SSD
1.SSD网络模型
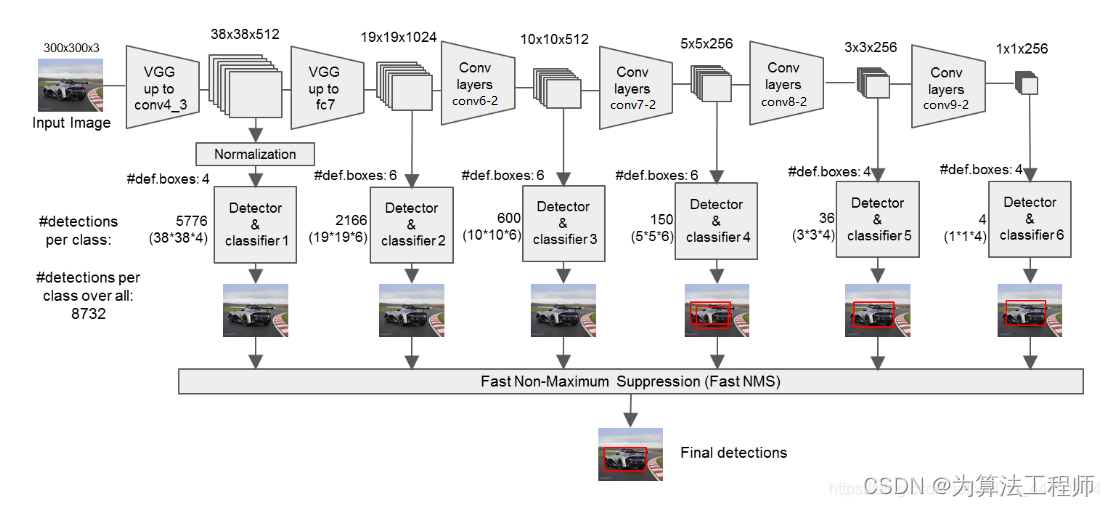
SSD全称为Single Shot MultiBox Detector,一种one-stage目标检测模型,其网络结构图为:
1. SSD模型的主干网络采用VGG网络模块,并进行一些改进:
- 将VGG16的FC6层和FC7层转变为卷积层(原用于分类)
- 去除所有的Dropout层的FC8层
- 新增加Conv6层、Conv7层、Conv8层、Conv9层
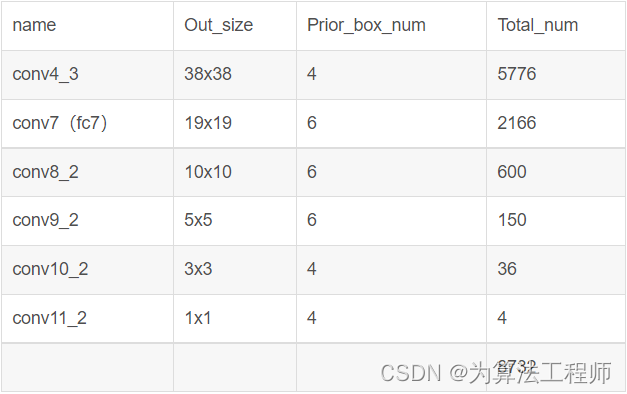
2. SSD模型采用的特征图为:(与图中编号有差别)
- Conv4的第三次卷积的特征:3838512
- Conv7卷积的特征:19191024
- Conv8的第二次卷积的特征:1010512
- Conv9的第二次卷积的特征:55256
- Conv10的第二次卷积的特征:33256
- Conv11的第二次卷积的特征:11256
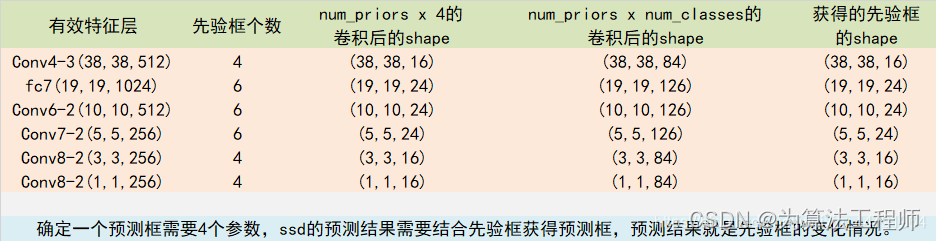
SSD模型采用的有效特征层共6个,用于进行检测框的预测和目标分类。对每个有效特征层进行如下的操作:一次num_anchors x 4的卷积和一次num_anchors x num_classes的卷积。
num_classes为数据集总的类别数加上背景类别。
num_anchors为该特征层每一个特征点所拥有的先验框的数量。对于上述的六个特征层来说,每个特征层中的每个特征点对应的先验框数量为{4,6,6,6,4,4}。
那么有:所有的特征层对应的预测结果的shape如下
并且每个特征层的先验框(box)的数量及总量为:
SSD模型的实现代码为:
class SSD300(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, base, backbone_name, pretrained=False):
super(SSD300, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.base = base
self.backbone_name = backbone_name
if self.backbone_name == 'vgg':
print('using vgg backbone')
self.vgg = vgg(self.base, pretrained)
self.extras = add_extras(1024, self.backbone_name)
self.L2Norm = L2Norm(512, 20)
mbox = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4]
loc_layers = []
conf_layers = []
backbone_source = [21, -1]
"""
在SSD中vgg网络模块获得的特征层里
第21层和第33层可以用于进行回归预测和分类预测
分别是conv4-3和conv7的输出
"""
for k, v in enumerate(backbone_source):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(self.vgg[v].out_channels, mbox[k] * 4,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(self.vgg[v].out_channels,
mbox[k] * num_classes,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
"""
在SSD中add_extras网络模块的特征层中
第1层、第三层、第五层、第七层可以用于进行回归预测和分类预测
其大小分别为(10, 10, 512)、(5, 5, 256)、(3, 3, 256)、(1, 1, 256)
"""
for k, v in enumerate(self.extras[1::2], 2):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels,
mbox[k] * 4,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels,
mbox[k] * num_classes,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
else:
print('using mobilenetv2 backbone')
self.mobilenet = mobilenet_v2(pretrained).features
self.extras = add_extras(1280, self.backbone_name)
self.L2Norm = L2Norm(96, 20)
mbox = [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]
loc_layers = []
conf_layers = []
backbone_source = [13, -1]
for k, v in enumerate(backbone_source):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(self.mobilenet[v].out_channels,
mbox[k] * 4,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(self.mobilenet[v].out_channels,
mbox[k] * num_classes,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
for k, v in enumerate(self.extras, 2):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels,
mbox[k] * 4,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels,
mbox[k] * num_classes,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=1)]
self.loc = nn.ModuleList(loc_layers)
self.conf = nn.ModuleList(conf_layers)
def forward(self, x):
# ---------------------------#
# x是300,300,3
# ---------------------------#
sources = list()
loc = list()
conf = list()
# ---------------------------#
# 获得conv4_3的内容
# shape为38,38,512
# ---------------------------#
if self.backbone_name == "vgg":
for k in range(23):
x = self.vgg[k](x)
else:
for k in range(14):
x = self.mobilenet[k](x)
# ---------------------------#
# conv4_3的内容
# 需要进行L2标准化
# ---------------------------#
s = self.L2Norm(x)
sources.append(s)
# ---------------------------#
# 获得conv7的内容
# shape为19,19,1024
# ---------------------------#
if self.backbone_name == "vgg":
for k in range(23, len(self.vgg)):
x = self.vgg[k](x)
else:
for k in range(14, len(self.mobilenet)):
x = self.mobilenet[k](x)
sources.append(x)
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
# 在add_extras获得的特征层里
# 第1层、第3层、第5层、第7层可以用来进行回归预测和分类预测。
# shape分别为(10,10,512), (5,5,256), (3,3,256), (1,1,256)
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
for k, v in enumerate(self.extras):
x = F.relu(v(x), inplace=True)
if self.backbone_name == "vgg":
if k % 2 == 1:
sources.append(x)
else:
sources.append(x)
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
# 为获得的6个有效特征层添加回归预测和分类预测
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
for (x, l, c) in zip(sources, self.loc, self.conf):
loc.append(l(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())
conf.append(c(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
# 进行reshape方便堆叠
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
loc = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in loc], 1)
conf = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in conf], 1)
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
