一、简介
对于ziplist,实现复杂,为了逆序遍历,每个entry中包含前一个entry的长度,这样导致在ziplist中间修改或者插入entry时可能产生级联更新。为了实现更紧凑、更快的解析,更简单的实现,重写实现了ziplist,listpack由此诞生。
二、结构图
2.1 整体结构
- 头比ziplist少了4字节
- 每个元素中只有自己的总长度来实现逆序遍历,更新时不会出现级联更新
2.2 数据编码
元素编码分为三部分,encoding,data, element-total-len, 对于数字类型字符串在int64_t范围内的都可以编码为数字型,将无data字段,元素值存储在encoding中。
2.2.1 encoding编码
- 整数
- 字符串
2.2.2 element-total-len编码
element-total-len表示当前元素的总长度,用于逆序遍历listpack时使用。
- 使用大端序
- 逆序读取,从右往左逐字节读取
- 每个字节只是用7bit表示数字,最高位表示是否还有数据,1表示还需要读取下一字节,0表示结束了
三、实现
3. 1 位操作定义
#define LP_HDR_SIZE 6 /* 32 bit total len + 16 bit number of elements. */
#define LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN UINT16_MAX
#define LP_MAX_INT_ENCODING_LEN 9
#define LP_MAX_BACKLEN_SIZE 5
#define LP_MAX_ENTRY_BACKLEN 34359738367ULL
#define LP_ENCODING_INT 0
#define LP_ENCODING_STRING 1
#define LP_ENCODING_7BIT_UINT 0
#define LP_ENCODING_7BIT_UINT_MASK 0x80
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_7BIT_UINT(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_7BIT_UINT_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_7BIT_UINT)
#define LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR 0x80
#define LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR_MASK 0xC0
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_6BIT_STR(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR)
#define LP_ENCODING_13BIT_INT 0xC0
#define LP_ENCODING_13BIT_INT_MASK 0xE0
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_13BIT_INT(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_13BIT_INT_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_13BIT_INT)
#define LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR 0xE0
#define LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR_MASK 0xF0
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_12BIT_STR(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR)
#define LP_ENCODING_16BIT_INT 0xF1
#define LP_ENCODING_16BIT_INT_MASK 0xFF
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_16BIT_INT(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_16BIT_INT_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_16BIT_INT)
#define LP_ENCODING_24BIT_INT 0xF2
#define LP_ENCODING_24BIT_INT_MASK 0xFF
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_24BIT_INT(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_24BIT_INT_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_24BIT_INT)
#define LP_ENCODING_32BIT_INT 0xF3
#define LP_ENCODING_32BIT_INT_MASK 0xFF
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_INT(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_32BIT_INT_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_32BIT_INT)
#define LP_ENCODING_64BIT_INT 0xF4
#define LP_ENCODING_64BIT_INT_MASK 0xFF
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_64BIT_INT(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_64BIT_INT_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_64BIT_INT)
#define LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR 0xF0
#define LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR_MASK 0xFF
