1、概述
spring retry是spring框架的一个模块,它提供了重新调用失败操作的功能。
2、使用场景
远程调用和网络通信:由于网络不稳定或服务不可用,可能会出现连接问题。
数据库交互:执行SQL查询或更新操作时,数据库服务器可能会出现临时性的问题,如死锁或连接丢失。
外部依赖:如果你的应用程序依赖于外部服务、硬件设备或其他不可控因素,而这些依赖可能会偶尔出现故障或不可用状态,那么Spring Retry可以帮助你处理这些情况,确保应用程序在某些情况下能够自动进行重试。
并发控制:在多线程环境中,可能会出现竞争条件或并发问题,导致某些操作失败。
复杂的业务逻辑:某些业务逻辑可能需要多次尝试才能成功
一般情况下,可重试的操作呈现出瞬时性故障,重试有意义。
3、使用方法
maven引入:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
<version>1.3.4</version>
</dependency>
启用spring retry
增加@EnableRetry到我们的@Configuration类。
@Configuration
@EnableRetry
public class AppConfig { ... }
使用spring retry
1、通过@Retryable进行重试
@Retryable
public void baseUse() {
System.out.println("基础使用。发生于" + System.currentTimeMillis());
throw new RuntimeException("基础使用业务方法出错了");
}
此方法将会执行3次,且执行间隔为1秒钟。
Retryable注解(v1.3.4)详解:
maxAttempts:最大尝试次数(包括第一次失败),默认为 3
maxAttemptsExpression:一个表达式,用于计算最大尝试次数(包括第一次失败),默认为 3,可以覆盖 maxAttempts()。
value:可重试的异常类型。与 includes() 同义。默认为空(如果 excludes 也为空,则会重试所有异常)。
include:同义于value
exclude:不可重试的异常类型。默认为空(如果 includes 也为空,则会重试所有异常)。如果 includes 为空但 excludes 不为空,则会重试所有未被排除的异常。
backoff:指定重试此操作的退避属性。
recover:用于恢复的类中方法的名称。该方法必须标记有 @Recover。
interceptor:应用于可重试方法的拦截器的 bean 名称。配置了它,其他属性将失效。
label:当steteful为true时,标记着为有状态的重试,这个为state的key值。
stateful:表示重试是否具有状态:即异常被重新抛出,但重试策略会应用于具有相同参数的后续调用。如果为 false,则不会重新抛出可重试的异常。
exceptionExpression:指定在 {@code SimpleRetryPolicy.canRetry()} 返回 true 后评估的表达式 - 可用于有条件地抑制重试。仅在抛出异常后调用。用于评估的根对象是最后一个 {@code Throwable}。可以引用上下文中的其他 bean。例如:{@code "message.contains('you can retry this')"}和 {@code"@someBean.shouldRetry(#root)"}
Backoff注解(v1.3.4)详解:
value:延迟时间(毫秒),默认为 1000。当delay不为零时,忽略此元素的值
delay:延迟时间。在指数情况下用作初始值,并在均匀情况下用作最小值。当此元素的值为 0 时,采用value() 的值,否则采用此元素的值。
maxDelay:重试之间的最大等待时间(毫秒)。如果小于 delay(),则应用默认值ExponentialBackOffPolicy. DEFAULT_MAX_INTERVAL(30000)。
multiplier:如果为正数,将用作生成下一个退避延迟的乘数。默认为0,表示忽略。
delayExpression:计算延迟时间的表达式,在指数情况下用作初始值,并在均匀情况下用作最小值。
maxDelayExpression:计算maxDelay的表达式。
multiplierExpression:计算下一个乘数的表达式。
random:当multiplier>0,并且设置该值为true,使退避延迟随机化。以便最大延迟是前一个延迟的 multiplier 倍,分布在两个值之间是均匀的
randomExpression:计算random的表达式。
通常是一个SpEL(Spring Expression Language)表达式,你可以在其中引用方法参数、返回值等。
2、@Recover 注解
定义了一个单独的恢复方法,当 @Retryable 方法因为指定的异常而失败时会调用该恢复方法。
@Recover
public void recover(Throwable throwable) {
System.err.println(Utils.getStackTrace(throwable));
}
// 打印业务异常信息
3、使用RetryTemplate
需要先注入RetryTemplate Bean
@Bean
public RetryTemplate retryTemplate() {
RetryTemplate retryTemplate = new RetryTemplate();
// 退避策略
FixedBackOffPolicy fixedBackOffPolicy = new FixedBackOffPolicy();
fixedBackOffPolicy.setBackOffPeriod(2000L);
retryTemplate.setBackOffPolicy(fixedBackOffPolicy);
// 重试策略
SimpleRetryPolicy retryPolicy = new SimpleRetryPolicy();
retryPolicy.setMaxAttempts(2);
retryTemplate.setRetryPolicy(retryPolicy);
return retryTemplate;
}
简单调用:
retryTemplate.execute(new RetryCallback<Object, Throwable>() {
@Override
public Object doWithRetry(RetryContext context) throws Throwable {
// 业务逻辑
springRetryService.templateRetry();
return "成功";
}
});
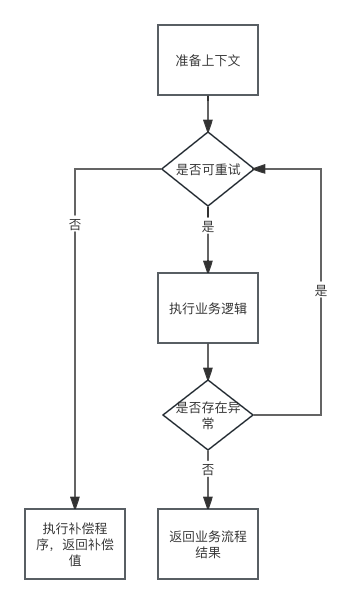
4、原理
核心逻辑流程图
模块:
RetryTemplate(重试模板):RetryTemplate 是 Spring Retry 的核心组件之一,它封装了重试的逻辑。它提供了一组 execute() 方法,允许您执行带有重试逻辑的方法。RetryTemplate 可以配置不同的重试策略、退避策略和监听器。
RetryPolicy(重试策略):RetryPolicy 决定了是否应该重试方法。Spring Retry 提供了不同的 RetryPolicy 实现,例如 SimpleRetryPolicy(固定次数重试)、ExponentialBackOffPolicy(指数退避重试)等。您可以根据需求选择合适的策略。
