unity插件Excel转换Proto插件-ExcelToProtobufferTool
- Excel数值配置填充规则
- **Excel 文档配置规则说明(更新版)**
- **字典字段的定义规则**
- **通用规则**
- **示例详解**
- **定义**
- **数据**
- **最终生成的数据结构**
- **示例代码(C#)**
- **输出结果**
- **说明**
- **总结**
- **自定义类数据填充注意事项**
- **总结**
ExcelToProtobufTool 插件文档
1. 插件概述
ExcelToProtobufTool 是一个 Unity 插件,用于将 Excel 配置文件转换为 Protobuf 数据格式,并生成对应的 C# 脚本或 DLL 文件。通过配置类 DefaultIProtoPathConfig,开发者可以自定义 Excel 文件路径、Protobuf 数据生成路径、DLL 生成路径等。
不支持.Net Standard,需要将功成切换到.Net Framework.
2. 默认配置类:DefaultIProtoPathConfig
属性说明
| 属性名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
PackagesRootPathName | string | 包根目录名称,默认值为 "Packages"。 |
PackagesFullName | string | 完整的包路径,组合了根目录名称和包名。 |
PackagesPath | string | 包路径的完整路径,通过 DirectoryInfo 获取。 |
IsDebug | bool | 是否启用调试模式,默认值为 true。 |
IsUsedDLL | bool | 是否使用生成的 DLL 文件。true 为打包成 DLL,false 为生成 C# 脚本。 |
ExcelPath | string | Excel 文件路径,默认指向 Config/Excel/Game。 |
GenerateProtoPath | string | Protobuf 文件路径,默认指向 Config/ProtoFiles。 |
GenerateProtoDataPath | string | Protobuf 生成的 Data 文件路径,默认指向 Res/ProtoData。 |
GenerateProtoCsRootPath | string | 生成的 Protobuf C# 脚本路径,默认指向 Assets/Scripts/ProtoCSharp。 |
ProtoDllName | string | Protobuf 脚本生成的 DLL 文件名,默认值为 CompanyName.ProtoBuffData。 |
GenerateCsCachePath | string | 脚本或 DLL 的缓存路径,默认指向 Library/ProtoCache。 |
GenerateProtoDllPath | string | Protobuf 生成的 DLL 路径,默认指向 Assets/Plugins/ProtoBuffData。 |
ProtocPath | string | Protobuf 文件解析工具(protoc)的路径,根据平台动态调整。 |
GoogleProtobufPath | string | Google Protobuf 库的 DLL 路径,默认指向插件内置的 Google.Protobuf.dll。 |
3. 自定义配置类
定义规则
-
继承
DefaultIProtoPathConfig:- 自定义配置类必须继承自
DefaultIProtoPathConfig。
- 自定义配置类必须继承自
-
添加
[ExecuteInEditMode]特性:- 确保配置在 Unity 编辑模式下生效。
-
实现静态构造函数:
- 在静态构造函数中注册自定义配置到
ProtoPathConfig.CurProtoPathConfig。
- 在静态构造函数中注册自定义配置到
-
重写需要自定义的属性:
- 根据项目需求,重写以下常用属性:
ExcelPath:Excel 文件路径。GenerateProtoDataPath:Protobuf 数据比特流文件路径。IsUsedDLL:是否使用生成的 DLL 文件。GenerateProtoDllPath:Protobuf 生成的 DLL 路径。GenerateProtoCsRootPath:Protobuf 生成的 C# 脚本路径。
- 根据项目需求,重写以下常用属性:
示例代码
using UnityEngine;
using HuaXianQu.ProtoBuffEx.Runtime;
// 添加 [ExecuteInEditMode] 特性,使脚本在编辑模式下运行
[ExecuteInEditMode]
public class CustomProtoPathConfig : DefaultIProtoPathConfig
{
// 静态构造函数,用于注册自定义配置
static CustomProtoPathConfig()
{
// 自动注册自定义配置
ProtoPathConfig.CurProtoPathConfig = new CustomProtoPathConfig();
}
// 自定义 Excel 文件路径
public override string ExcelPath => $"{Application.dataPath}/../../Config/Excel/CustomGame";
// 自定义 Protobuf 数据比特流文件路径
public override string GenerateProtoDataPath => $"{Application.dataPath}/Res/CustomProtoData";
// 启用 DLL 模式
public override bool IsUsedDLL => true;
// 自定义 Protobuf 生成的 DLL 路径
public override string GenerateProtoDllPath => "Assets/Plugins/CustomProtoBuffData";
// 自定义 Protobuf 生成的 C# 脚本路径
public override string GenerateProtoCsRootPath => "Assets/Scripts/CustomProtoCSharp";
}
4. 使用方式
4.1 默认路径
如果不自定义配置类,插件将使用默认路径:
- Excel 文件路径:
$"{Application.dataPath}/../../Config/Excel/Game"。 - Protobuf 数据路径:
$"{Application.dataPath}/Res/ProtoData"。 - C# 脚本路径:
"Assets/Scripts/ProtoCSharp"。
4.2 自定义路径
如果需要自定义路径,请按照以下步骤操作:
-
创建自定义配置类:
- 按照上述规则创建自定义配置类,并重写需要自定义的属性。
-
将自定义配置类放置在项目中:
- 将
CustomProtoPathConfig类放置在项目的任意脚本文件夹中(如Assets/Scripts)。
- 将
-
插件自动使用配置:
- 插件会自动调用静态构造函数,注册并使用自定义配置。
4.3 Excel 配置规则
具体请查看 Excel数值配置填充规则章节
-
Excel 文件格式:
-
使用 CSV 文件格式存储数据,方便生成 Excel 文件。
-
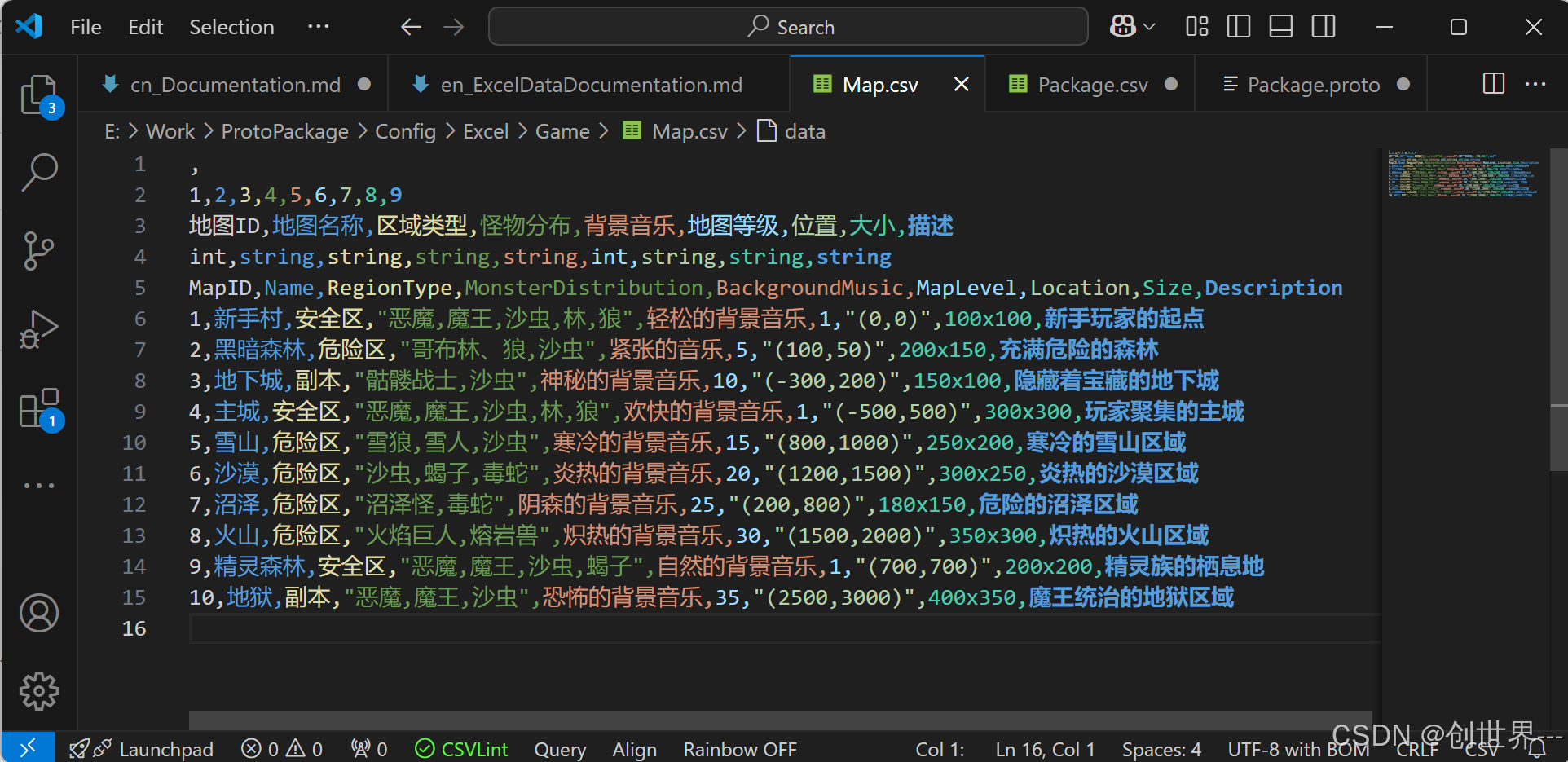
示例数据:
, 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 地图ID,地图名称,区域类型,怪物分布,背景音乐,地图等级,位置,大小,描述 int,string,string,string,string,int,string,string,string MapID,Name,RegionType,MonsterDistribution,BackgroundMusic,MapLevel,Location,Size,Description 1,新手村,安全区,"恶魔,魔王,沙虫,林,狼",轻松的背景音乐,1,"(0,0)",100x100,新手玩家的起点 2,黑暗森林,危险区,"哥布林、狼,沙虫",紧张的音乐,5,"(100,50)",200x150,充满危险的森林 3,地下城,副本,"骷髅战士,沙虫",神秘的背景音乐,10,"(-300,200)",150x100,隐藏着宝藏的地下城 4,主城,安全区,"恶魔,魔王,沙虫,林,狼",欢快的背景音乐,1,"(-500,500)",300x300,玩家聚集的主城 5,雪山,危险区,"雪狼,雪人,沙虫",寒冷的背景音乐,15,"(800,1000)",250x200,寒冷的雪山区域 6,沙漠,危险区,"沙虫,蝎子,毒蛇",炎热的背景音乐,20,"(1200,1500)",300x250,炎热的沙漠区域 7,沼泽,危险区,"沼泽怪,毒蛇",阴森的背景音乐,25,"(200,800)",180x150,危险的沼泽区域 8,火山,危险区,"火焰巨人,熔岩兽",炽热的背景音乐,30,"(1500,2000)",350x300,炽热的火山区域 9,精灵森林,安全区,"恶魔,魔王,沙虫,蝎子",自然的背景音乐,1,"(700,700)",200x200,精灵族的栖息地 10,地狱,副本,"恶魔,魔王,沙虫",恐怖的背景音乐,35,"(2500,3000)",400x350,魔王统治的地狱区域