#define LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_STR(byte) (((byte)&LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR_MASK)==LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR)
#define LP_EOF 0xFF
#define LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR_LEN(p) ((p)[0] & 0x3F)
#define LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR_LEN(p) ((((p)[0] & 0xF) << 8) | (p)[1])
#define LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR_LEN(p) (((uint32_t)(p)[1]<<0) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[2]<<8) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[3]<<16) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[4]<<24))
#define lpGetTotalBytes(p) (((uint32_t)(p)[0]<<0) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[1]<<8) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[2]<<16) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[3]<<24))
#define lpGetNumElements(p) (((uint32_t)(p)[4]<<0) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[5]<<8))
#define lpSetTotalBytes(p,v) do { \
(p)[0] = (v)&0xff; \
(p)[1] = ((v)>>8)&0xff; \
(p)[2] = ((v)>>16)&0xff; \
(p)[3] = ((v)>>24)&0xff; \
} while(0)
#define lpSetNumElements(p,v) do { \
(p)[4] = (v)&0xff; \
(p)[5] = ((v)>>8)&0xff; \
} while(0)
3.2 创建一个空的listpack
unsigned char *lpNew(void) {
unsigned char *lp = lp_malloc(LP_HDR_SIZE+1);
if (lp == NULL) return NULL;
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,LP_HDR_SIZE+1);
lpSetNumElements(lp,0);
lp[LP_HDR_SIZE] = LP_EOF;
return lp;
}
3.3 插入
- 插入:p之前和p之后,实际插入时,都会转换为p’之前
3.3.1 例1.结尾插入“123”, len=3
1. 计算插入位置
unsigned char *lpAppend(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *ele, uint32_t size) {
uint64_t listpack_bytes = lpGetTotalBytes(lp);
unsigned char *eofptr = lp + listpack_bytes - 1;
return lpInsert(lp,ele,size,eofptr,LP_BEFORE,NULL);
}
2. 转换插入方式
如果是插入p之后,将跳过当前节点,指向下一个节点p`,然后插入p`之前
if (where == LP_AFTER) {
p = lpSkip(p);
where = LP_BEFORE;
}
本例中是插入之前,所以不需要
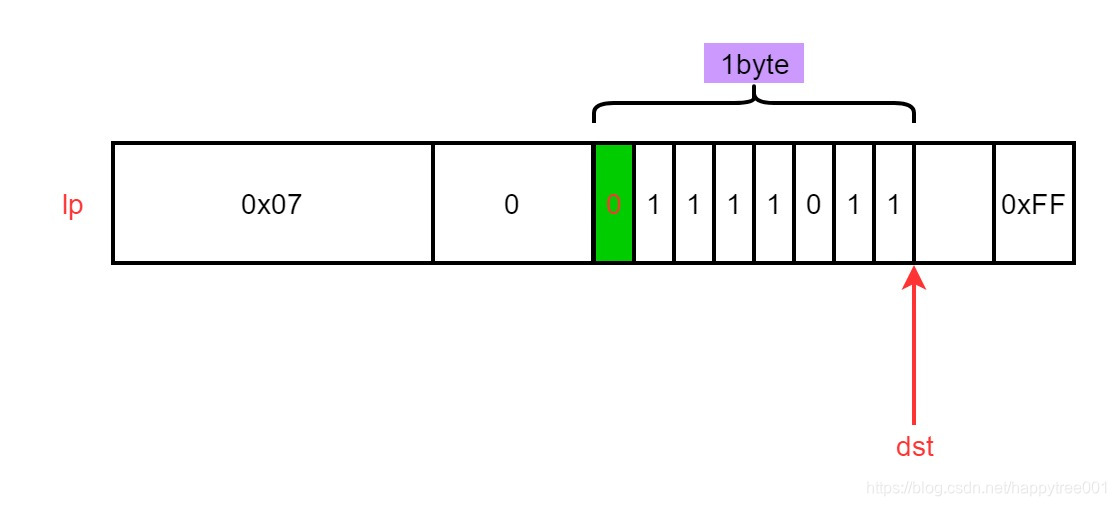
3. 计算插入位置的偏移量
用于后续扩容后,重写定位到插入位置
unsigned long poff = p-lp;
本例中poff = 6
4. 获取编码类型
- 尝试将插入的值转换位int64_t的数值,如果成功,则使用整数进行编码
- 否则使用字符串编码
int lpEncodeGetType(unsigned char *ele, uint32_t size, unsigned char *intenc, uint64_t *enclen) {
int64_t v;
if (lpStringToInt64((const char*)ele, size, &v)) {
if (v >= 0 && v <= 127) {
/* Single byte 0-127 integer. */
intenc[0] = v;
*enclen = 1;
} else if (v >= -4096 && v <= 4095) {
/* 13 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<13)+v;
intenc[0] = (v>>8)|LP_ENCODING_13BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
*enclen = 2;
} else if (v >= -32768 && v <= 32767) {
/* 16 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<16)+v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_16BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
intenc[2] = v>>8;
*enclen = 3;
} else if (v >= -8388608 && v <= 8388607) {
/* 24 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<24)+v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_24BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
intenc[2] = (v>>8)&0xff;
intenc[3] = v>>16;
*enclen = 4;
} else if (v >= -2147483648 && v <= 2147483647) {