BackOffPolicy(退避策略):BackOffPolicy 控制重试尝试之间的退避(等待)时间。Spring Retry 提供了不同的 BackOffPolicy 实现,包括 FixedBackOffPolicy(固定等待时间)、ExponentialBackOffPolicy(指数退避)等。
RetryListener(重试监听器):RetryListener 接口定义了在重试期间的回调方法,包括在重试之前、重试之后以及每次不成功的尝试之后。可以在重试过程中进行增强操作。
RetryContext(重试上下文):RetryContext 是用于在重试过程中传递信息的上下文对象。它可以包含有关重试次数、异常信息等的信息。例如:RetryContextSupport包含父类上下文、中止标志、重试次数、上次异常信息。辅助RetryPolicy判断是否应该重试。
BackOffContext(退避上下文):管理和跟踪在重试操作中应用的回退(backoff)策略的上下文信息。回退策略通常用于控制在重试尝试之间的等待时间,以防止连续的重试操作过于频繁。
RetryCallback(重试回调):RetryCallback 是一个接口,允许您定义需要重试的业务逻辑。您可以在 RetryCallback 中编写方法的执行逻辑,并在其中捕获可能导致失败的异常。
RecoveryCallback(补偿措施回调):所有重试都失败后,执行的托底补偿措施。
1、RetryTemplate核心逻辑
RetryListener:监听器提供了在重试时额外的回调。在其中我们可以加入自己的处理逻辑。
它定义了三个方法:
public interface RetryListener {
/**
* 在重试的第一次尝试之前调用。false将会否决重试流程,也不会执行业务代码。
例如,实现者可以设置需要由 {@link RetryOperations} 中的策略所需的状态。通过从此方法返回 false,可以否决整个重试过程,在这种情况下将抛出 {@link TerminatedRetryException}。
* @param回调返回的对象类型
* @param它声明可能会抛出的异常类型
* @param context 当前的 {@link RetryContext}。
* @param callback 当前的 {@link RetryCallback}。
* @return 如果应继续重试,则为 true。
*/
boolean open(RetryContext context, RetryCallbackcallback);
/**
* 在最后一次尝试之后调用。允许拦截器在控制返回给重试调用者之前清理它所持有的任何资源。
* @param context 当前的 {@link RetryContext}。
* @param callback 当前的 {@link RetryCallback}。
* @param throwable 回调抛出的最后一个异常。
* @param异常类型
* @param返回值
*/
void close(RetryContext context, RetryCallbackcallback, Throwable throwable);
/**
* 在每次不成功的重试尝试之后调用。
* @param context 当前的 {@link RetryContext}。
* @param callback 当前的 {@link RetryCallback}。
* @param throwable 回调抛出的最后一个异常。
* @param返回值
* @param要抛出的异常
*/
void onError(RetryContext context, RetryCallbackcallback, Throwable throwable);
}
retrytemplate核心方法:
/**
* 如果策略允许,执行一次回调操作,否则执行恢复回调。
* @param recoveryCallback 恢复回调(RecoveryCallback)
* @param retryCallback 重试回调(RetryCallback)
* @param state 重试状态(RetryState)
* @param <T> 返回值的类型
* @param <E> 要抛出的异常类型
* @throws ExhaustedRetryException 如果重试已经耗尽。
* @throws E 如果重试操作失败,则抛出异常
* @return T 重试后的值
*/
protected <T, E extends Throwable> T doExecute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback,
RecoveryCallback<T> recoveryCallback, RetryState state) throws E, ExhaustedRetryException {
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = this.retryPolicy;
BackOffPolicy backOffPolicy = this.backOffPolicy;
// 无状态的:RetryPolicy初始化自己
// 有状态的:根据策略,每次新建/从缓存获取
RetryContext context = open(retryPolicy, state);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("RetryContext retrieved: " + context);
}
// 注册到threadlocal中,确保线程内全局可用
RetrySynchronizationManager.register(context);
Throwable lastException = null;
// 是否重试完
boolean exhausted = false;
try {
// 给客户端一个机会来增强上下文。调用注册的所有监听器,执行其open方法,
boolean running = doOpenInterceptors(retryCallback, context);
// 任意一个监听器open方法返回false,结果为false,抛出异常
if (!running) {
throw new TerminatedRetryException("Retry terminated abnormally by interceptor before first attempt");
}
// 获取或启动退避上下文
BackOffContext backOffContext = null;
Object resource = context.getAttribute("backOffContext");
if (resource instanceof BackOffContext) {
backOffContext = (BackOffContext) resource;
}
if (backOffContext == null) {
// 启用退避上下文
backOffContext = backOffPolicy.start(context);
if (backOffContext != null) {
context.setAttribute("backOffContext", backOffContext);
}
}
/*
