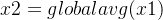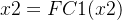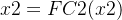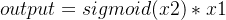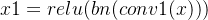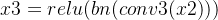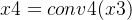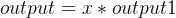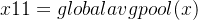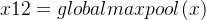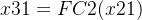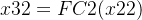目录
SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks
一:SE(Squeeze-and-Excitation)
1.1 SENet网络的创新点:
在于关注channel之间的关系,希望模型可以自动学习到不同channel特征的重要程度。
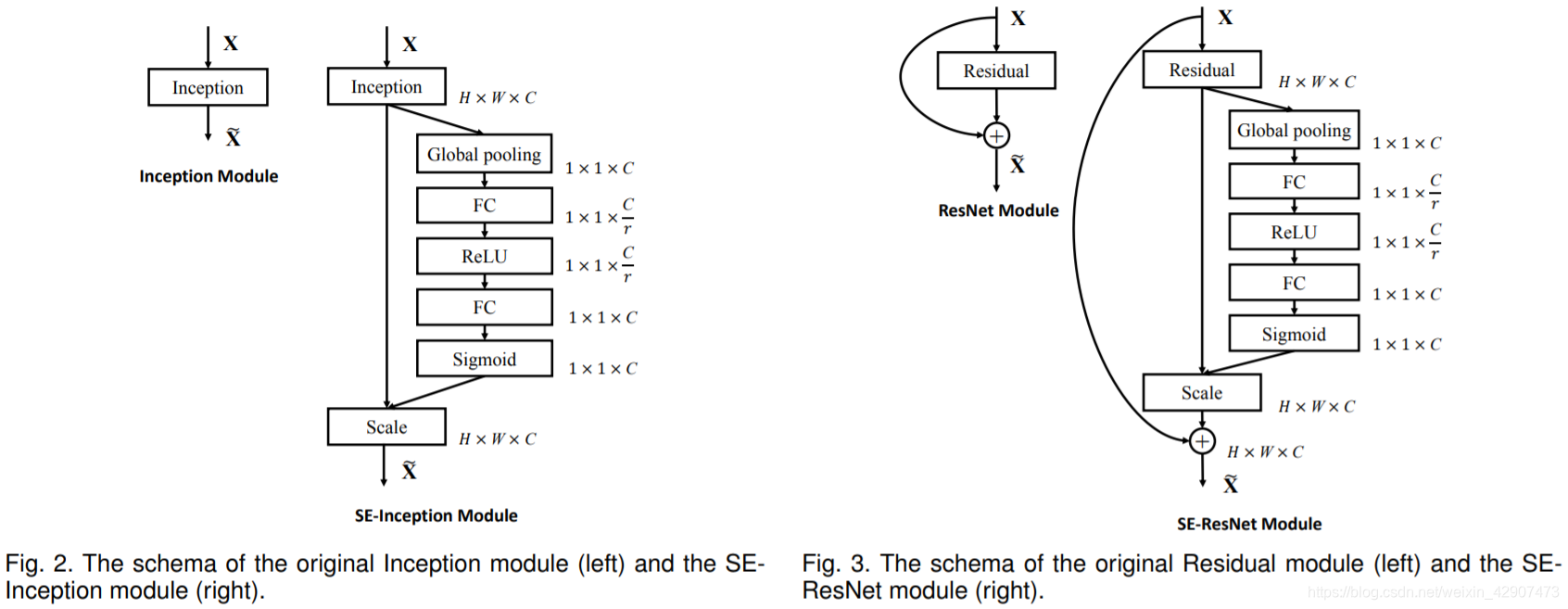
1.2 SE结构
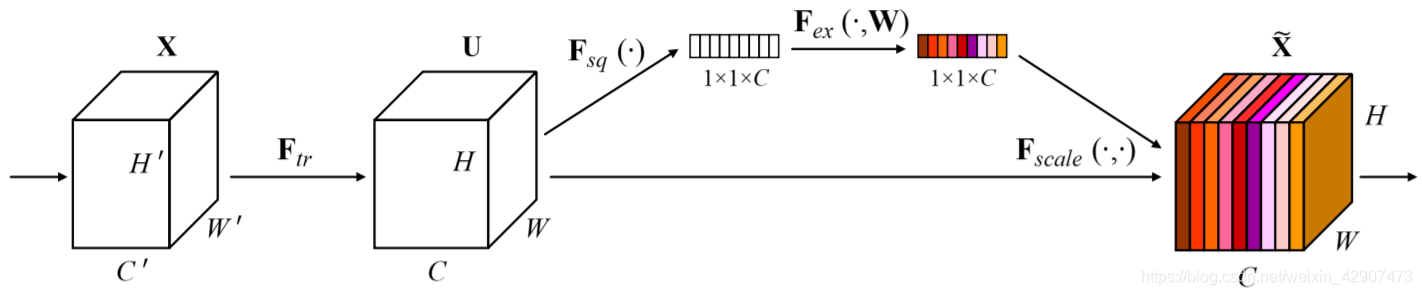
如上图所示,为SE的结构,一个SEblock的过程分为 Squeeze(压缩) 和 Excitation(激发) 两个步骤:
1.Squeeze(压缩) 通过在Feature Map层上执行Global Average Pooling,得到当前Feature Map的全局压缩特征量;
2.Excitation(激发) 通过两层全连接的bottleneck结构得到Feature Map中每个通道的权值,并将加权后的Feature Map作为下一层网络的输入。
1.3 SE的操作细节
首先设输入的是一个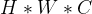
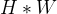
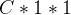
然后经过两个全连接层进行非线性的处理。
第一个全连接层,FC1(C,C/16)
第二个全连接层,FC2(C/16,C)
两个全连接操作,先是降维,然后是升维,这样可以拟合通道之间的复杂相关性。之后再接上一个sigmoid层,得到一个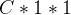
1.4 SE的应用
具体实现的代码:
resnet_se的实现
import torch.nn as nn
import math
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
__all__ = ['SENet', 'se_resnet_18', 'se_resnet_34', 'se_resnet_50', 'se_resnet_101',
'se_resnet_152']
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
if planes == 64:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(56, stride=1)
elif planes == 128:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(28, stride=1)
elif planes == 256:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(14, stride=1)
elif planes == 512:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features=planes, out_features=round(planes / 16))
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=round(planes / 16), out_features=planes)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
original_out = out
out = self.globalAvgPool(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.fc1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
out = self.sigmoid(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), out.size(1), 1, 1)
out = out * original_out
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