/* 32 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<32)+v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_32BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
intenc[2] = (v>>8)&0xff;
intenc[3] = (v>>16)&0xff;
intenc[4] = v>>24;
*enclen = 5;
} else {
/* 64 bit integer. */
uint64_t uv = v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_64BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = uv&0xff;
intenc[2] = (uv>>8)&0xff;
intenc[3] = (uv>>16)&0xff;
intenc[4] = (uv>>24)&0xff;
intenc[5] = (uv>>32)&0xff;
intenc[6] = (uv>>40)&0xff;
intenc[7] = (uv>>48)&0xff;
intenc[8] = uv>>56;
*enclen = 9;
}
return LP_ENCODING_INT;
} else {
if (size < 64) *enclen = 1+size;
else if (size < 4096) *enclen = 2+size;
else *enclen = 5+size;
return LP_ENCODING_STRING;
}
}
本例中“123”可以转换为123, 并且123 在[0,127]范围内,所以只需一字节表示
intenc[0] = 123(01111011);*enclen = 1;
5. 获取插入元素的总长度编码
unsigned long lpEncodeBacklen(unsigned char *buf, uint64_t l) {
if (l <= 127) {
if (buf) buf[0] = l;
return 1;
} else if (l < 16383) {
if (buf) {
buf[0] = l>>7;
buf[1] = (l&127)|128;
}
return 2;
} else if (l < 2097151) {
if (buf) {
buf[0] = l>>14;
buf[1] = ((l>>7)&127)|128;
buf[2] = (l&127)|128;
}
return 3;
} else if (l < 268435455) {
if (buf) {
buf[0] = l>>21;
buf[1] = ((l>>14)&127)|128;
buf[2] = ((l>>7)&127)|128;
buf[3] = (l&127)|128;
}
return 4;
} else {
if (buf) {
buf[0] = l>>28;
buf[1] = ((l>>21)&127)|128;
buf[2] = ((l>>14)&127)|128;
buf[3] = ((l>>7)&127)|128;
buf[4] = (l&127)|128;
}
return 5;
}
}
因为上一步骤计算出来总长度为1字节,1<= 127满足,所以总长度编码也只需要1字节,backlen_size=1
6. 计算新的整个listpack总长度
uint64_t new_listpack_bytes = old_listpack_bytes + enclen + backlen_size
- replaced_len;
if (new_listpack_bytes > UINT32_MAX) return NULL;
本例中是插入,所以replaced_len=0,old_listpack_bytes为原始的总长度7,new_listpack_bytes=7 + 1 + 1 - 0 = 9
7. 获取插入目标位置
unsigned char *dst = lp + poff; /* May be updated after reallocation. */
8. 扩容
/* Realloc before: we need more room. */
if (new_listpack_bytes > old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
9. 移动数据,以腾出插入位置
if(where == LP_BEFORE) {
memmove(dst+enclen+backlen_size,dst,old_listpack_bytes-poff);
}
mommove(dst+1+1,dst, 7 - 6) -> mommove(dst+2, dst, 1)
10. 写入encoding以及data
if (enctype == LP_ENCODING_INT) {
memcpy(dst,intenc,enclen);
}
dst += enclen;
11. 写入插入节点totallen
memcpy(dst,backlen,backlen_size);
dst += backlen_size;
12. 更新元素个数
- ele为空,则表示删除节点
/* Update header. */
if (where != LP_REPLACE || ele == NULL) {
uint32_t num_elements = lpGetNumElements(lp);
if (num_elements != LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN) {
if (ele)
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements+1);
else
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements-1);
}
}
13. 更新整个listpakc总长度
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,new_listpack_bytes);
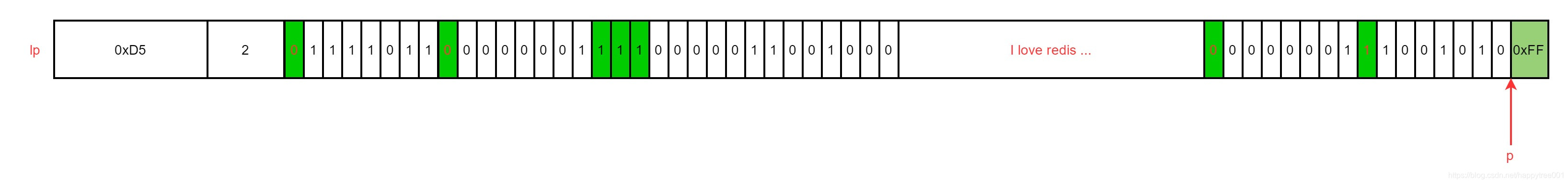
3.3.2 例2. 尾部插入“I love redis …”, len=200
1. 计算插入位置
2. 转换插入方式
如果是插入p之后,将跳过当前节点,指向下一个节点p`,然后插入p`之前
本例中是插入之前,所以不需要
3. 计算插入位置的偏移量
poff=8
4. 获取编码类型
- 尝试将插入的值转换位int64_t的数值,如果成功,则使用整数进行编码
- 否则使用字符串编码
int lpEncodeGetType(unsigned char *ele, uint32_t size, unsigned char *intenc, uint64_t *enclen) {
int64_t v;
if (lpStringToInt64((const char*)ele, size, &v)) {
...
return LP_ENCODING_INT;
} else {
if (size < 64) *enclen = 1+size;
else if (size < 4096) *= 2+size;
else *enclen = 5+size;
return LP_ENCODING_STRING;
}
}
本例中不能转为数值,长度200在[64, 4096), 所以需要2字节编码
*enclen = 2 + 200 = 202
5. 获取插入元素的总长度编码
202 在(127, 16383), 所以需要2字节,backlen_size=2
6. 计算新的整个listpack总长度
new_listpack_bytes = 9 + 202 + 2 - 0 = 213
7. 获取插入目标位置
8. 扩容
9. 移动数据,以腾出插入位置
memmove(dst+enclen+backlen_size,dst,old_listpack_bytes-poff);
memmove(dst+202+2,dst, 9-8) -> mommove(dst+204, dst, 1)
10. 写入encoding以及data
void lpEncodeString(unsigned char *buf, unsigned char *s, uint32_t len) {
if (len < 64) {
buf[0] = len | LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR;
memcpy(buf+1,s,len);
} else if (len < 4096) {
buf[0] = (len >> 8) | LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR;
buf[1] = len & 0xff;
memcpy(buf+2,s,len);
} else {
buf[0] = LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR;
buf[1] = len & 0xff;
buf[2] = (len >> 8) & 0xff;
buf[3] = (len >> 16) & 0xff;
buf[4] = (len >> 24) & 0xff;
memcpy(buf+5,s,len);
}
}
if (enctype == LP_ENCODING_INT) {
memcpy(dst,intenc,enclen);
} else {
lpEncodeString(dst,ele,size);
}
dst += enclen;
字符串200在[64,4096)范围内,所以需要两个字节
11. 写入插入节点totallen
总长度202(11001010)-> 0000001, 1001010
12. 更新元素个数
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements+1);
13. 更新整个listpakc总长度
3.4 逆序遍历
unsigned char *ele = lpLast(lp);
while (ele) {
ele = lpPrev(lp,ele);
}
- 定位到结尾
- 读取element-total-len,获取元素总长度elem-len
- 根据读取的elem-len,往前移elem-len,到元素开头
- 重复步骤2.和3.
