要求
- 支持设定过期时间,精确到秒
- 支持设定最大内存,当内存超过时做出合适的处理
- 支持并发安全
- 按照以下接口安全
type Cache interface{
//size : 1KB 100KB 1MB 2MB 1GB
SetMaxMemory(size string )bool
//将value写入缓存
Set(key string, val interface{},expire time.Duration)bool
//根据key值获取value
Get(key string )(interface{},bool)
//删除key
Del(key string)bool
//判断key是否存在
Exists(key string)bool
//清空所有key
Flush()bool
//获取缓存中所有key的数量
Keys()int64
}
- 使用示例
cache := NewMemCache()
cache.SetMaxMemory("100MB")
cache.Set("int",1)
cache.Set("bool",false)
cache.Set("data",map[string]interface(){"a":1})
cache.Get("int")
cache.Del("int")
cache.Flush()
cache.Keys()
首先创建对应文件夹
其中main.go中填入测试案例
package main
import (
"memCache/cache"
"time"
)
func main() {
cache := cache.NewMemCache()
cache.SetMaxMemory("200MB")
cache.Set("int", 1, time.Second)
cache.Set("bool", false, time.Second)
cache.Set("data", map[string]interface{}{"a": 1}, time.Second)
//cache.Set("int",1)
//cache.Set("bool",false)
//cache.Set("data",map[string]interface{}{"a":1})
cache.Get("int")
cache.Del("int")
cache.Flush()
cache.Keys()
//num, str := cache.ParseSize("2KB")
//fmt.Println(num, str)
}
定义cache.go的接口
package cache
import "time"
type Cache interface {
//size : 1KB 100KB 1MB 2MB 1GB
SetMaxMemory(size string) bool
//将value写入缓存
Set(key string, val interface{}, expire time.Duration) bool
//根据key值获取value
Get(key string) (interface{}, bool)
//删除key
Del(key string) bool
//判断key是否存在
Exists(key string) bool
//清空所有key
Flush() bool
//获取缓存中所有key的数量
Keys() int64
}
然后在memCache.go中实现
package cache
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
type memCache struct {
//最大内存 -- 单位字节
maxMemorySize int64
//最大内存字符串表示
maxMemorySizeStr string
//当前内存大小 -- 单位字节
currentMemorySize int64
}
func NewMemCache() Cache {
return &memCache{}
}
// size : 1KB 100KB 1MB 2MB 1GB
func (mc *memCache) SetMaxMemory(size string) bool {
mc.maxMemorySize, mc.maxMemorySizeStr = ParseSize(size)
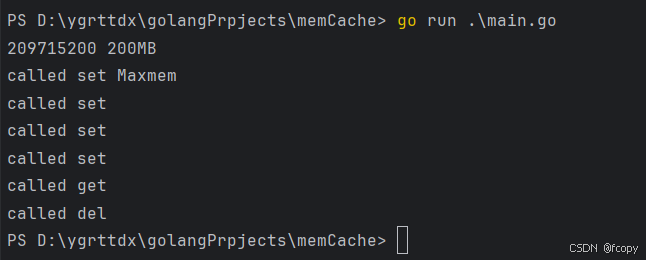
fmt.Println(mc.maxMemorySize, mc.maxMemorySizeStr)
fmt.Println("called set Maxmem")
return false
}
// 将value写入缓存
func (mc *memCache) Set(key string, val interface{}, expire time.Duration) bool {
fmt.Println("called set")
return false
}
// 根据key值获取value
func (mc *memCache) Get(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
fmt.Println("called get")
return nil, false
}
// 删除key
func (mc *memCache) Del(key string) bool {
fmt.Println("called del")
return false
}
// 判断key是否存在
func (mc *memCache) Exists(key string) bool {
return false
}
// 清空所有key
func (mc *memCache) Flush() bool {
return false
}
// 获取缓存中所有key的数量
func (mc *memCache) Keys() int64 {
return 0
}
实现设置最大内存数中
// size : 1KB 100KB 1MB 2MB 1GB
func (mc *memCache) SetMaxMemory(size string) bool {
mc.maxMemorySize, mc.maxMemorySizeStr = ParseSize(size)
fmt.Println(mc.maxMemorySize, mc.maxMemorySizeStr)
fmt.Println("called set Maxmem")
return false
}
ParseSize()方法在util.go文件中实现
const (
B = 1 << (iota * 10)
KB
MB
GB
TB
PB
)
func ParseSize(size string) (int64, string) {
//默认大小为 100MB
re, _ := regexp.Compile("[0-9]+")
//fmt.Println(re)
unit := string(re.ReplaceAll([]byte(size), []byte("")))