* 是否可重试并且重试次数未耗尽。 业务逻辑可外部调用RetryContext.setExhaustedOnly进行干预
*/
while (canRetry(retryPolicy, context) && !context.isExhaustedOnly()) {
try {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Retry: count=" + context.getRetryCount());
}
// 重置上次异常,以便如果成功,关闭拦截器不会认为我们失败了...
lastException = null;
return retryCallback.doWithRetry(context);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
lastException = e;
try {
// 记录异常 RetryPolicy.registerThrowable,记录异常并增加重试次数
registerThrowable(retryPolicy, state, context, e);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new TerminatedRetryException("Could not register throwable", ex);
}
finally {
// 异常增强器 RetryListener.onError
doOnErrorInterceptors(retryCallback, context, e);
}
if (canRetry(retryPolicy, context) && !context.isExhaustedOnly()) {
try {
// 退避
backOffPolicy.backOff(backOffContext);
}
catch (BackOffInterruptedException ex) {
lastException = e;
// 被另一个线程阻止的退避 - 失败的重试
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Abort retry because interrupted: count=" + context.getRetryCount());
}
throw ex;
}
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Checking for rethrow: count=" + context.getRetryCount());
}
// 允许有状态的重试在此抛出异常,阻止重试
if (shouldRethrow(retryPolicy, context, state)) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Rethrow in retry for policy: count=" + context.getRetryCount());
}
throw RetryTemplate.<E>wrapIfNecessary(e);
}
}
/*
* 但是如果有状态的重试走到这一步可能终止,比如断路器或回滚分类器。
*/
if (state != null && context.hasAttribute(GLOBAL_STATE)) {
break;
}
}
if (state == null && this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Retry failed last attempt: count=" + context.getRetryCount());
}
exhausted = true;
// 重试完成且失败了,补偿措施 RecoveryCallback.recover
return handleRetryExhausted(recoveryCallback, context, state);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
throw RetryTemplate.<E>wrapIfNecessary(e);
}
finally {
// 资源回收
close(retryPolicy, context, state, lastException == null || exhausted);
doCloseInterceptors(retryCallback, context, lastException);
RetrySynchronizationManager.clear();
}
}2、RetryPolicy重试策略
重试策略类
描述
MaxAttemptsRetryPolicy
设置最大的重试次数,超过之后执行recover
BinaryExceptionClassifierRetryPolicy
可以指定哪些异常需要重试,哪些异常不需要重试
SimpleRetryPolicy
支持次数和自定义异常
TimeoutRetryPolicy
在一段时间内(可配置)重试
ExceptionClassifierRetryPolicy
支持异常和重试策略的映射,不同异常可以使用不同策略
CompositeRetryPolicy
策略类的组合类,支持两种模式,乐观模式:只要一个重试策略满足即执行,悲观模式:所有策略模式满足再执行
CircuitBreakerRetryPolicy
熔断器模式
ExpressionRetryPolicy
符合表达式就重试
AlwaysRetryPolicy
一直重试
NeverRetryPolicy
从不重试
3、BackOffPolicy退避策略
策略类
描述
FixedBackOffPolicy
间隔固定时间重试。直接Thread.sleep固定时间
NoBackOffPolicy
无等待,立马重试
UniformRandomBackOffPolicy
在一个设置的时间区间内。随机等待后重试
ExponentialBackOffPolicy
在一个设置的时间区间内,等待时长为上一次时长的递增
ExponentialRandomBackOffPolicy
乘数随机的ExponentialBackOffPolicy
4、RetryState有状态的重试
/**
* 根据state获取RetryContext上下文
*
*/
protected RetryContext open(RetryPolicy retryPolicy, RetryState state) {
if (state == null) {
// 无状态的重试,每次生成新的RetryContext
return doOpenInternal(retryPolicy);
}
Object key = state.getKey();
if (state.isForceRefresh()) {
// 有状态的测试,如果要求强制刷新,也会重新生成。
return doOpenInternal(retryPolicy, state);
}
// 如果没有缓存命中,我们可以避免缓存重新填充的可能费用。
if (!this.retryContextCache.containsKey(key)) {
// 只有在发生失败时才使用缓存。
return doOpenInternal(retryPolicy, state);
}
RetryContext context = this.retryContextCache.get(key);