unsigned char *lpPrev(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *p) {
if (p-lp == LP_HDR_SIZE) return NULL;
p--; /* Seek the first backlen byte of the last element. */
uint64_t prevlen = lpDecodeBacklen(p);
prevlen += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,prevlen);
return p-prevlen+1; /* Seek the first byte of the previous entry. */
}
unsigned char *lpLast(unsigned char *lp) {
unsigned char *p = lp+lpGetTotalBytes(lp)-1; /* Seek EOF element. */
return lpPrev(lp,p); /* Will return NULL if EOF is the only element. */
}
- 定位到结尾
unsigned char *p = lp+lpGetTotalBytes(lp)-1; /* Seek EOF element. */
- 判断是否有数据,必须大于头长度
if (p-lp == LP_HDR_SIZE) return NULL;
- 定位到最后一个元素最后一个字节
p--; /* Seek the first backlen byte of the last element. */
- 计算元素总长度
uint64_t prevlen = lpDecodeBacklen(p);
uint64_t lpDecodeBacklen(unsigned char *p) {
uint64_t val = 0;
uint64_t shift = 0;
do {
val |= (uint64_t)(p[0] & 127) << shift;
if (!(p[0] & 128)) break; //判断最好位是否1,是1则表示还需要继续读取
shift += 7;
p--; //读取前一个字节
if (shift > 28) return UINT64_MAX;
} while(1);
return val;
}
这里 1001010 | (1<<7) = 11001010 = 202
- 根据计算到的元素总长度,进行计算长度编码字段
prevlen += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,prevlen);
unsigned long lpEncodeBacklen(unsigned char *buf, uint64_t l) {
if (l <= 127) {
if (buf) buf[0] = l;
return 1;
} else if (l < 16383) {
if (buf) {
buf[0] = l>>7;
buf[1] = (l&127)|128;
}
return 2;
}
...
}
总长度202,长度编码2字节, 所以prevlen=202+2=204
- 偏移到元素开始
return p-prevlen+1; /* Seek the first byte of the previous entry. */
- 重复上述步骤
- 判断是否还有元素
if (p-lp == LP_HDR_SIZE) return NULL;本例中还有数据 - 往前移动一字节
p--; /* Seek the first backlen byte of the last element. */
- 计算元素数据总长度
00000001, 因此元素1字节 - 计算长度编码字节数
1字节长度只需要1字节表示,prevlen = 1+ 1 = 2 - 偏移到元素开头
- 重复
- 判断是否还有元素
if (p-lp == LP_HDR_SIZE) return NULL;
这里刚好等于头长度,所以没元素了
3.5 替换
3.5.1 例1. 将第一个元素替换成“-32767”
1. 计算偏移量
unsigned long poff = p-lp;
poff = p - lp = header = 6
2. 计算替换数据“-32767”的编码
if (ele) {
enctype = lpEncodeGetType(ele,size,intenc,&enclen);
- "-32767"可以转换为int64_t范围内,所以使用整数编码
- -32767在范围 [-32768, 32767]中,所以需要3字节编码
- 因为是负数,所以需要转换为正数数
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<16)+v;, v = 32769
int lpEncodeGetType(unsigned char *ele, uint32_t size, unsigned char *intenc, uint64_t *enclen) {
int64_t v;
if (lpStringToInt64((const char*)ele, size, &v)) {
if (v >= 0 && v <= 127) {
/* Single byte 0-127 integer. */
intenc[0] = v;
*enclen = 1;
} else if (v >= -4096 && v <= 4095) {
/* 13 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<13)+v;
intenc[0] = (v>>8)|LP_ENCODING_13BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
*enclen = 2;
} else if (v >= -32768 && v <= 32767) {
/* 16 bit integer. */
if (v < 0) v = ((int64_t)1<<16)+v;
intenc[0] = LP_ENCODING_16BIT_INT;
intenc[1] = v&0xff;
intenc[2] = v>>8;
*enclen = 3;
}
...
return LP_ENCODING_INT;
}
...
