分类:
分类:
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
一、前言
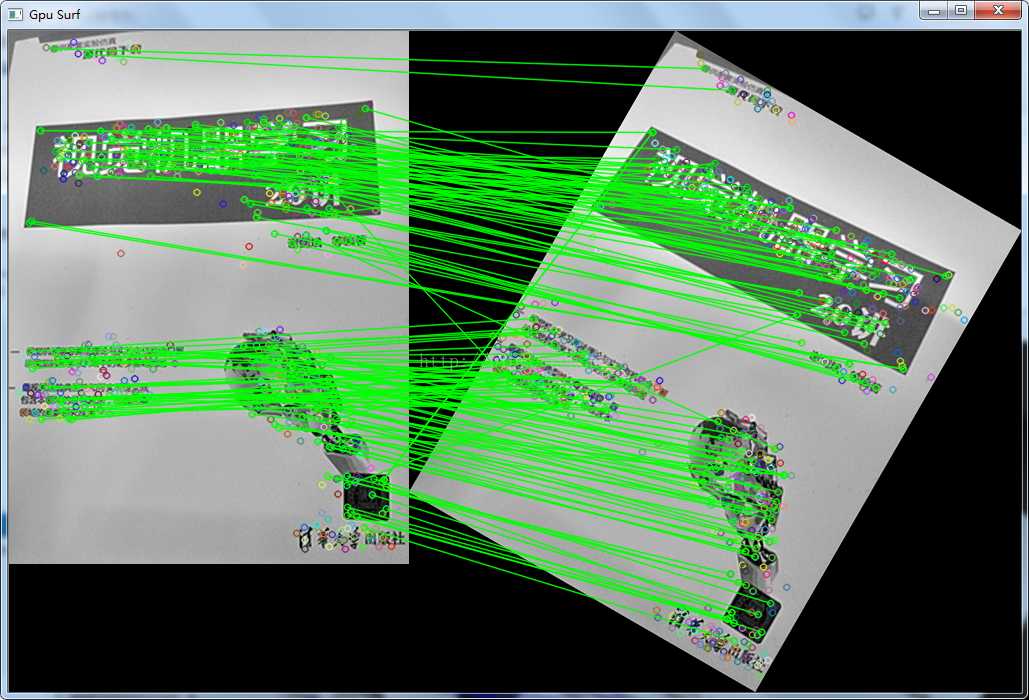
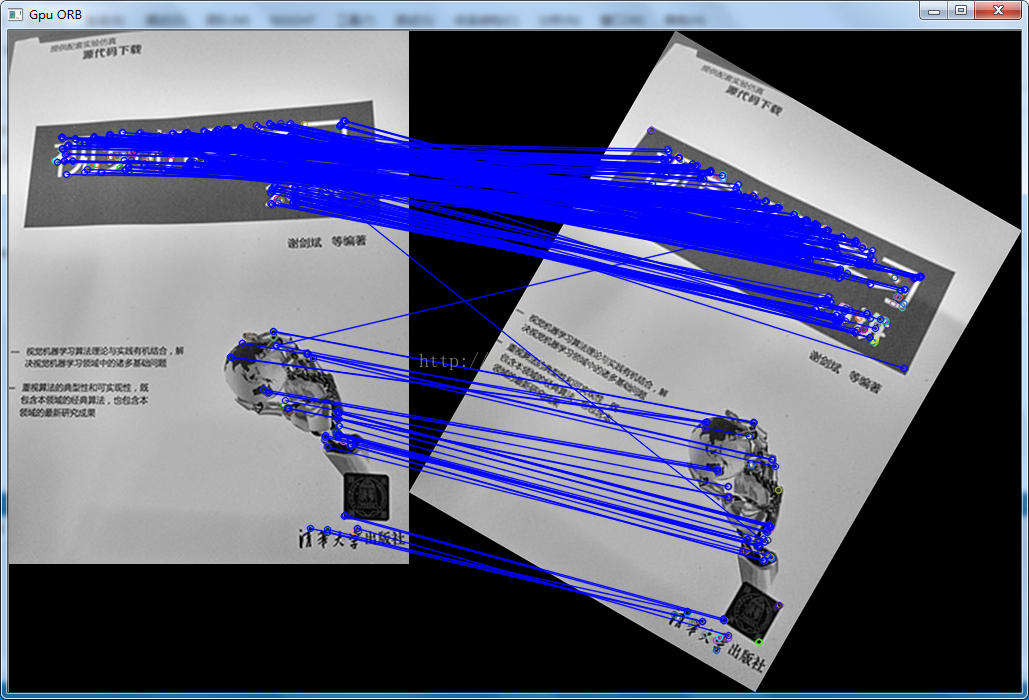
本文主要实现了使用OpenCV里的gpu版surf特征检测器和gpu版orb检测器,分别对图片进行特征点提取及匹配,并对寻获的特征点进行了距离筛选,将匹配较为好的特征点进行展示
二、实现代码
我不生产代码,我只是代码的搬运工和修改工
- //main.cpp//
- #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/gpu/gpu.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/nonfree/gpu.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp>
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- using namespace cv;
- Mat rotatedImage(const Mat & _src, double _degree)
- {
- int width_src = _src.cols;
- int height_src = _src.rows;
- float center_x = width_src / 2.0;
- float center_y = height_src / 2.0;
- double angle = _degree * CV_PI / 180.;
- double a = sin(angle), b = cos(angle);
- Mat map_matrix = getRotationMatrix2D(Point2f(center_x, center_y), _degree, 1.0);//获得旋转矩阵
- int height_rotated = height_src*fabs(b) + width_src*fabs(a);
- int width_rotated = height_src*fabs(a) + width_src*fabs(b);
- map_matrix.at<double>(0, 2) += (width_rotated - width_src) / 2.0; //将坐标移到中点
- map_matrix.at<double>(1, 2) += (height_rotated - height_src) / 2.0; //将坐标移到中点
- Mat dst;
- warpAffine(_src, dst, map_matrix, Size(width_rotated, height_rotated),
- CV_INTER_CUBIC | CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS, BORDER_CONSTANT, cvScalarAll(0));
- return dst;
- }
- //主要获得surf特征点、描述子、及特征点匹配
- void surfExtractor(Mat& _src_Img, Mat& _dst_Img )
- {
- gpu::GpuMat src_gpu(_src_Img);
- gpu::GpuMat dst_gpu(_dst_Img);
- std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_src;
- std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_dst;
- std::vector<DMatch> matches;
- gpu::SURF_GPU FeatureFinder_gpu(500);
- gpu::GpuMat keypoints_gpu_src, keypoints_gpu_dst;
- gpu::GpuMat descriptors_gpu_src, descriptors_gpu_dst;
- std::vector<float> descriptors_v1, descriptors_v2;
- //计算特征点和特征描述子
- FeatureFinder_gpu(src_gpu, gpu::GpuMat(), keypoints_gpu_src, descriptors_gpu_src);
- FeatureFinder_gpu(dst_gpu, gpu::GpuMat(), keypoints_gpu_dst, descriptors_gpu_dst);
- //将特征点下载回cpu,便于画图使用
- FeatureFinder_gpu.downloadKeypoints(keypoints_gpu_src, keypoints_src);
- FeatureFinder_gpu.downloadKeypoints(keypoints_gpu_dst, keypoints_dst);
- //使用gpu提供的BruteForceMatcher进行特征点匹配
- gpu::BruteForceMatcher_GPU< L2<float> > matcher_lk;