-
-
创建 Excel 文件:
-
在
ExcelPath指定的路径下创建 CSV 文件(如Map.csv)。
-
将上述数据复制到 CSV 文件中。
-
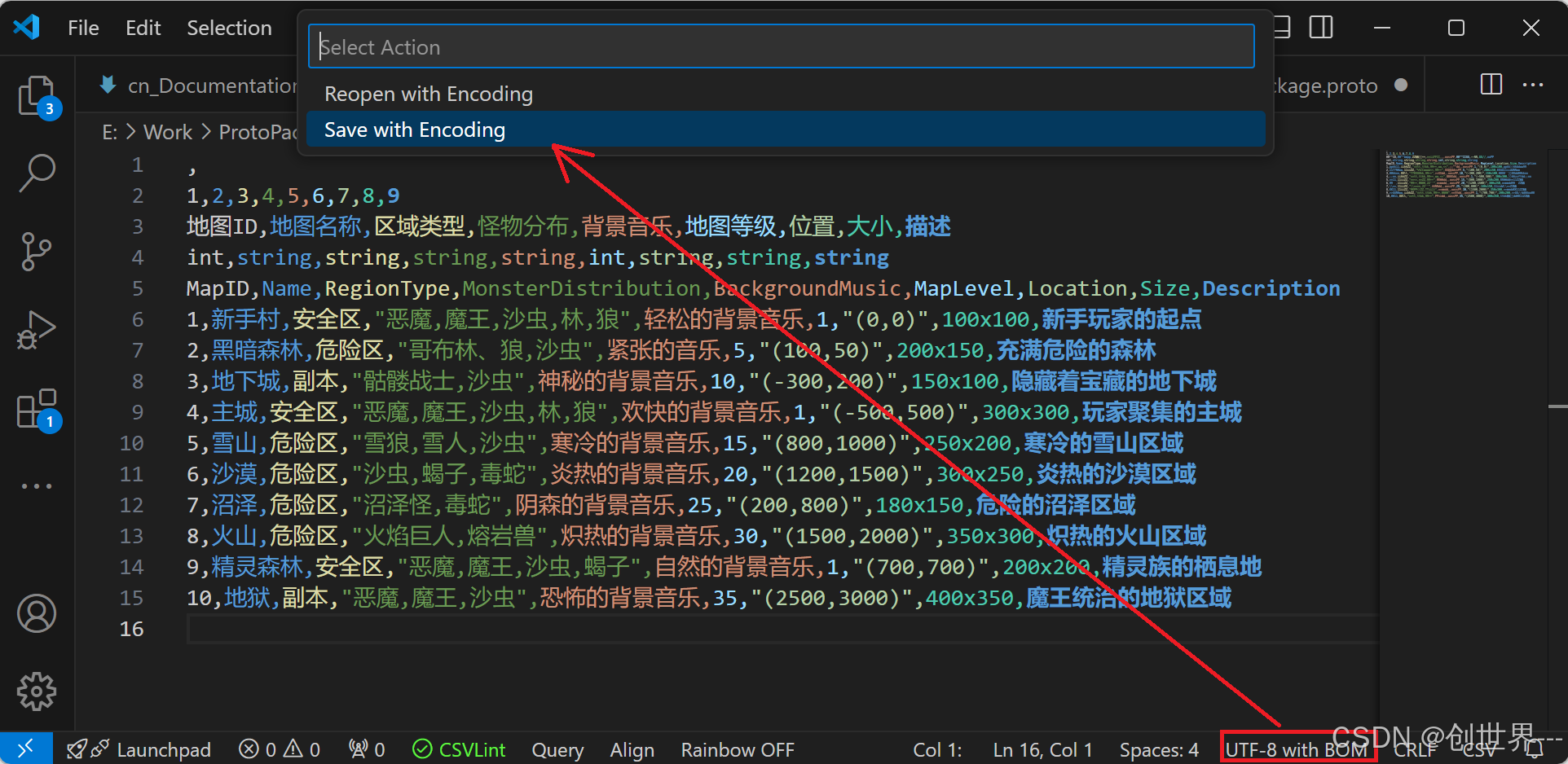
注意:保存格式必须为 UTF-8 with BOM,步骤如下:
-
打开 CSV 文件。
-
选择
文件 -> 另存为。 -
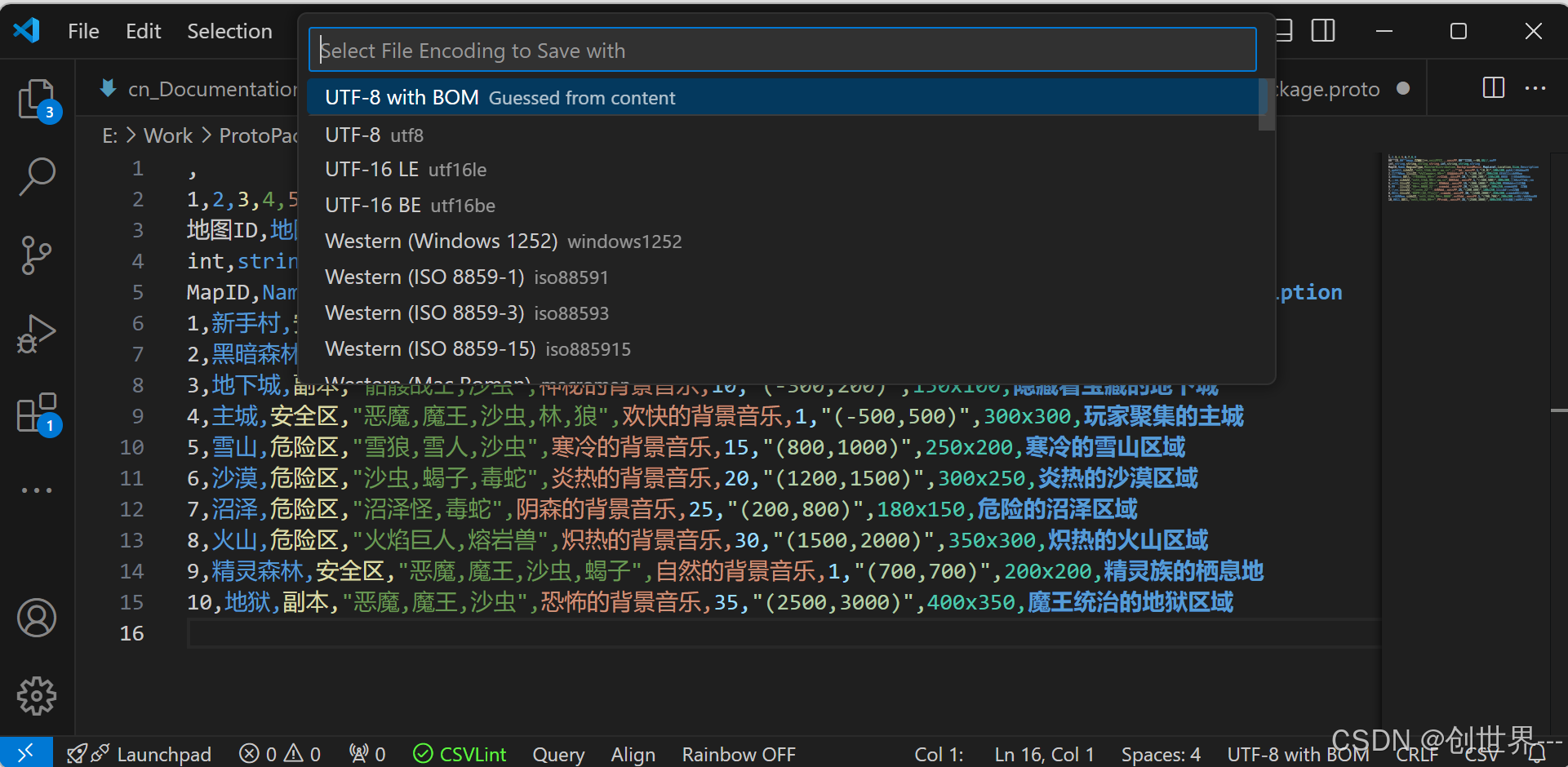
在保存对话框中,选择编码格式为 UTF-8 with BOM。
选择编码格式为 UTF-8 with BOM
-
保存文件。
-
-
-
转换为 Excel 文件:
- 使用 Excel 打开 CSV 文件,保存为
.xlsx格式。
- 使用 Excel 打开 CSV 文件,保存为
-
生成 Protobuf 文件:
- 在 Unity 中,导航到菜单栏
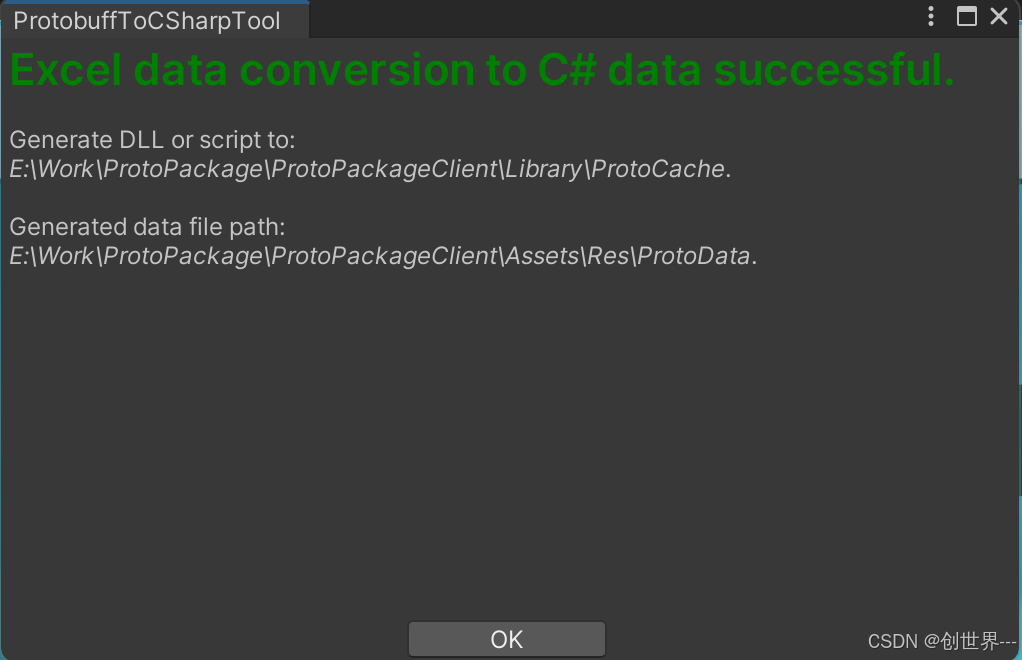
Tools -> ExcelToCsharp。 - 等待进度完成,插件将在配置目录中生成对应的 Protobuf 文件、C# 脚本或 DLL 文件。
- 成功后会弹出提示窗口:
- 在 Unity 中,导航到菜单栏
-
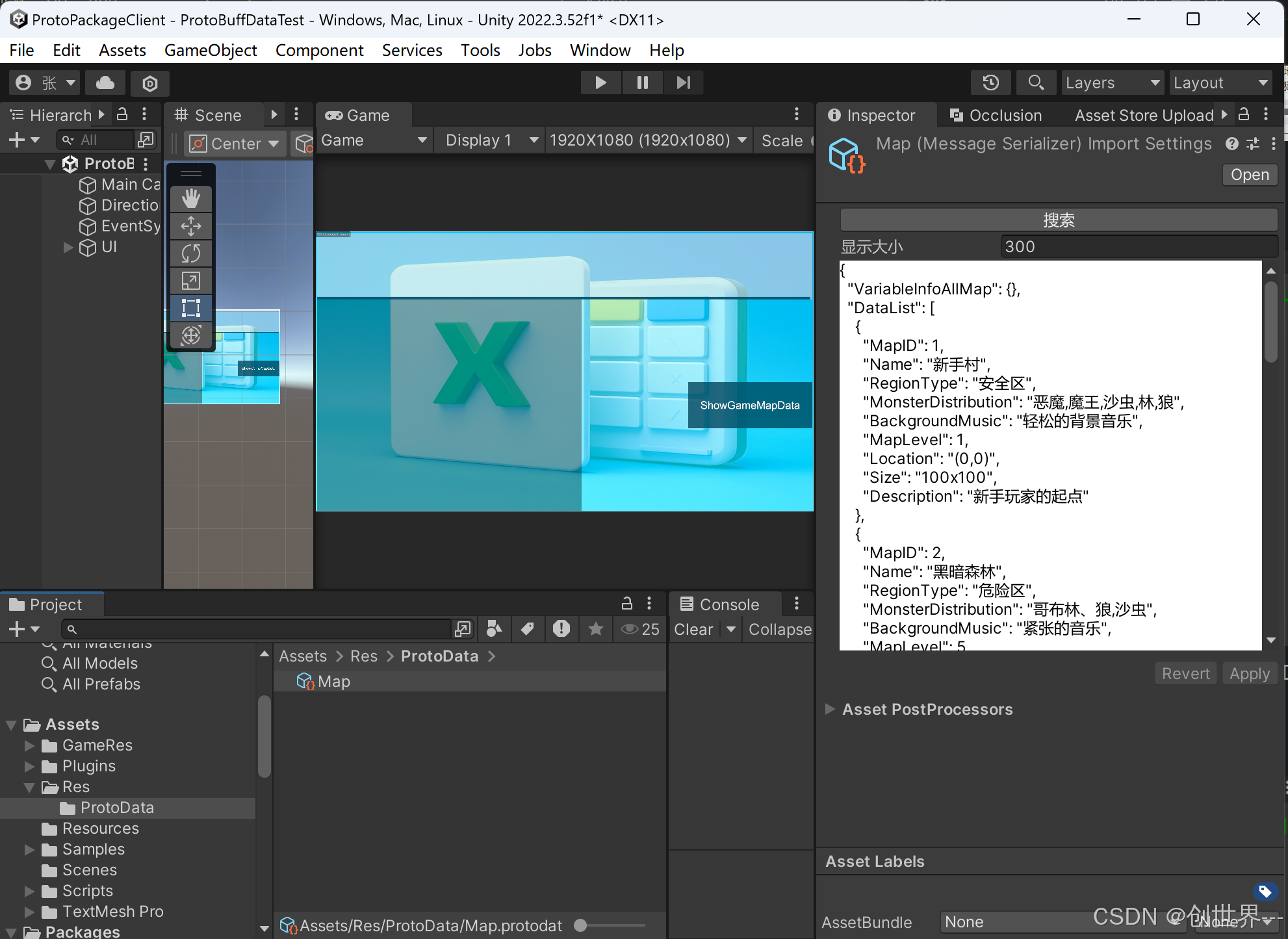
查看生成的数据:
- 生成的 Protobuf 数据将以 JSON 形式显示在 Unity 的属性面板中。
- 生成的 Protobuf 数据将以 JSON 形式显示在 Unity 的属性面板中。
5. 注意事项
-
路径配置:
- 确保自定义路径(如
ExcelPath、GenerateProtoDataPath等)在项目中存在且有效。
- 确保自定义路径(如
-
避免重复注册:
- 如果项目中存在多个自定义配置类,确保只有一个配置类被注册到
ProtoPathConfig.CurProtoPathConfig,避免冲突。
- 如果项目中存在多个自定义配置类,确保只有一个配置类被注册到
-
编辑模式测试:
- 由于
[ExecuteInEditMode]特性的存在,可以在 Unity 编辑器中直接测试配置是否生效,无需进入运行模式。
- 由于
测试实例
打开PackageManager导入实例
如下图
打开ProtoBuffDataTest.unity场景
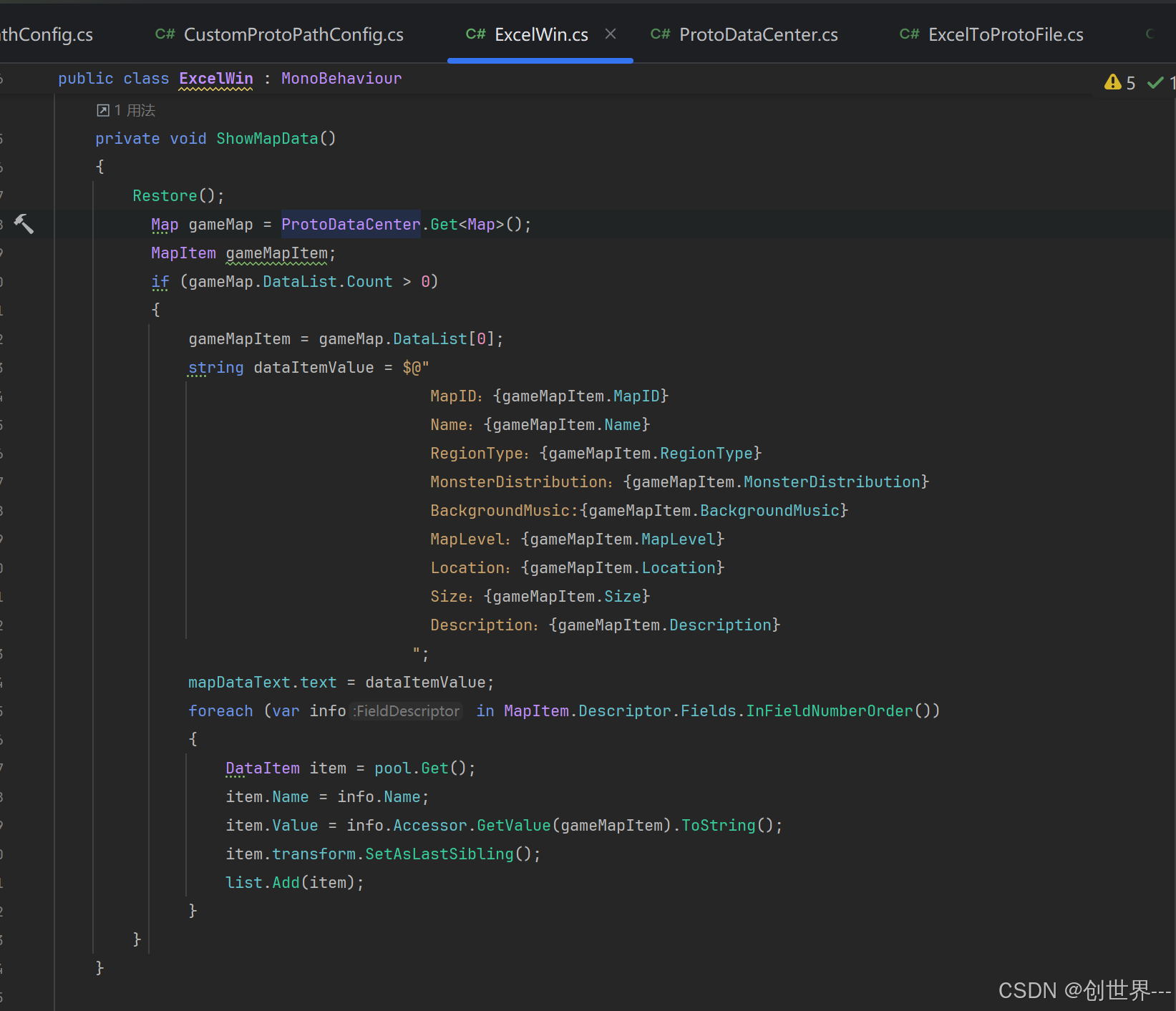
主要测试代码ExcelWin.cs
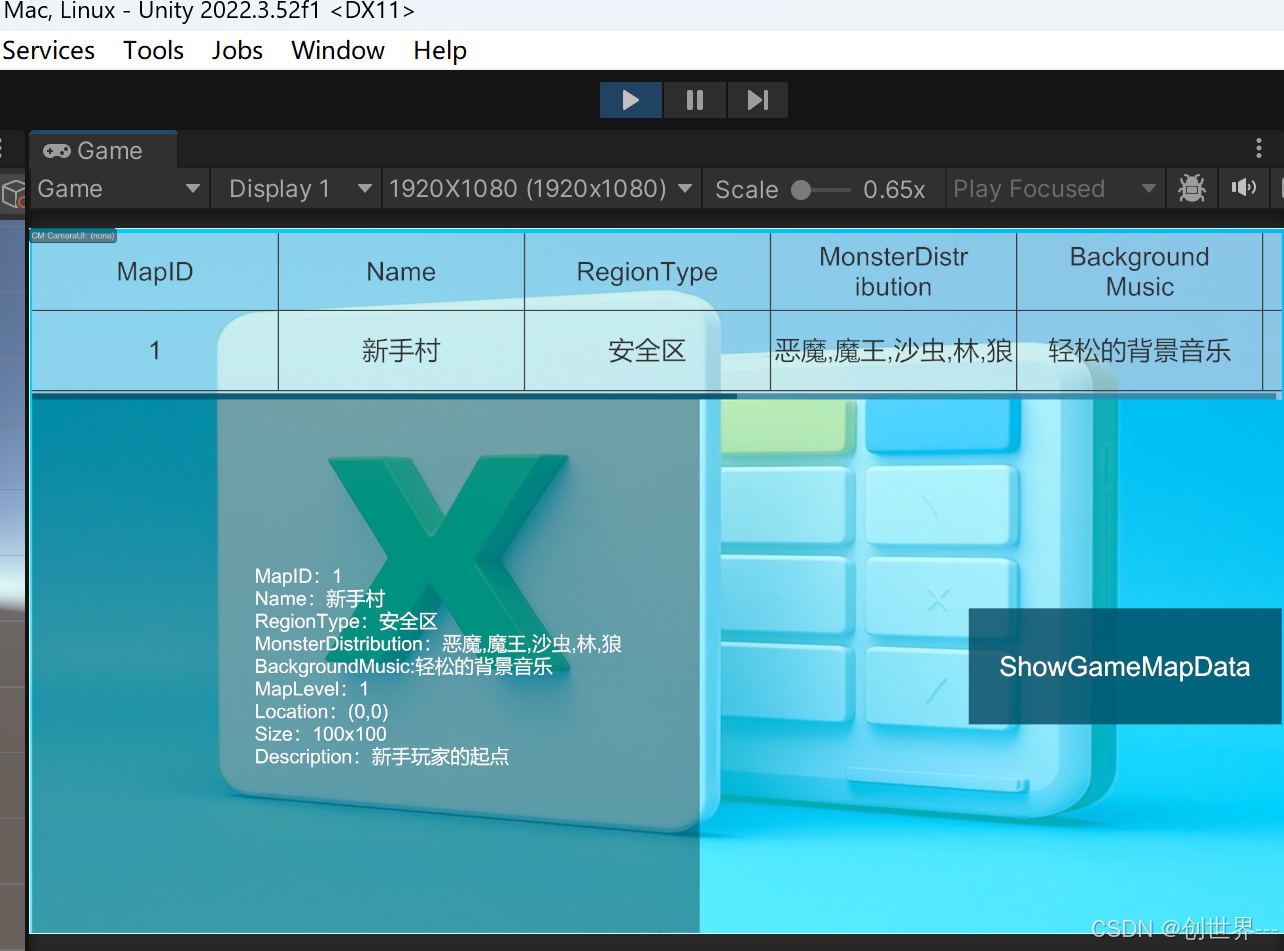
运行结果
值得注意说明的是ExcelWin使用的Map.cs和MapItem使用的是案例里面的脚本。不是生成的脚本。原因是为了使测试用例运行正常。如果使用新编译的脚本或者dll请删除测试用例的脚本并修改HuaXianQu.ProtoBuffEx.Tests.Sample.asmdef
6. 总结
通过创建自定义配置类并重写相关属性,可以轻松配置 ExcelToProtobufTool 插件的行为。只需将自定义配置类放置在项目中,插件会自动使用自定义配置。结合 Excel 配置规则,开发者可以快速将 Excel 数据转换为 Protobuf 格式,并生成对应的 C# 脚本或 DLL 文件。
Excel数值配置填充规则
Excel 文档配置规则说明(更新版)
1. 概述
本文档详细说明了如何定义 枚举、类 和 列表类 的字段和数据,并生成对应的 Proto 文件 和 C# 脚本。通过遵循这些规则,您可以快速定义配置文件并生成代码。
2. 工作表页签命名规则
- 枚举表:以
_Enum为后缀。- 示例:
ItemType_Enum、EffectType_Enum。
- 示例:
- 类定义表:以
_Class为后缀。- 示例:
EffectItem_Class、BackpackItem_Class。
- 示例:
- 列表类表:直接使用大驼峰命名法,无需后缀。
- 示例:
Backpack、Character。
- 示例:
3. 枚举表(_Enum 后缀)
文件结构
- 第一列:枚举名称,使用大驼峰命名法(PascalCase)。
- 其他列:枚举值定义,格式为
枚举值名称:枚举值。- 第一个枚举值必须为
0。 - 枚举值名称使用大驼峰命名法(PascalCase)。
- 枚举值为整数,从
0开始递增。
- 第一个枚举值必须为
示例
ItemType,Consumable:0,Equipment:1,QuestItem:2,Currency:3
EffectType,Heal:0,Buff:1,Poison:2
转换为 Excel 表格
| ItemType | Consumable:0 | Equipment:1 | QuestItem:2 | Currency:3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EffectType | Heal:0 | Buff:1 | Poison:2 |
生成 Proto 文件
enum ItemType {
Consumable = 0;
Equipment = 1;
QuestItem = 2;
Currency = 3;
}
enum EffectType {
Heal = 0;
Buff = 1;
Poison = 2;
}
生成 C# 脚本
public enum ItemType
{
Consumable = 0, // 消耗品
Equipment = 1, // 装备
QuestItem = 2, // 任务物品
Currency = 3 // 货币
}
public enum EffectType
{
Heal = 0, // 治疗
Buff = 1, // 增益
Poison = 2 // 中毒
}
4. 类定义表(_Class 后缀)
文件结构
- 第一列:类名,使用大驼峰命名法(PascalCase)。
- 其他列:成员定义,格式为
成员字段类型:成员字段名称:Proto文件字段编码。- 支持基础类型、枚举类型、自定义类型、列表类型和字典类型。
示例
EffectItem,string:Name:1,int:Level:2,int:ID:3
BackpackItem,int:ItemID:1,string:ItemName:2,ItemType:ItemType:3,SellInfo:Sellable:4
SellInfo,bool:IsSellable:1,string:CurrencyType:2,PriceRange:Range:3
PriceRange,double:MinPrice:1,double:MaxPrice:2
ItemPrices,int:ItemID:1,"Dictionary<string,EffectItem>:Prices:2"
转换为 Excel 表格
| EffectItem | string:Name:1 | int:Level:2 | int:ID:3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BackpackItem | int:ItemID:1 | string:ItemName:2 | ItemType:ItemType:3 |
| SellInfo | bool:IsSellable:1 | string:CurrencyType:2 | PriceRange:Range:3 |
| PriceRange | double:MinPrice:1 | double:MaxPrice:2 | |
| ItemPrices | int:ItemID:1 | Dictionary<string,EffectItem>:Prices:2 |
生成 Proto 文件
message EffectItem {
string Name = 1;
int32 Level = 2;
int32 ID = 3;
}
message BackpackItem {
int32 ItemID = 1;
string ItemName = 2;
ItemType ItemType = 3;
SellInfo Sellable = 4;
}
message SellInfo {
bool IsSellable = 1;
string CurrencyType = 2;
PriceRange Range = 3;
}
message PriceRange {
double MinPrice = 1;
double MaxPrice = 2;
}
message ItemPrices {
int32 ItemID = 1;
map<string,EffectItem> Prices = 2;
}