if planes == 64:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(56, stride=1)
elif planes == 128:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(28, stride=1)
elif planes == 256:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(14, stride=1)
elif planes == 512:
self.globalAvgPool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features=planes * 4, out_features=round(planes / 4))
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=round(planes / 4), out_features=planes * 4)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
original_out = out
out = self.globalAvgPool(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.fc1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
out = self.sigmoid(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0),out.size(1),1,1)
out = out * original_out
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class SENet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000):
self.inplanes = 64
super(SENet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def se_resnet_18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = SENet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
return model
def se_resnet_34(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-34 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = SENet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
return model
def se_resnet_50(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = SENet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
return model
def se_resnet_101(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = SENet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)
return model
def se_resnet_152(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-152 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = SENet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs)
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
resnet_model=se_resnet_50(pretrained=False)
print(resnet_model)二:BAM (Bottlenet attention Module)
2.1BAM结构的创新点
它的优势:
第一有效的得到全局上下文信息,CNN堆积许多卷积层和池化层来获取上下文信息,虽然有效,但是增加了时间和空间复杂度。
第二忽略了底层特征,而BAM可以放在模块的开始,那么底层特征也能得到上下文信息
BAM结构通过两个分离的路径 channel和spatial,可以结合到任何前向传播卷积神经网络中,得到一个注意力图(Attention Map)。
2.2BAM结构
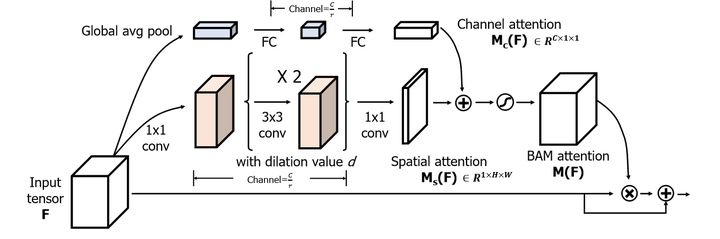
如上图所示,BAM由两个部分组成:channel和spatial分支组成。
channel attention branch
其中通道分支,由一个全局平均池化,两个全连接构成
spatial attention branch
其中空间分支,由两个1*1的卷积,两个3*3的空洞卷积