}
3. 计算元素长度需要的长度编码
unsigned long backlen_size = ele ? lpEncodeBacklen(backlen,enclen) : 0;
当前enclen=3,在[0,127] 范围内,所以只需要1字节, backlen_size=1
4. 计算需要替换元素的总长度
uint32_t replaced_len = 0;
if (where == LP_REPLACE) {
replaced_len = lpCurrentEncodedSize(p);
replaced_len += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,replaced_len);
}
本例中第一个元素2字节长度, 所以replaced_len=2
5. 计算新的总大小
uint64_t new_listpack_bytes = old_listpack_bytes + enclen + backlen_size
- replaced_len;
new_listpack_bytes = 0xD5 + 3 + 1 - 2 = 0xD5 + 2 = 0xD7
6. 计算目标位置
unsigned char *dst = lp + poff; /* May be updated after reallocation. */
dst = lp + poff = lp + 6
7. 扩容
/* Realloc before: we need more room. */
if (new_listpack_bytes > old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
替换后,长度增加了,所以需要扩容
8.数据移动
/* LP_REPLACE. */
long lendiff = (enclen+backlen_size)-replaced_len;
memmove(dst+replaced_len+lendiff,
dst+replaced_len,
old_listpack_bytes-poff-replaced_len);
lendiff=(3+1)-2=2
memmove(dst+2+2,dst+2,0xD5-6-2) -> memmove(dst+4, dst+2, 205)
9. 写入数据
if (enctype == LP_ENCODING_INT) {
memcpy(dst,intenc,enclen);
} else {
lpEncodeString(dst,ele,size);
}
dst += enclen;
这里是整数
10. 写入元素长度编码
memcpy(dst,backlen,backlen_size);
dst += backlen_size;
11. 更新元素个数
不需要,未插入或者删除
12. 更新总长度
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,new_listpack_bytes);
3.6 删除
删除和替换以及插入差不多,只是elem参数为null,并且删除操作就是replace操作
unsigned char *lpDelete(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *p, unsigned char **newp) {
return lpInsert(lp,NULL,0,p,LP_REPLACE,newp);
}
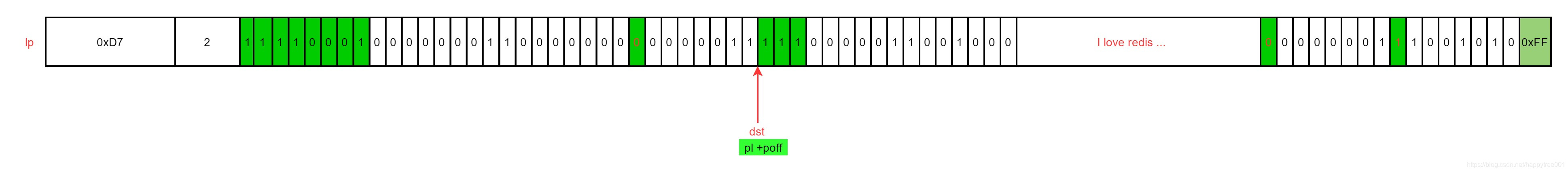
3.6.1 例1. 删除第二个元素
首先通过p = lpSeek(lp, 1) ;获取删除元素首指针
1. 设置方式为replace
ele为空,则表示删除,删除方式只能是replace
if (ele == NULL) where = LP_REPLACE;
2. 计算偏移量
unsigned long poff = p-lp;
poff = p - lp = 10
3. 设置数据编码长度
enctype = -1;
enclen = 0;
4. 设置长度编码
backlen_size = 0
5. 计算删除元素的总长度
if (where == LP_REPLACE) {
replaced_len = lpCurrentEncodedSize(p);
replaced_len += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,replaced_len);
}
本例中,总长度replaced_len = 202+2 = 204
6. 计算删除后新的总长度
uint64_t new_listpack_bytes = old_listpack_bytes + enclen + backlen_size
- replaced_len;
new_listpack_bytes = 0xD7 + 0 + 0 - 204 = 11
7. 计算目标地址
unsigned char *dst = lp + poff; /* May be updated after reallocation. */
8. 移动数据
long lendiff= (enclen+backlen_size)-replaced_len;
memmove(dst+replaced_len+lendiff,
dst+replaced_len,
old_listpack_bytes-poff-replaced_len);
lendiff = (0+0)-204=-204
memmove(dst+204+(-204), dst+204, 0xD7-10-204) -> memmove(dst, dst+204, 1)
9. 缩容
/* Realloc after: we need to free space. */
if (new_listpack_bytes < old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
10. 更新元素个数
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements-1);
11. 更新总长度
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,new_listpack_bytes);
3.7 定位到index的元素
- index如果是负数,则逆序定位
- 如果index
unsigned char *lpSeek(unsigned char *lp, long index) {
int forward = 1; /* Seek forward by default. */
/* We want to seek from left to right or the other way around
* depending on the listpack length and the element position.