生成 C# 脚本
public class EffectItem
{
public string Name { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public int Level { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
public int ID { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 3
}
public class BackpackItem
{
public int ItemID { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public string ItemName { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
public ItemType ItemType { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 3
public SellInfo Sellable { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 4
}
public class SellInfo
{
public bool IsSellable { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public string CurrencyType { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
public PriceRange Range { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 3
}
public class PriceRange
{
public double MinPrice { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public double MaxPrice { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
}
public class ItemPrices
{
public int ItemID { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public MapField<string,EffectItem> Prices { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
}
5. 列表类表
文件结构
- 第一行:字段的附加属性(类似 C# 的特性),用
{}括起来,包含多个键值对。- 示例:
{key;EffectName:1,lan:Public,DefaultValue:0}。
- 示例:
- 第二行:字段的编码值,从
1开始递增,表示生成 Proto 文件时变量对应的编码值。- 示例:
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13。
- 示例:
- 第三行:字段的功能描述,用中文简要说明每一列的作用。
- 示例:
唯一ID,物品名称,物品类型,最大堆叠数,是否可交易,是否可销毁,出售信息,出售价格列表,图标资源路径,描述,关联道具列表,效果列表,属性加成。
- 示例:
- 第四行:字段类型,用于转换成 C# 类型。
- 支持类型:
- 基础类型:
int、uint、long、ulong、double、float、bool、string。 - 枚举类型:如
ItemType。 - 自定义类型:如
EffectItem。 - 列表类型:如
List<EffectItem>。 - 字典类型:如
Dictionary<string, EffectItem>。
- 基础类型:
- 支持类型:
- 第五行:字段属性名称(大驼峰命名),方便代码调用。
- 示例:
ItemID,ItemName,ItemType,MaxStack,Tradable,Destructible,Sellable,SellPrices,IconPath,Description,LinkedItemIDs,Effects,AttributeBonus。
- 示例:
- 第六行及以后:具体数据,按照字段类型和属性名称逐行填写。
示例
"{key;EffectName:1,lan:Public,DefaultValue:0}",
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14
Unique ID,Item Name,Item Type,Max Stack Size,Tradable,Destructible,Sell Info,Sell Price List,Icon Path,Description,Linked Item IDs,Effects,Attribute Bonuses,Package Info
int,string,ItemType,int,bool,bool,SellInfo,List<PriceInfo>,string,string,List<int>,"Dictionary<string, EffectItem>","Dictionary<string, double>","Dictionary<int, ItemPrices>"
ItemID,ItemName,ItemType,MaxStack,Tradable,Destructible,Sellable,SellPrices,IconPath,Description,LinkedItemIDs,Effects,AttributeBonus,Info
1,Small Healing Potion,Consumable,99,TRUE,TRUE,"{TRUE,Gold,{10.0,20.0}}","{{Gold,10.0},{Silver,20.0},{Copper,30.0}}",icons/potion_small.png,Restores a small amount of health,"{1,2,3}","Name:{{Heal,1,50},{Buff,2,10},{Poison,3,30}}","::{Consumable:1.5,Equipment:0.5,QuestItem:2.0}","::{1:{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}}, 2:{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,9}}}}"
2,Large Healing Potion,Consumable,99,TRUE,TRUE,"{TRUE,Diamond,{50.0,100.0}}","{{Diamond,50.0},{Gold,100.0},{Silver,150.0}}",icons/potion_large.png,Restores a large amount of health,"{4,5}","Name:{{Heal,1,100},{Buff,2,20},{Poison,3,60}}","::{Consumable:2.0,Equipment:1.0,QuestItem:3.0}","::{1:{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}}, 2:{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,9}}}}"
3,Iron Sword,Equipment,1,TRUE,TRUE,"{FALSE,Gold,{200.0,400.0}}","{{Gold,200.0},{Silver,400.0},{Copper,600.0}}",icons/sword_iron.png,A common iron sword,{},"Name:{{Buff,2,15},{Poison,3,45},{Heal,1,75}}","::{Equipment:3.0,Consumable:1.0,QuestItem:0.5}","::{1:{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}}, 2:{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,11}}}}"
转换为 Excel 表格
| {key;EffectName:1,lan:Public,DefaultValue:0} | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |
| 唯一ID | 物品名称 | 物品类型 | 最大堆叠数 | 是否可交易 | 是否可销毁 | 出售信息 | 出售价格列表 | 图标路径 | 描述 | 关联道具列表 | 效果 | 属性加成 | 背包信息 |
