应用的集群部署或分布式部署,经常遇到session共享的问题,要么在nginx代理解决(比如ip hash),要么在tomcat的context.xml配置redis。spring boot也提供了session用redis解决共享的方法。
pom.xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!-- <version>${spring_versin}</version> -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<!-- <version>${spring_versin}</version> -->
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
application.yml的配置
logging:
config: classpath:logback.xml
path: d:/logs
server:
port: 8080
session-timeout: 60
spring:
redis:
database: 0
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password:
timeout: 0
pool:
max-active: 8
max-wait: -1
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
session:
store-type: noneRedisSessionConfig.java
package com.fei.springboot.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.EnableRedisHttpSession;
@Configuration
//maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds 默认是1800秒过期,这里测试修改为60秒
@EnableRedisHttpSession(maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds=60)
public class RedisSessionConfig{
}
如果不需要做特殊处理,只需直接使用注解@EnableRedisHttpSession即可,打开 @EnableRedisHttpSession源码,发现maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds session的过期时间默认是1800秒即30分钟,如果需要修改,注解时进行修改即可。如果想对redisSession做一些特殊处理。看@EnableRedisHttpSession源码,头部的注释,也给出了一些方案。
注解@interface EnableRedisHttpSession的源码
/*
* Copyright 2014-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.session.SessionRepository;
import org.springframework.session.config.annotation.web.http.EnableSpringHttpSession;
import org.springframework.session.data.redis.RedisFlushMode;
/**
* Add this annotation to an {@code @Configuration} class to expose the
* SessionRepositoryFilter as a bean named "springSessionRepositoryFilter" and backed by
* Redis. In order to leverage the annotation, a single {@link RedisConnectionFactory}
* must be provided. For example: <pre>
* <code>
* {@literal @Configuration}
* {@literal @EnableRedisHttpSession}
* public class RedisHttpSessionConfig {
*
* {@literal @Bean}
* public JedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory() throws Exception {
* return new JedisConnectionFactory();
* }
*
* }
* </code> </pre>
*
* More advanced configurations can extend {@link RedisHttpSessionConfiguration} instead.
*
* @author Rob Winch
* @since 1.0
* @see EnableSpringHttpSession
*/
@Retention(java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE })
@Documented
@Import(RedisHttpSessionConfiguration.class)
@Configuration
public @interface EnableRedisHttpSession {
int maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds() default 1800;
/**
* <p>
* Defines a unique namespace for keys. The value is used to isolate sessions by
* changing the prefix from "spring:session:" to
* "spring:session:<redisNamespace>:". The default is "" such that all Redis
* keys begin with "spring:session".
* </p>
*
* <p>
* For example, if you had an application named "Application A" that needed to keep
* the sessions isolated from "Application B" you could set two different values for
* the applications and they could function within the same Redis instance.
* </p>
*
* @return the unique namespace for keys
*/
String redisNamespace() default "";
/**
* <p>
* Sets the flush mode for the Redis sessions. The default is ON_SAVE which only
* updates the backing Redis when
* {@link SessionRepository#save(org.springframework.session.Session)} is invoked. In
* a web environment this happens just before the HTTP response is committed.
* </p>
* <p>
* Setting the value to IMMEDIATE will ensure that the any updates to the Session are
* immediately written to the Redis instance.