# loc会reshape到batch_size, num_anchors, 4
# conf会reshap到batch_size, num_anchors, self.num_classes
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
output = (
loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4),
conf.view(conf.size(0), -1, self.num_classes),
)
return output
VGG网络实现:
base = [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'C', 512, 512, 512, 'M',
512, 512, 512]
def vgg(pretrained=False):
layers = []
in_channels = 3
for v in base:
if v == 'M':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
elif v == 'C':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=1)
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
in_channels = v
# 19, 19, 512 -> 19, 19, 512
pool5 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
# 19, 19, 512 -> 19, 19, 1024
conv6 = nn.Conv2d(512, 1024, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=6, dilation=(6, 6))
# 19, 19, 1024 -> 19, 19, 1024
conv7 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1))
layers += [pool5, conv6,
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), conv7, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
model = nn.ModuleList(layers)
if pretrained:
state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url("https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg16-397923af.pth",
model_dir="./model_data")
state_dict = {k.replace('features.', ''): v for k, v in state_dict.items()}
model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
return model
扩展网络模块实现:
def add_extras(in_channels, backbone_name):
layers = []
if backbone_name == 'vgg':
# Block 6
# 19,19,1024 -> 19,19,256 -> 10,10,512
layers += [nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=1)]
# Block 7
# 10,10,512 -> 10,10,128 -> 5,5,256
layers += [nn.Conv2d(512, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=1)]
# Block 8
# 5,5,256 -> 5,5,128 -> 3,3,256
layers += [nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))]
# Block 9
# 3,3,256 -> 3,3,128 -> 1,1,256
layers += [nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))]
layers += [nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))]
else:
layers += [InvertedResidual(in_channels, 512, stride=2, expand_ratio=0.2)]
layers += [InvertedResidual(512, 256, stride=2, expand_ratio=0.25)]
layers += [InvertedResidual(256, 256, stride=2, expand_ratio=0.5)]
layers += [InvertedResidual(256, 64, stride=2, expand_ratio=0.25)]
return nn.ModuleList(layers)
2. 先验框的准备(default box//Prior box)
Prior box是指实际训练中用于训练的Default box,即Default box是一种概念,Prior box则是实际的选取。
训练过程中,当一张图片送入模型后获得各个特征层(feature map),那么对于正样本来说,需要先将prior box与ground truth box进行匹配,若匹配则该prior box包含某个真实目标,但距离完整目标的ground truth box还存在差距,而训练的目的就是保证default box的分类confidence的同时将prior box尽可能回归到ground truth box。
Defalut box生成规则:
对于每个特征层(feature map)上的每个特征点,将其中点作为中心,生成一系列同心的default box。此外,中心点的坐标会乘以step,相当于从feature map位置映射回原图位置。特征层的default box数量与aspect_ratios有关。
SSD模型:
# 先验框的长边比例
# [1, 2] -> [1, 1, 2, 1/2]
# [1, 2, 3] -> [1, 1, 2, 1/2, 3, 1/3]
aspect_ratios = [[1, 2], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2], [1, 2]]
对于每个特征层来说,根据其对应的aspect_ratio,会有两个正方形及不等的长方形。
规定default box的边长为anchors_size = [30, 60, 111, 162, 213, 264, 315]
对于6中特征层,会有6中不同的[min_size, max_size]的组合。
那么, default box边长的计算方式为:
- 小正方形的边长为: m i n _ s i z e min\_size min_size
- 大正方形的边长为: m i n _ s i z e × m a x _ s i z e \sqrt{min\_size \times max\_size} min_size×max_size
- 长方形默认框的height为: 1 a s p e c t _ r a t i o × m i n _ s i z e \frac{1}{\sqrt{aspect\_ratio}} \times min\_size aspect_ratio1×min_size
- 长方形默认框的height为: a s p e c t _ r a t i o × m i n _ s i z e \sqrt{aspect\_ratio} \times min\_size aspect_ratio×min_size
对于default box的[min_size, max_size],是由如下的方式计算而来的。
#coding:utf-8
import math
min_dim = 300 #######维度
# conv4_3 ==> 38 x 38
# fc7 ==> 19 x 19
# conv6_2 ==> 10 x 10
# conv7_2 ==> 5 x 5
# conv8_2 ==> 3 x 3
# conv9_2 ==> 1 x 1
mbox_source_layers = ['conv4_3', 'fc7', 'conv6_2', 'conv7_2', 'conv8_2', 'conv9_2'] #####prior_box来源层,可以更改。很多改进都是基于此处的调整。
# in percent %
min_ratio = 20 ####这里即是论文中所说的Smin=0.2,Smax=0.9的初始值,经过下面的运算即可得到min_sizes,max_sizes。具体如何计算以及两者代表什么,请关注我的博客SSD详解。这里产生很多改进。
max_ratio = 90
##math.floor()函数表示:求一个最接近它的整数,它的值小于或等于这个浮点数。
step = int(math.floor((max_ratio - min_ratio) / (len(mbox_source_layers) - 2)))####取一个间距步长,即在下面for循环给ratio取值时起一个间距作用。可以用一个具体的数值代替,这里等于17。
print('step:',step)
min_sizes = [] ###经过以下运算得到min_sizes和max_sizes。
max_sizes = []
for ratio in range(min_ratio, max_ratio + 1, step): ####从min_ratio至max_ratio+1每隔step=17取一个值赋值给ratio。注意xrange函数的作用。
#####min_sizes.append()函数即把括号内部每次得到的值依次给了min_sizes。
min_sizes.append(min_dim * ratio / 100.)