- matcher_lk.match(descriptors_gpu_src, descriptors_gpu_dst, matches, gpu::GpuMat());
- float max_distance = 0.2; //定义特征点好坏衡量距离
- std::vector<DMatch> good_matches; //收集较好的匹配点
- for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_gpu_src.rows; i++) {
- if (matches[i].distance < max_distance) {
- good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
- }
- }
- Mat image_matches;
- drawMatches(_src_Img, keypoints_src, _dst_Img, keypoints_dst, good_matches,
- image_matches, Scalar(0, 255, 0) , Scalar::all(-1), vector<char>(), 0);
- imshow("Gpu Surf", image_matches);
- }
- void orbExtractor(Mat& _src_Img, Mat& _dst_Img)
- {
- gpu::GpuMat src_gpu(_src_Img);
- gpu::GpuMat dst_gpu(_dst_Img);
- std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_src, keypoints_dst;
- gpu::GpuMat descriptors_gpu_src, descriptors_gpu_dst;
- std::vector<DMatch> matches;
- gpu::ORB_GPU orb_finder(500);
- orb_finder.blurForDescriptor = true; //设置模糊
- cv::gpu::GpuMat fullmask_1(src_gpu.size(), CV_8U, 0xFF);
- cv::gpu::GpuMat fullmask_2(dst_gpu.size(), CV_8U, 0xFF);
- orb_finder(src_gpu, fullmask_1, keypoints_src, descriptors_gpu_src);
- orb_finder(dst_gpu, fullmask_2, keypoints_dst, descriptors_gpu_dst);
- //使用gpu提供的BruteForceMatcher进行特征点匹配
- gpu::BruteForceMatcher_GPU< HammingLUT > matcher_lk;
- matcher_lk.match(descriptors_gpu_src, descriptors_gpu_dst, matches, gpu::GpuMat());
- float max_distance = 60; //定义特征点好坏衡量距离
- std::vector<DMatch> good_matches; //收集较好的匹配点
- for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_gpu_src.rows; i++) {
- if (matches[i].distance < max_distance) {
- good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
- }
- }
- Mat image_matches;
- drawMatches(_src_Img, keypoints_src, _dst_Img, keypoints_dst, good_matches,
- image_matches, Scalar(255, 0, 0), Scalar::all(-1), vector<char>(), 0);
- imshow("Gpu ORB", image_matches);
- }
- int main()
- {
- int num_devices = cv::gpu::getCudaEnabledDeviceCount();
- if (num_devices <= 0)
- {
- std::cerr << "There is no device." << std::endl;
- return -1;
- }
- int enable_device_id = -1;
- for (int i = 0; i < num_devices; i++)
- {
- cv::gpu::DeviceInfo dev_info(i);
- if (dev_info.isCompatible())
- {
- enable_device_id = i;
- }
- }
- if (enable_device_id < 0)
- {
- std::cerr << "GPU module isn't built for GPU" << std::endl;
- return -1;
- }