//fmt.Println("unit: " + unit)
num, _ := strconv.ParseInt(strings.Replace(size, unit, "", 1), 10, 64)
//fmt.Println("num: ", num)
unit = strings.ToUpper(unit)
var byteNum int64 = 0
switch unit {
case "B":
byteNum = num
case "KB":
byteNum = num * KB
case "MB":
byteNum = num * MB
case "GB":
byteNum = num * GB
case "TB":
byteNum = num * TB
case "PB":
byteNum = num * PB
default:
byteNum = 0
num = 0
}
if num == 0 {
log.Println("ParseSize 仅支持 B,KB,MB,GB,TB,PB")
num = 100
byteNum = num * MB
unit = "MB"
}
sizeStr := strconv.FormatInt(num, 10) + unit
return byteNum, sizeStr
}
初步测试
说明ParseSize实现无误
接下来是实现Set方法
在memCache.go中添加
type memCacheValue struct {
//value值
val interface{}
//过期时间
expiration time.Time
//value 大小
size int64
}
来存储每一块内存的信息,包括大小,值,过期时间
对于Set操作,我们需要创建一些方法来辅助执行
如:get,add,del操作
// 将value写入缓存
func (mc *memCache) Set(key string, val interface{}, expire time.Duration) bool {
mc.locker.Lock()
defer mc.locker.Unlock()
v := &memCacheValue{
val: val,
expireTime: time.Now().Add(expire),
size: GetValSize(val),
}
mc.del(key)
mc.add(key, v)
if mc.currentMemorySize > mc.maxMemorySize {
mc.del(key)
panic(fmt.Sprintf("max memory size %s", mc.maxMemorySize))
}
return false
}
func (mc *memCache)del(key string) {
tmp,ok:=mc.get(key)
if ok && tmp != nil {
mc.currentMemorySize -= tmp.size
delete(mc.values, key)
}
}
func (mc *memCache)add(key string, val *memCacheValue) {
mc.values[key] = val
mc.currentMemorySize += val.size
}
func (mc *memCache)get(key string) (*memCacheValue,bool) {
val,ok := mc.values[key]
return val,ok
}
同理也可以利用上面创建的add,del,get方法来实现Get操作
// 根据key值获取value
func (mc *memCache) Get(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
mc.locker.RLock()
defer mc.locker.RUnlock()
mcv, ok := mc.get(key)
if ok{
//判断缓存是否过期
if mcv.expireTime.Before(time.Now()) {
mc.del(key)
return nil, false
}
return mcv.val, true
}
fmt.Println("called get")
return nil, false
}
Del操作的实现
// 删除key
func (mc *memCache) Del(key string) bool {
mc.locker.Lock()
defer mc.locker.Unlock()
mc.del(key)
fmt.Println("called del")
return false
}
剩余其他操作
// 判断key是否存在
func (mc *memCache) Exists(key string) bool {
mc.locker.RLock()
defer mc.locker.RUnlock()
_,ok := mc.values[key]
return ok
}
// 清空所有key
func (mc *memCache) Flush() bool {
mc.locker.Lock()
defer mc.locker.Unlock()
mc.values = make(map[string]*memCacheValue)
mc.currentMemorySize = 0
return false
}
// 获取缓存中所有key的数量
func (mc *memCache) Keys() int64 {
mc.locker.RLock()
defer mc.locker.RUnlock()
return int64(len(mc.values))
}
现在的问题是,我们只是设置了,在过期之后,就不能访问了,但是实际上还占用着缓存,只有在再一次Get的时候,发现过期了,才会删除掉
所以现在我们做一个定期清空的轮询访问
// 定期清除缓存
func (mc *memCache) clearExpiredItem() {
timeTicker := time.NewTicker(mc.clearExpiredItemTimeInerval)
defer timeTicker.Stop()
for {
fmt.Println("轮询检查")
select {
case <-timeTicker.C:
for key, item := range mc.values {
if item.expireTime.Before(time.Now()) {
mc.locker.Lock()
mc.del(key)
mc.locker.Unlock()
fmt.Println("check")
}
}
}
}
}
测试案例
之后,我们创建一个代理层,带使用测试案例
在cache-server中的cache.go文件中
创建对象,添加代理
package cache_server
import (
"memCache/cache"
"time"
)