print(min_sizes)
max_sizes.append(min_dim * (ratio + step) / 100.)
min_sizes = [min_dim * 10 / 100.] + min_sizes ## 在min_sizes前拼接上30
max_sizes = [min_dim * 20 / 100.] + max_sizes
###steps即计算卷积层产生的prior_box距离原图的步长,先验框中心点的坐标会乘以step,相当于从feature map位置映射回原图位置,
###比如conv4_3输出特征图大小为38*38,而输入的图片为300*300,所以38*8约等于300,所以映射步长为8。这是针对300*300的训练图片。
steps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
aspect_ratios = [[2], [2, 3], [2, 3], [2, 3], [2], [2]]
print('min_sizes:',min_sizes)
print('max_sizes:',max_sizes)
那么,先验框的准备为:
class AnchorBox:
def __init__(self, input_shape, min_size, max_size=None, aspect_ratios=None):
# 获取输入图片的大小, 300*300
self.input_shape = input_shape
# 先验框的短边
self.min_size = min_size
# 先验框的长边
self.max_size = max_size
# 先验框的长边比例
# [1, 2] -> [1, 1, 2, 1/2]
# [1, 2, 3] -> [1, 1, 2, 1/2, 3, 1/3]
self.aspect_ratios = []
for ar in aspect_ratios:
self.aspect_ratios.append(ar)
self.aspect_ratios.append(1.0 / ar)
def call(self, layer_shape):
# 获取输入特征层的宽和高, 比如38*38
layer_height = layer_shape[0]
layer_width = layer_shape[1]
# 获取输入图片的宽和高
img_height = self.input_shape[0]
img_width = self.input_shape[1]
box_widths, box_heights = [], []
# self.aspect_ratios一般有两个值:[1, 1, 2, 1/2];[1, 1, 2, 1/2, 3, 1/3]
for ar in self.aspect_ratios:
# 首先添加较小的正方形
if ar == 1 and len(box_widths) == 0:
box_widths.append(self.min_size)
box_heights.append(self.min_size)
# 然后添加较大的正方形
elif ar == 1 and len(box_widths) > 0:
box_widths.append(np.sqrt(self.min_size * self.max_size))
box_heights.append(np.sqrt(self.min_size * self.max_size))
# 添加长方形
elif ar != 1:
box_widths.append(self.min_size * np.sqrt(ar))
box_heights.append(self.min_size / np.sqrt(ar))
# 获取所有先验框的1/2的宽高
box_widths = 0.5 * np.array(box_widths)
box_heights = 0.5 * np.array(box_heights)
# 获取每一个特征层对应的步长
step_x = img_width / layer_width
step_y = img_height / layer_height
# 生成网格中心,并构建网络
# --------------------------------------------------- #
linx = np.linspace(0.5 * step_x, img_width - 0.5 * step_x, layer_width)
liny = np.linspace(0.5 * step_y, img_height - 0.5 * step_y, layer_height)
centers_x, centers_y = np.meshgrid(linx, liny)
centers_x = centers_x.reshape(-1, 1)
centers_y = centers_y.reshape(-1, 1)
# 每一个先验框需要两个(centers_x, centers_y),前一个用于计算左上角,后一个用于计算右下角
num_anchors = len(self.aspect_ratios)
anchor_boxes = np.concatenate((centers_x, centers_y), axis=1)
anchor_boxes = np.tile(anchor_boxes, (1, 2 * num_anchors))
# 获得先验框的左上角和右下角
anchor_boxes[:, ::4] -= box_widths
anchor_boxes[:, 1::4] -= box_heights
anchor_boxes[:, 2::4] += box_widths
anchor_boxes[:, 3::4] += box_heights
# 将先验框变成小数形式,同时进行归一化
# --------------------------------------------------- #
anchor_boxes[:, ::2] /= img_width
anchor_boxes[:, 1::2] /= img_height
anchor_boxes = anchor_boxes.reshape(-1, 4)
anchor_boxes = np.minimum(np.maximum(anchor_boxes, 0.0), 1.0)
return anchor_boxes
3. VOC格式数据集的准备
首先,VOC图片数据集的存放方式为:
|-VOCdevkit
|---VOC2007
|-----Annotations
|-----ImageSets
|-----JPEGImages
其中,Annotations存放每张图片的XML文件,XML文件中图片的object信息表示这张图片所对应的目标检测框位置及其类别名称,每个图片可能会包含多个object。difficult表示识别难度。
XML文件包含的信息为:
<annotation>
<folder>VOC2007</folder>
<filename>000003.jpg</filename>
<source>
<database>The VOC2007 Database</database>
<annotation>PASCAL VOC2007</annotation>
<image>flickr</image>
<flickrid>138563409</flickrid>
</source>
<owner>
<flickrid>RandomEvent101</flickrid>
<name>?</name>
</owner>
<size>
<width>500</width>
<height>375</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>sofa</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>123</xmin>
<ymin>155</ymin>
<xmax>215</xmax>
<ymax>195</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>chair</name>
<pose>Left</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>239</xmin>
<ymin>156</ymin>
<xmax>307</xmax>
<ymax>205</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
ImageSets的Main文件则是存放划分的训练集、验证集、测试集的文件索引信息文件,每个索引对应着图片的文件名称。
JPEGImages则用于存放原始图片。
数据集的准备工作是生成用于训练的.txt文件,该文件每行对应一张图片,且包含了图片的图片路径及其目标框的位置、类别,如:
./data/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/000005.jpg 263,324,211,339,8 165,253,264,372,8 241,295,194,299,8
./data/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/000007.jpg 141,500,50,330,6
用于生成的代码为:
import os
import random
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from utils.utils import get_classes
def convert_annotation(voc_devkit_path, year, image_id, list_file, classes):
file_path = os.path.join(voc_devkit_path, 'VOC%s/Annotations/%s.xml' % (year, image_id))
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
tree = ET.parse(f)
root = tree.getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = 0
if obj.find('difficult') is not None:
difficult = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or difficult == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xml_box = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xml_box.find('xmin').text), float(xml_box.find('xmax').text),
float(xml_box.find('ymin').text), float(xml_box.find('ymax').text))
list_file.write(' ' + ','.join([str(int(a)) for a in b]) + ',' + str(cls_id))
if __name__ == '__main__':
random.seed(0)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# annotation_mode用于指定该文件运行时计算的内容
# annotation_mode为0代表整个标签处理过程,包括获得VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets里面的txt以及训练用的2007_train.txt、2007_val.txt
# annotation_mode为1代表获得VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets里面的txt
# annotation_mode为2代表获得训练用的2007_train.txt、2007_val.txt
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
annotation_mode = 2
# -------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 必须要修改,用于生成2007_train.txt、2007_val.txt的目标信息
# 与训练和预测所用的classes_path一致即可
# 如果生成的2007_train.txt里面没有目标信息, 那么就是因为classes没有设定正确
# 仅在annotation_mode为0和2的时候有效
# -------------------------------------------------------------------#
classes_path = "data/voc_classes.txt"
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# trainval_percent用于指定(训练集+验证集)与测试集的比例,默认情况下 (训练集+验证集):测试集 = 9:1
# train_percent用于指定(训练集+验证集)中训练集与验证集的比例,默认情况下 训练集:验证集 = 9:1
# 仅在annotation_mode为0和1的时候有效
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
trainval_percent = 0.9
train_percent = 0.9
# -------------------------------------------------------#
# 指向VOC数据集所在的文件夹
# 默认指向根目录下的VOC数据集
# -------------------------------------------------------#
voc_devkit_path = "./data/VOCdevkit"
VOCdevkit_sets = [('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val')]
classes, classes_num = get_classes(classes_path)
if annotation_mode == 0 or annotation_mode == 1:
print("Generate txt in ImageSets...")
