageData
line_Color = content["lineColor"]
fill_Color = content["fillColor"]
imagePath = content["imagePath"]
imageData = content["imageData"]
#lineColor是数组,获取并存储lineColor
for i in range(len(line_Color)):
str_tmp += str(line_Color[i]) + " "
str_tmp += "\n" #换行效果
#fillColor与lineColor一样,也为数组,获取并存储fillColor
for i in range(len(fill_Color)):
str_tmp += str(fill_Color[i]) + " "
str_tmp += "\n" #换行效果
str_tmp += str(imagePath) + " " + str(imageData) + "\n" ##暂存内容
fp = open(filename_txt, mode="r+", encoding="utf-8")
file_str = str_tmp
line_data = fp.readlines()
if len(line_data) != 0:
fp.write('\n' + file_str)
else:
fp.write(file_str)
fp.close()
def main():
files= os.listdir(json_dir) #得到文件夹下的所有文件名称
s = []
for file in files: #遍历文件夹
filename = file.split('.')[0]
# print(tmp)
get_json(json_dir+file, filename)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3 效果图
三 样例3 json文件单样本
1 json文件内容
{"marks":[[240.47823834196888,57.812953367875636],[226.80673575129526,388.58290155440415],[235.33316062176164,227.56113989637305]],"slots":[[3,1, 1,90],[2,3,1,90]]}
2 代码转化
import os
import json
json_dir = 'C:/Users/YourName/Desktop/train/' # 放json文件路径,train是放json文件的文件夹
out_dir = 'C:/Users/YourName/Desktop/output/' # 输出的 txt 文件路径,output是放txt文件的文件夹
def get_json(json_file, filename):
# 读取 json 文件数据
with open(json_file, 'r') as load_f:
content = json.load(load_f)
# # 循环处理
tmp = filename
filename_txt = out_dir + tmp + '.txt'
#创建txt文件
fp = open(filename_txt, mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
#将数据写入文件
#首先是mark,二维数组3*2,提取数据如下
x1y1 = content["marks"][0][0]
x1y2 = content["marks"][0][1]
x2y1 = content["marks"][1][0]
x2y2 = content["marks"][1][1]
x3y1 = content["marks"][2][0]
x3y2 = content["marks"][2][1]
#slots为2*4的二维数组,提取数据如下
s_x1y1 = content["slots"][0][0]
s_x1y2 = content["slots"][0][1]
s_x1y3 = content["slots"][0][2]
s_x1y4 = content["slots"][0][3]
s_x2y1 = content["slots"][1][0]
s_x2y2 = content["slots"][1][1]
s_x2y3 = content["slots"][1][2]
s_x2y4 = content["slots"][1][3]
#数据写入txt文档
fp = open(filename_txt, mode="r+", encoding="utf-8")
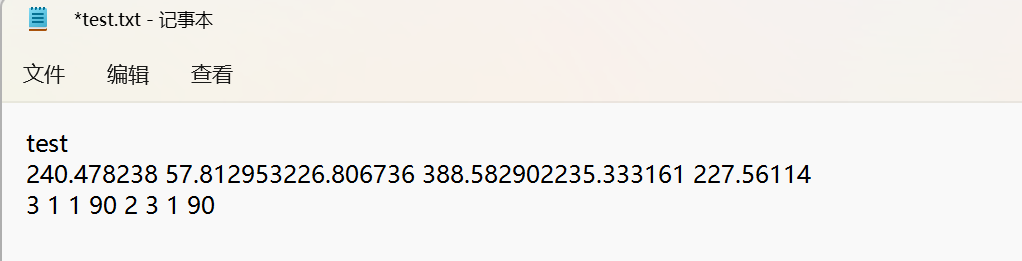
file_str = str(filename) + '\n' + str(round(x1y1, 6)) + ' ' + str(round(x1y2, 6)) + ' ' +\
str(round(x2y1, 6)) + ' ' + str(round(x2y2, 6)) + str(round(x3y1, 6)) + ' ' + \
str(round(x3y2, 6)) + '\n' + str(round(s_x1y1, 6)) +' ' + str(round(s_x1y2, 6)) + ' ' + \
str(round(s_x1y3, 6)) + ' ' + str(round(s_x1y4, 6)) +' ' + str(round(s_x2y1, 6)) + \
str(round(s_x2y2, 6)) + ' ' + str(round(s_x2y3, 6)) +' ' + str(round(s_x2y4, 6))
line_data = fp.readlines()
if len(line_data) != 0:
fp.write('\n' + file_str)
else:
fp.write(file_str)
fp.close()
def main():
files= os.listdir(json_dir) #得到文件夹下的所有文件名称
s = []
for file in files: #遍历文件夹
filename = file.split('.')[0]
# print(tmp)
get_json(json_dir+file, filename)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()