* </p>
*
* @return the {@link RedisFlushMode} to use
* @since 1.1
*/
RedisFlushMode redisFlushMode() default RedisFlushMode.ON_SAVE;
}
spring boot中的session redis配置就如此简单。
写个controller测试下
package com.fei.springboot.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value="/getSessionId")
@ResponseBody
public String getSessionId(HttpServletRequest request){
Object o = request.getSession().getAttribute("springboot");
if(o == null){
o = "spring boot 牛逼了!!!有端口"+request.getLocalPort()+"生成";
request.getSession().setAttribute("springboot", o);
}
return "端口=" + request.getLocalPort() + " sessionId=" + request.getSession().getId() +"<br/>"+o;
}
}
写个启动类
package com.fei.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer;
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(basePackages={"com.fei.springboot"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer implements EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer{
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
public void customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer configurableEmbeddedServletContainer) {
// configurableEmbeddedServletContainer.setPort(9090);
}
}
修改application.yml中的server.port的端口为80,执行启动类,然后修改为8080,再次执行启动类。
浏览器测试
http://127.0.0.1/getSessionId
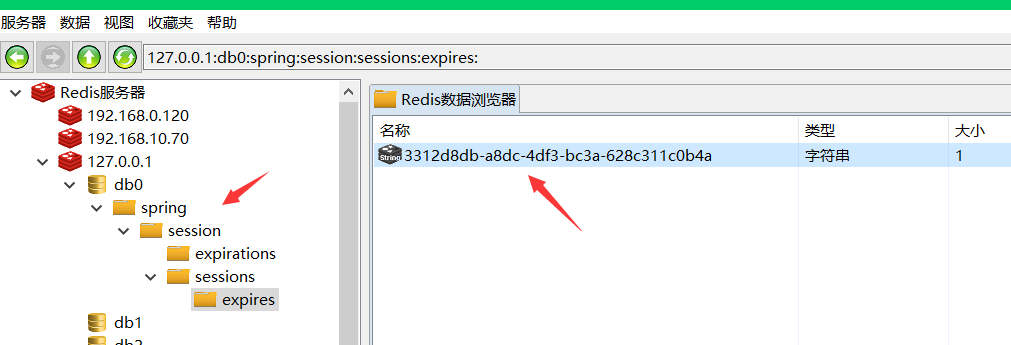
得得的结果是
端口=80 sessionId=3312d8db-a8dc-4df3-bc3a-628c311c0b4a
spring boot 牛逼了!!!有端口80生成得到的结果是
端口=8080 sessionId=3312d8db-a8dc-4df3-bc3a-628c311c0b4a
spring boot 牛逼了!!!有端口80生成使用redis-client,查看
注意事项:
如果启动时发现报错:
ERR Unsupported CONFIG parameter: notify-keyspace-events; nested exception is redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.JedisDataException
这是因为redis服务器版本和jar包版本不一致造成的。
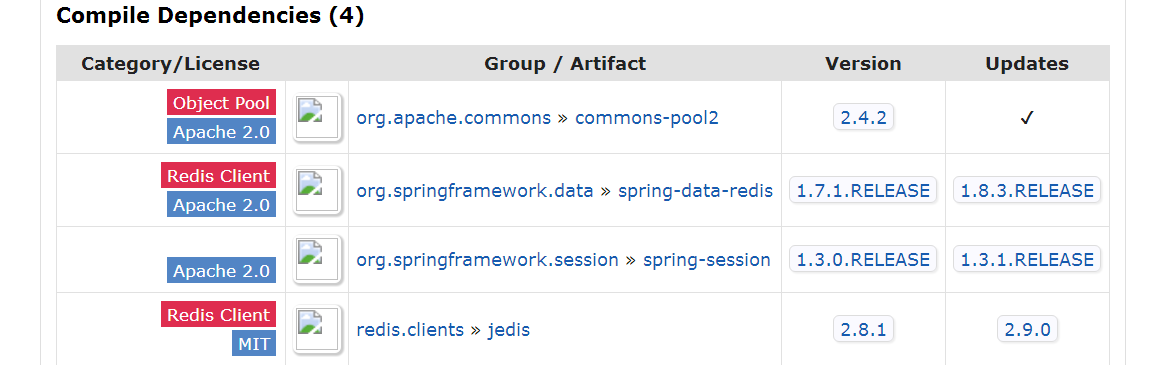
比如说,我这用的spring-session-data-redis版本是1.3.0,到maven 仓库中查询http://mvnrepository.com/
发现redis是2.8.1,看了下我用的服务器是2.6的,我立刻下载了个最新版的3.x,我是本地测试的,用window的。更换redis服务器后,不再报错了。