if (context == null) {
if (this.retryContextCache.containsKey(key)) {
throw new RetryException("Inconsistent state for failed item: no history found. "
+ "Consider whether equals() or hashCode() for the item might be inconsistent, "
+ "or if you need to supply a better ItemKeyGenerator");
}
// 缓存在containsKey()调用之间可能已经过期,所以我们必须接受这一点。
// 因为如果不是全局的state,会在重试执行完毕后,销毁相关资源包括RetryContext上下文。
// 所以如果没从retryContextCache获取到上下文,还是得重新创建一个
return doOpenInternal(retryPolicy, state);
}
// 为其他可能检查状态的人开始一个干净的状态
context.removeAttribute(RetryContext.CLOSED);
context.removeAttribute(RetryContext.EXHAUSTED);
context.removeAttribute(RetryContext.RECOVERED);
return context;
}
有状态的重试允许你在不同的重试中共享相同的上下文,可以让你依赖先前的结果。
5、CircuitBreakerRetryPolicy断路器实现
CircuitBreakerRetryPolicy核心方法
public boolean canRetry(RetryContext context) {
CircuitBreakerRetryContext circuit = (CircuitBreakerRetryContext) context;
if (circuit.isOpen()) {
// 断路器处于打开状态,增加断路次数
circuit.incrementShortCircuitCount();
return false;
}
else {
circuit.reset();
}
// 交于实际策略类判断是否能重试
return this.delegate.canRetry(circuit.context);
}
// 断路器的retry上下文信息
static class CircuitBreakerRetryContext extends RetryContextSupport {
// 持有委托的重试策略的上下文信息
private volatile RetryContext context;
private final RetryPolicy policy;
// 断路器上下文启动的时间
private volatile long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 断路器的重置超时时间,即在断路器打开后,经过了这段时间后会自动尝试重新关闭断路器。
private final long timeout;
// 触发断路器打开的时间窗口。如果委托的重试策略无法进行重试,并且从上下文启动以来的时间少于这个时间窗口,那么断路器将被打开。
private final long openWindow;
// 断路器打开状态下的熔断次数
private final AtomicInteger shortCircuitCount = new AtomicInteger();
public CircuitBreakerRetryContext(RetryContext parent, RetryPolicy policy, long timeout, long openWindow) {
super(parent);
this.policy = policy;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.openWindow = openWindow;
this.context = createDelegateContext(policy, parent);
// 设置为全局可重试状态,重试完毕后,也不会回收上下文信息,会一直在缓存中
setAttribute("state.global", true);
}
public void reset() {
shortCircuitCount.set(0);
setAttribute(CIRCUIT_SHORT_COUNT, shortCircuitCount.get());
}
public void incrementShortCircuitCount() {
shortCircuitCount.incrementAndGet();
setAttribute(CIRCUIT_SHORT_COUNT, shortCircuitCount.get());
}
private RetryContext createDelegateContext(RetryPolicy policy, RetryContext parent) {
RetryContext context = policy.open(parent);
reset();
return context;
}
public boolean isOpen() {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - this.start;
boolean retryable = this.policy.canRetry(this.context);
if (!retryable) {
if (time > this.timeout) {
// 不可执行时间大于重置时间,重新生成上下文
logger.trace("Closing");
this.context = createDelegateContext(policy, getParent());
this.start = System.currentTimeMillis();
retryable = this.policy.canRetry(this.context);
}
else if (time < this.openWindow) {
if (!hasAttribute(CIRCUIT_OPEN) || (Boolean) getAttribute(CIRCUIT_OPEN) == false) {
// 不包含断路器打开标志,标记断路器打开,重置start时间。
// 时间间隔短,第一次熔断
logger.trace("Opening circuit");
setAttribute(CIRCUIT_OPEN, true);
this.start = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
return true;
}
}
else {
if (time > this.openWindow) {
// 大于窗口时间就重置
logger.trace("Resetting context");
this.start = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.context = createDelegateContext(policy, getParent());