xml_file_path = os.path.join(voc_devkit_path, 'VOC2007/Annotations')
save_base_path = os.path.join(voc_devkit_path, 'VOC2007/ImageSets/Main')
temp_xml = os.listdir(xml_file_path)
total_xml = []
for xml in temp_xml:
if xml.endswith('.xml'):
total_xml.append(xml)
num = len(total_xml)
list_ = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
print("train and val size: ", tv)
print("train size: ", tr)
ftrainval = open(os.path.join(save_base_path, 'trainval.txt'), 'w')
ftest = open(os.path.join(save_base_path, 'test.txt'), 'w')
ftrain = open(os.path.join(save_base_path, 'train.txt'), 'w')
fval = open(os.path.join(save_base_path, 'val.txt'), 'w')
for i in list_:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
print("Generate txt in ImageSets done!")
if annotation_mode == 0 or annotation_mode == 2:
print("Generate 2007_train.txt and 2007_val.txt for model training...")
for year, data_name in VOCdevkit_sets:
images_id_path = os.path.join(voc_devkit_path, 'VOC' + year, 'ImageSets', 'Main', data_name + '.txt')
with open(images_id_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
image_ids = f.read().strip().split()
with open('./data/%s_%s.txt' % (year, data_name), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for image_id in image_ids:
f.write('%s/VOC%s/JPEGImages/%s.jpg' % (voc_devkit_path, year, image_id))
convert_annotation(voc_devkit_path, year, image_id, f, classes)
f.write('\n')
print("Generate 2007_train.txt and 2007_val.txt for model training done!")
4. 模型训练
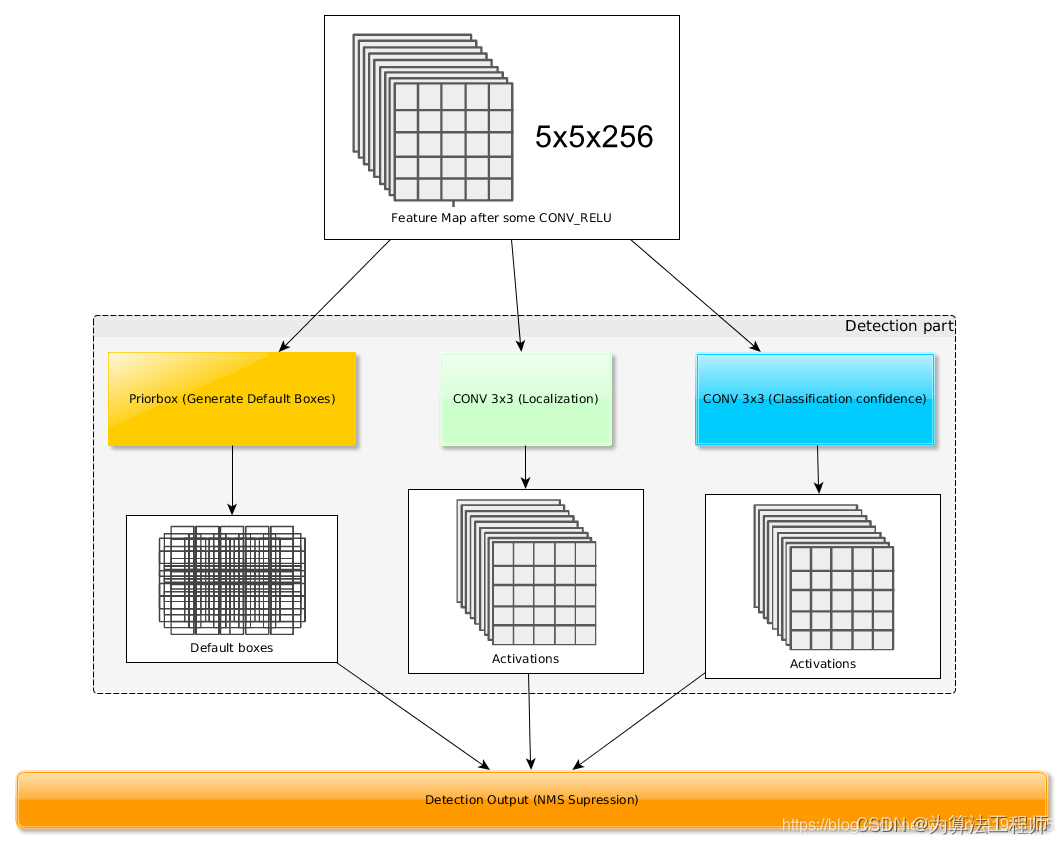
4.1 模型如何从特征中获取预测结果
SSD模型采用的有效特征层共6个,首先针对每个特征图中的每个特征点预设default boxes,具体为:mbox_sizes = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4],分别对应feature_map = [Conv4_3, Conv7, Conv8_2 , Conv9_2, Conv10_2 , Conv11_2],同时feature_map的尺寸分别为feature_map_shape = [38*38, 19*19, 10*10, 5*5, 3*3, 1*1],可以计算出总的default boxes数量为8732。
对于一张图片来说,其包含的目标可能有多个,因此需要判断出哪些预设的default boxes是否包含目标,以及判断出目标的类别(分类);对于真实包含目标的default boxes,需要对其进行调整来获得最终的预测框(回归预测)。因此,对这六个有效特征图的输出进行两个3*3的卷积计算,分别用于回归预测和分类预测。
- 对于分类预测:数据集的类别数为
num_classes,对于特征图K,其卷积后输出为mbox_size[k]*num_classes - 对于回归预测:每个框是由中心点
(
x
,
y
)
(x, y)
(x,y)和宽高
(
w
,
h
)
(w,h)
(w,h)决定的,因此,对于特征图K,其卷积后的输出为
mbox[k]*4
# feature_map = [Conv4_3, Conv7, Conv8_2 , Conv9_2, Conv10_2 , Conv11_2]
for k, v in enumerate(backbone_source):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(self.vgg[v].out_channels, mbox[k] * 4, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(self.vgg[v].out_channels, mbox[k] * num_classes, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=1)]
for k, v in enumerate(self.extras[1::2], 2):
loc_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels, mbox[k] * 4, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=1)]
conf_layers += [nn.Conv2d(v.out_channels, mbox[k] * num_classes, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding=1)]
loc = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in loc], 1)
conf = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in conf], 1)
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
# loc会reshape到batch_size, num_anchors, 4
# conf会reshap到batch_size, num_anchors, self.num_classes
# -------------------------------------------------------------#
output = (loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4), conf.view(conf.size(0), -1, self.num_classes),)
4.2 ground truth box(gt box)与default boxes的匹配
SSD模型首先针对每个特征层会生成许多default boxes,但我们需要对其进行筛选,从而匹配出与gt box相对应的Prior box,以便用于训练。
简单来说:首先获得图片的回归预测结果以及分类置信度(概率);其次,针对每一张图片进行解码,获取预测框的真实框的情况;然后针对每一类别,取出大于阈值的对应框,并利用非极大抑制筛选出较好的结果;最终将label、置信度、框的位置进行堆叠并返回result。
class BBoxUtility(object):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
self.num_classes = num_classes
def ssd_correct_boxes(self, box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image):
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 把y轴放前面是因为方便预测框和图像的宽高进行相乘
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
input_shape = np.array(input_shape)
image_shape = np.array(image_shape)
if letterbox_image:
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 这里求出来的offset是图像有效区域相对于图像左上角的偏移情况
# new_shape指的是宽高缩放情况
# -----------------------------------------------------------------#
new_shape = np.round(image_shape * np.min(input_shape / image_shape))
offset = (input_shape - new_shape) / 2. / input_shape
scale = input_shape / new_shape
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
box_hw *= scale
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
boxes = np.concatenate([box_mins[..., 0:1], box_mins[..., 1:2], box_maxes[..., 0:1], box_maxes[..., 1:2]],
axis=-1)
boxes *= np.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape], axis=-1)
return boxes
def decode_boxes(self, mbox_loc, anchors, variances):
# 获得先验框的宽与高
anchor_width = anchors[:, 2] - anchors[:, 0]
anchor_height = anchors[:, 3] - anchors[:, 1]