| int | string | ItemType | int | bool | bool | SellInfo | List | string | string | List | Dictionary<string, EffectItem> | Dictionary<ItemType, double> | Dictionary<string,ItemPrices> |
| ItemID | ItemName | ItemType | MaxStack | Tradable | Destructible | Sellable | SellPrices | IconPath | Description | LinkedItemIDs | Effects | AttributeBonus | Info |
| 1 | 小型治疗药水 | Consumable | 99 | TRUE | TRUE | {TRUE,Gold,{10.0,20.0}} | {{Gold,10.0},{Silver,20.0},{Copper,30.0}} | icons/potion_small.png | 回复少量生命值 | {1,2,3} | Name:{{Heal,1,50},{Buff,2,10},{Poison,3,30}} | ::{Consumable:1.5,Equipment:0.5,QuestItem:2.0} | ::{1:{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}}, 2:{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,9}}}} |
| 2 | 大型治疗药水 | Consumable | 99 | TRUE | TRUE | {TRUE,Diamond,{50.0,100.0}} | {{Diamond,50.0},{Gold,100.0},{Silver,150.0}} | icons/potion_large.png | 回复大量生命值 | {4,5} | Name:{{Heal,1,100},{Buff,2,20},{Poison,3,60}} | ::{Consumable:2.0,Equipment:1.0,QuestItem:3.0} | ::{1:{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}}, 2:{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,9}}}} |
| 3 | 铁剑 | Equipment | 1 | TRUE | TRUE | {FALSE,Gold,{200.0,400.0}} | {{Gold,200.0},{Silver,400.0},{Copper,600.0}} | icons/sword_iron.png | 一把普通的铁剑 | {} | Name:{{Buff,2,15},{Poison,3,45},{Heal,1,75}} | ::{Equipment:3.0,Consumable:1.0,QuestItem:0.5} | ::{1:{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}}, 2:{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,9}}}} |
生成 Proto 文件
message EffectItem {
string Name = 1;
int32 Level = 2;
int32 ID = 3;
}
message BackpackItem {
int32 ItemID = 1;
string ItemName = 2;
ItemType ItemType = 3;
SellInfo Sellable = 4;
}
message SellInfo {
bool IsSellable = 1;
string CurrencyType = 2;
PriceRange Range = 3;
}
message PriceRange {
double MinPrice = 1;
double MaxPrice = 2;
}
message ItemPrices {
int32 ItemID = 1;
map<string,EffectItem> Prices = 2;
}
message BackpackItem {
int32 ItemID = 1;
string ItemName = 2;
ItemType ItemType = 3;
int32 MaxStack = 4;
bool Tradable = 5;
bool Destructible = 6;
SellInfo Sellable = 7;
repeated PriceInfo SellPrices = 8;
string IconPath = 9;
string Description = 10;
repeated int32 LinkedItemIDs = 11;
map<string, EffectItem> Effects = 12;
map<ItemType, double> AttributeBonus = 13;
map<ItemType, ItemPrices> Info = 13;
}
生成 C# 脚本
public class EffectItem
{
public string Name { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public int Level { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
public int ID { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 3
}
public class BackpackItem
{
public int ItemID { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public string ItemName { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
public ItemType ItemType { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 3
public SellInfo Sellable { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 4
}
public class SellInfo
{
public bool IsSellable { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public string CurrencyType { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
public PriceRange Range { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 3
}
public class PriceRange
{
public double MinPrice { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public double MaxPrice { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
}
public class ItemPrices
{
public int ItemID { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 1
public MapField<string,EffectItem> Prices { get; set; } // Proto 编码: 2
}
public class BackpackItem
{
public int ItemID { get; set; }
public string ItemName { get; set; }
public ItemType ItemType { get; set; }
public int MaxStack { get; set; }
public bool Tradable { get; set; }
public bool Destructible { get; set; }
public SellInfo Sellable { get; set; } // 嵌套类
public List<PriceInfo> SellPrices { get; set; } // 列表类(嵌套类)