* However if the listpack length cannot be obtained in constant time,
* we always seek from left to right. */
uint32_t numele = lpGetNumElements(lp);
if (numele != LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN) {
if (index < 0) index = (long)numele+index;
if (index < 0) return NULL; /* Index still < 0 means out of range. */
if (index >= numele) return NULL; /* Out of range the other side. */
/* We want to scan right-to-left if the element we are looking for
* is past the half of the listpack. */
if (index > numele/2) {
forward = 0;
/* Right to left scanning always expects a negative index. Convert
* our index to negative form. */
index -= numele;
}
} else {
/* If the listpack length is unspecified, for negative indexes we
* want to always scan right-to-left. */
if (index < 0) forward = 0;
}
/* Forward and backward scanning is trivially based on lpNext()/lpPrev(). */
if (forward) {
unsigned char *ele = lpFirst(lp);
while (index > 0 && ele) {
ele = lpNext(lp,ele);
index--;
}
return ele;
} else {
unsigned char *ele = lpLast(lp);
while (index < -1 && ele) {
ele = lpPrev(lp,ele);
index++;
}
return ele;
}
}
3.8 获取值
unsigned char *lpGet(unsigned char *p, int64_t *count, unsigned char *intbuf) {
int64_t val;
uint64_t uval, negstart, negmax;
if (LP_ENCODING_IS_7BIT_UINT(p[0])) {
negstart = UINT64_MAX; /* 7 bit ints are always positive. */
negmax = 0;
uval = p[0] & 0x7f;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_6BIT_STR(p[0])) {
*count = LP_ENCODING_6BIT_STR_LEN(p);
return p+1;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_13BIT_INT(p[0])) {
uval = ((p[0]&0x1f)<<8) | p[1];
negstart = (uint64_t)1<<12;
negmax = 8191;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_16BIT_INT(p[0])) {
uval = (uint64_t)p[1] |
(uint64_t)p[2]<<8;
negstart = (uint64_t)1<<15;
negmax = UINT16_MAX;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_24BIT_INT(p[0])) {
uval = (uint64_t)p[1] |
(uint64_t)p[2]<<8 |
(uint64_t)p[3]<<16;
negstart = (uint64_t)1<<23;
negmax = UINT32_MAX>>8;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_INT(p[0])) {
uval = (uint64_t)p[1] |
(uint64_t)p[2]<<8 |
(uint64_t)p[3]<<16 |
(uint64_t)p[4]<<24;
negstart = (uint64_t)1<<31;
negmax = UINT32_MAX;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_64BIT_INT(p[0])) {
uval = (uint64_t)p[1] |
(uint64_t)p[2]<<8 |
(uint64_t)p[3]<<16 |
(uint64_t)p[4]<<24 |
(uint64_t)p[5]<<32 |
(uint64_t)p[6]<<40 |
(uint64_t)p[7]<<48 |
(uint64_t)p[8]<<56;
negstart = (uint64_t)1<<63;
negmax = UINT64_MAX;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_12BIT_STR(p[0])) {
*count = LP_ENCODING_12BIT_STR_LEN(p);
return p+2;
} else if (LP_ENCODING_IS_32BIT_STR(p[0])) {
*count = LP_ENCODING_32BIT_STR_LEN(p);
return p+5;
} else {
uval = 12345678900000000ULL + p[0];
negstart = UINT64_MAX;
negmax = 0;
}
/* We reach this code path only for integer encodings.
* Convert the unsigned value to the signed one using two's complement
* rule. */
if (uval >= negstart) {
/* This three steps conversion should avoid undefined behaviors
* in the unsigned -> signed conversion. */
uval = negmax-uval;
val = uval;
val = -val-1;
} else {
val = uval;
}
/* Return the string representation of the integer or the value itself
* depending on intbuf being NULL or not. */
if (intbuf) {
*count = snprintf((char*)intbuf,LP_INTBUF_SIZE,"%lld",(long long)val);
return intbuf;
} else {
*count = val;
return NULL;
}
}
uval = (uint64_t)p[1] |(uint64_t)p[2]<<8 = (00000001) | (10000000)<<8 = 32769
negstart = (uint64_t)1<<15 = 32768
negmax = UINT16_MAX
uval > negstart 成立, 所以源数据为负数
uval = negmax-uval = 65535 - 32769 = 32766
val = uval = 32766
val = -val -1 = -32767, 和元素数据一致。