- gpu::setDevice(enable_device_id);
- Mat src_Img = imread("book.bmp" , 0);
- Mat dst_Img = rotatedImage(src_Img, -30.0);
- surfExtractor(src_Img, dst_Img);
- orbExtractor(src_Img, dst_Img);
- cv::waitKey(0);
- return 0;
- }
三、运行结果
运行环境为vs2013+opencv2.4.9+cuda7.0,结果展示如下,orb算法寻找特征点及计算描述子速度较快,gpu版的surf特征点对输入图片大小有要求,不能太小
使用GPU提取SURF局部特征
GPU做SURF特征提取的接口和CPU版本有所不同,不过这一部分可以完全参考<opencv_source_directory>/samples/gpu/surf_keypoint_matcher.cpp的例子代码。
我这里给出一个更加简化的例子,并添加一些中文注释和说明。
/*surf.cpp*/
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d/cuda.hpp>
#include <opencv2/cudafeatures2d.hpp>
using namespace std;
int GetMatchPointCount(const char * pic_path_1,const char * pic_path_2) {
/*指定使用的GPU序号,相关的还有下面几个函数可以使用
cv::cuda::getCudaEnabledDeviceCount();
cv::cuda::getDevice();
cv::cuda::DeviceInfo*/
cv::cuda::setDevice(0);
/*向显存加载两张图片。这里需要注意两个问题:
第一,我们不能像操作(主)内存一样直接一个字节一个字节的操作显存,也不能直接从外存把图片加载到显存,一般需要通过内存作为媒介
第二,目前opencv的GPU SURF仅支持8位单通道图像,所以加上参数IMREAD_GRAYSCALE*/
cv::cuda::GpuMat gmat1;
cv::cuda::GpuMat gmat2;
gmat1.upload(cv::imread(pic_path_1,cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE));
gmat2.upload(cv::imread(pic_path_2,cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE));
/*下面这个函数的原型是:
explicit SURF_CUDA(double
_hessianThreshold, //SURF海森特征点阈值
int _nOctaves=4, //尺度金字塔个数
int _nOctaveLayers=2, //每一个尺度金字塔层数
bool _extended=false, //如果true那么得到的描述子是128维,否则是64维
float _keypointsRatio=0.01f,
bool _upright = false
);
要理解这几个参数涉及SURF的原理*/
cv::cuda::SURF_CUDA surf(
100,4,3
);
/*分配下面几个GpuMat存储keypoint和相应的descriptor*/
cv::cuda::GpuMat keypt1,keypt2;
cv::cuda::GpuMat desc1,desc2;
/*检测特征点*/
surf(gmat1,cv::cuda::GpuMat(),keypt1,desc1);
surf(gmat2,cv::cuda::GpuMat(),keypt2,desc2);
/*匹配,下面的匹配部分和CPU的match没有太多区别,这里新建一个Brute-Force Matcher,一对descriptor的L2距离小于0.1则认为匹配*/
auto matcher=cv::cuda::DescriptorMatcher::createBFMatcher(cv::NORM_L2);
vector<cv::DMatch> match_vec;
matcher->match(desc1,desc2,match_vec);
int count=0;
for(auto & d:match_vec){
if(d.distance<0.1) count++;
}
return count;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
GetMatchPointCount(argv[1],argv[2]);
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
最后,编译这个例子,可以参考下面通用的编译命令:
g++ -std=c++11 surf.cpp `pkg-config --cflags opencv` `pkg-config --libs opencv`
- 1
- 1
更简化的编译命令:
g++ -std=c++11 surf.cpp -lopencv_xfeatures2d -lopencv_cudafeatures2d