day55
事务
MySQL:每一条语句都属于独立事务,默认自动管理提交的。
如果需要把多条语句当成一个整体,那么就需要把多条语句放在一个事务里面
开启事务:start transaction
提交事务:commit;
回滚事务:rollback
封装事务
JDBC操作事务1
1.模拟银行用户转账,就是对数控库账户的操作【最开始是两个事务,事务是默认自动管理提交】
会出现问题:当在两个事务之间加一个错误,就会出现脏数据【一个账务减了钱,另一个账户没有加钱】,还有项目崩掉也可能出现
- 将加减钱放在一个事务里面,也要考虑同一个连接对象的问题【连接对象的共享】;
public class Test01 {
/**
* 知识点:数据库知识点的梳理
* 1.数据库概念(数据库服务器、数据库、数据表、字段、数据行)
* 2.使用SQL(DDL、DML、DCL)
* 3.深入SQL(数据类型、约束、索引、视图、触发器、存储过程、函数)
* 4.JDBC(使用Java语法操作数据库的技术,Connection、Statement、ResultSet)
* 5.SQL注入
* 6.封装DBUtil - v1.0(使用配置文件 - DBConfig.properties)
* 7.封装DBUtil - v2.0(更新方法、主键回填方法、查询方法)
* 8.事务
* 9.封装DBUtil - v3.0(封装事务)
* 10.批处理
* 11.CBLob - 了解
* 12.自定义连接池
* 13.Druid连接池
* 14.封装DBUtil - v3.0(封装连接池)
*
* 知识点:使用JDBC操作事务
* 需求:模拟银行用户转账
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = nu
PreparedStatement statement1 = null;
PreparedStatement statement2 = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql1 = "UPDATE bank SET money=money-200 WHERE id=1;";
statement1 = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
statement1.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(10/0);
String sql2 = "UPDATE bank SET money=money+200 WHERE id=2;";
statement2 = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
statement2.executeUpdate();
//提交事务
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚事务
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null,statement2,null);
DBUtil.close(connection,statement1,null);
}
}
}
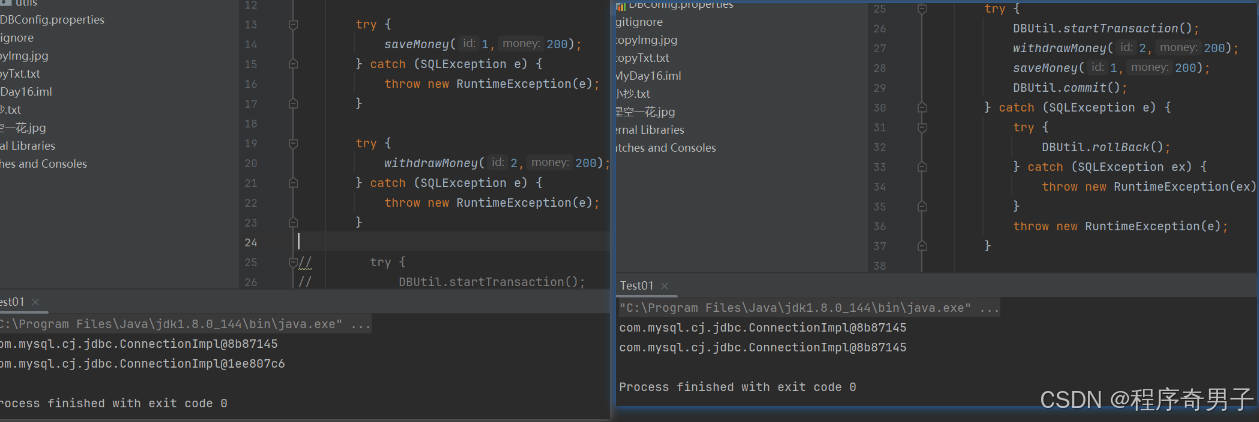
JDBC操作事务2
对操作1中代码升级
这里设计存钱和取钱的方法时,改用抛出异常,让调用方去处理
public class Test01 {
/**
* 知识点:使用JDBC操作事务
* 需求:模拟银行用户转账
* 程序设计的要求:
* 设计存钱和取钱的方法
* public static void saveMoney(int id,float money) -- 存钱
* public static void withdrawMoney(int id,float money) -- 取钱
* 单独调用存钱和取钱的方法
* 联合调用存钱和取钱的方法 -- 转账
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// //场景一:单独调用存钱和取钱的方法
// try {
// saveMoney(1,200);
// } catch (SQLException e) {
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
// }
//
// try {
// withdrawMoney(2,300);
// } catch (SQLException e) {
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
// }
//场景二:转账
try {
DBUtil.startTransaction();
withdrawMoney(1,200);
//System.out.println(10/0);
saveMoney(2,200);
DBUtil.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
DBUtil.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
public static void withdrawMoney(int id,float money) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
String sql = "update bank set money=money-? where id=?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setFloat(1,money);
statement.setInt(2,id);
statement.executeUpdate();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
public static void saveMoney(int id,float money) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
String sql = "update bank set money=money+? where id=?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setFloat(1,money);
statement.setInt(2,id);
statement.executeUpdate();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
}
连接对象比较:
封装DBUtil
单独调用存钱和取钱的方法【不同得连接对象】
联合调用存钱和取钱的方法 – 转账【同一个连接对象】
考虑模拟转账的问题对连接对象和事务的处理:
利用线程得局部共享变量local,将new得连接对象connection存起来,又封装了事务控制,connection.getAutoCommit()进行判断是否把连接对象处理,而实现对连接对象的控制【注意setAutoCommit()和getAutoCommit()】
/**
* 数据库工具类
*/
public class DBUtil {
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> local;
static{
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(DBUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("DBConfig.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
String driverName = properties.getProperty("driverName");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
try {
Class.forName(driverName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
local = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
/**
* 获取连接对象
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = local.get();//获取当前线程的Connection对象
if(connection == null){
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
local.set(connection);//将Connection对象添加到local中
}
return connection;
}
/**
* 关闭资源
*/
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet){
if(resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(statement != null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
if(connection.getAutoCommit()){
connection.close();
local.set(null);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 开启事务
*/
public static void startTransaction() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
}
/**
* 提交事务
*/
public static void commit() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = local.get();
if(connection != null){
connection.commit();
connection.close();
local.set(null);
}
}
public static void rollback() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = local.get();
if(connection != null){
connection.rollback();
connection.close();
local.set(null);
}
}
/**
* 更新数据(添加、删除、修改)
*/
public static int commonUpdate(String sql,Object... params) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
paramHandler(statement,params);
int num = statement.executeUpdate();
return num;
}finally {
close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
/**
* 添加数据 - 主键回填(主键是int类型可以返回)
*/
public static int commonInsert(String sql,Object... params) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql,PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
paramHandler(statement,params);
statement.executeUpdate();
resultSet = statement.getGeneratedKeys();
int primaryKey = 0;
if(resultSet.next()){
primaryKey = resultSet.getInt(1);
}
return primaryKey;
}finally {
close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
/**
* 查询多个数据
*/
public static <T> List<T> commonQueryList(Class<T> clazz,String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
paramHandler(statement,params);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//获取表数据对象
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//获取字段个数
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(resultSet.next()){
T t = clazz.newInstance();
//获取字段名及数据
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
String fieldName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
Object fieldVal = resultSet.getObject(fieldName);
setField(t,fieldName,fieldVal);
}
list.add(t);
}
return list;
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
/**
* 查询单个数据
*/
public static <T> T commonQueryObj(Class<T> clazz,String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
paramHandler(statement,params);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//获取表数据对象
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//获取字段个数
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
if(resultSet.next()){
T t = clazz.newInstance();
//获取字段名及数据
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
String fieldName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
Object fieldVal = resultSet.getObject(fieldName);
setField(t,fieldName,fieldVal);
}
return t;
}
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 处理statement对象参数数据的处理器
*/
private static void paramHandler(PreparedStatement statement,Object... params) throws SQLException {
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
statement.setObject(i+1,params[i]);
}
}
/**
* 获取当前类及其父类的属性对象
* @param clazz class对象
* @param name 属性名
* @return 属性对象
*/
private static Field getField(Class<?> clazz,String name){
for(Class<?> c = clazz;c != null;c = c.getSuperclass()){
try {
Field field = c.getDeclaredField(name);
return field;
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
} catch (SecurityException e) {
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 设置对象中的属性
* @param obj 对象
* @param name 属性名
* @param value 属性值
*/
private static void setField(Object obj,String name,Object value){
Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), name);
if(field != null){
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(obj, value);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
事务的特点
事务的特性:ACID
原子性( Atomicity )、一致性( Consistency )、隔离性( Isolation )和持久性( Durability )
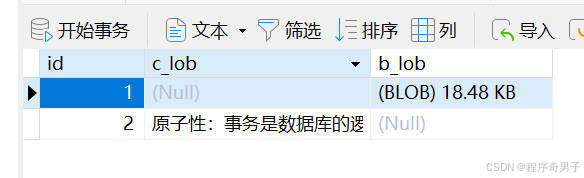
原子性:
事务是数据库的逻辑工作单位,事务中包含的各操作要么都完成,要么都不完成
一致性:
事务执行的结果必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。因此当数据库只包含成功事务提交的结果时,就说数据库处于一致性状态。如果数据库系统 运行中发生故障,有些事务尚未完成就被迫中断,这些未完成事务对数据库所做的修改有一部分已写入物理数据库,这时数据库就处于一种不正确的状态,或者说是 不一致的状态。
隔离性:
一个事务的执行不能其它事务干扰。即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对其它并发事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
持久性:
指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中的数据的改变就应该是永久性的。接下来的其它操作或故障不应该对其执行结果有任何影响。
事务的隔离级别:
属于事务的。都已开启了事务为前提。不考虑事务的隔离级别,会出现以下的情况
脏读:一个线程中的事务读到了另外一个线程中未提交的数据。
不可重复读:一个线程中的事务读到了另外一个线程中已经提交的update的数据。
l虚读:一个线程中的事务读到了另外一个线程中已经提交的insert的数据。
要想避免以上现象,通过更改事务的隔离级别来避免:
READ UNCOMMITTED(读未提交): 脏读、不可重复读、虚读有可能发生。
READ COMMITTED(读已提交): 避免脏读的发生,不可重复读、虚读有可能发生。
REPEATABLE READ(可重复读) :避免脏读、不可重复读的发生,虚读有可能发生。
SERIALIZABLE(可串行化): 避免脏读、不可重复读、虚读的发生。
级别依次升高,效率依次降低。
MySQL:默认REPEATABLE READ
ORACLE:默认READ COMMITTED
做实验
1.开两个黑窗口
2.登录数据库:mysql -u root -p
3:使用需要操作的指定数据库:use 数据库名
4:设置不同的隔离级别:
黑窗口对照设置同一隔离级别
set transaction isolation level SERIALIZABLE;
5.启动事务:start transaction;
- 就可对数据库进行操作,在相应情况进行查询,体会隔离级别不同;
7.提交 commit;
批处理 — 批量处理sql语句
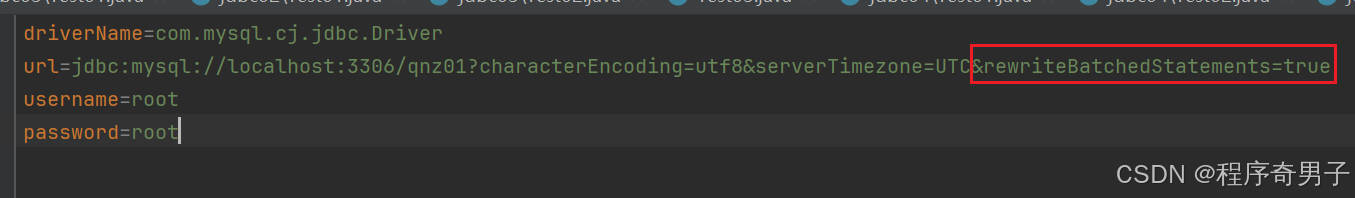
添加参数
在jdbc的url中添加rewriteBatchedStatements=true参数,不然
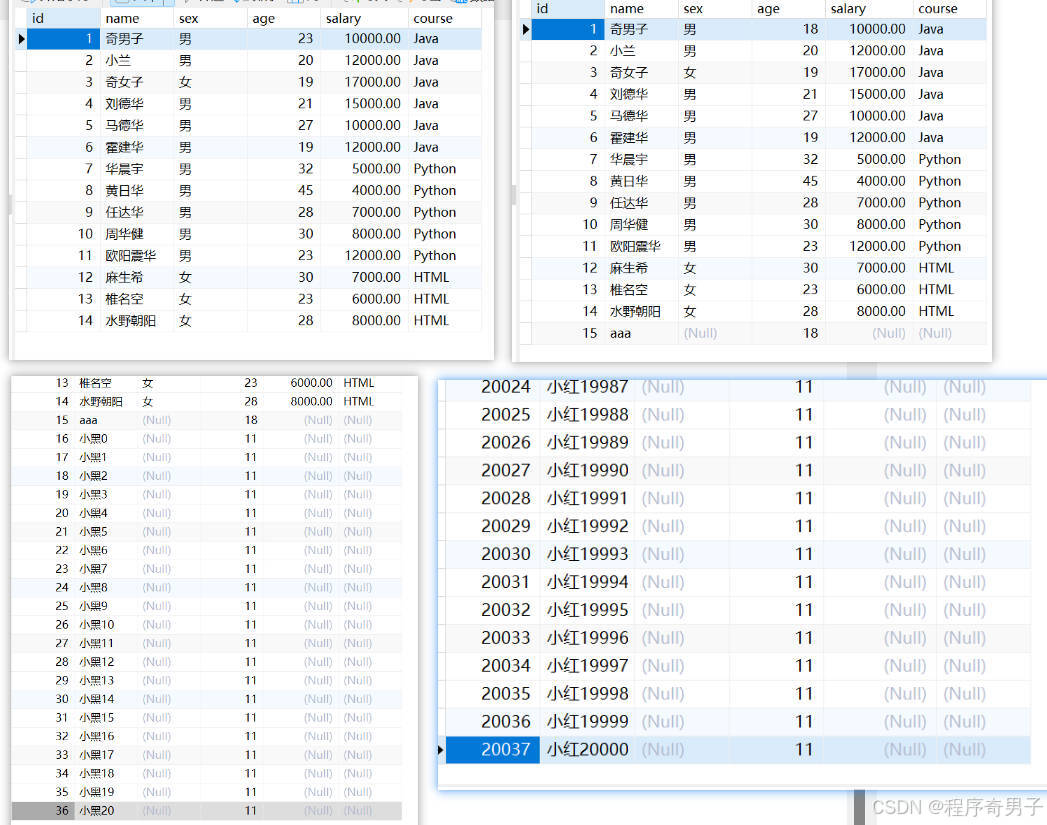
运行图
1.多条SQL命令不一样的情况
public class Test01 {
/**
* 知识点:批处理
* 理解:批量处理数据
* 原理:将多条SQL命令添加到Batch包中,JDBC将Batch包发送给数据库管理系统,数据库管理系统再做批量操作
* 注意:URL添加上rewriteBatchedStatements=true,否则会数据库驱动无视Batch包
*
* 场景一:多条SQL命令不一样的情况
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//将多条sql命令添加到Batch包中
String sql1 = "insert into student(name,course_id,class_id,age) values('ccc',1,3,20)";
String sql2 = "update student set age=19 where id=2";
statement.addBatch(sql1);
statement.addBatch(sql2);
//发送Batch包
statement.executeBatch();
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
2.多条SQL命令一样但参数不一样的情况
public class Test02 {
/**
* 知识点:批处理
* 理解:批量处理数据
* 原理:将多条SQL命令添加到Batch包中,JDBC将Batch包发送给数据库管理系统,数据库管理系统再做批量操作
* 注意:URL添加上rewriteBatchedStatements=true,否则会数据库驱动无视Batch包
*
* 场景二:多条SQL命令一样但参数不一样的情况
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into student(name,course_id,class_id,age) values(?,1,3,20)";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
statement.setString(1,"小黑"+i);
statement.addBatch();
}
statement.executeBatch();
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
3.分批发送+预处理
public class Test03 {
/**
* 知识点:批处理
* 理解:批量处理数据
* 原理:将多条SQL命令添加到Batch包中,JDBC将Batch包发送给数据库管理系统,数据库管理系统再做批量操作
* 注意:URL添加上rewriteBatchedStatements=true,否则会数据库驱动无视Batch包
*
* 场景三:多条SQL命令一样但参数不一样的情况 -- 大量数据
* 经验:
* 1.分批次发送Batch包 -- 减少数据库压力
* 2.使用事务 ---------- 让数据库预处理
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "insert into student(name,course_id,class_id,age) values(?,1,3,20)";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 1; i <= 20000; i++) {
statement.setString(1,"小红"+i);
statement.addBatch();
if(i%1000 == 0){
statement.executeBatch();
statement.clearBatch();//清空Batch包中的数据
}
}
connection.commit();
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
CBLOB
回顾数据库
经验: 在项目中不会把文件写入到数据库中(因为写入到数据库中,数据库的压力会很大),在项目中如果要存储文件,可以将文件的地址写入到数据库中
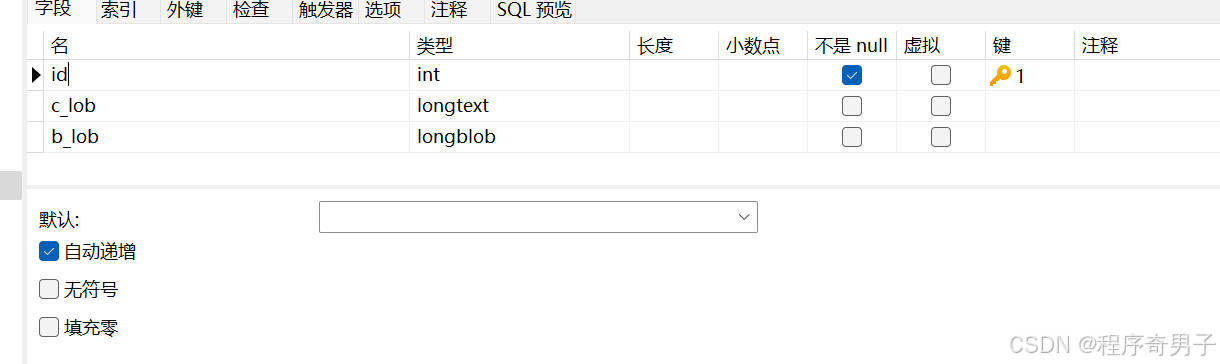
数据库建表
插入数据库
从数据库读取出来
blob
public class Test01 {
/**
* 知识点:CBLob
*
* 理解:
* JDBC可以向数据库存储二进制数据或长文本数据
* BLob - Binary(二进制)Lob - 存储二进制数据 - 注意:数据库字段类型 - BLOB/LONGBLOB
* CLob - Character(字符)Lob - 存储长文本数据 - 注意:数据库字段类型 - TEXT/LONGTEXT
*
* 经验:
* 了解CBLob的技术
* 在项目中不会把文件写入到数据库中(因为写入到数据库中,数据库的压力会很大)
* 在项目中如果要存储文件,可以将文件的地址写入到数据库中
*/
@Test
public void test01() throws SQLException, FileNotFoundException {
//将图片插入到数据库中
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into cblob(b_lob) values (?)";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("星空一花.jpg");
statement.setBinaryStream(1,in);
statement.executeUpdate();
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
@Test
public void test02() throws SQLException, IOException {
//将数据库中的图片读取到本地
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from cblob where id=1";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()){
InputStream in = resultSet.getBinaryStream("b_lob");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("copyImg.jpg");
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = in.read(bs)) != -1){
out.write(bs,0,len);
}
in.close();
out.close();
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
clob
public class Test02 {
@Test
public void test01() throws SQLException, FileNotFoundException {
//将长文本数据插入到数据库中
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into cblob(c_lob) values (?)";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
FileReader reader = new FileReader("小抄.txt");
statement.setCharacterStream(1,reader);
statement.executeUpdate();
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
@Test
public void test02() throws SQLException, IOException {
//将数据库中的长文本数据读取到本地
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from cblob where id=2";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()){
Reader reader = resultSet.getCharacterStream("c_lob");
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("copyText.txt");
char[] cs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = reader.read(cs)) != -1){
writer.write(cs,0,len);
}
reader.close();
writer.close();
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}