Spring——事务管理
一、事务的基本概念及其准备工作
1、什么事务
(1)事务是数据库操作最基本单元,逻辑上一组操作,要么都成功,如果有一个失败所有操作都失败
(2)典型场景:银行转账
- lucy 转账100 元给mary
- lucy 少100,mary 多100
2、事务四个特性(ACID)
(1)原子性
(2)一致性
(3)隔离性
(4)持久性
3、准备工作
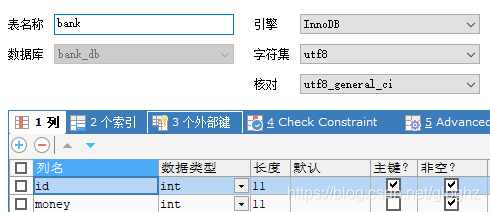
在数据库bank_db下新建一个bank表:
maben依赖:
<!-- springmvc中包含spring核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring对jdbc的封装 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>4.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用德鲁伊的数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql数据库连接 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.35</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.10</version>
</dependency>
搭建结构:
开启包扫描,配置JdbcTemplate:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.glp"></context:component-scan>
<bean id="dataSource"
class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///bank_db" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="mysql" />
<property name="driverClassName"
value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
码云源码:Spring——事务管理
三、编程式事务管理
将事务管理代码嵌到业务方法中来控制事务的提交和回滚,try catch。
必须在每个事务操作业务逻辑中包含额外的事务管理代码,耦合度较高。
try{
//1 开启事务
//2 进行业务操作
//3 没有异常产生,提交事务
}catch(Exception e){
//4 出现异常,事务回滚
}
注意:
事务一般应用在service层中。
四、声明式事务管理
- Spring 进行声明式事务管理,底层使用AOP 原理。
- 将事务管理代码从业务方法中分离出来,以声明的方式来实现事务管理。
将事务管理作为横切关注点,通过aop方法模块化。Spring中通过Spring AOP框架支持声明式事务管理。
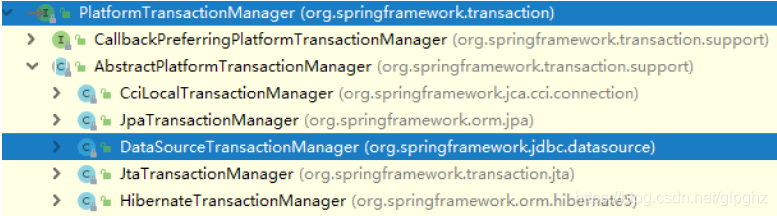
Spring提供了一个PlatformTransactionManager接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对不同的框架提供不同的实现类
- JdbcTemplate和Mybatis框架,都是用DataSourceTransactionManager接口实现事务
- Hibernate框架,使用HibernateTransactionManager接口实现事务
1 基于注解方式
(1)在spring 配置文件配置事务管理器
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
(2)在spring 配置文件中开启事务注解:tx
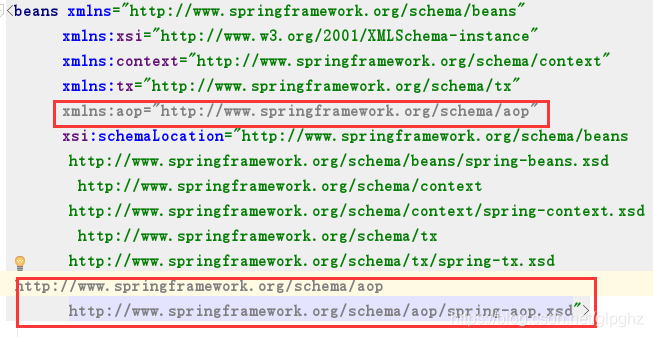
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
<!--开启事务注解-->
<tx:annotation-driven
transaction-manager="transactionManager"> </tx:annotation-driven>
(3)在service 的类或方法上面添加事务注解@Transactional
- @Transactional,这个注解添加到类上面,也可以添加方法上面
- 如果把这个注解添加类上面,这个类里面所有的方法都添加事务
- 如果把这个注解添加方法上面,为这个方法添加事务
(4)在@Transactional注解中可以配置事务的相关属性:
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
1)propagation: 事务传播行为
事务传播行为:事务方法调用时,事务是如何管理的。
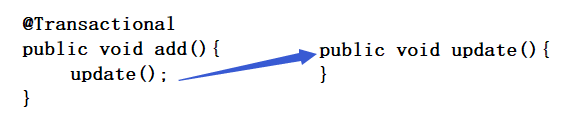
举个例子说明以下 REQUIRED和REQUIRED_NEW:
REQUIRED:如果add方法有事务,当调用没有事务的update方法时,update方法加入add方法中的事务;如果add方法没有事务,当调用没有事务的update方法时,创建一个新的事务。
REQUIRED_NEW:当调用没有事务的update方法时,无论add方法是否有事务,都会调用一个新的事务。
2)isolation:事务的隔离级别
有三个读的问题:脏读、不可重复读、幻读
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ)
public void accountMoney(){
userDao.reduceMoney();
userDao.addMoney();
}
参考博客:事务的四种隔离级别
3)timeout:超时时间
事务需要在一定的时间内进行提交,如果超时则进行回滚,默认不开启,默认值是-1,时间为秒为单位。
4)readOnly:是否只读
- readOnly 默认值false,表示可以查询,可以添加修改删除操作
- 设置readOnly 值是true,设置成true 之后,只能查询
5)rollbackFor:回滚
设置出现哪些异常进行事务回滚
6)noRollbackFor:不回滚
设置出现哪些异常不进行事务回滚
2、基于xml 配置文件方式
(1)引入aop约束
(2)配置事务管理器以及通知
<!--1 创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--2 配置通知-->
<tx:advice id="txadvice">
<!--配置事务参数-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--指定在哪种方法上面添加事务-->
<tx:method name="accountMoney" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!--account开头的都添加事务:<tx:method name="account*"/>-->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--3 配置切入点和切面-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.glp.service.UserService.*(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
</aop:config>
3、完全注解声明式事务管理
@Configuration //配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.atguigu") //组件扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务
public class TxConfig {
//创建数据库连接池
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDruidDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///user_db");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root"); return dataSource;
}
//创建JdbcTemplate对象
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
//到ioc容器中根据类型找到dataSource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//注入dataSource
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
//创建事务管理器
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager =
new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
为什么需要配置声明式事务?
- 如果不配置,就需要我们手动提交控制事务;
- 事务在项目开发过程非常重要,涉及到数据的一致性的问题
- 不改变源码的情况下,增加事务