public string IconPath { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public List<int> LinkedItemIDs { get; set; }
public MapField<string, EffectItem> Effects { get; set; }
public MapField<ItemType, double> AttributeBonus { get; set; }
}
6. 第一行词典 Key 的规则补充说明
1. 规则说明
- 数据填充格式:
- 第一行使用
{key;EffectDict:编码}定义嵌套字典的 Key。 - 编码:决定 Key 的排序优先级(从 1 开始递增,数字越小优先级越高)。
- 示例:
{key;EffectDict:1}表示该字段作为第一层 Key,{key;EffectDict:2}表示该字段作为第二层 Key,依此类推。
- 第一行使用
2. 示例:地图 Map 配置
以下是一个地图配置的示例,定义了嵌套字典的 Key 和 Value。
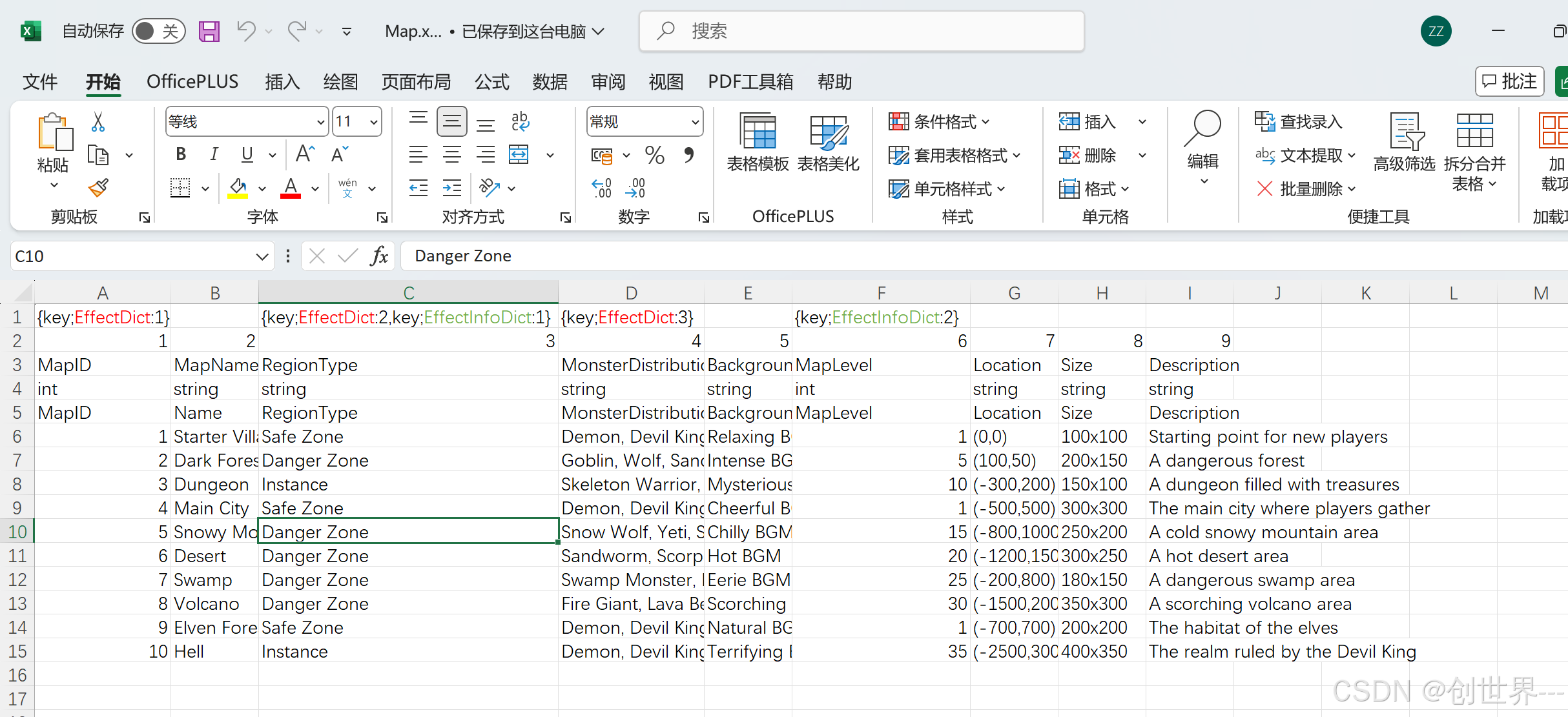
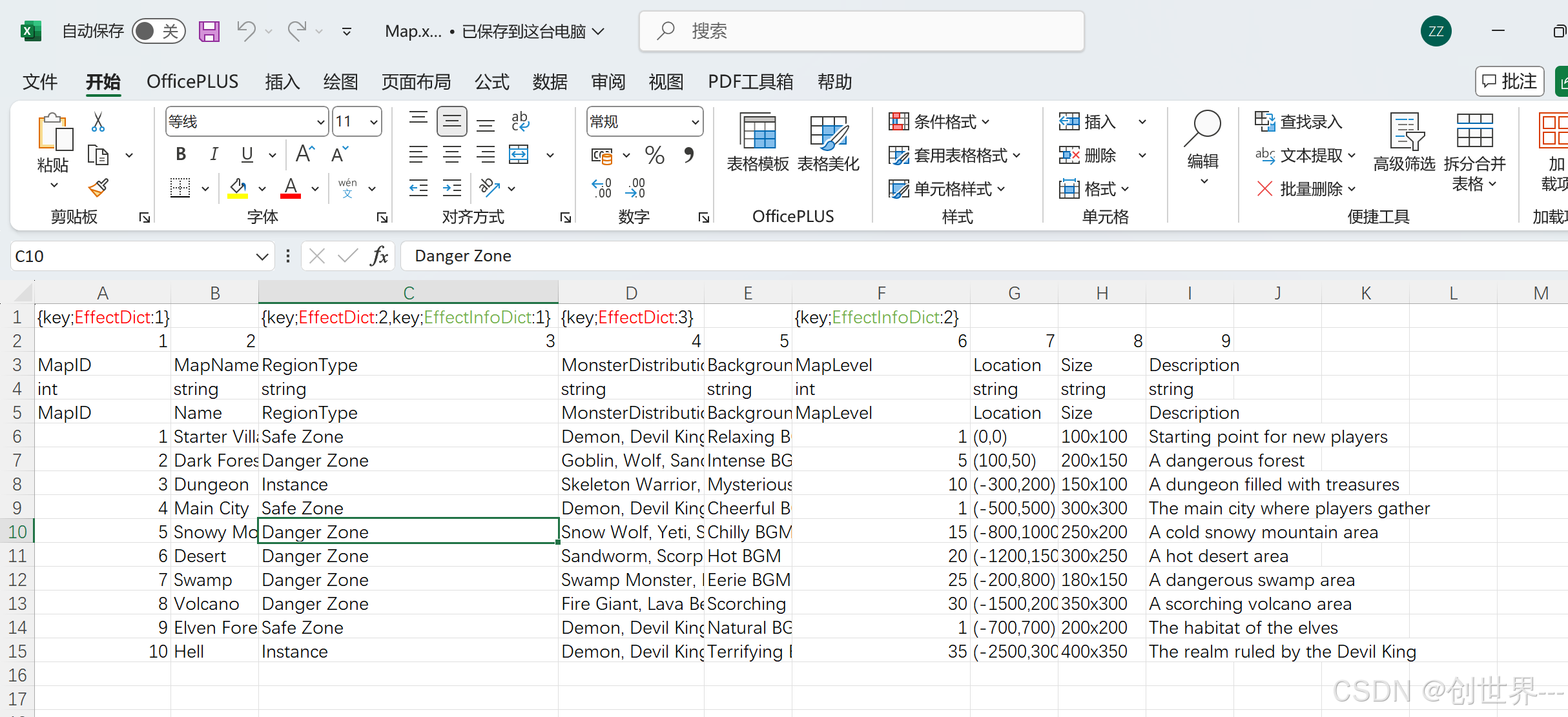
{key;EffectDict:1},,"{key;EffectDict:2,key;EffectInfoDict:1}",{key;EffectDict:3},,{key;EffectInfoDict:2},,,
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
MapID,MapName,RegionType,MonsterDistribution,BackgroundMusic,MapLevel,Location,Size,Description
int,string,string,string,string,int,string,string,string
MapID,Name,RegionType,MonsterDistribution,BackgroundMusic,MapLevel,Location,Size,Description
1,Starter Village,Safe Zone,"Demon, Devil King, Sandworm, Forest, Wolf",Relaxing BGM,1,"(0,0)",100x100,Starting point for new players
2,Dark Forest,Danger Zone,"Goblin, Wolf, Sandworm",Intense BGM,5,"(100,50)",200x150,A dangerous forest
3,Dungeon,Instance,"Skeleton Warrior, Sandworm",Mysterious BGM,10,"(-300,200)",150x100,A dungeon filled with treasures
4,Main City,Safe Zone,"Demon, Devil King, Sandworm, Forest, Wolf",Cheerful BGM,1,"(-500,500)",300x300,The main city where players gather
5,Snowy Mountain,Danger Zone,"Snow Wolf, Yeti, Sandworm",Chilly BGM,15,"(-800,1000)",250x200,A cold snowy mountain area
6,Desert,Danger Zone,"Sandworm, Scorpion, Poisonous Snake",Hot BGM,20,"(-1200,1500)",300x250,A hot desert area
7,Swamp,Danger Zone,"Swamp Monster, Poisonous Snake",Eerie BGM,25,"(-200,800)",180x150,A dangerous swamp area
8,Volcano,Danger Zone,"Fire Giant, Lava Beast",Scorching BGM,30,"(-1500,2000)",350x300,A scorching volcano area
9,Elven Forest,Safe Zone,"Demon, Devil King, Sandworm, Scorpion",Natural BGM,1,"(-700,700)",200x200,The habitat of the elves
10,Hell,Instance,"Demon, Devil King, Sandworm",Terrifying BGM,35,"(-2500,3000)",400x350,The realm ruled by the Devil King
对应对的excel
3. 定义嵌套字典的 Key 和 Value
- Key:
- 由
{key;词典名称:编码}定义的字段组成。 - 示例中:
MapID作为第一层 Key({key;EffectDict:1})。RegionType作为第二层 Key({key;EffectDict:2})。MonsterDistribution作为第三层 Key({key;EffectDict:3})。
- 由
- Value:
- 最后一个字段是嵌套字典的 Value,即
MapItem类型的数据。
- 最后一个字段是嵌套字典的 Value,即
4. 生成的数据结构
上面共定义两个词典EffectDict和EffectInfoDict
最终生成的数据结构为:
Dictionary<int, Dictionary<string, Dictionary<string, MapItem>>>EffectDict;
Dictionary<string, Dictionary<int, MapItem>>EffectInfoDict;
- EffectDict的Key:
- 第一层:
MapID(int类型)。 - 第二层:
RegionType(string类型)。 - 第三层:
MonsterDistribution(string类型)。
- 第一层:
- EffectDict的Value:
MapItem类型的数据。
- EffectInfoDict的Key:
- 第一层:
RegionType(string类型)。 - 第二层:
MapLevel(string类型)。
- 第一层:
- EffectInfoDict的Value:
MapItem类型的数据。
这两个词典有一个相同的key是RegionType。就是说一个字段可以作为多个词典的key
5. 生成逻辑
解析脚本的核心逻辑如下:
- 读取 CSV 数据:
- 跳过表头,从数据行开始解析。
- 解析每一行数据:
- 根据字段类型和属性名称,提取嵌套字典的 Key 和 Value。
- 构建嵌套字典:
- 使用
MapID作为第一层 Key。 - 使用
RegionType作为第二层 Key。 - 使用
MonsterDistribution作为第三层 Key。 - 将
MapItem数据作为 Value。
- 使用
6. 总结
-
{key;词典名称:编码}:- 用于定义嵌套字典的每一层 Key。
- 编码决定 Key 的排序优先级(从 1 开始递增,数字越小优先级越高)。
-
嵌套字典结构:
- 多个字段共同组成嵌套字典的 Key。
- 最后一个字段是嵌套字典的 Value。
- 示例中生成的结构为
Dictionary<int, Dictionary<string, Dictionary<string, MapItem>>>。
-
解析脚本:
- 通过逐行解析 CSV 数据,构建嵌套字典。
- 支持异步编程,使用
ConcurrentDictionary。
在使用词典时先调用实现IProtoInit的Init方法,目的用于性能优化,预加载,如下示例代码:
if (messageData is IProtoInit protoInit)
{
protoInit.Init();
}
在插件演示示例的ProtoDataCenter脚本完整的示例代码
public T _Get<T>(Action<T> callFun) where T : class, IMessage, new()
{
Type type = typeof(T);
T messageData = (T)protoDataDict.GetOrAdd(type, _ =>
{
T messageData = Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(T)) as T;
if (GetBytes(type.Name, out byte[] protoData))
{
messageData.MergeFrom(protoData);
if (messageData is IProtoInit protoInit)
{
protoInit.Init();
}
}
return messageData;
});
callFun?.Invoke(messageData);
