目录
39. 组合总和
题目
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。
7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。
仅有这两种组合。
示例2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
示例3:
输入: candidates = [2], target = 1
输出: []
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 302 <= candidates[i] <= 40candidates的所有元素 互不相同1 <= target <= 40
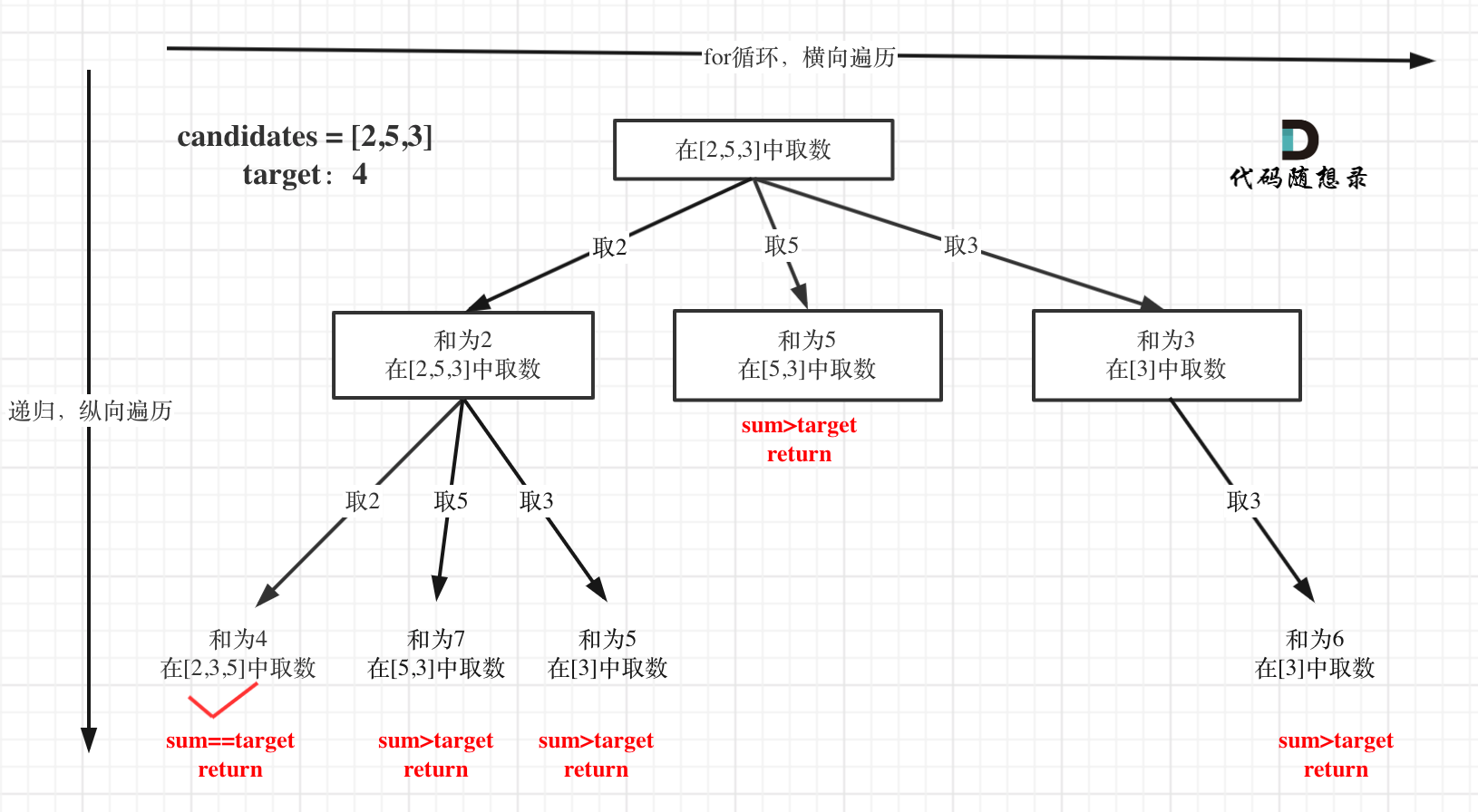
思路
树形结构如下:
题解
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
backtrack(candidates, target, 0);
return res;
}
void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (target <= 0) {
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
//剪枝,当前元素大于剩余目标值时直接跳过
if(target<candidates[i])
continue;
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
40.组合总和Ⅱ
题目
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
**注意:**解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
输出:
[
