20240725
一、矩阵
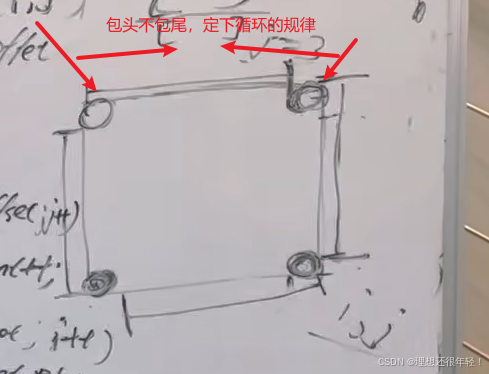
54.螺旋矩阵(循环不变量)
一个矩阵,循环遍历出来,就得按照顺序去遍历,然后插到我们定义的矩阵里面去
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] nums = new int[n][n];//定义一个矩阵
int startX = 0, startY = 0; // 每一圈的起始点
int offset = 1;
int count = 1; // 矩阵中需要填写的数字
int loop = 1; // 记录当前的圈数
int i, j; // j 代表列, i 代表行;
while (loop <= n / 2) {
// 顶部
// 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, j 不能等于 n - offset
for (j = startY; j < n - offset; j++) {
nums[startX][j] = count++;
}
// 右列
// 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, i 不能等于 n - offset
for (i = startX; i < n - offset; i++) {
nums[i][j] = count++;
}
// 底部
// 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, j != startY
for (; j > startY; j--) {
nums[i][j] = count++;
}
// 左列
// 左闭右开,所以判断循环结束时, i != startX
for (; i > startX; i--) {
nums[i][j] = count++;
}
startX++;
startY++;
offset++;
loop++;
}
if (n % 2 == 1) { // n 为奇数时,单独处理矩阵中心的值
nums[startX][startY] = count;
}
return nums;
}
}
二、链表
1 移除链表元素
1.1 原链表删除元素:
/**
* 不添加虚拟节点and pre Node方式
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while(head!=null && head.val==val){//head!=null用于防止空指针错误,如果头节点就等于val的话
直接让头节点指向下一位。
head = head.next;
}
ListNode curr = head;//把头节点的位置拿到
while(curr!=null){//防止空指针
while(curr.next!=null && curr.next.val == val){//头指针的下一个也不为null,下一个为
val,那么我们的的next就要等于next.next了
curr.next = curr.next.next;
}
curr = curr.next;//把等于的值的curr返回。
}
return head;
}
1.2 虚拟头节点(!!!)
/**
* 添加虚节点方式
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 因为删除可能涉及到头节点,所以设置dummy节点,统一操作
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
2. 设计链表
//单链表
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(){}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val=val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
//size存储链表元素的个数
int size;
//虚拟头结点
ListNode head;
//初始化链表
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
}
//获取第index个节点的数值,注意index是从0开始的,第0个节点就是头结点
public int get(int index) {
//如果index非法,返回-1
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return -1;
}
ListNode currentNode = head;
//包含一个虚拟头节点,所以查找第 index+1 个节点
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode.val;
}
//在链表最前面插入一个节点,等价于在第0个元素前添加
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0, val);
}
//在链表的最后插入一个节点,等价于在(末尾+1)个元素前添加
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
// 在第 index 个节点之前插入一个新节点,例如index为0,那么新插入的节点为链表的新头节点。
// 如果 index 等于链表的长度,则说明是新插入的节点为链表的尾结点
// 如果 index 大于链表的长度,则返回空
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > size) {
return;
}
if (index < 0) {
index = 0;
}
size++;
//找到要插入节点的前驱
ListNode pred = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pred = pred.next;
}
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
toAdd.next = pred.next;
pred.next = toAdd;
}
//删除第index个节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return;
}
size--;
if (index == 0) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode pred = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index ; i++) {
pred = pred.next;
}
pred.next = pred.next.next;
}
}
//双链表
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next,prev;
ListNode() {};
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
//记录链表中元素的数量
int size;
//记录链表的虚拟头结点和尾结点
ListNode head,tail;
public MyLinkedList() {
//初始化操作
this.size = 0;
this.head = new ListNode(0);
this.tail = new ListNode(0);
//这一步非常关键,否则在加入头结点的操作中会出现null.next的错误!!!