type cacheServer struct {
memCache cache.Cache
}
func NewMemCache() *cacheServer {
return &cacheServer{
memCache: cache.NewMemCache(),
}
}
// size : 1KB 100KB 1MB 2MB 1GB
func (cs *cacheServer) SetMaxMemory(size string) bool {
return cs.memCache.SetMaxMemory(size)
}
// 将value写入缓存
func (cs *cacheServer) Set(key string, val interface{}, expire ...time.Duration) bool {
expireTs := time.Second * 0
if len(expire) > 0 {
expireTs = expire[0]
}
return cs.memCache.Set(key, val, expireTs)
}
// 根据key值获取value
func (cs *cacheServer) Get(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
return cs.memCache.Get(key)
}
// 删除key
func (cs *cacheServer) Del(key string) bool {
return cs.memCache.Del(key)
}
// 判断key是否存在
func (cs *cacheServer) Exists(key string) bool {
return cs.memCache.Exists(key)
}
// 清空所有key
func (cs *cacheServer) Flush() bool {
return cs.memCache.Flush()
}
// 获取缓存中所有key的数量
func (cs *cacheServer) Keys() int64 {
return cs.memCache.Keys()
}
可以注意到,我们在代理层中对Set方法进行了可变长参数化
使得我们的Set方法的time部分参数为可选择填写0-n个参数,但我们只使用第一个expire[0]作为我们使用的参数
此时main函数可改成测试案例
cache := cache_server.NewMemCache()
cache.SetMaxMemory("200MB")
cache.Set("int", 1, 20*time.Second)
cache.Set("bool", false, 10*time.Second)
cache.Set("data", map[string]interface{}{"a": 1}, time.Second)
cache.Set("int", 1)
cache.Set("bool", false)
cache.Set("data", map[string]interface{}{"a": 1})
cache.Get("int")
cache.Del("int")
cache.Flush()
cache.Keys()
time.Sleep(time.Second * 25)
GetValSize函数
我们使用GetValSize函数
func GetValSize(val interface{}) int64 {
size := unsafe.Sizeof(val)
fmt.Println(int64(size))
return int64(size)
}
cache.GetValSize(1)
cache.GetValSize(false)
cache.GetValSize("adwaeqweqwr")
cache.GetValSize(map[string]string{
"a": "b",
"c": "d",
})
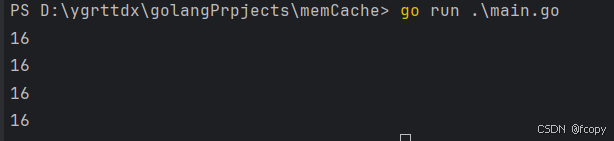
会发现
无论输入什么,size都是16
unsafe.Sizeof 来获取一个接口值(interface{})的大小时,它实际上返回的是接口结构体本身的大小,而不是接口中存储的具体值的大小
我们可以利用json序列化,来直接获得序列长度来代表val的大小
func GetValSize(val interface{}) int64 {
byte, _ := json.Marshal(val)
size := int64(len(byte))
fmt.Println(size)
return int64(size)
}
可以看出,我们就可以得到实际的一个大小
加分项,单元测试
我们在cache目录中,新建一个单元测试,memCache_test.go
package cache
import (
"testing"
"time"
)
func TestCacheOP(t *testing.T) {
testData := []struct {
key string
val interface{}
expire time.Duration
}{
{"slawe", 234623, time.Second * 10},
{"sawe", false, time.Second * 11},
{"serytje", true, time.Second * 12},
{"w35wyhe", map[string]interface{}{"a": 2, "B": false}, time.Second * 13},
{"swetwgb", "fiyu85", time.Second * 14},
}
c := NewMemCache()
c.SetMaxMemory("10MB")
for _, item := range testData {
c.Set(item.key, item.val, item.expire)
val, ok := c.Get(item.key)
if !ok {
t.Error("缓存取值失败")
}
if item.key != "w35wyhe" && val != item.val {
t.Error("缓存取值数据与预期不一致")
}
_, ok1 := val.(map[string]interface{})
if item.key == "w35wyhe" && !ok1 {
t.Error("map缓存取值数据与预期不一致")
}
}
if int64(len(testData)) != c.Keys() {
t.Error("缓存数量不一致")
}
c.Del(testData[0].key)
c.Del(testData[1].key)
if int64(len(testData)) != c.Keys()+2 {
t.Error("缓存数量不一致")
}
time.Sleep(17 * time.Second)
if c.Keys() != 0 {
t.Error("缓存未清空")
}
}
单元测试通过!!!