[1,1,6],
[1,2,5],
[1,7],
[2,6]
]
示例2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
输出:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 1001 <= candidates[i] <= 501 <= target <= 30
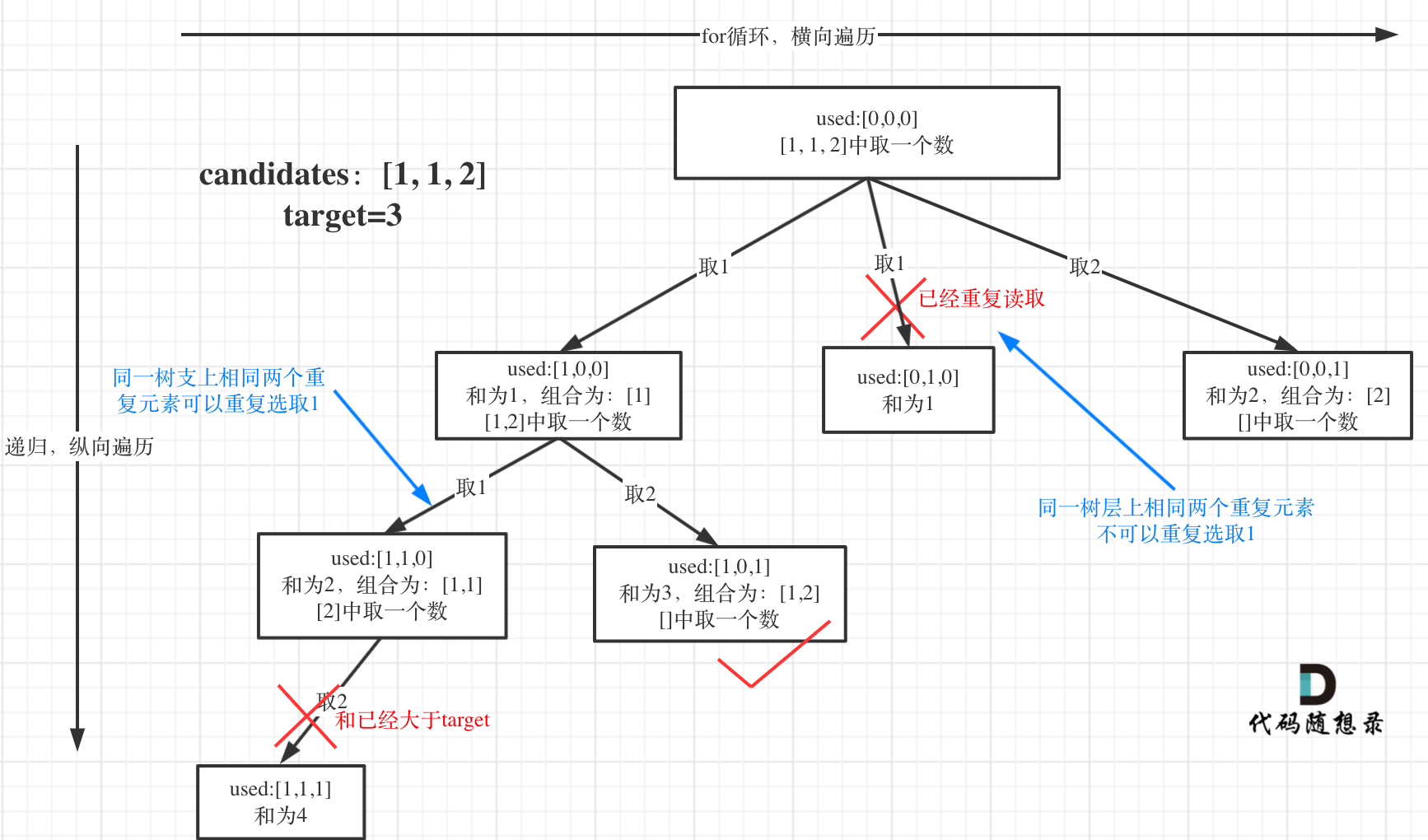
思路
- 对数组进行排序
- 去重,在回溯过程已经使用过的元素不能再使用,如果当前元素与前一个元素相同,跳过以避免重复组合
- 剪枝,如果当前元素大于剩余的目标值,直接跳出循环
树形结构如下:
题解
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrack(candidates, target, 0);
return res;
}
void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
if (target < 0)
return;
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
//剪枝
if (candidates[i] > target)
break;
//去重
if (i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1])
continue;
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
131.分割回文串
题目
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例1:
输入:s = "aab"
输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
示例2:
输入:s = "a"
输出:[["a"]]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 16s仅由小写英文字母组成
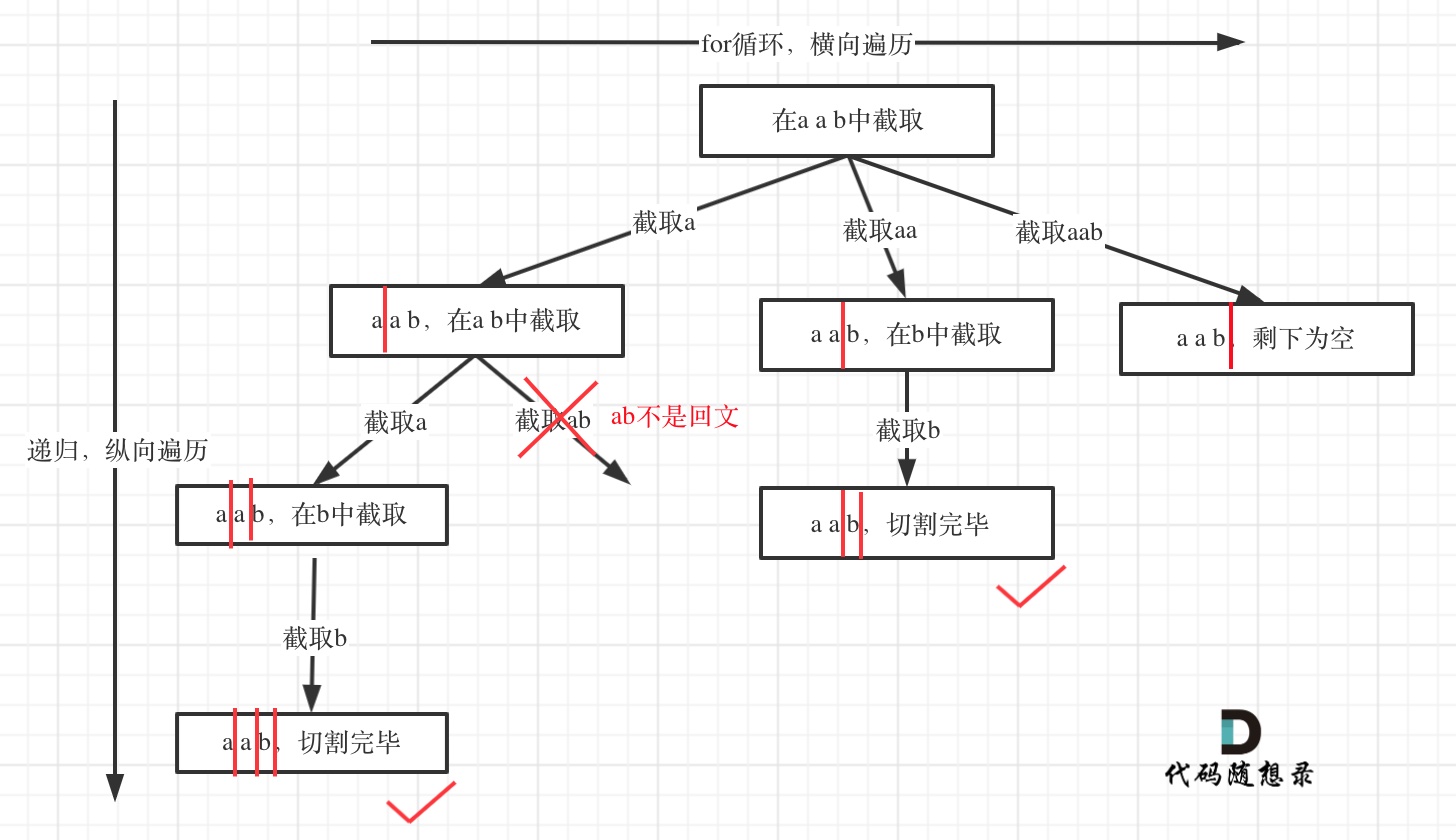
思路
树形结构:
题解
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtrack(s, 0, res, path);
return res;
}
void backtrack(String s, int startIndex) {
if (startIndex == s.length()) {
res.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
//调用库函数,优点是代码简洁,缺点是复杂度高
//String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
//String reversedStr = new StringBuilder(str).reverse().toString();
//if(!str.equals(reversedStr))
// continue;
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
if (!isPalindrome(str))
continue;
path.add(str);
backtrack(s, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
//判断是否回文
boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int left = 0;
int right = s.length() - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}