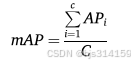Evaluation metrics/Performance metrics即评价指标,是常见于论文实验部分的内容,几乎是一i篇论文不可缺少的部分。评价指标部分的写作不具有太大的难点,唯一需要解决的一个问题就是如何写得跟别人不一样。因为我们知道,评价指标无非就是P,R,mAP,F1,FPS,Flops等等这些,如何写出新意很重要
我将从文字和公式两个方面来说明这个段落的写法:
文字:
文字是查重的重灾区,倘若不能够处理得当的话查重时就是一片红!我们还是通过具体的论文来看看别人是怎么控制重复率的。
1、少写:
写得少查重的时候就能少算点重复率,也能够通过一些换词换序尽可能避免重复,例如这篇题为:Underwater small and occlusion object detection with feature fusion and global context decoupling head‑based YOLO的文章
Underwater small and occlusion object detection with feature fusion and global context decoupling head-based YOLO | Multimedia Systems The underwater light scattering, absorption, and camera or target moving often bring issues such as blurring, distortion, and color deviation in underwater
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-024-01410-zTo validate the performance of SG-YOLO, we utilize mAP50 and mAP50-95 as the primary evaluation metrics. Here, mAP denotes the mean average precision. Specifcally, mAP50 represents the mAP at an Intersection over Union (IOU) threshold of 0.5, and mAP50-95 signifes the average precision with IOU ranging from 0.5 to 0.95 at intervals of 0.05.
为了验证 SG-YOLO 的性能,我们使用 mAP50 和 mAP50-95 作为主要评估指标。这里,mAP 表示平均精度。具体来说,mAP50 表示联合交叉(IOU)阈值为 0.5 时的 mAP,mAP50-95 表示 IOU 在 0.5 到 0.95 之间、间隔为 0.05 时的平均精度。
在这篇文章里,作者只把mAP50和mAP50-95作为主要评价指标,却忽略了其他的常用指标,很显然这里就考虑到了咱们自己模型的效果究竟如何,可以选择性地突出一些特别优秀的指标
2、串写:
串写即串起来写,这是我发明的一个叫法,其实就是通过一个比较有逻辑的表达将你想说明的几个评价指标串在一起写。例如这篇题为Lightweight marine biodetection model based on improved YOLOv10的文章:
Redirecting
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2025.01.077
When evaluating the size of a network model, two key metrics are typically considered: parameter count and weight file size. The parameter count represents the total number of parameters that need to be trained within the model, while the weight file size refers to the size of the file containing the trained weights. Smaller parameter counts and weight file sizes make the model easier to deploy on mobile devices. Additionally, computational cost (GFLOPs) is used to quantify the model’s computational efficiency; lower GFLOP values indicate that fewer computational resources are required for task execution, leading to higher efficiency. Frames Per Second (FPS) measures the number of images the model can process per unit time, where a higher FPS value implies better real-time performance.To comprehensively assess model deployment and operational efficiency, this study evaluates the model based on parameter count, weight file size, computational cost, and FPS.Accuracy (𝑃), recall (𝑅), Average Precision (AP), and mean Average Precision (mAP) are used to assess the accuracy of object detection methods. Precision (𝑃) represents the ratio of true positive samples among the predicted positive samples, as shown in Eq. (1): Recall ( 𝑅) represents the ratio of correctly predicted positive samples to labeled positive samples, as shown in Eq. (2):
Recall ( 𝑅) represents the ratio of correctly predicted positive samples to labeled positive samples, as shown in Eq. (2): Precision and recall are inversely related, so to fully evaluate the algorithm’s performance, a PR curve is often plotted with recall as the horizontal axis and precision as the vertical axis. The area under the PR curve represents the AP value, as shown in Eq. (3):
Precision and recall are inversely related, so to fully evaluate the algorithm’s performance, a PR curve is often plotted with recall as the horizontal axis and precision as the vertical axis. The area under the PR curve represents the AP value, as shown in Eq. (3): The mean Average Precision (mAP) is the average of AP values across multiple categories.在评估网络模型的大小时,通常会考虑两个关键指标:参数数量和权重文件大小。参数数代表模型中需要训练的参数总数,而权重文件大小指的是包含训练过的权重的文件大小。较小的参数数和权重文件大小使模型更容易在移动设备上部署。此外,计算成本(GFLOPs)用于量化模型的计算效率;GFLOPs 值越低,说明执行任务所需的计算资源越少,效率越高。每秒帧数(FPS)衡量模型在单位时间内可处理的图像数量,FPS 值越高,表示实时性越好。
The mean Average Precision (mAP) is the average of AP values across multiple categories.在评估网络模型的大小时,通常会考虑两个关键指标:参数数量和权重文件大小。参数数代表模型中需要训练的参数总数,而权重文件大小指的是包含训练过的权重的文件大小。较小的参数数和权重文件大小使模型更容易在移动设备上部署。此外,计算成本(GFLOPs)用于量化模型的计算效率;GFLOPs 值越低,说明执行任务所需的计算资源越少,效率越高。每秒帧数(FPS)衡量模型在单位时间内可处理的图像数量,FPS 值越高,表示实时性越好。
为了全面评估模型的部署和运行效率,本研究根据参数数量、权重文件大小、计算成本和 FPS 对模型进行了评估。
精度(𝑃)、召回率(𝑅)、平均精度(AP)和平均精度平均值(mAP)用于评估物体检测方法的精度。精度 (𝑃) 表示真阳性样本与预测阳性样本的比率,如公式 (1) 所示:
召回率 (𝑅) 表示正确预测的阳性样本与标记的阳性样本之比,如公式 (2) 所示:
精确度和召回率成反比,因此为了全面评估算法的性能,通常以召回率为横轴、精确度为纵轴绘制 PR 曲线。PR 曲线下的面积代表 AP 值,如公式 (3) 所示:
平均精度(mAP)是多个类别中 AP 值的平均值。
这篇文章主要介绍了GFLOPs、FPS、P、R、AP和mAP几个指标,有的指标列了公式,有的指标进行了语言表达。我们在写作的时候也需要多用“在评估网络模型的大小时,通常会考虑两个关键指标”“为了全面评估模型的部署和运行效率”这样的表达,使文章具有逻辑性。
公式:

如果要写公式,那么这三个就是常常会出现的。我们知道有的查重算法会把可编辑的公式也算作考察标准,这就很令人头疼了。于是我们的办法就是改符号、写过程!
例如:
像这样把数学过程写详细一些;
像这样使用新定义的符号;
还可以把P、R、F1等等都写成完整的,Precision,Recall,F1 Score等等。
当然,像FPS、GFLOPs这种我们也可以用公式来表达一下。
总结:
本文主要讨论了论文中评价指标部分的写作技巧,强调如何避免查重并提高创新性。首先,通过减少写作的篇幅和巧妙换词换序,可以减少重复率。其次,采用串写的方式,即将多个评价指标有逻辑地连接在一起,增强文章的流畅性和逻辑性。
另外,在涉及公式时,可以通过改变符号或详细写出数学过程来避开查重系统的检测。此外,使用完整的术语(如Precision、Recall、F1 Score等)也有助于降低重复率。
总的来说,创新性地表达评价指标,并确保写作的逻辑性和清晰性,是提升论文质量和避免查重的关键。