return messageData;
}
如果不调用接口也能正确使用词典。因为在词典属性里将会自定初始化并调用这个方法,如:
private ConcurrentDictionary<int, ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>>
_EffectDictMap = null;
ConcurrentDictionary<int, ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>> EffectDictMap
{
get
{
if (_EffectDictMap == null)
{
_EffectDictMap =
new ConcurrentDictionary<int,
ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>>();
Init();
}
return _EffectDictMap;
}
set => _EffectDictMap = value;
}
7. 生成的解析脚本
以下是根据上述配置生成的解析脚本:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using Google.Protobuf;
using HuaXianQu.ProtoBuffEx.Runtime.ProtoInterface;
public partial class Map : IProtoInit
{
private ConcurrentDictionary<int, ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>>
_EffectDictMap = null;
ConcurrentDictionary<int, ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>> EffectDictMap
{
get
{
if (_EffectDictMap == null)
{
_EffectDictMap =
new ConcurrentDictionary<int,
ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>>();
Init();
}
return _EffectDictMap;
}
set => _EffectDictMap = value;
}
private ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<int, MapItem>> _EffectInfoDictMap = null;
ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<int, MapItem>> EffectInfoDictMap
{
get
{
if (_EffectInfoDictMap == null)
{
_EffectInfoDictMap = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<int, MapItem>>();
Init();
}
return _EffectInfoDictMap;
}
set => _EffectInfoDictMap = value;
}
public void Init()
{
if (_EffectDictMap == null)
{
_EffectDictMap =
new ConcurrentDictionary<int, ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>>();
}
if (_EffectInfoDictMap == null)
{
_EffectInfoDictMap = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<int, MapItem>>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < DataList.Count; i++)
{
var item = DataList[i];
InitEffectDict(item);
InitEffectInfoDict(item);
}
}
private void InitEffectDict(MapItem item)
{
var MapIDMap = EffectDictMap.GetOrAdd(item.MapID,
key => new ConcurrentDictionary<string, ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>>());
var RegionTypeMap = MapIDMap.GetOrAdd(item.RegionType, key => new ConcurrentDictionary<string, MapItem>());
RegionTypeMap.TryAdd(item.MonsterDistribution, item);
}
private void InitEffectInfoDict(MapItem item)
{
var RegionTypeMap =
EffectInfoDictMap.GetOrAdd(item.RegionType, key => new ConcurrentDictionary<int, MapItem>());
RegionTypeMap.TryAdd(item.MapLevel, item);
}
public bool GetEffectDictMap<T>(int MapID, out T value) where T : IDictionary
{
value = default(T);
if (EffectDictMap.TryGetValue(MapID, out var MapIDMap))
{
value = (T)(IDictionary)MapIDMap;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public bool GetEffectDictMap<T>(int MapID, string RegionType, out T value) where T : IDictionary
{
value = default(T);
if (EffectDictMap.TryGetValue(MapID, out var MapIDMap))
{
if (MapIDMap.TryGetValue(RegionType, out var RegionTypeMap))
{
value = (T)(IDictionary)RegionTypeMap;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public bool GetEffectDictMap<T>(int MapID, string RegionType, string MonsterDistribution, out T value)
where T : IMessage
{
value = default(T);
if (EffectDictMap.TryGetValue(MapID, out var MapIDMap))
{
if (MapIDMap.TryGetValue(RegionType, out var RegionTypeMap))
{
if (RegionTypeMap.TryGetValue(MonsterDistribution, out var MonsterDistributionMap))
{
value = (T)(IMessage)MonsterDistributionMap;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public bool GetEffectInfoDictMap<T>(string RegionType, out T value) where T : IDictionary
{
value = default(T);
if (EffectInfoDictMap.TryGetValue(RegionType, out var RegionTypeMap))
{
value = (T)(IDictionary)RegionTypeMap;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public bool GetEffectInfoDictMap<T>(string RegionType, int MapLevel, out T value) where T : IMessage
{
value = default(T);
if (EffectInfoDictMap.TryGetValue(RegionType, out var RegionTypeMap))