# 获得先验框的中心点
anchor_center_x = 0.5 * (anchors[:, 2] + anchors[:, 0])
anchor_center_y = 0.5 * (anchors[:, 3] + anchors[:, 1])
# 真实框距离先验框中心的xy轴偏移情况
decode_bbox_center_x = mbox_loc[:, 0] * anchor_width * variances[0]
decode_bbox_center_x += anchor_center_x
decode_bbox_center_y = mbox_loc[:, 1] * anchor_height * variances[0]
decode_bbox_center_y += anchor_center_y
# 真实框的宽与高的求取
decode_bbox_width = torch.exp(mbox_loc[:, 2] * variances[1])
decode_bbox_width *= anchor_width
decode_bbox_height = torch.exp(mbox_loc[:, 3] * variances[1])
decode_bbox_height *= anchor_height
# 获取真实框的左上角与右下角
decode_bbox_xmin = decode_bbox_center_x - 0.5 * decode_bbox_width
decode_bbox_ymin = decode_bbox_center_y - 0.5 * decode_bbox_height
decode_bbox_xmax = decode_bbox_center_x + 0.5 * decode_bbox_width
decode_bbox_ymax = decode_bbox_center_y + 0.5 * decode_bbox_height
# 真实框的左上角与右下角进行堆叠
decode_bbox = torch.cat((decode_bbox_xmin[:, None],
decode_bbox_ymin[:, None],
decode_bbox_xmax[:, None],
decode_bbox_ymax[:, None]), dim=-1)
# 防止超出0与1
decode_bbox = torch.min(torch.max(decode_bbox, torch.zeros_like(decode_bbox)), torch.ones_like(decode_bbox))
return decode_bbox
def decode_box(self, predictions, anchors, image_shape, input_shape, letterbox_image, variances=[0.1, 0.2],
nms_iou=0.3, confidence=0.5):
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# :4是回归预测结果
# ---------------------------------------------------#
mbox_loc = predictions[0]
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得种类的置信度
# ---------------------------------------------------#
mbox_conf = nn.Softmax(-1)(predictions[1])
results = []
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 对每一张图片进行处理,由于在predict.py的时候,我们只输入一张图片,所以for i in range(len(mbox_loc))只进行一次
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
for i in range(len(mbox_loc)):
results.append([])
# --------------------------------#
# 利用回归结果对先验框进行解码
# --------------------------------#
decode_bbox = self.decode_boxes(mbox_loc[i], anchors, variances)
for c in range(1, self.num_classes):
# --------------------------------#
# 取出属于该类的所有框的置信度
# 判断是否大于门限
# --------------------------------#
c_confs = mbox_conf[i, :, c]
c_confs_m = c_confs > confidence
if len(c_confs[c_confs_m]) > 0:
# -----------------------------------------#
# 取出得分高于confidence的框
# -----------------------------------------#
boxes_to_process = decode_bbox[c_confs_m]
confs_to_process = c_confs[c_confs_m]
keep = nms(
boxes_to_process,
confs_to_process,
nms_iou
)
# -----------------------------------------#
# 取出在非极大抑制中效果较好的内容
# -----------------------------------------#
good_boxes = boxes_to_process[keep]
confs = confs_to_process[keep][:, None]
labels = (c - 1) * torch.ones((len(keep), 1)).cuda() if confs.is_cuda else (c - 1) * torch.ones(
(len(keep), 1))
# -----------------------------------------#
# 将label、置信度、框的位置进行堆叠。
# -----------------------------------------#
c_pred = torch.cat((good_boxes, labels, confs), dim=1).cpu().numpy()
# 添加进result里
results[-1].extend(c_pred)
if len(results[-1]) > 0:
results[-1] = np.array(results[-1])
box_xy, box_wh = (results[-1][:, 0:2] + results[-1][:, 2:4]) / 2, results[-1][:, 2:4] - results[-1][:,
0:2]
results[-1][:, :4] = self.ssd_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image)
return results
4.3 损失函数
SSD模型针对包含多个的目标的图片进行处理,其损失函数包括两部分:置信度损失和位置损失,计算方式为:
L
(
x
,
c
,
l
,
g
)
=
1
N
[
L
c
o
n
f
(
x
,
c
)
+
α
L
l
o
c
(
x
,
l
,
g
)
]
L(x, c , l, g) = \frac{1}{N} [L_{conf}(x, c) + \alpha L_{loc}(x, l, g)]
L(x,c,l,g)=N1[Lconf(x,c)+αLloc(x,l,g)]
其中:
- c, l, g 分别表示为类别置信度预测值、预测框和真实框的参数(宽高和中心位置)
- N表示正样本的数量
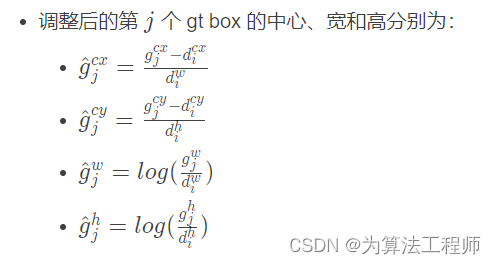
- x表示一个示性函数,即 x i j p = { 1 , 0 } x^{p}_{ij} = \{1, 0\} xijp={1,0},1表示第 i i i个default box和类别为 p p p的第 j j j的gt box相匹配;0表示未匹配。
- L c o n f L_{conf} Lconf和 L l o c L_{loc} Lloc分别表示置信度损失和位置损失。
位置损失采用
s
m
o
o
t
h
L
1
smooth_{L1}
smoothL1 Loss,该损失是计算需要回归至default bounding box 的中心及宽度、高度的偏移量,其计算方式为:
L
c
o
n
f
(
x
,
l
,
g
)
=
∑
i
∈
P
o
s
i
t
i
v
e
N
∑
m
∈
{
c
x
,
c
y
,
w
,
h
}
x
i
j
k
s
m
o
o
t
h
L
1
(
l
i
m
−
g
^
j
m
)
L_{conf} (x, l, g) = \sum^{N}_{i \in Positive} \sum_{m \in \{cx, cy, w, h\}} x^k_{ij} smooth_{L1}(l^m_{i} - \hat{g}^m_j)
Lconf(x,l,g)=i∈Positive∑Nm∈{cx,cy,w,h}∑xijksmoothL1(lim−g^jm)
由于
x
i
j
p
=
{
1
,
0
}
x^{p}_{ij} = \{1, 0\}
xijp={1,0}, 位置损失只针对正样本来进行计算,其中:
-
l
i
m
l_i^m
lim,
g
^
i
m
\hat{g}^m_i
g^im分别表示第
i
i
i个预测框
l
l
l和调整的第
j
j
j个gt box 的中心、宽和高。
置信度损失采用多个类别上的softmax损失:
L c o n f = − ∑ i ∈ P o s i t i v e N x i j p l o g ( c ^ i p ) − ∑ i ∈ N e g a t i v e l o g ( c ^ i 0 ) , c ^ i p = e x p ( c i p ) ∑ p e x p ( c i p ) L_{conf} = - \sum^{N}_{i \in Positive} x^{p}_{ij} log(\hat{c}^{p}_{i}) - \sum_{i \in Negative} log(\hat{c}^{0}_{i}), \quad \hat{c}_{i}^{p} = \frac{exp(c^p_{i})}{\sum_p exp(c^p_i)} Lconf=−i∈Positive∑Nxijplog(c^ip)−i∈Negative∑log(c^i0),c^ip=∑pexp(cip)exp(cip)