2.3BAM的实现细节
channel attention branch
首先设输入的是一个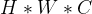
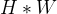
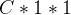
然后经过两个全连接层进行非线性的处理。
第一个全连接层,FC1(C,C/16)
第二个全连接层,FC2(C/16,C)
把得到的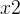
spatial attention branch
首先设输入的是一个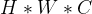
然后经过四次卷积操作:
第一次卷积:conv1(C,C/16,k=1,s=1)
第二次卷积:conv2(C/16,C/16,k=3,p=4,s=4)
第三次卷积:conv3(C/16,C/16,k=3,p=4,s=4)
第四次卷积:conv4(C/16,C,k=1,s=1)
最后两个通道进行融合:
最后和原始特征图进行融合:
这样就用BAM得到了一个空间的注意力特征图。
2.4BAM的应用
BAM可以嵌套resnet中。
代码实现:
import torch
import math
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.size(0), -1)
class ChannelGate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gate_channel, reduction_ratio=16, num_layers=1):
super(ChannelGate, self).__init__()
# self.gate_activation = gate_activation
self.gate_c = nn.Sequential()
self.gate_c.add_module( 'flatten', Flatten() )
gate_channels = [gate_channel]
gate_channels += [gate_channel // reduction_ratio] * num_layers
gate_channels += [gate_channel]
for i in range( len(gate_channels) - 2 ):
self.gate_c.add_module( 'gate_c_fc_%d'%i, nn.Linear(gate_channels[i], gate_channels[i+1]) )
self.gate_c.add_module( 'gate_c_bn_%d'%(i+1), nn.BatchNorm1d(gate_channels[i+1]) )
self.gate_c.add_module( 'gate_c_relu_%d'%(i+1), nn.ReLU() )
self.gate_c.add_module( 'gate_c_fc_final', nn.Linear(gate_channels[-2], gate_channels[-1]) )
def forward(self, in_tensor):
avg_pool = F.avg_pool2d( in_tensor, in_tensor.size(2), stride=in_tensor.size(2) )
return self.gate_c( avg_pool ).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3).expand_as(in_tensor)
class SpatialGate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gate_channel, reduction_ratio=16, dilation_conv_num=2, dilation_val=4):
super(SpatialGate, self).__init__()
self.gate_s = nn.Sequential()
self.gate_s.add_module( 'gate_s_conv_reduce0', nn.Conv2d(gate_channel, gate_channel//reduction_ratio, kernel_size=1))
self.gate_s.add_module( 'gate_s_bn_reduce0', nn.BatchNorm2d(gate_channel//reduction_ratio) )
self.gate_s.add_module( 'gate_s_relu_reduce0',nn.ReLU() )
for i in range( dilation_conv_num ):
self.gate_s.add_module( 'gate_s_conv_di_%d'%i, nn.Conv2d(gate_channel//reduction_ratio, gate_channel//reduction_ratio, kernel_size=3, \
padding=dilation_val, dilation=dilation_val) )