{
if (RegionTypeMap.TryGetValue(MapLevel, out var MapLevelMap))
{
value = (T)(IMessage)MapLevelMap;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
8. 注意事项
key;EffectDict:编码:EffectDict是标记相同词典的名称。- 一个字段可以有多个
key;词典名称:编码,但词典名称不能相同。
- 初始化:
- 在初始化
Map数据时,需要调用Init方法实现IProtoInit接口。
- 在初始化
- 异步支持:
- 使用
ConcurrentDictionary支持异步编程。
- 使用
通过以上规则和示例,您可以灵活定义复杂的嵌套字典结构,并生成对应的代码和配置文件。
7. 字典类型的规则补充说明
在原有的字典类型规则基础上,进一步明确 Key 的类型限制,并补充相关示例。
1. Key 的类型限制
- Key 只能为基础类型:
- 支持的基础类型包括:
int、uint、long、ulong、double、float、bool、string。 - 不支持枚举类型、自定义类型、列表类型或字典类型作为 Key。
- 支持的基础类型包括:
- Value 可以是任意类型:
- 支持基础类型、枚举类型、自定义类型、列表类型或字典类型。
字典字段的定义规则
字典字段的定义规则分为两种情况,具体取决于 : 前面的字符:
情况 1:: 前面是非 : 的字符
- 含义:
:前面的字符表示 类成员名称,用于定义 Key。 - 规则:
- Key:由类成员名称决定,通常是类中的某个字段。
- Value:是类本身的数据。
- 格式:
类成员名称:{类数据}。 - 示例:
- 定义类:
Effects,string:EffectName:1,EffectItem:EffectData:2 - 数据:
EffectName:{{Heal,1,50},{Buff,2,10},{Poison,3,30}} - 解释:
EffectName是Effects类的一个成员字段,作为 Key。{Heal,1,50}、{Buff,2,10}、{Poison,3,30}是Effects类的数据,作为 Value。- 最终生成
Dictionary<string, Effects>类型。
- 定义类:
情况 2:: 前面是 ::
- 含义:
::表示 Key 是 基础类型,直接使用值作为 Key。 - 规则:
- Key:基础类型的值(如
int、string等)。 - Value:可以是 基础类型、枚举类型 或 自定义类型。
- 不支持直接使用列表类型或字典类型作为 Value。
- 如果需要在 Value 中使用列表或字典类型,可以通过 自定义类型 嵌套实现。
- 格式:
- 如果 Value 是 基础类型,直接填写值。
- 如果 Value 是 枚举类型,直接填写 枚举值 或 枚举值名称。
- 如果 Value 是 自定义类型,使用
{类数据}格式。
- 示例:
- 定义类:
SellInfo,bool:IsSellable:1,string:CurrencyType:2,PriceRange:Range:3 - 数据:
::{1:{TRUE,Gold,{10.0,20.0}},2:{FALSE,Silver,{15.0,25.0}}} - 解释:
1和2是 Key 值(int类型)。{TRUE,Gold,{10.0,20.0}}和{FALSE,Silver,{15.0,25.0}}是SellInfo类的数据,作为 Value。- 最终生成
Dictionary<int, SellInfo>类型。
- 定义类:
- Key:基础类型的值(如
通用规则
| 情况 | Key 定义 | Value 定义 | 格式 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
: 前面是非 : 的字符 | 类成员名称(如 EffectName) | 类数据 | 类成员名称:{类数据} | EffectName:{{Heal,1,50},{Buff,2,10},{Poison,3,30}} |
: 前面是 :: | 基础类型的值(如 1、"key1") | 基础类型、枚举类型、自定义类型 | ::{Key值:Value数据} | ::{1:10, 2:20} 或 ::{1:Heal, 2:Buff} 或 ::{1:{TRUE,Gold,{10.0,20.0}}} |
示例详解
示例 1:Value 为基础类型
- 定义:
ItemPrices,int:ItemID:1,double:Price:2 - 数据:
::{1:10.5, 2:20.0, 3:30.75} - 解释:
1、2、3是 Key 值(int类型)。10.5、20.0、30.75是 Value 值(double类型)。- 最终生成
Dictionary<int, double>类型。
示例 2:Value 为枚举类型
- 定义:
ItemEffects,int:ItemID:1,EffectType:Effect:2 - 数据:
或::{1:0, 2:1, 3:2}::{1:Heal, 2:Buff, 3:Poison} - 解释:
1、2、3是 Key 值(int类型)。0(或Heal)、1(或Buff)、2(或Poison)是 Value 值(EffectType枚举类型)。- 最终生成
Dictionary<int, EffectType>类型。
示例 3:Value 为自定义类型
- 定义:
SellInfo,bool:IsSellable:1,string:CurrencyType:2,PriceRange:Range:3 - 数据:
::{1:{TRUE,Gold,{10.0,20.0}}, 2:{FALSE,Silver,{15.0,25.0}}} - 解释:
1和2是 Key 值(int类型)。{TRUE,Gold,{10.0,20.0}}和{FALSE,Silver,{15.0,25.0}}是SellInfo类的数据,作为 Value。- 最终生成
Dictionary<int, SellInfo>类型。
示例 4:自定义类型中嵌套列表类型
- 定义:
ItemAttributes,int:ItemID:1,List<string>:Attributes:2 - 数据:
::{1:{300,{Attack,Defense}}, 2:{400,{Speed,Agility}}} - 解释:
1和2是 Key 值(int类型)。{300,{Attack,Defense}}和{400,{Speed,Agility}}是ItemAttributes类的数据,作为 Value。1和2是ItemID字段。{Attack,Defense}和{Speed,Agility}是Attributes字段(List<string>类型)。
- 最终生成
Dictionary<int, ItemAttributes>类型。
示例 5:自定义类型中嵌套字典类型
- 定义:
ItemPrices,int:ItemID:1,Dictionary<string,double>:Prices:2 - 数据:
::{1:{10,::{Gold:10.0,Silver:20.0}}, 2:{20,::{Gold:15.0,Silver:25.0}}} - 解释:
1和2是 Key 值(int类型)。{10,::{Gold:10.0,Silver:20.0}}和{20,::{Gold:15.0,Silver:25.0}}是ItemPrices类的数据,作为 Value。10和20是ItemID字段。{Gold:10.0,Silver:20.0}和{Gold:15.0,Silver:25.0}是Prices字段(Dictionary<string, double>类型)。
- 最终生成
Dictionary<int, ItemPrices>类型。
这个示例展示了如何在自定义类型中嵌套字典类型,并通过 CSV 格式定义和存储数据。以下是详细的解释和结构化说明:
定义
1. EffectItem 类型的定义
EffectItem,string:Name:1,int:Level:2,int:ID:3
EffectItem:自定义类型。- 字段:
Name:string类型,表示特效名称。Level:int类型,表示特效等级。ID:int类型,表示特效的唯一标识符。
2. ItemPrices 类型的定义
ItemPrices,int:ItemID:1,Dictionary<string,EffectItem>:Prices:2
ItemPrices:自定义类型。- 字段:
ItemID:int类型,表示物品的唯一标识符。Prices:Dictionary<string, EffectItem>类型,表示以EffectItem的Name为键的字典。
数据
::{
1:{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}},
2:{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,9}}}