head.next=tail;
tail.prev=head;
}
public int get(int index) {
//判断index是否有效
if(index<0 || index>=size){
return -1;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
//判断是哪一边遍历时间更短
if(index >= size / 2){
//tail开始
cur = tail;
for(int i=0; i< size-index; i++){
cur = cur.prev;
}
}else{
for(int i=0; i<= index; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
//等价于在第0个元素前添加
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
//等价于在最后一个元素(null)前添加
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
//index大于链表长度
if(index>size){
return;
}
//index小于0
if(index<0){
index = 0;
}
size++;
//找到前驱
ListNode pre = this.head;
for(int i=0; i<index; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
//新建结点
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = pre.next;
pre.next.prev = newNode;
newNode.prev = pre;
pre.next = newNode;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
//判断索引是否有效
if(index<0 || index>=size){
return;
}
//删除操作
size--;
ListNode pre = this.head;
for(int i=0; i<index; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next.next.prev = pre;
pre.next = pre.next.next;
}
}
206. 反转链表(双向指针和递归)
双指针
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode prev=null;
ListNode temp=null;
while(cur != null){
temp=cur.next;//上面这俩位置是把拿到的值拼凑到一起
cur.next=prev;
prev=cur;//下面这俩位置,是用来去拿数的
cur=temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
递归
// 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
交换链表中的元素
虚拟头节点法
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dumyhead = new ListNode(-1); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
dumyhead.next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方便后面做删除操作
ListNode cur = dumyhead;
ListNode temp; // 临时节点,保存两个节点后面的节点
ListNode firstnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第一个节点
ListNode secondnode; // 临时节点,保存两个节点之中的第二个节点
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
temp = cur.next.next.next;
firstnode = cur.next;
secondnode = cur.next.next;
cur.next = secondnode; // 步骤一
secondnode.next = firstnode; // 步骤二
firstnode.next = temp; // 步骤三
cur = firstnode; // cur移动,准备下一轮交换
}
return dumyhead.next;
}
}
递归法
// 递归版本
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// base case 退出提交
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// 获取当前节点的下一个节点
ListNode next = head.next;
// 进行递归
ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next);
// 这里进行交换
next.next = head;
head.next = newNode;
return next;
}
}
删除链表的倒数第N个节点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
//新建一个虚拟头节点指向head
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
dummyNode.next = head;
//快慢指针指向虚拟头节点
ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
// 只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
}
while (fastIndex != null) {
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
}
// 此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
// 具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
// 检查 slowIndex.next 是否为 null,以避免空指针异常
if (slowIndex.next != null) {
slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {// 有环
ListNode index1 = fast;
ListNode index2 = head;
// 两个指针,从头结点和相遇结点,各走一步,直到相遇,相遇点即为环入口
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1.next;
index2 = index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
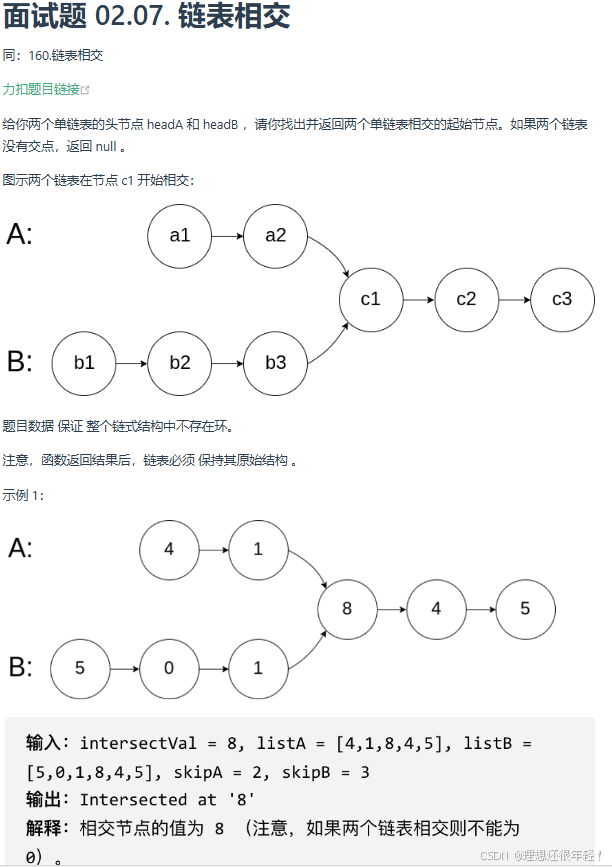
链表相交(学习思路)
(版本一)先行移动长链表实现同步移动
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != null) { // 求链表A的长度
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while (curB != null) { // 求链表B的长度
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
// 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度
if (lenB > lenA) {
//1. swap (lenA, lenB);
int tmpLen = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = tmpLen;
//2. swap (curA, curB);
ListNode tmpNode = curA;
curA = curB;
curB = tmpNode;
}
// 求长度差
int gap = lenA - lenB;
// 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐)
while (gap-- > 0) {
curA = curA.next;
}
// 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回
while (curA != null) {
if (curA == curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
(版本二) 合并链表实现同步移动
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// p1 指向 A 链表头结点,p2 指向 B 链表头结点
ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB;
while (p1 != p2) {
// p1 走一步,如果走到 A 链表末尾,转到 B 链表
if (p1 == null) p1 = headB;
else p1 = p1.next;
// p2 走一步,如果走到 B 链表末尾,转到 A 链表
if (p2 == null) p2 = headA;
else p2 = p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}