1、创建工程
|
1
|
scrapy startproject movie
|
2、创建爬虫程序
|
1
2
|
cd movie
scrapy genspider meiju meijutt.com
|
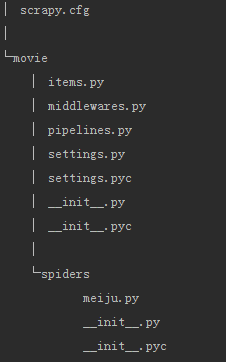
3、自动创建目录及文件
4、文件说明:
- scrapy.cfg 项目的配置信息,主要为Scrapy命令行工具提供一个基础的配置信息。(真正爬虫相关的配置信息在settings.py文件中)
- items.py 设置数据存储模板,用于结构化数据,如:Django的Model
- pipelines 数据处理行为,如:一般结构化的数据持久化
- settings.py 配置文件,如:递归的层数、并发数,延迟下载等
- spiders 爬虫目录,如:创建文件,编写爬虫规则
注意:一般创建爬虫文件时,以网站域名命名
5、设置数据存储模板
items.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
import scrapy
class
MovieItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
name = scrapy.Field()
|
6、编写爬虫
meiju.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
from
movie.items import MovieItem
class
MeijuSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name =
"meiju"
allowed_domains = [
"meijutt.com"
]
start_urls = [
'http://www.meijutt.com/new100.html'
]
def parse(self, response):
movies = response.xpath(
'//ul[@class="top-list fn-clear"]/li'
)
for
each_movie
in
movies:
item = MovieItem()
item[
'name'
] = each_movie.xpath(
'./h5/a/@title'
).extract()[0]
yield item
|
7、设置配置文件
settings.py增加如下内容
|
1
|
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'movie.pipelines.MoviePipeline'
:100}
|
8、编写数据处理脚本
pipelines.py
|
1
2
3
4
|
class
MoviePipeline(
object
):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
with open(
"my_meiju.txt"
,
'a'
)
as
fp:
fp.write(item[
'name'
].encode(
"utf8"
) +
'\n'
)
|
9、执行爬虫
|
1
2
|
cd movie
scrapy crawl meiju --nolog
|
10、结果