其中, c ^ i p \hat{c}_{i}^{p} c^ip表示的在 p p p类别中,第 i i i个default box 的置信度, p = 0 p = 0 p=0是背景。
class MultiboxLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, alpha=1.0, neg_pos_ratio=3.0,
background_label_id=0, negatives_for_hard=100.0):
super(MultiboxLoss, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.alpha = alpha
self.neg_pos_ratio = neg_pos_ratio
if background_label_id != 0:
raise Exception('Only 0 as background label id is supported')
self.background_label_id = background_label_id
self.negatives_for_hard = torch.FloatTensor([negatives_for_hard])[0]
def _l1_smooth_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
abs_loss = torch.abs(y_true - y_pred)
sq_loss = 0.5 * (y_true - y_pred) ** 2
l1_loss = torch.where(abs_loss < 1.0, sq_loss, abs_loss - 0.5)
return torch.sum(l1_loss, -1)
def _softmax_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
y_pred = torch.clamp(y_pred, min=1e-7)
softmax_loss = -torch.sum(y_true * torch.log(y_pred),
axis=-1)
return softmax_loss
def forward(self, y_true, y_pred):
# --------------------------------------------- #
# y_true batch_size, 8732, 4 + self.num_classes + 1
# y_pred batch_size, 8732, 4 + self.num_classes
# --------------------------------------------- #
num_boxes = y_true.size()[1]
y_pred = torch.cat([y_pred[0], nn.Softmax(-1)(y_pred[1])], dim=-1)
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 分类的loss
# batch_size,8732,21 -> batch_size,8732
# --------------------------------------------- #
conf_loss = self._softmax_loss(y_true[:, :, 4:-1], y_pred[:, :, 4:])
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 框的位置的loss
# batch_size,8732,4 -> batch_size,8732
# --------------------------------------------- #
loc_loss = self._l1_smooth_loss(y_true[:, :, :4],
y_pred[:, :, :4])
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 获取所有的正标签的loss
# --------------------------------------------- #
pos_loc_loss = torch.sum(loc_loss * y_true[:, :, -1],
axis=1)
pos_conf_loss = torch.sum(conf_loss * y_true[:, :, -1],
axis=1)
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 每一张图的正样本的个数
# num_pos [batch_size,]
# --------------------------------------------- #
num_pos = torch.sum(y_true[:, :, -1], axis=-1)
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 每一张图的负样本的个数
# num_neg [batch_size,]
# --------------------------------------------- #
num_neg = torch.min(self.neg_pos_ratio * num_pos, num_boxes - num_pos)
# 找到了哪些值是大于0的
pos_num_neg_mask = num_neg > 0
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 如果所有的图,正样本的数量均为0
# 那么则默认选取100个先验框作为负样本
# --------------------------------------------- #
has_min = torch.sum(pos_num_neg_mask)
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 从这里往后,与视频中看到的代码有些许不同。
# 由于以前的负样本选取方式存在一些问题,
# 我对该部分代码进行重构。
# 求整个batch应该的负样本数量总和
# --------------------------------------------- #
num_neg_batch = torch.sum(num_neg) if has_min > 0 else self.negatives_for_hard
# --------------------------------------------- #
# 对预测结果进行判断,如果该先验框没有包含物体
# 那么它的不属于背景的预测概率过大的话
# 就是难分类样本
# --------------------------------------------- #
confs_start = 4 + self.background_label_id + 1
confs_end = confs_start + self.num_classes - 1
# --------------------------------------------- #
# batch_size,8732
# 把不是背景的概率求和,求和后的概率越大
# 代表越难分类。
# --------------------------------------------- #
max_confs = torch.sum(y_pred[:, :, confs_start:confs_end], dim=2)
# --------------------------------------------------- #
# 只有没有包含物体的先验框才得到保留
# 我们在整个batch里面选取最难分类的num_neg_batch个
# 先验框作为负样本。
# --------------------------------------------------- #
max_confs = (max_confs * (1 - y_true[:, :, -1])).view([-1])
_, indices = torch.topk(max_confs, k=int(num_neg_batch.cpu().numpy().tolist()))
neg_conf_loss = torch.gather(conf_loss.view([-1]), 0, indices)
# 进行归一化
num_pos = torch.where(num_pos != 0, num_pos, torch.ones_like(num_pos))
total_loss = torch.sum(pos_conf_loss) + torch.sum(neg_conf_loss) + torch.sum(self.alpha * pos_loc_loss)
total_loss = total_loss / torch.sum(num_pos)
return total_loss
4.4 模型训练
- 获取数据集类别名称及数目、预设先验框、模型(使用预训练权重的情况下进行预训练权重初始化)、损失函数
class_names, num_classes = get_classes(classes_path)
num_classes += 1 # 含背景类别
anchors = get_anchors(input_shape, anchors_size, backbone)
model = SSD300(num_classes, backbone, pretrained)
# 不使用预训练权重时,随机初始化模型
if not pretrained:
weights_init(model)
# 使用SSD模型预训练权重或只使用VGG主干网络权重
if model_path != '':
print('Load weights {}.'.format(model_path))
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model_dict = model.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
pretrained_dict = {k: v for k, v in pretrained_dict.items() if np.shape(model_dict[k]) == np.shape(v)}
model_dict.update(pretrained_dict)
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
criterion = MultiboxLoss(num_classes, neg_pos_ratio=3.0)
- 读取数据集(生成的train2007.txt和val2007.txt)