}
-
外层字典:
- 键值对为
1和2(int类型)。 - 对应的值分别为
{10,Name:{{Fireball,5,9},{Thunderstorm,5,9}}}和{20,Name:{{Blink,5,9},{BlackHole,5,9}}}(ItemPrices类型)。
- 键值对为
-
ItemPrices结构:ItemID:10和20(int类型)。Prices:Dictionary<string, EffectItem>类型。- 键为
Name(string类型)。 - 值为
EffectItem类型的数据,例如{Fireball,5,9}和{Thunderstorm,5,9}。
- 键为
-
EffectItem结构:Fireball,5,9表示Name="Fireball",Level=5,ID=9。Thunderstorm,5,9表示Name="Thunderstorm",Level=5,ID=9。
最终生成的数据结构
Dictionary<int, ItemPrices>
- Key:
1和2(int类型)。 - Value:
ItemPrices类型,包含:ItemID:10和20(int类型)。Prices:Dictionary<string, EffectItem>类型,包含:- Key:
Name(string类型)。 - Value:
EffectItem类型,例如{Fireball,5,9}和{Thunderstorm,5,9}。
- Key:
示例代码(C#)
以下是用 C# 表示的等效数据结构:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class EffectItem
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Level { get; set; }
public int ID { get; set; }
}
public class ItemPrices
{
public int ItemID { get; set; }
public Dictionary<string, EffectItem> Prices { get; set; }
}
public class ProtoTest:MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// 创建 EffectItem 实例
var fireball = new EffectItem { Name = "Fireball", Level = 5, ID = 9 };
var thunderstorm = new EffectItem { Name = "Thunderstorm", Level = 5, ID = 9 };
var blink = new EffectItem { Name = "Blink", Level = 5, ID = 9 };
var blackHole = new EffectItem { Name = "BlackHole", Level = 5, ID = 9 };
// 创建 ItemPrices 实例
var item1 = new ItemPrices
{
ItemID = 10,
Prices = new Dictionary<string, EffectItem>
{
{ fireball.Name, fireball },
{ thunderstorm.Name, thunderstorm }
}
};
var item2 = new ItemPrices
{
ItemID = 20,
Prices = new Dictionary<string, EffectItem>
{
{ blink.Name, blink },
{ blackHole.Name, blackHole }
}
};
// 创建外层字典
var itemPricesDict = new Dictionary<int, ItemPrices>
{
{ 1, item1 },
{ 2, item2 }
};
// 输出结果
foreach (var kvp in itemPricesDict)
{
Debug.Log(($"Key: {kvp.Key}");
Debug.Log(($"ItemID: {kvp.Value.ItemID}");
foreach (var price in kvp.Value.Prices)
{
Debug.Log(($" Price Key: {price.Key}");
Debug.Log(($" EffectItem: {price.Value.Name}, Level={price.Value.Level}, ID={price.Value.ID}");
}
}
}
}
输出结果
Key: 1
ItemID: 10
Price Key: Fireball
EffectItem: Fireball, Level=5, ID=9
Price Key: Thunderstorm
EffectItem: Thunderstorm, Level=5, ID=9
Key: 2
ItemID: 20
Price Key: Blink
EffectItem: Blink, Level=5, ID=9
Price Key: BlackHole
EffectItem: BlackHole, Level=5, ID=9
说明
- 该数据结构是一个嵌套字典,外层字典的键为
int,值为ItemPrices类型。 ItemPrices包含一个int类型的ItemID和一个Dictionary<string, EffectItem>类型的Prices。EffectItem是一个自定义类型,包含Name、Level和ID字段。- 这种结构适合用于存储复杂的游戏数据,例如物品价格及其关联的特效信息。
总结
- 字典字段的格式:
{Key1:Value1,Key2:Value2,...}。- Key 和 Value 之间用
:分隔,多个键值对之间用,分隔。
- Key 的类型:
- Key 只能是基础类型(如
int、string等)。
- Key 只能是基础类型(如
- Value 的类型:
- Value 可以是基础类型、枚举类型或自定义类型。
- 如果 Value 是自定义类型,使用
{类数据}格式。
自定义类数据填充注意事项
1. 数据填充必须与自定义类的成员个数对应且成员总数相同
- 数据填充时,必须确保每个字段都有对应的值,即使为空也需要用空字符占位。
- 示例:
public class EffectItem { public string Name { get; set; } public string Prices { get; set; } public int Level { get; set; } public int ID { get; set; } }- 数据填充为:
{Fireball,,1,2}Name为Fireball,Prices为空,Level为1,ID为2。
- 数据填充为:
2. 数据填充顺序与 Proto 编码顺序一致
-
Proto 文件中的字段编码决定了数据填充的顺序。
-
示例:
- 定义类:
EffectItem,string:Name:1,int:Level:2,int:ID:3 - 生成的 Proto 文件:
message EffectItem { string Name = 1; int32 Level = 2; int32 ID = 3; } - 数据填充为:
{Fireball,56,100}Name为Fireball,Level为56,ID为100。
- 定义类:
-
如果修改字段编码顺序:
- 定义类:
EffectItem,string:Name:2,int:Level:1,int:ID:3 - 生成的 Proto 文件:
message EffectItem { int32 Level = 1; string Name = 2; int32 ID = 3; } - 数据填充为:
{56,Fireball,100}Level为56,Name为Fireball,ID为100。
- 定义类:
-
注意事项:
- 数据填充必须按照字段编码顺序进行,否则会导致数据错乱。
- 建议字段编码从小到大使用,以避免混淆。
3. 数据填充需要转义字符
- 当数据中包含特殊字符(如英文逗号
,、大括号{})时,需要在前面添加\进行转义。 - 示例:
- 数据中包含逗号:
{Fireball\, the Great,56,100}Name为Fireball, the Great,Level为56,ID为100。
- 数据中包含大括号:
{Fireball\{Special\},56,100}Name为Fireball{Special},Level为56,ID为100。
- 数据中包含逗号:
总结
- 数据填充必须与类成员个数一致,空值用空字符占位。
- 数据填充顺序必须与 Proto 编码顺序一致,否则会导致数据错乱。
- 特殊字符需要转义,使用
\进行标记。
通过遵循以上规则,可以确保数据填充的准确性和一致性,避免因数据错乱导致的转换错误。