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Open: " + !retryable);
}
setAttribute(CIRCUIT_OPEN, !retryable);
return !retryable;
}
@Override
public int getRetryCount() {
return this.context.getRetryCount();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.context.toString();
}
}6、@Retryable的实现原理
@EnableRetry中使用@Import(RetryConfiguration.class),引入RetryConfiguration配置类。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
this.retryContextCache = findBean(RetryContextCache.class);
this.methodArgumentsKeyGenerator = findBean(MethodArgumentsKeyGenerator.class);
this.newMethodArgumentsIdentifier = findBean(NewMethodArgumentsIdentifier.class);
this.retryListeners = findBeans(RetryListener.class);
this.sleeper = findBean(Sleeper.class);
Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> retryableAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<? extends Annotation>>(1);
retryableAnnotationTypes.add(Retryable.class);
this.pointcut = buildPointcut(retryableAnnotationTypes);
this.advice = buildAdvice();
if (this.advice instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) this.advice).setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
}
RetryConfiguration类设置切入点为@Retryable标记的方法,切面为AnnotationAwareRetryOperationsInterceptor。
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
MethodInterceptor delegate = getDelegate(invocation.getThis(), invocation.getMethod());
if (delegate != null) {
return delegate.invoke(invocation);
}
else {
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
private MethodInterceptor getDelegate(Object target, Method method) {
ConcurrentMap<Method, MethodInterceptor> cachedMethods = this.delegates.get(target);
if (cachedMethods == null) {
cachedMethods = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MethodInterceptor>();
}
MethodInterceptor delegate = cachedMethods.get(method);
if (delegate == null) {
MethodInterceptor interceptor = NULL_INTERCEPTOR;
Retryable retryable = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, Retryable.class);
if (retryable == null) {
retryable = classLevelAnnotation(method, Retryable.class);
}
if (retryable == null) {
retryable = findAnnotationOnTarget(target, method, Retryable.class);
}
if (retryable != null) {
// 如果注解自定义interceptor,则使用该interceptor
if (StringUtils.hasText(retryable.interceptor())) {
interceptor = this.beanFactory.getBean(retryable.interceptor(), MethodInterceptor.class);
}
// 如果是有状态的,使用StatefulRetryOperationsInterceptor
else if (retryable.stateful()) {
interceptor = getStatefulInterceptor(target, method, retryable);
}
else {
// 默认使用无状态,RetryOperationsInterceptor
interceptor = getStatelessInterceptor(target, method, retryable);
}
}
cachedMethods.putIfAbsent(method, interceptor);
delegate = cachedMethods.get(method);
}
this.delegates.putIfAbsent(target, cachedMethods);
return delegate == NULL_INTERCEPTOR ? null : delegate;
}执行业务方法时,被AnnotationAwareRetryOperationsInterceptor,根据注解配置,获取到对应的
MethodInterceptor。
如果注解自定义interceptor,则使用该interceptor
如果是有状态的,使用StatefulRetryOperationsInterceptor
默认使用无状态,RetryOperationsInterceptor
RetryOperationsInterceptor和StatefulRetryOperationsInterceptor持有委托对象retryOperations(是RetryTemplate),实际方法执行委托给RetryTemplate执行。
spring retry分为三大模块,主要是RetryPolicy、BackOffPolicy、RecoveryCallback,大家如果需要扩展也主要从这三块着手,RetryListener也在一定程度上让用户增强自己的业务逻辑