with open(train_annotation_path, encoding='utf-8') as f:
train_lines = f.readlines()
with open(val_annotation_path, encoding='utf-8') as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
num_train = len(train_lines)
num_val = len(val_lines)
train_dataset = SSDDataset(train_lines, input_shape, anchors, batch_size, num_classes, train=True)
val_dataset = SSDDataset(val_lines, input_shape, anchors, batch_size, num_classes, train=False)
gen = DataLoader(train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=ssd_dataset_collate)
gen_val = DataLoader(val_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=ssd_dataset_collate)
- 优化器设置
nbs = 64
lr_limit_max = 1e-3 if optimizer_type == 'sgd' else 5e-2
lr_limit_min = 3e-4 if optimizer_type == 'adam' else 5e-5
Init_lr_fit = min(max(batch_size / nbs * Init_lr, lr_limit_min), lr_limit_max)
Min_lr_fit = min(max(batch_size / nbs * Min_lr, lr_limit_min * 1e-2), lr_limit_max * 1e-2)
# 根据optimizer_type选择优化器
optimizer = {'adam': optim.Adam(model.parameters(), Init_lr_fit, betas=(momentum, 0.999), weight_decay=weight_decay),
'sgd': optim.SGD(model.parameters(), Init_lr_fit, momentum=momentum, nesterov=True,
weight_decay=weight_decay)}[optimizer_type]
# 获得学习率下降的公式
lr_scheduler_func = get_lr_scheduler(lr_decay_type, Init_lr_fit, Min_lr_fit, UnFreeze_Epoch)
- 开始训练
for epoch in range(Init_Epoch, UnFreeze_Epoch):
# 如果模型有冻结学习部分
# 则解冻,并设置参数
# ---------------------------------------#
if epoch >= Freeze_Epoch and not UnFreeze_flag and Freeze_Train:
batch_size = Unfreeze_batch_size
# 判断当前batch_size,自适应调整学习率
nbs = 64
lr_limit_max = 1e-3 if optimizer_type == 'adam' else 5e-2
lr_limit_min = 3e-4 if optimizer_type == 'adam' else 5e-5
Init_lr_fit = min(max(batch_size / nbs * Init_lr, lr_limit_min), lr_limit_max)
Min_lr_fit = min(max(batch_size / nbs * Min_lr, lr_limit_min * 1e-2), lr_limit_max * 1e-2)
# 获得学习率下降的公式
lr_scheduler_func = get_lr_scheduler(lr_decay_type, Init_lr_fit, Min_lr_fit, UnFreeze_Epoch)
if backbone == "vgg":
for param in model.vgg[:28].parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
else:
for param in model.mobilenet.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
epoch_step = num_train // batch_size
epoch_step_val = num_val // batch_size
if epoch_step == 0 or epoch_step_val == 0:
raise ValueError("数据集过小,无法继续进行训练,请扩充数据集。")
gen = DataLoader(train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers,
pin_memory=True,drop_last=True, collate_fn=ssd_dataset_collate)
gen_val = DataLoader(val_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers,
pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=ssd_dataset_collate)
UnFreeze_flag = True
set_optimizer_lr(optimizer, lr_scheduler_func, epoch)
fit_one_epoch(model_train, model, criterion, loss_history, optimizer, epoch,
epoch_step, epoch_step_val, gen, gen_val, UnFreeze_Epoch, Cuda, fp16, scaler, save_period,
save_dir)
5. 测试,获取mAP
针对测试集进行测试,获取mAP.
if __name__ == "__main__":
'''
Recall和Precision不像AP是一个面积的概念,在门限值不同时,网络的Recall和Precision值是不同的。
map计算结果中的Recall和Precision代表的是当预测时,门限置信度为0.5时,所对应的Recall和Precision值。
此处获得的./map_out/detection-results/里面的txt的框的数量会比直接predict多一些,这是因为这里的门限低,
目的是为了计算不同门限条件下的Recall和Precision值,从而实现map的计算。
'''
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# map_mode用于指定该文件运行时计算的内容
# map_mode为0代表整个map计算流程,包括获得预测结果、获得真实框、计算VOC_map。
# map_mode为1代表仅仅获得预测结果。
# map_mode为2代表仅仅获得真实框。
# map_mode为3代表仅仅计算VOC_map。
# map_mode为4代表利用COCO工具箱计算当前数据集的0.50:0.95map。需要获得预测结果、获得真实框后并安装pycocotools才行
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
map_mode = 0
# -------------------------------------------------------#
# 此处的classes_path用于指定需要测量VOC_map的类别
# 一般情况下与训练和预测所用的classes_path一致即可
# -------------------------------------------------------#
classes_path = './data/voc_classes.txt'
# -------------------------------------------------------#
# MINOVERLAP用于指定想要获得的mAP0.x
# 比如计算mAP0.75,可以设定MINOVERLAP = 0.75。
# -------------------------------------------------------#
MINOVERLAP = 0.5
# -------------------------------------------------------#
# map_vis用于指定是否开启VOC_map计算的可视化
# -------------------------------------------------------#
map_vis = False
# -------------------------------------------------------#
# 指向VOC数据集所在的文件夹
# 默认指向根目录下的VOC数据集
# -------------------------------------------------------#
VOCdevkit_path = './data/VOCdevkit'
# -------------------------------------------------------#
# 结果输出的文件夹,默认为map_out
# -------------------------------------------------------#
map_out_path = 'map_out'
image_ids = open(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt")).read().strip().split()
if not os.path.exists(map_out_path):
os.makedirs(map_out_path)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional'))
class_names, _ = get_classes(classes_path)
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 1:
print("Load model.")