self.gate_s.add_module( 'gate_s_bn_di_%d'%i, nn.BatchNorm2d(gate_channel//reduction_ratio) )
self.gate_s.add_module( 'gate_s_relu_di_%d'%i, nn.ReLU() )
self.gate_s.add_module( 'gate_s_conv_final', nn.Conv2d(gate_channel//reduction_ratio, 1, kernel_size=1) )
def forward(self, in_tensor):
return self.gate_s( in_tensor ).expand_as(in_tensor)
class BAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gate_channel):
super(BAM, self).__init__()
self.channel_att = ChannelGate(gate_channel)
self.spatial_att = SpatialGate(gate_channel)
def forward(self,in_tensor):
att = 1 + F.sigmoid( self.channel_att(in_tensor) * self.spatial_att(in_tensor) )
return att * in_tensor三:CBAM
3.1CBAM结构的创新点
作者将注意力过程分为两个独立的部分,通道注意力模块和空间注意力模块。这样不仅可以节约参数和计算力,而且保证了其可以作为即插即用的模块集成到现有的网络架构中去。
3.2CBAM结构
CBAM由两个部分组成
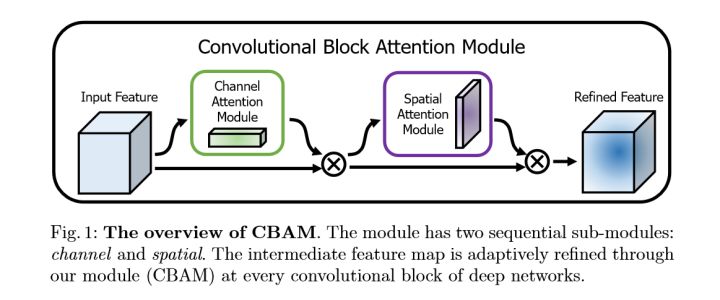
3.3CBAM的实现细节
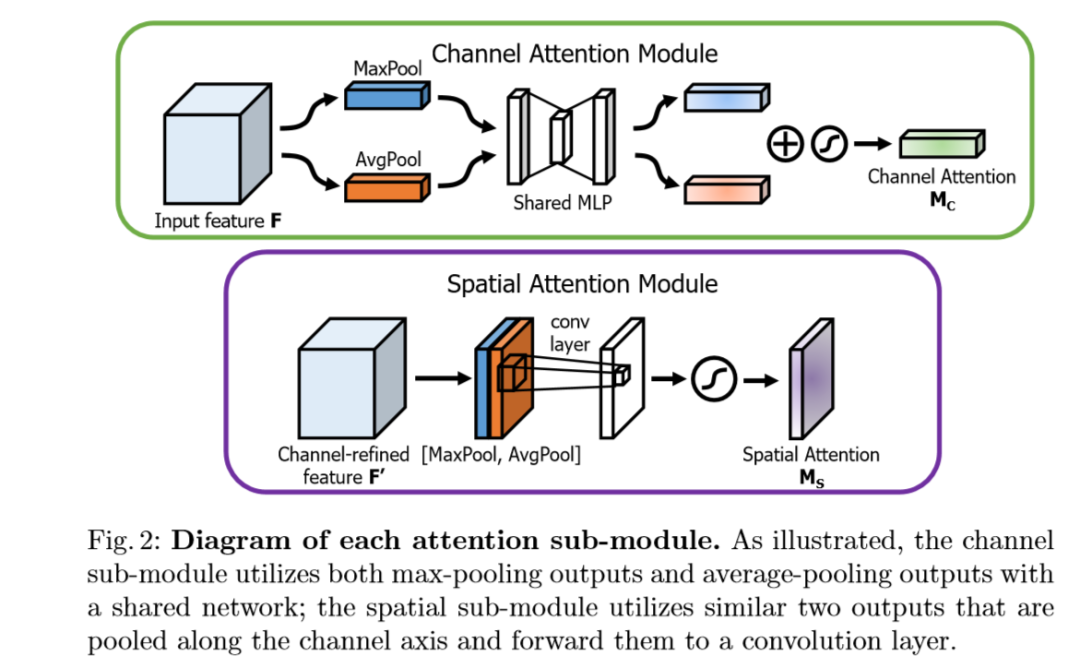
CBAM
channel attention branch
首先设输入的是一个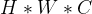
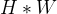
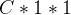
然后经过两个全连接层进行非线性的处理。
第一个全连接层,FC1(C,C/16)
第二个全连接层,FC2(C/16,C)
把得到的两个特征图进行融合后,经过非线性变换后再与原始特征图进行融合:
spatial attention branch
其输入是通道分支的输出,首先进行两次通道维度的操作:
avg_out = torch.mean(output1, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(output1, dim=1, keepdim=True)
x1 = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)然后进行一个卷积,卷积核的大小为7*7或者3*3
经过非线性变换后再与原始特征图进行融合:
3.4CBAM的应用
CBAM可以嵌套到一些主干网络中
代码实现:
import torch
import math
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, relu=True, bn=True, bias=False):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.out_channels = out_planes
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes,eps=1e-5, momentum=0.01, affine=True) if bn else None
self.relu = nn.ReLU() if relu else None
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
if self.bn is not None:
x = self.bn(x)
if self.relu is not None:
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.size(0), -1)
class ChannelGate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gate_channels, reduction_ratio=16, pool_types=['avg', 'max']):
super(ChannelGate, self).__init__()
self.gate_channels = gate_channels
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
Flatten(),
nn.Linear(gate_channels, gate_channels // reduction_ratio),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(gate_channels // reduction_ratio, gate_channels)
)