ssd = SSD(confidence=0.01, nms_iou=0.5)
print("Load model done.")
print("Get predict result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
image_path = os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/JPEGImages/" + image_id + ".jpg")
image = Image.open(image_path)
if map_vis:
image.save(os.path.join(map_out_path, "images-optional/" + image_id + ".jpg"))
ssd.get_map_txt(image_id, image, class_names, map_out_path)
print("Get predict result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 2:
print("Get ground truth result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
with open(os.path.join(map_out_path, "ground-truth/" + image_id + ".txt"), "w") as new_f:
root = ET.parse(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/Annotations/" + image_id + ".xml")).getroot()
for obj in root.findall('object'):
difficult_flag = False
if obj.find('difficult') != None:
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
if int(difficult) == 1:
difficult_flag = True
obj_name = obj.find('name').text
if obj_name not in class_names:
continue
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
left = bndbox.find('xmin').text
top = bndbox.find('ymin').text
right = bndbox.find('xmax').text
bottom = bndbox.find('ymax').text
if difficult_flag:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s difficult\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
else:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
print("Get ground truth result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 3:
print("Get map.")
get_map(MINOVERLAP, True, path=map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")
if map_mode == 4:
print("Get map.")
get_coco_map(class_names=class_names, path=map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")
6 图片预测和FPS测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
ssd = SSD()
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# mode用于指定测试的模式:
# 'predict'表示单张图片预测,如果想对预测过程进行修改,如保存图片,截取对象等,可以先看下方详细的注释
# 'video'表示视频检测,可调用摄像头或者视频进行检测,详情查看下方注释。
# 'fps'表示测试fps,使用的图片是img里面的street.jpg,详情查看下方注释。
# 'dir_predict'表示遍历文件夹进行检测并保存。默认遍历img文件夹,保存img_out文件夹,详情查看下方注释。
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
mode = "predict"
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# crop指定了是否在单张图片预测后对目标进行截取
# crop仅在mode='predict'时有效
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------#
crop = False
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# video_path用于指定视频的路径,当video_path=0时表示检测摄像头
# 想要检测视频,则设置如video_path = "xxx.mp4"即可,代表读取出根目录下的xxx.mp4文件。
# video_save_path表示视频保存的路径,当video_save_path=""时表示不保存
# 想要保存视频,则设置如video_save_path = "yyy.mp4"即可,代表保存为根目录下的yyy.mp4文件。
# video_fps用于保存的视频的fps
# video_path、video_save_path和video_fps仅在mode='video'时有效
# 保存视频时需要ctrl+c退出或者运行到最后一帧才会完成完整的保存步骤。
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
video_path = 0
video_save_path = ""
video_fps = 25.0
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# test_interval用于指定测量fps的时候,图片检测的次数
# 理论上test_interval越大,fps越准确。
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------#
test_interval = 100
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# dir_origin_path指定了用于检测的图片的文件夹路径
# dir_save_path指定了检测完图片的保存路径
# dir_origin_path和dir_save_path仅在mode='dir_predict'时有效
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------#
dir_origin_path = "img/"
dir_save_path = "img_out/"
if mode == "predict":
'''
1、该代码无法直接进行批量预测,如果想要批量预测,可以利用os.listdir()遍历文件夹,利用Image.open打开图片文件进行预测。
具体流程可以参考get_dr_txt.py,在get_dr_txt.py即实现了遍历还实现了目标信息的保存。
2、如果想要进行检测完的图片的保存,利用r_image.save("img.jpg")即可保存,直接在predict.py里进行修改即可。
3、如果想要获得预测框的坐标,可以进入ssd.detect_image函数,在绘图部分读取top,left,bottom,right这四个值。
4、如果想要利用预测框截取下目标,可以进入ssd.detect_image函数,在绘图部分利用获取到的top,left,bottom,right这四个值
在原图上利用矩阵的方式进行截取。
5、如果想要在预测图上写额外的字,比如检测到的特定目标的数量,可以进入ssd.detect_image函数,在绘图部分对predicted_class进行判断,
比如判断if predicted_class == 'car': 即可判断当前目标是否为车,然后记录数量即可。利用draw.text即可写字。
'''
while True:
img = input('Input image filename:')
try:
image = Image.open(img)
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
r_image = ssd.detect_image(image, crop=crop)
r_image.show()
elif mode == "video":
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
if video_save_path != "":
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
size = (int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(video_save_path, fourcc, video_fps, size)
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
raise ValueError("未能正确读取摄像头(视频),请注意是否正确安装摄像头(是否正确填写视频路径)。")
fps = 0.0
while True:
t1 = time.time()
# 读取某一帧
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
break
# 格式转变,BGRtoRGB
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 转变成Image
frame = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(frame))
# 进行检测
frame = np.array(ssd.detect_image(frame))
# RGBtoBGR满足opencv显示格式
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
fps = (fps + (1. / (time.time() - t1))) / 2
print("fps= %.2f" % fps)
frame = cv2.putText(frame, "fps= %.2f" % fps, (0, 40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("video", frame)
c = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xff
if video_save_path != "":
out.write(frame)
if c == 27:
capture.release()
break
print("Video Detection Done!")
capture.release()
if video_save_path != "":
print("Save processed video to the path :" + video_save_path)
out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
elif mode == "fps":
img = Image.open('img/street.jpg')
tact_time = ssd.get_FPS(img, test_interval)
print(str(tact_time) + ' seconds, ' + str(1 / tact_time) + 'FPS, @batch_size 1')
elif mode == "dir_predict":
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
img_names = os.listdir(dir_origin_path)
for img_name in tqdm(img_names):
if img_name.lower().endswith(
('.bmp', '.dib', '.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm', '.tif', '.tiff')):
image_path = os.path.join(dir_origin_path, img_name)
image = Image.open(image_path)
r_image = ssd.detect_image(image)
if not os.path.exists(dir_save_path):
os.makedirs(dir_save_path)
r_image.save(os.path.join(dir_save_path, img_name.replace(".jpg", ".png")), quality=95, subsampling=0)
else:
raise AssertionError("Please specify the correct mode: 'predict', 'video', 'fps' or 'dir_predict'.")