self.pool_types = pool_types
def forward(self, x):
channel_att_sum = None
for pool_type in self.pool_types:
if pool_type=='avg':
avg_pool = F.avg_pool2d( x, (x.size(2), x.size(3)), stride=(x.size(2), x.size(3)))
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( avg_pool )
elif pool_type=='max':
max_pool = F.max_pool2d( x, (x.size(2), x.size(3)), stride=(x.size(2), x.size(3)))
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( max_pool )
elif pool_type=='lp':
lp_pool = F.lp_pool2d( x, 2, (x.size(2), x.size(3)), stride=(x.size(2), x.size(3)))
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( lp_pool )
elif pool_type=='lse':
# LSE pool only
lse_pool = logsumexp_2d(x)
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( lse_pool )
if channel_att_sum is None:
channel_att_sum = channel_att_raw
else:
channel_att_sum = channel_att_sum + channel_att_raw
scale = F.sigmoid( channel_att_sum ).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3).expand_as(x)
return x * scale
def logsumexp_2d(tensor):
tensor_flatten = tensor.view(tensor.size(0), tensor.size(1), -1)
s, _ = torch.max(tensor_flatten, dim=2, keepdim=True)
outputs = s + (tensor_flatten - s).exp().sum(dim=2, keepdim=True).log()
return outputs
class ChannelPool(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return torch.cat( (torch.max(x,1)[0].unsqueeze(1), torch.mean(x,1).unsqueeze(1)), dim=1 )
class SpatialGate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SpatialGate, self).__init__()
kernel_size = 7
self.compress = ChannelPool()
self.spatial = BasicConv(2, 1, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=(kernel_size-1) // 2, relu=False)
def forward(self, x):
x_compress = self.compress(x)
x_out = self.spatial(x_compress)
scale = F.sigmoid(x_out) # broadcasting
return x * scale
class CBAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gate_channels, reduction_ratio=16, pool_types=['avg', 'max'], no_spatial=False):
super(CBAM, self).__init__()
self.ChannelGate = ChannelGate(gate_channels, reduction_ratio, pool_types)
self.no_spatial=no_spatial
if not no_spatial:
self.SpatialGate = SpatialGate()
def forward(self, x):
x_out = self.ChannelGate(x)
if not self.no_spatial:
x_out = self.SpatialGate(x_out)
return x_out四:SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43025525/article/details/118993052
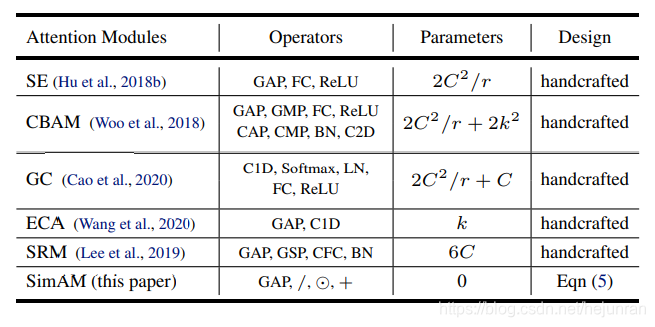
五:总结
相关注意力机制的参数: